Abstract
Recently, a patient with diabetes mellitus (DM) type 2 has been increasing in Japan. The patient should be managed not only by a specialist but also by himself focusing his attention on the improvement of his lifestyle at home. In the present study, we tried to develop a health management support system by which a diabetic patient in early stage can easily enter his daily life information, i.e. the biological information such as the data of blood sugar levels and blood pressure levels etc., the information of exercise and diet and send the information to the medical institution with a personal digital assistant (PDA). Afterwards, the patient can receive health instruction information by the physician in charge for self-care at his home with a PDA. The daily life information sent from the patient is stored in a server installed at the medical institution and analyzed. The physician can obtain the results of analysis by using a PC and send the instruction information necessary for patient management to the patient at home by using e-mail after diagnosing the patient’s condition by the system. To evaluate usability of the developed patient information input system with a PDA, an experiment was conducted by corporation of 20 volunteers who were possible self management and whose age’s range from 20s to 60s by questionnaire survey. As a result, almost examinees answered that lifestyle information could be easily entered by the sense like a mobile-phone and lots of positive opinions were obtained.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
In Japan, it is estimated that total persons with diabetes mellitus (DM) are about 18.7 millions including persons suspected of having DM and persons regarded strongly as diabetic patients are about 8.2 million by the survey report on diabetes in 2006 made by Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare [1]. Recently, a patient with DM type 2 has been increasing in Japan. DM is called one of the lifestyle diseases. If the patient is not care, he develops into various diseases such as diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic neuropathy, stroke, myocardial infarction and so on.
Therefore, the patient should be managed not only by a specialist but also by himself focusing his attention on the improvement of his lifestyle at home [2, 3].
Then, in the present study, we tried to develop a health management support system by which a diabetic patient in early stage can easily enter his daily life information, i.e. the biological information such as the data of blood sugar levels, blood pressure levels etc. and the information concerning exercise and food intake and send the information to the medical institution with a personal digital assistant (PDA). Afterwards, the patient can receive health instruction information such as nutrient intake and taking exercise by the physician in charge for self-care at his home.
In this paper, an outline of the health management support system and an evaluation of the system for operation are described.
System configuration
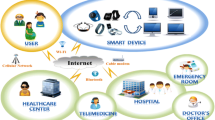
System architecture
This system is composed of a web server installed in the medical institution, personal computer (PC) operated by a physician and a PDA for the patient. Figure 1 shows a basic system configuration of the system.
Subsystem of patient information input system
The main function of the patient information input system is to enter essential information (patient’s ID, height, sex and target amount of calorie intake (kcal)), biological data (weight, body fat, blood sugar level, blood pressure level, and urine sugar level) and information concerning exercise (amount of exercise) and food intake (menu and amount), to make free text data concerning patient’s condition, to send the above-mentioned information and data, and to receive results of data analysis and a mail for health instruction information mail made by the physician.
The essential information is assumed to be a default setting and the information of calorie intake etc. is changed on demand.
Concerning the measurement of biological data, a measurement device or a sensor such as a blood sugar meter and an automatic sphygmomanometer is used.
An amount of energy consumption (kcal) is measured with a passometer as to exercise. Furthermore, rate of perceived exertion (RPE) classified into five stages is used and the exercise content is confirmed by entering the exercise time.
In Japan, dietary instruction for the diabetic patient is conducted based on “The food exchange table for the diabetic treatment” edited by Japan Diabetes Society in 1965, and revised in 2002 [4]. Concerning the input of the diet contents, we referred to the food exchange table. However, entry of information about all foods eaten by the patient in a day is not easy for him to sustain efforts of the entry, while the accurate information should be obtained. Therefore, we adopted a method of selecting not foods but the menu for the input of the diet contents.
In the menu selection method, the amount of diet has tendency to be vague by the level of patient’s consciousness for diet. Then, we contrived a food model of one unit (80 kcal) based on the food exchange table and the model is photographed and registered in the database. By the photographed model the patient can visually set up a standard of quantities of food from a browser at any time.
All information is entered by operating ten keys and the cursor, etc. and sent to the medical institution with a PDA.
Input method of diet content
The diet menu is selected by the procedure such as major classification → middle classification → menu (example: staple food → rice → curry and rice) for convenience. Figure 2 shows a flow of the input of the diet content.
The patient selects the major classification (such as staple diet, main dish, side dish, soup dish, others) from each input seat (such as breakfast, lunch, supper and between-meals eating), and enters the diet contents. The items of the middle classification selected from the major classification are shown as follows.
-
Items classified into staple food: rice, bread, noodles
-
Items classified into main dish: fish meal, meat meal, egg meal, bean curd
-
Items classified into side dish: vegetable cooking, salad and others
-
Items classified into soup dish: miso soup, soup
-
Items classified into other: fruit, goody, soft drink etc.
The food model reference
We made the programs for referring to the food model by using JSP (Java Server Pages) and MySQL for making a food model database.
The food model reference is conducted according to the following procedure: food classification screen → database (DB) inspection screen →image reference page. The item classified based on the food exchange table is selected on the food classification screen. The items of the classification tables are as follows.
-
Food classification table 1: grain, sweet potato, carbohydrate foods
-
Food classification table 2: fruit
-
Food classification table 3: fish and shellfish, meat, egg, cheese, soybeans and its products
-
Food classification table 4: milk, dairy products
-
Food classification table 5: fat and oil, fatty foods
-
Food classification table 6: vegetable, seaweeds mushroom etc.
-
Seasoning
-
Luxury goods
Each food classification items are stored in the database according to the table. The content of each table is displayed on the DB inspection screen. The food image pages were created by using HTML (Hyper Text Markup Language). And, the food name and the link tag that displayed each page were stored in the database. Additionally, the food model is comparable with a real size by photographing with the measure. Figure 3 is an example of a flow of the food model reference that makes the table 1 of the food classification screen (grain, sweet potato, and carbohydrate foods).
The basic duration of entering diet menus of the patient is based on seven days. The diet menu entered by the patient is converted into a calorie unit.
Subsystem of medical institution
The main function of the subsystem for the medical institution is to analyze the patient information and send instruction information etc. based on the analysis to the patient.
All information sent from the patient is accumulated in the server of the medical institution and analyzed. The database is allocated to every physician who participates in this system. However we made a database for only one physician in the trial system. The physician can obtain the results of analysis such as the ingredients of the foods taken by the patient by using a PC and send the instruction information by e-mail necessary for patient management after diagnosing the patient’s condition. The instruction or the advice is not made by system but made by the physician himself. The patient can refer to the result of analysis and receive the advice mail etc. In addition to the instruction information, the patient can see time serial data of his biological and lifestyle information and their charts on the screen of the PDA.
Furthermore, the ingredient balance included in diet is made as a chart, and the automatic diagnosis comment by the program is sent and displayed by the button operation with the PDA at patient’s home. Figure 4 shows an example of the automatic diagnosis comment image.
Template for instruction information report by e-mail
The instruction information (such as results of diagnosis and instruction content etc) sent to the patient is made as a report.
To make the report for the patient, it centers on text data as seen easily on the screen of a PDA by using a template. Using the template, evaluation and advice concerning management of body condition, diet and exercise, the answer for question from the patient, comprehensive evaluation of self-management by the patient etc. are described.
To evaluate the management of patient’s body condition, diet and exercise, the question items (Ex.: Is the management of the blood sugar level excellent?) that express the point of each management are set up and three stages evaluation (excellent, fair, poor) is used. The physician may select by the radio button. Figure 5 shows a part of the template in Japanese and English.
Evaluation
Method
To evaluate usability of the patient information input system including the food models reference tool, an experiment was conducted by questionnaire survey (five-grade evaluation: excellent, good, fair, poor, bad) by corporation of 20 volunteers who are possible self management and whose age’s range from 20s to 60s (including medical staff). The following is a table in which age, sex and experience in using a PC, a PDA and a mobile-phone of the volunteers is written (see Table 1). The experience in using a PDA of all volunteers is poor.
For this purpose, a PDA made by NEC Corporation was used for input of lifestyle information of examinees. They referred to pictures of polished rice in a small rice bowl and 4 foods (boiled wheat noodle, boiled soybean, strawberry and grape) on the same plate of about 15 cm in diameter according to the above-described procedure (see Fig. 3).
Result
As a result, 18 people answered that lifestyle information could be easily entered by the sense like a mobile-phone.
About understandability of the reference method of the food model image, 6 people answered excellent, 13 people answered good and 1 people answered poor. Unlike an actual patient, though there is no experience of receiving the dietary instruction, almost examinees answered that they were able to refer to the food model image who wanted to see without a complex procedure.
Then, about convenience of the food models reference tool, 6 people answered excellent, 13 people answered good (they used it in case of being) and 1 people answered no opinion. Positive opinions such as “the standard of the amount of quantities of food is easily understood” were obtained.
Opinions are divided into image quality and easiness to see influenced by the photographing procedure (excellent: 2 people, fair: 10 people, poor: 8 people).
About the most important evaluation for recognition of the real size of the food from photograph image with measure, 6 people answered excellent, 11 people answered good and nobody answered as bad. Opinions such as “a white plate is comprehensible in a black background” and “use of disposable chopsticks as one of scales ” were also obtained.
Discussion
In the present study, we constructed a health management support system for patients with DM at home by using a PDA.
Similar systems were already developed by several researchers and companies [5–11]. However, there are some problems in such systems. The most important problem is how to take information of the patient’s diet contents correctly [12]. That is, the indispensable point for the treatment of diabetes is an appropriate dietary therapy. Although a method of acquiring information concerning diet is very important, there is no system in which an appropriate method is used.
Therefore, the food model used by the epidemiological study etc. was made in the form of photograph registration in this study and this is the first trial. The food model reference with PDA got a lot of positive opinions to the reference method and convenience, etc. from the questionnaire survey results. In the future, it seems that the convenience improvement of the food model reference is expected by devising the photographing conditions etc. of the photograph image.
In addition, it was considered that it is easy to collect the accuracy information of diabetic patients due to simple operation by using the system. As a result, the analysis of the information and making comment by automatic diagnosis can be smoothly conducted. Especially, the templates made by us is considered to be useful for expressing patient’s condition easily.
Although this system has not been clinically utilized, some diabetic patients and physicians showed interest in it.
Conclusion
As a long series of diabetic self-management is not easy even if a diabetic patient has strong intention, poor management is not few to cause complication due to deterioration of the condition [3]. Then, in this study, a health management support system for patients with DM at home was constructed so that the patient may continue good self-management. By the system, it was recognized that the input of lifestyle information in daily can be facilitated with a portable terminal such as a PDA and the function as an easy-to-use tool is provided. As a result, the system can also facilitate improving the patient’s consciousness of diet and exercise. It was suggested that this system is useful for the doctor to diagnose the patient’s condition based on the result of analysis of the transmitted patient’s information and to make and send the instruction information for the patient.
From the evaluation result of usability of the patient information input system, it became clear that almost examinees were interested in the use of the food model reference function and this system was easily operated by the sense like a mobile-phone. At the present time, though the system has not been tried for clinical use yet, it is expected that the system is useful for the management support of patients with DM at home by the experiment concerning operation and from the opinions of diabetic patients and specialists.
At the beginning of using the system, users (patients and physicians) must enter the given ID number and password. SSL (Secure Socket Layer), one kind of the communication in cipher is used for data transmission. It is considered that the system has no problem concerning security.
Although this system is now under the trial and clinical outcomes cannot be obtained, some diabetic patients and physicians showed interest in it.
References
Ministry of Health: Labour and Welfare, The national health and nutrition survey in 2006. http://www.mhlw.go.jp/houdou/2008/04/h0430-2.html (in Japanese).
Azuma, M., and Kawaguchi, T., Utility of Telenursing for Diabetes Self-Management. Promoting Center for Nursing Research, University of Hyogo. Coll. Nurs. Art Sci. 2:1–47, 2004(in Japanese).
Azuma, M., Kawaguchi, T., Advances in nursing using the telenursing system part 2: its application in home nursing for diabetes mellitus patients. Promoting Center for Nursing Research, University of Hyogo. Coll. Nurs. Art Sci. 1:7–11, 2003(in Japanese).
Japan Diabetes Society. List of food exchange for the diabetic treatment: the sixth edition. BUNKODO CO., LTD. 2002 (in Japanese).
Wakamatsu, H., and Takahashi, T., Remote information system for control and support of everyday life.. J. Jpn. Soc. Health Sci. 24(1):105–117, 2008(in Japanese).
Giorgino, T., Azzini, I., Rognoni, C., Quaglini, S., Stefanelli, M., Gretter, R. et al., Automated spoken dialogue system for hypertensive patient home management. Int. J. Med. Inform. 74:159–167, 2005 doi:10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2004.04.026.
Prado, M., Roa, L. M., and Reina-Tosina, J., Viability study of a personalized and adaptive knowledge-generation telehealthcare system for nephrology (NEFROTEL). Int. J. Med. Inform. 75:646–657, 2006 doi:10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2006.03.005.
Levin, E., and Levin, A., Evaluation of spoken dialogue technology for real-time health data collection. J. Med. Internet Res. 8(4): e30, 2006. doi:10.2196/jmir.8.4.e30.
Kollmann, A., Riedl, M., Kastner, P., Schreier, G., and Ludvik, B., Feasibility of a mobile phone-based data service for functional insulin treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus patients. J. Med. Internet Res. 9(5): e36, 2007. doi:10.2196/jmir.9.5.e36.
Ma, C., Warren, J., Phillips, P., and Stanek, J., Empowering patients with essential information and communication support in the context of diabetes. Int. J. Med. Inform. 75:577–596, 2006 doi:10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2005.09.001.
Kwon, H. S., Cho, J. H., Kim, H. S., Song, B. R., Ko, S. H., Lee, J. M. et al., Establishment of blood glucose monitoring system using the internet. Diabetes Care. 27(2): 478–483, 2004 doi:10.2337/diacare.27.2.478.
Honda, M., Toyasaki, M., Kazumi, T., Nanbu, S., Diabetes medical nutrition therapy in general physicians supported by International Institute for Diabetes Education and Study. J Jpn. Diabetes Soc. 49(2): 163–169, 2006. (in Japanese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tani, S., Marukami, T., Matsuda, A. et al. Development of a Health Management Support System for Patients with Diabetes Mellitus at Home. J Med Syst 34, 223–228 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-008-9233-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-008-9233-x