Abstract
This research aims to present a bibliometric analysis of the published documents on spirituality, religion and health. Despite the increasing number of publications spirituality, religion and health research in recent years, there is still little information about the effects of these publications in the literature. “Religion,” “spirituality,” “spiritual,” “health” and “medicine” keywords were used to search the Web of Science (WoS) database. Bibliometric analysis was conducted on the articles published between 1975 and 2017. The analysis was presented with network and density maps. The analysis also included the regression analysis to predict a number of publications in 2018. A total number of 1674 publications were found: 818 of these publications were articles. Of the 818 articles, 210 were religion, 198 were Public Environmental Occupational Health, 139 were Psychology, and 77 were performed in the field of Psychiatry. The most productive journal with 107 articles and 1129 citations was the Journal of Religion and Health. The USA (495; 60.5%) was the most productive country on spirituality, religion and health publications. The author who had the highest number of publications and citations was Koenig HG (33 publications; 4.03% and 1617 citations), the document who had the highest number of citations was Ellison CG and Levin JS (633 citations), and the author who had the highest number of citations in the references was Koenig HG, 2001, (126 citations). Duke Univ was the top institution in the number of publication (50 Article). This study will lead the researchers especially in terms of the important journals, active countries, authors, top-cited articles and current topics in spirituality, religion and health research.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Spirituality was defined as “the personal quest for understanding answers to ultimate questions about life, about meaning and about relationship to the sacred or transcendent, which may (or may not) lead to or arise from the development of religious rituals and the formation of community” (Koenig et al. 2001), and religion was defined as “an organized system of beliefs, practices, rituals and symbols designed to facilitate closeness to the sacred or transcendent (God, higher power, or ultimate truth/reality) by Koenig et al. (2001 and Damiano et al. (2016). Religion and spirituality are two different concepts related to belief. Spirituality is all of the spiritual values and behaviors that cause a person to have good or bad characteristics. Religion is belief in a God and the practices that are related with this belief, such as worshiping in a church, mosque or temple.
Bibliometric analysis is the method that provides statistical analysis of publications such as articles and books (Şenel and Demir 2018; Ozsoy and Demir 2018). Citation analysis is a way of measuring the relative impact of an article, publication or author by counting how many times it has been cited by other studies (Muslu 2018; Senel et al. 2016). Advanced bibliometric analysis is an important method for determining the authors, articles or institutions. Many bibliometric researchers have been carried out in various fields (Van Raan 2003; Clarke et al. 2007) since the bibliometric study by Garfield was published in JAMA Journal in 1987 (Ozsoy and Demir 2017; Garfield 1987).
The number of researchers interested in this field has been increasing rapidly in recent years. Although the publications of religion have increased rapidly in recent years, there is still very little information about the effects of these publications in the literature. This research aims to present a bibliometric analysis of the published documents on spirituality, religion and health (SR/H) research during 1975–2017.
Materials and Methods
The data analyzed in this study were obtained from Web of Science (WoS; Thomson Reuters, New York, NY, USA) index on 23 February 2018. “Religion” and “health” or “religion” and “medicine” or “spirituality” and “health” or “spiritual” and “health” or “spirituality” and “medicine” or “spiritual” and “medicine” keywords were used to search the WoS database. The documents published between 1975 (Publications before 1975 are not available in the WoS) and 2017 were included in the study. Bibliometric network visualizations were performed by using VOSviewer (version 1.6.6) software (Van Eck and Waltman 2010). Regression analyses were conducted using SPSS (version 22.0, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA, license: Hitit University). Regression analysis with curve fitting was used to estimate the number of publications in the year 2018. A P value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
A total number of 1674 publications were found in the WoS database. Of all these publications, 818 (48.87%) were articles, 364 (21.74%) book reviews, 157 (9.38%) meeting abstracts, 125 (7.47%) editorial materials, 86 (5.14%) letters, 60 (3.58%) reviews, 58 (3.47%) proceedings papers, and the remaining publications 32 (1.91%). A total of 818 articles received 14,137 total citations (without self-citations 12,928), and the average number of citations per publication was 17.28. By language, 766 (93.6%) of these articles have been published in English, 15 (1.8%) in French, 13 (1.6%) in German, 7 (0.9%) in Portuguese, 5 (0.6%) in Spanish, 2 (0.2%) in Czech, 2 (0.2%) in Italian, 2 (0.2%) in Russian, 1 (0.1%) in Hungarian, 1 (0.1%) in Serbian, 1 (0.1%) in Slovak, 1 (0.1%) in Slovenian, 1 (0.1%) in Ukrainian and 1 (0.1%) in Turkish. Additionally, active research areas on SR/H are given in Table 1.
Development of Publications and Citations and Prediction of the Publications for 2018
The distribution of the number of publications and citations by years is shown in Figs. 1 and 2, respectively. There seems to be a significant increase in the number of publications and citations after 1999 (see Figs. 1, 2). Besides, cubic curves were fitted to estimate the number of publications in 2018. The publication number on the topic of SR/H for 2018 was estimated by using publication numbers based on the publications between 1975 and 2017. It could be calculated that the estimated publication number will be 82 (R2 = 0.964) in 2018. The cubic curve is given in Fig. 3.
Productive Countries
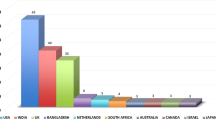
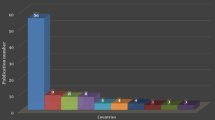
Authors from 63 different countries contributed to the literature about SR/H. The USA, with 495 (60.5%) publications, was the most productive country, which was followed by England (39), Canada (36), Iran (29), Australia (28), Germany (26), Brazil (19), India (17), Saudi Arabia (15), South Africa (15), Israel (13), China (11), Sweden (10), Switzerland (10), France (9), Scotland (9), Taiwan (8), Austria (7), Italy (6), Japan (6) and Norway (6), respectively. The distribution of the number of publications according to world countries is presented on the world map (see Fig. 4).
In addition, international collaboration between the active countries was investigated. A bibliometric analysis was performed with 33 countries (out of 63) which had at least 3 articles (6 countries without international collaboration not included on the map) and is presented in Fig. 5. Australia, Austria, Canada, Italy and Tanzania were in the first cluster; Iran, Israel, Norway, China and Sweden were in the second cluster; Brazil, Denmark, India, Indonesia and Saudi Arabia were in the third cluster; Japan, South Korea, Thailand and the USA were in the fourth cluster; England, Jordan and Wales were in the fifth cluster; Belgium, Germany and South Africa were in the sixth cluster; France and Switzerland were in the seventh cluster. All collaborations are demonstrated in Fig. 5.
Active Journals
Table 2 shows the top active 22 journals with the highest number of publications about SR/H. “Journal of religion and health” journal had the highest number of publications (107, 13.1%) and citations (1129 citations), and the second highest number of publications was in the “Religions” journal (14; 1.7%). Other journals are given in Table 2. Figure 6 demonstrates network visualization map of citation analysis of active journals with 31 (out of 418) journals which had minimum of 4 articles.
Active Institutions
The highest number of publications is from Duke University (48; 5.9%), and the second highest number of publications is from University of Michigan (24; 2.9%). Figure 7 shows network visualization of citations analysis of active institutions. Other institutions are seen in Fig. 7.
Network visualization map of citation analysis of active organizations. Circle size shows the number of publications, 46 institutions (out of 852) with minimum 5 publications. Top 3 institutions by number of publications are Duke Univ (44 Article, 2070 citations), Univ. Michigan (23 Article, 882 citations), Harvard Univ. (16 Article, 312 citations) respectively
Active Authors
According to the number of publications, the authors who contributed most to the literature are shown in Table 3. The author with the highest number of publications (33; 4.0%) and citations (1617) was Koenig HG (33; 4.0%). Other authors are shown in Table 3.
Co-Citation Analysis
Figure 8 demonstrates the density map of co-citation analysis of 50 (out of 23,627 cited references) articles who were cited minimum 20 times. Top-cited 5 articles in references included “Koenig et al. (2001)” (126 citation) “Pargament (1997)” (69 citation), “Sloan et al. (1999)” (54 citation), “Hill et al. (2003)” (54 citation) and “Powell et al. (2003)” (53 citation), respectively (Fig. 8).
Top-Cited Articles
Table 4 demonstrates the 15 most cited manuscripts on SR/H between 1975 and 2017. According to a total number of citations, with total 633 and average 90.40 citations yearly, the article entitled “The religion-health connection: Evidence, theory, and future directions” written by Ellison and Levin (1998) was the top-cited article. The second most cited publication was the study entitled “The daily spiritual experience scale: Development, theoretical description, reliability, exploratory factor analysis, and preliminary construct validity using health-related data” written by Underwood and Teresi (2002).
Frequently Used Terms
Network visualization map of most frequently used keywords in abstracts according to years is shown in Fig. 9. Of the 1273 terms in the abstracts of the 818 articles, 47 words occurred more than 5 times. The most frequently used 10 keywords are spirituality (number of use; 247), religion (169) health (91), mental health (59), religiosity (35), depression (21), quality of life (21), spiritual care (21), spiritual health (17), medicine (16), respectively (see Fig. 9). The other keywords are given in Table 5.
Discussion
Parallel to the development of complementary and alternative medicine applications, the number of publications on SR/H has increased rapidly in recent years. But there are so few bibliometric studies in the literature on this subject. We found two bibliometric studies in the literature (Damiano et al. 2016; Lucchetti and Lucchetti 2014). This bibliometric research, which includes a world map, the largest network visualization maps, international collaborations and publication forecasting, is the most comprehensive study in the literature.
The USA was the most contributed country, which was followed by England and Canada, according to a number of publications in this area. In the SR/H researches, it was found that not only the developed countries but also the developing countries like Iran, Brazil, India, Saudi Arabia and South Africa contributed a considerable amount to the literature. The article entitled “Spirituality, Religion, and Health: Over the Last 15 Years of Field Research (1999–2013)” written by Lucchetti and Lucchetti (2014) and published in “The International Journal of Psychiatry” journal reported last 15 years’ articles about SR/H in the literature and analyzed the features of these articles. Similarly, this article has already stated the significant contribution of these countries (Lucchetti and Lucchetti 2014). Unlike these studies, the present study found that “Journal of Religion and Health” was featured and the most contributed journal in this area. Journal of Religion and Health is an important journal in the field of SR/H.
The Duke University was the most contributed university, which was followed by the University of Michigan, according to a number of publications. Also we estimate the number of publications to be published in 2018. According to curve fitting results, we estimate that there will be 82 publications in 2018 in the WoS database on the topic of SR/H.
Top-cited three authors were found to be Koenig HG, Krause N and Levin JS, in our study. On the other hand, Koenig HG, Pargament KI and Sloan RP were the most frequently co-cited authors, respectively, according to co-citation analysis of active authors.
Ellison and Levin (1998) received the highest citations in their articles entitled “The religion-health connection: Evidence, theory, and future directions.” The second most cited publication was the study entitled “The daily spiritual experience scale: Development, theoretical description, reliability, exploratory factor analysis, and preliminary construct validity using health-related data” written by Underwood and Teresi (2002). These two publications could be considered by a researcher in particular.
As a result of the analysis of the most commonly used keywords in the abstracts section, trend topics are presented in Fig. 9 and Table 5. The most current keywords are “spiritual care,” “spiritual health,” “happiness,” “mindfulness,” “well-being,” “religious coping,” “adolescence” and “health-related quality of life,” “recovery,” “mental health,” “healing.” This indicated that spirituality and religion are important concepts in healthy life.
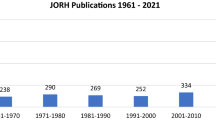
The present study had one limitation. We did not use PubMed, Google Scholar or Scopus databases which include more documents than Web of Science (WoS). We preferred the WoS database because it published articles in journals with high impact factors. Besides the first publication was in 1961 in Journal of Religion and Health, we could obtain publications in 1975 and beyond by searching in WoS.
Conclusion
This research found that there was a significant increase in the number of publications between the years 1999 and 2017, particularly after 2009. According to the results of this study, “Journal of Religion and Health” was featured and was the most effective journal in this area. The USA was the leading publisher according to a number of publications in this area. Although developed countries are the most productive countries in terms of contribution to the literature publications, contribution in some developed countries, such as Iran, Brazil, India, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, had significantly higher amounts.
Spirituality, religious beliefs and health are important concepts that complement each other in the improvement of patient health. This study will lead the researchers especially in terms of the important journals, active countries, authors, top-cited articles and current topics in SR/H research.
References
Clarke, A., Gatineau, M., Grimaud, O., et al. (2007). A bibliometric overview of public health research in Europe. European Journal of Public Health, 17, 43–49.
Damiano, R. F., Costa, L. A., Viana, M. T. S. A., Moreira-Almeida, A., Lucchetti,. Alessandra L. G., & Lucchetti, G. (2016). Brazilian scientific articles on “Spirituality, Religion and Health”. Archives of Clinical Psychiatry (São Paulo), 43(1), 11–16.
Ellison, C. G., & Levin, J. S. (1998). The religion-health connection: Evidence, theory, and future directions. Health Education & Behavior, 25, 700–720.
Garfield, E. (1987). 100 Citation classics from the Journal of the American Medical Association. JAMA, 257, 52–59.
Hill, P. C., & Pargament, K. I. (2003). Advances in the conceptualization and measurement of religion and spirituality: Implications for physical and mental health research. American Psychologist, 58(1), 64–74.
Koenig, H. G., McCullough, M. E., & Larson, D. B. (2001). Handbook of religion and health. New York: Oxford University Press.
Lucchetti, G., & Lucchetti, A. L. (2014). Spirituality, religion, and health: over the last 15 years of field research (1999–2013). The International Journal of Psychiatry in Medicine, 48(3), 199–215.
Muslu, Ü. (2018). The evolution of breast reduction publications: A bibliometric analysis. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, 42(3), 679–691.
Ozsoy, Z., & Demir, E. (2017). The evolution of bariatric surgery publications and global productivity: A bibliometric analysis. Obesity Surgery, 28(4), 1117–1129.
Ozsoy, Z., & Demir, E. (2018). Which bariatric procedure is the most popular in the world? A Bibliometric Comparison, OBES SURG, 28(8), 2339–2352.
Pargament, K. I. (1997). The psychology of religion and coping: Theory, research, practice. New York: Guilford.
Powell, L. H., Shahabi, L., & Thoresen, C. E. (2003). Religion and spirituality: Linkages to physical health. American Psychologist, 58(1), 36–52.
Şenel, E., & Demir, E. (2018). Bibliometric and scientometric analysis of the articles published in the Journal of Religion and Health Between 1975 and 2016. Journal of Religion and Health, 57(4), 1473–1482.
Senel, E., Demir, E., & Alkan, R. M. (2016). Bibliometric analysis on global Behcet disease publications during 1980–2014: Is there a Silk Road in the literature? Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, 31, 518–522.
Sloan, R. P., Bagiella, E., & Powell, T. (1999). Religion, spirituality, and medicine. Lancet, 353, 664–667.
Underwood, L. G., & Teresi, J. A. (2002). The Daily Spiritual Experience Scale: Development, theoretical description, reliability, exploratory factor analysis, and preliminary construct validity using health-related data. Annals of Behavioral Medicine, 24(1), 22–33.
Van Eck, N. J., & Waltman, L. (2010). Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics, 84(2), 523–538.
Van Raan, A. F. J. (2003). The use of bibliometric analysis in research performance assessment and monitoring of interdisciplinary scientific developments. Technikfolgenabschätzung, Theorie und Praxis, 1, 20–29.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Demir, E. The Evolution of Spirituality, Religion and Health Publications: Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow. J Relig Health 58, 1–13 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10943-018-00739-w
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10943-018-00739-w