Abstract
Background:
Studies associate sleeping and eating late in the day with poor dietary quality and higher obesity risk but differences in sleep duration confound this association. We aimed to determine whether sleep and meal timing, independent of sleep duration, influenced food intake in healthy adults.
Methods:
This was a controlled, 2 × 2 inpatient crossover study with normal (0000-0800 h) or late (0330-1130 h) sleep and normal (1, 5, 11, and 12.5 h after awakening) or late (4.5, 8.5, 14.5, and 16 h after awakening) meals. Food intake was controlled while blood samples were obtained for determination of appetite-regulating hormones on days 3-4. Self-selected food intake was assessed on day 5. Data were analyzed using linear mixed model analysis with sleep, meal, and sleep x meal interaction as dependent variables.
Results:
Five participants completed all phases (mean age 25.1 ± [SD] 3.9 y, body mass index 29.2 ± 2.7 kg/m2). There was a significant sleep x meal interaction on energy intake (P = 0.035) and trends on fat and sodium intakes (P < 0.10). Overnight ghrelin concentrations were higher under normal sleep and meal conditions relative to late (P < 0.005) but lower when both were combined (P < 0.001). Overnight leptin concentrations were higher under normal meal conditions (P = 0.012). There was a significant sleep x meal interaction on ghrelin (P = 0.032) and glucagon-like peptide 1 (P = 0.041) concentrations, but not leptin (P = 0.83), in response to a test meal.
Conclusions:
Our results suggest that alignment of sleep and meals may influence food choice and energy balance. Additional research is necessary to expand and confirm our findings.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
There is observational evidence that eating and sleeping at unconventional hours is associated with greater risk of obesity and an adverse metabolic profile. Indeed, studies have shown greater prevalence of obesity in those with shift work [1, 2] and social jetlag [3] (shifts in the timing of sleep between work days and free days). Sleeping later in the day is also related to greater body mass index (BMI) and poor dietary habits: lower intakes of fruits and vegetables and greater intakes of sugar-sweetened beverages and fast foods [4]. Those who sleep late also eat more after 2000h, a behavior associated with greater BMI, independent of sleep timing and duration. However, human studies in this field have largely been observational. This is problematic because individuals who sleep late also have short sleep duration and the timing of their food intake is shifted relative to those who sleep earlier [4], making inferences related to sleep timing and meal timing difficult to isolate. We [5] and others [6,7,8] have previously shown that sleep restriction increases food intake. Furthermore, in sleep restriction studies when the timing of sleep is delayed to the second half of the night, or early morning hours, there is increased eating at night [7].
Although animal studies cannot model for changes in sleep timing, rodent studies support the notion that eating during the biological night has negative effects on weight status. Mice fed during their light cycle (inactive period) gain more weight and tend to have greater percent body fat despite similar energy intakes and physical activity as mice fed during the active period [9]. Others have found greater weight gain as a result of increased food intake and reduced fat oxidation in mice fed only during the light cycle [10] or maintained in constant light or on a light/dim light cycle [11]. Corresponding data in humans can be provided from shift work interventions: working at night leads to increased intake of high-fat foods compared to a control day condition [12].
This intervention study was conducted to isolate the impact of sleep and meal times on appetite-regulating hormones and food intake, under conditions of identical sleep duration. We hypothesized that delaying sleep and meal times by 3.5 h would lead to a hormonal profile indicative of greater appetite and lower satiety and that this would result in greater overall food intake relative to sleeping and eating at earlier times. We further expected greater fat and carbohydrate intakes, particularly saturated fat and sugar, in late sleep and meal conditions.
Methods
Four men and two women, 20–49 y of age, with a body mass index between 25–34.9 kg/m2, were recruited to participate in this study. All participants underwent 2 weeks of sleep monitoring with actigraphy as part of the screening process, as previously reported [5]. Participants were required to sleep an average of 7–9 h/night, have an intermediate chronotype based on the Ostberg Morningness-Eveningness questionnaire, and a midpoint of sleep at 0400 h or earlier, to be eligible. We excluded individuals who did not habitually eat breakfast, defined as food intake within 1 h of awakening at least 4 times/week, and those with sleep, eating, or other psychological disorders. The study was approved by the institutional review boards of Columbia University Medical Center and New York University Langone Medical Center (New York, NY) and was registered on Clinicaltrials.gov (#NCT02347020). All participants were given the opportunity to review and ask questions about the protocol prior to providing informed consent.
Experimental design
This study employed a 2 × 2 factorial design with two sleep (normal or late) and meal (normal or late) times (Table 1), resulting in 24 possible phase order combinations. Once enrolled, participants were randomly assigned one of those combinations generated from a randomization schedule. Bedtimes, wake times, and meal times in the normal conditions were based on data from Baron et al. [4]. We modeled bedtimes for the late sleep (Ls) phases based on self-reported bedtimes for late sleepers from that same study [4] but delayed wake time to achieve the same duration of time in bed as the normal sleep (Ns) condition. Differences in bed times between Ns and Ls in the study by Baron et al. was 3.5 h [4]. Meal times for the late meal (Lm) phases were delayed by this same amount relative to normal meal (Nm) times to achieve equal inter-meal intervals between study phases.
Participants were inpatients in the Columbia University Medical Center Irving Institute for Clinical and Translational Research (CTSA) for all 4 study phases. The first 3 d of each phase were conducted under controlled feeding conditions, wherein participants consumed a weight-maintenance diet, as estimated using the Mifflin-St. Jeor equation [13]. Breakfast provided 25% of estimated energy requirements, lunch 30%, dinner 35%, and the remaining 10% was provided as a post-dinner snack. All foods and beverages were consumed in their entirety during this period. All meals were prepared at the CTSA Bionutrition Unit by study personnel.
On day 3, visual analog scales to assess appetite were filled out immediately before and at 15, 30, 45, 60, 90, and 120 min after meals. Questions included: (1) how hungry do you feel? (2) how satisfied do you feel? (3) how full do you feel? (4) how much food would you like to eat? (5) how energetic do you feel? (6) how sluggish do you feel? (7) how much would like to eat something sweet? (8) something salty? (9) something savory? (10) fruits and vegetables? Questions were anchored with “not at all” at 0 and “very much so” at 100 mm [14].
Blood samples were obtained starting on the night of day 3 and into day 4 for hormone and metabolite assessments. An insulin-modified frequently-sampled i.v. glucose tolerance test was performed at scheduled breakfast time and a meal tolerance test (MTT) was done at the scheduled lunch time. The meal consisted of a liquid meal replacement (Boost Plus, Nestle Nutritionals, Highland Park, MI). Blood samples during the overnight period and in response to the MTT were analyzed for leptin, ghrelin, and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). Serum leptin was measured using a double-antibody RIA (Linco Research Products Inc., St. Charles, MO). Blood samples were collected in EDTA-coated chilled tubes for the measurement of peptide hormones. The tubes were pre-treated with addition of aprotinin (0.6 TIU/mL of blood) and DPP-IV inhibitor (10 μL/mL of blood) to prevent hormone degradation. Total ghrelin was assessed using RIA (Linco Research). Total GLP-1 was measured by RIA (Phoenix Pharmaceutical, Belmont, CA) after plasma extraction with 95% ethanol.
On day 5, participants were permitted to self-select their food intake, both food type and amount, at their scheduled meal and snack times. All foods were dispensed by research personnel and weighed prior to and post consumption. Participants could choose foods from our standard diet menu or elsewhere. They were given a $25 allowance to purchase foods of their liking from neighborhood food establishments (fast food restaurants and grocery stores). The only restriction placed on purchases was the availability of nutrition information for the foods and beverages chosen. Dietary intakes were analyzed using Nutrition Data System for Research (NDSR, Nutrition Coordinating Center, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN).
Statistical methods
Food intake data were analyzed using linear mixed model analysis with energy and macronutrient variables as outcomes, and sex, weight, sleep timing, meal timing, sleep x meal timing interaction as independent variables. When significant, phase was used as an independent variable. Subject ID was used as a grouping variable.
Clock time was categorized as morning (0600–1200 h), afternoon (1200–1800 h), evening (1800–2400 h), and overnight (0000–0600 h) for use as an independent variable. For MTT outcomes, only evening and afternoon clock times are present in the data. Linear mixed model analyses were used to assess ghrelin and leptin as outcomes. In each case, subject ID was used the grouping variable. Sleep timing, meal timing and their interaction were used as independent variables. The analyses were done separately for overnight and MTT. GLP-1 data were tested for normality using Shapiro-Wilk test of normality, and were determined to be non-normal; subsequently data were transformed using log2. The log2 transformation was chosen so that one unit change in the transformed outcome variable corresponds to doubling of the raw value of the outcome variable. Repeated measures ANOVA and mixed-model regression analysis were performed on each outcome (leptin, ghrelin, GLP-1). The independent variables were sleep timing, meal timing and their interaction. Raw data are presented in tables and figures as means ± SD. Statistical significance was set at P < 0.05. Data are available, upon request, from the authors.
Results
A total of 6 participants were recruited and enrolled into the study (Table 2). Of those, 5 completed all 4 phases; one failed to complete the last phase (Ls/Lm). Information on the phase of the menstrual cycle for the 2 female participants is unknown; phases were scheduled 4 wk apart to approximate a regular cycle length of 28 d.
Hormone data
Ghrelin concentrations during the overnight hours were significantly affected by sleep timing (P < 0.0001), meal timing (P = 0.0044), and sleep x meal timing interaction (P < 0.0001) (Fig. 1A). There was also a significant sleep x meal timing interaction on ghrelin concentrations during the MTT (P = 0.032) (Fig. 2A). The timing of the test was also a significant variable affecting ghrelin concentrations during the MTT (P = 0.041) with evening times resulting in lower ghrelin levels and the combination of Ns and Nm associated with higher ghrelin concentrations.
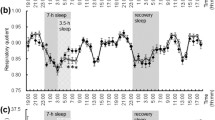
Ghrelin (a) and Leptin (b) overnight concentrations under late and normal sleep and meal timing conditions: Ns/Nm solid line/sold markers; Ns/Lm, solid line/open markers; Ls/Nm, dotted line/solid markers; Ls/Lm, dotted line/open markers. Ghrelin concentrations were significantly affected by sleep timing (P < 0.0001), meal timing (P = 0.0044), and sleep x meal timing interaction (P < 0.0001). Leptin concentrations were significantly affected by meal timing (P = 0.012)
Ghrelin (a), Leptin (b), and GLP-1 (c) concentrations during the MTT under late and normal sleep and meal timing conditions: Ns/Nm solid line/sold markers; Ns/Lm, solid line/open markers; Ls/Nm, dotted line/solid markers; Ls/Lm, dotted line/open markers. There was a significant sleep x meal timing interaction on ghrelin concentrations (P = 0.032). There was no effect of sleep timing, meal timing, and their interaction on leptin concentrations. There was a significant sleep x meal timing interaction on GLP-1 concentrations (P = 0.041)
Overnight leptin concentrations were significantly affected by meal timing (P = 0.012), with higher concentrations associated with Nm (Fig. 1B). There was no effect of sleep timing or sleep x meal interaction on overnight leptin concentrations. Sleep timing, meal timing, and their interaction did not influence leptin concentrations during the MTT although tests conducted in the evening hours tended to be associated with lower concentrations (P = 0.070) (Fig. 2B).
GLP-1 concentrations were only assessed during the MTT. There were no main effects of meal and sleep timing on GLP-1 but there was a significant sleep x meal timing interaction (P = 0.041) (Fig. 2C). Having Ns and Nm together yielded higher GLP-1 concentrations relative to either one separately or having both Ls and Lm.
Food intake data
There was a significant effect of sleep timing (P = 0.019) and sleep x meal timing interaction (P = 0.035) on energy intake during the ad libitum food consumption day (Table 3). There was also a trend for an effect of meal timing (P = 0.095). In general, independently, Ns and Nm timing were associated with increased intake relative to late timing but, when combined, resulted in a negative coefficient. Similarly, there were significant effects of sleep timing on total fat (P = 0.010), saturated fat (P = 0.039), monounsaturated fat (P = 0.0025), and polyunsaturated fat (P = 0.032) intakes. There was a significant effect of meal timing on monounsaturated fat intakes (P = 0.016) with a trend for polyunsaturated fat intakes (P = 0.074). The sleep timing x meal timing interaction was significant for monounsaturated fat intakes only (P = 0.0086) but trends were observed for total fat (P = 0.091) and polyunsaturated fat (P = 0.089) intakes. There were no effects of sleep timing, meal timing, or their interaction on carbohydrate, protein, fiber, sugar, or sodium intakes although there was a trend for a sleep x meal timing interaction on sodium intakes (P = 0.092), favoring lower sodium intakes when sleep and meal timing were normal relative to late.
Discussion
Our study showed that, in the absence of sleep restriction and under identical sleep duration and food intake, conditions that combine earlier sleep and meal times lead to lower overnight ghrelin but higher concentrations in response to a test meal. On the other hand, GLP-1 concentrations were higher in conditions combining earlier sleep and meal times in response to a test meal. Additionally, earlier meal times resulted in higher leptin concentrations overnight with no clear impact of sleep or meal times on its responses to a meal. We also showed that sleep timing tended to exert a greater influence on food intake parameters than meal timing. However, the effects of sleep timing were influenced by meal timing, as reflected by the significant sleep x meal interactions.
We expected the Ls/Lm conditions to result in higher ghrelin and lower leptin and GLP-1 concentrations overall compared to Ns/Nm and that Ns/Lm and Ls/Nm conditions would have intermediate effects. However, literature shows that sleep stimulates ghrelin secretion, with levels peaking at night [15] in healthy participants, as observed in our Ns/Nm phase. Natalucci et al. also observed that ghrelin was secreted in a pulsatile fashion over a 24-h fasting period in healthy individuals [16]. In that small study, higher ghrelin levels were observed in participants with low BMI and lower levels were noted in those with higher BMI. In the present study, there was no effect of meal or sleep time, or their interaction, on the timing of the ghrelin peak and trough, peak and trough values, and average ghrelin daily concentrations (data not presented). Therefore, our results related to Ns and Nm seem to correspond to habitual ghrelin rhythms, whereas delaying sleep or meal times may disrupt this balance. For the other hormones under consideration in this study, Scheer and colleagues concluded that there was no evidence of an endogenous circadian pattern for GLP-1 secretion or leptin, independent of sleep/wake, feeding/fasting cycles under forced desynchrony conditions [17]. Indeed, we also found that sleep and meal times influenced these hormones throughout the measurement period. Higher GLP-1 concentrations in response to a meal consumed closer to wake time relative to later may lead to improved satiation and this may be more important in those with late sleep patterns. There is evidence that skipping breakfast, equivalent to our Lm conditions, increases hunger and reduces satiety in habitual breakfast eaters and reduces GLP-1 concentrations at the lunch meal in both habitual breakfast eaters and skippers [18]. Moreover, we have previously shown that sleep restriction reduces GLP-1 levels in women [19]. Combined, these results suggest that sleep and meal timing, along with the duration of sleep, could influence hormonal levels related to satiety and food intake.
We expected Ls/Lm to result in greatest energy intakes, followed by Ns/Lm and Ls/Nm. Reid et al., in a convenient sample of young adults, found that time of last meal and time lapse between last meal and sleep onset were associated with energy intakes after controlling for age, sex, sleep duration and sleep timing [20]. Eating frequency, however, explained the relation between eating close to bedtime and energy intake. In the present study, we found Ls/Lm to produce the lowest energy intake and Ns/Lm, the highest energy intake. Those 2 conditions both provided participants with the opportunity to consume a snack immediately before bedtime. Interestingly, under Ls/Lm condition, only one participant chose to consume a snack at the scheduled snack time, 0330 h (62 kcal), whereas 3/6 participants consumed a snack in the Ns/Lm condition, at midnight (average intake 363.7 ± 118.1 kcal). In contrast, in the Nm conditions, all participants consumed a snack in Ns, at 2030 h (351.5 ± 177.4 kcal) and 5/6 participants consumed one in Ls, at midnight (277.7 ± 257.7 kcal). Interestingly, and in line with data from Reid et al. [20], intakes were highest when a large snack was consumed close to bedtime (Ns/Lm) and lowest when food intake was further from bedtime (3.5 h in Ns/Nm and Ls/Nm).
It is important to contrast our study and prior research. In previous studies, participants were examined in free-living situations where sleep and meals were not controlled but were measured. In our study, participants were required to eat at fixed times, although food intake was self-selected and measured. It is possible that the rigid meal schedule prevented participants from eating at their preferred time and led to reductions in intake. This seems most evident in the Ls/Lm phase when bedtimes and meals were delayed relative to the participants’ preferred behavior (all participants were regular breakfast eaters with midpoint of sleep ~ 0400 h). We observed that skipping breakfast, as in Lm conditions, seems to induce increased food intake when sleep is normal (0000–0800 h) but not when sleep is delayed (0330–1130 h). However, in pilot testing a prior version of this protocol, allowing participants to consume meals at self-selected times during the ad libitum feeding portion of the study resulted in participants eating a meal immediately upon awakening in all 4 conditions, essentially obliterating the Lm conditions. This observation guided our decision to implement the fixed meal schedule in this iteration of the protocol. Another limitation of this study is the small and heterogenous sample size. However, the within subject, cross over design of the study and our excellent participant retention rate provide robustness to our results. Finally, all participants had a BMI in the overweight and obese categories and results may not be generalizable to those in the normal weight category.
Future studies should be done in a larger group of men and women to uncover the causality of the relation between sleep timing, meal timing, and food choice. It is possible that shifting the alignment of sleep and meals in relation to each other is a critical factor in the association between shift work and obesity and cardiometabolic risk. With this information, additional examinations of personalized sleep/meal time recommendations should be done to determine whether risk can be minimized for those who need to work or maintain wakefulness at unconventional times.
References
Di Lorenzo L, De Pergola G, Zocchetti C, L’Abbate N, Basso A, Pannacciulli N, et al. Effect of shift work on body mass index: results of a study performed in 319 glucose-tolerant men working in a Southern Italian industry. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2003;27:1353–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802419
van Drongelen A, Boot CR, Merkus SL, Smid T, van der Beek AJ. The effects of shift work on body weight change - a systematic review of longitudinal studies. Scandinavian journal of work, environment & health. 2011;37:263–75. https://doi.org/10.5271/sjweh.3143
Roenneberg T, Allebrandt KV, Merrow M, Vetter C. Social jetlag and obesity. Curr Biol. 2012;22:939–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2012.03.038
Baron KG, Reid KJ, Kern AS, Zee PC. Role of sleep timing in caloric intake and BMI. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2011;19:1374–81. e-pub ahead of print 2011/04/30; doi: oby2011100 [pii] 10.1038/oby.2011.100
St-Onge M-P, Roberts A, Chen J, Kelleman M, O’Keeffe M, Jones P. Short sleep duration increases energy intakes but does not change expenditure in normal weight individuals. The American journal of clinical nutrition. 2011;94:410–6. e-pub ahead of print2011 Jun29.
Nedeltcheva AV, Kilkus JM, Imperial J, Kasza K, Schoeller DA, Penev PD. Sleep curtailment is accompanied by increased intake of calories from snacks. The American journal of clinical nutrition. 2009;89:126–33.
Spaeth AM, Dinges DF, Goel N. Effects of experimental sleep restriction on weight gain, caloric intake and meal timing in healthy adults. Sleep. 2013;36:981–90.
Markwald RR, Melanson EL, Smith MR, Higgins J, Perreault L, Eckel RH, et al. Impact of insufficient sleep on total daily energy expenditure, food intake, and weight gain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2013;110:5695–5700. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1216951110
Arble DM, Bass J, Laposky AD, Vitaterna MH, Turek FW. Circadian timing of food intake contributes to weight gain. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2009;17:2100–2. e-pub ahead of print 2009/09/05; doi: oby2009264 [pii]10.1038/oby.2009.264
Bray MS, Ratcliffe WF, Grenett MH, Brewer RA, Gamble KL, Young ME. Quantitative analysis of light-phase restricted feeding reveals metabolic dyssynchrony in mice. International journal of obesity. 2012. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2012.137. e-pub ahead of print 2012/08/22
Fonken LK, Workman JL, Walton JC, Weil ZM, Morris JS, Haim A, et al. Light at night increases body mass by shifting the time of food intake. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2010;107:18664–9. e-pub ahead of print 2010/10/13; doi: 1008734107 [pii] 10.1073/pnas.1008734107
Cain SW, Filtness AJ, Phillips CL, Anderson C. Enhanced preference for high-fat foods following a simulated night shift. Scandinavian journal of work, environment & health. 2015;41:288–93. https://doi.org/10.5271/sjweh.3486
Mifflin MD, St Jeor ST, Hill LA, Scott BJ, Daugherty SA, Koh YO. A new predictive equation for resting energy expenditure in healthy individuals. The American journal of clinical nutrition. 1990;51:241–7. e-pub ahead of print1990/02/01
Kissileff HR, Wentzlaff TH, Guss JL, Walsh BT, Devlin MJ, Thornton JC. A direct measure of satiety disturbance in patients with bulimia nervosa. Physiology & behavior. 1996;60:1077–85. e-pub ahead of print1996/10/01
Dzaja A, Dalal MA, Himmerich H, Uhr M, Pollmacher T, Schuld A. Sleep enhances nocturnal plasma ghrelin levels in healthy subjects. American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism. 2004;286:E963–967. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00527.2003
Natalucci G, Riedl S, Gleiss A, Zidek T, Frisch H. Spontaneous 24-h ghrelin secretion pattern in fasting subjects: maintenance of a meal-related pattern. Eur J Endocrinol. 2005;152:845–50. https://doi.org/10.1530/eje.1.01919
Scheer FA, Hilton MF, Mantzoros CS, Shea SA. Adverse metabolic and cardiovascular consequences of circadian misalignment. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2009;106:4453–8. e-pub ahead of print 2009/03/04; 0808180106 [pii] 10.1073/pnas.0808180106
Thomas EA, Higgins J, Bessesen DH, McNair B, Cornier MA. Usual breakfast eating habits affect response to breakfast skipping in overweight women. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2015;23:750–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.21049
St-Onge MP, O’Keeffe M, Roberts AL, RoyChoudhury A, Laferrere B. Short sleep duration, glucose dysregulation and hormonal regulation of appetite in men and women. Sleep. 2012;35:1503–10. https://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.2198. e-pub ahead of print 2012/11/02
Reid KJ, Baron KG, Zee PC. Meal timing influences daily caloric intake in healthy adults. Nutr Res. 2014;34:930–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nutres.2014.09.010
Author Contributions
MPSO designed the study, analyzed and interpreted data, and wrote the manuscript. She takes full responsibility for the data contained in this report. TP and KK conducted the study, analyzed data, and contributed to writing the manuscript. BL provided medical supervision for the study, assisted with data interpretation and manuscript preparation. AR performed statistical analysis of the data and assisted with data interpretation and manuscript preparation.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Institutes of Health grants R56HL0119945 (MPSO) and DK26687, and also in part by Columbia University’s CTSA grant UL1 TR000040 from NCATS/NIH. This article is published as part of a supplement sponsored by the Mediterranean Diet Foundation and the Diputació de Barcelona.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
M-PS-O received grant support from the National Institutes of Health. ARC owns stock in Alphabet Inc and received grant support National Institutes of Health and National Science Foundation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
St-Onge, MP., Pizinger, T., Kovtun, K. et al. Sleep and meal timing influence food intake and its hormonal regulation in healthy adults with overweight/obesity. Eur J Clin Nutr 72 (Suppl 1), 76–82 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-018-0312-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-018-0312-x
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
The Impact of Meal Timing on Risk of Weight Gain and Development of Obesity: a Review of the Current Evidence and Opportunities for Dietary Intervention
Current Diabetes Reports (2022)
-
Integration of Time-Based Recommendations with Current Pediatric Health Behavior Guidelines: Implications for Obesity Prevention and Treatment in Youth
Current Obesity Reports (2022)
-
Culturally-consistent diet among individuals of Mexican descent at the US-Mexico border is associated with sleep duration and snoring
BMC Nutrition (2021)
-
The Challenge of Maintaining Metabolic Health During a Global Pandemic
Sports Medicine (2020)