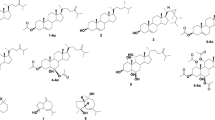
A new sesquiterpene, named spheciospongone C (1), and a known compound fucosterol (2) were isolated from the brown algae Sargassum polycystum. The structure and absolute configuration of compound 1 were identified by comprehensive 1D, 2D NMR, HR-ESI-MS spectral data and compared the circular dichroism (CD) data with the literature.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
The genus Sargassum, belonging to the Sargassaceae family, consists of 250 species in the world, widely distributed in tropical and temperate sea zones, there are 60 species found in China [1]. The species of S. polycystum has been used as traditional Chinese medicine to treat barbiers, edema, and indigestion [2]. S. polycystum can produce a great number of flavonoids and polyphenols with strong antioxidant activities [3], and steroids, phenols, tannins, saponins, flavonoids, terpenoids and glycosides were also isolated from S. polycystum [4]. The species of S. polycystum also has great development value in industrial raw material [5] in the fields of food [6], medicine [7,8,9], agriculture [10], and ecological restoration [11]. In our search for bioactive constituents from S. polycystum, a new sesquiterpene spheciospongone C (1), along with a known compound fucosterol (2) were isolated. Herein we describe the isolation and structural determination of the isolated compounds.
Compound 1 was obtained as a yellowish oil. Its molecular formula C15H22O5 (five degrees of unsaturation) was determined by the HR-ESI-MS spectrum, and further supported by the evidence of 13C NMR spectral data (Table 1). In the 1H NMR spectrum (Table 1), the presence of five methyl groups at δH (0.81, 1.02, 1.38, 2.00, and 2.29), and an olefinic proton signal at δ (5.58, s), indicated that compound 1 has a sesquiterpene skeleton [12]. The combination of 1H, 13C NMR, and HSQC spectra data showed 15 carbon signals, including one ketone carbon at δC 208.2, one ester carbon at δ 172.3, two olefin carbon groups at δ 192.7 and 108.2, three oxygenated carbons at δ 93.9, 76.0, and 69.2, two methylene carbon groups at δ 42.9 and 42.3, one quaternary carbon at δ 40.0, and five methyl groups at δ 26.7, 25.9, 22.2, 21.2, and 16.4. The preceding NMR data indicated that compound 1 was similar to spheciospongone A [13], except for the presence of one acetyl group at C-14 (δ 172.3, C) and C-15 [δ 21.2 (CH3) and δH (2.00, s)] in 1 in the 1H and 13C NMR spectra.

The whole structure was further confirmed by the 2D NMR spectral (Fig. 1). The COSY correlations from H-3 to H-2a/H-2b/H-4a/H-4b established a moiety of CH2(2)-CH(3)OH-CH2(4). The HMBC correlations from CH3-11 and CH3-12 to C-1/C-2/C-6, CH3-13 to C-4/C-5/C-6, disclosed a substructure of 1,1,5-trimethyl-cyclohexane [12]. Furthermore, the HMBC correlations from CH3-10 to C-8/C-9, and from H-8 to C-6/C-7/C-9 enabled the formation of a 7-oxo-9-methyl-6,7-dihydrofuran ring to be located at C-6 in a spiro form (Fig. 1).
The relative configuration of 1 was based on the NOESY correlations as indicated in Fig. 1. The NOESY correlations of CH3-11 to CH3-13, CH3-13 to CH3-15, and CH3-12 to H-3 indicated that CH3-11, CH3-13, and CH3-15 were on the opposite side of the H-3 and CH3-12. In addition, the CD spectrum of 1 was in good agreement with the literature CD spectrum [12], the negative Cotton effect (CE) (Δε271 nm –26.527) for the n–π* transition and the positive CE (Δε218 nm +5.004) for the π–π* transition when applying the right-handed helicity rule (Fig. 2). Accordingly, the chiral centers of C-3, C-5, and C-6 were determined to be 3S, 5R, and 6R; thus, the structure of 1 was established to be spheciospongone C. By comparing physical and spectroscopic data with values found in the literature, the known compound 2 was determined as fucosterol [14].
Experimental
General. 1D and 2D NMR spectra were measured on an NMR spectrometer (JEOL, 600 MHz, Japan) and a Bruker AV-400 (Bruker Corporation, Switzerland) instrument with TMS as the internal standard ESI-MS and HR-ESI-MS spectra were obtained on a Bruker Daltonics Apex-Ultra 7.0 T (Bruker Corporation, Billerica, MA, USA) and a Q-TOF Ultima Global GAA076 LC mass spectrometer. For semipreparative HPLC, an Agilent 1100 prep-HPLC system with a Waters C18 semipreparative column (9.4 × 250 mm, 7 μm) was used. Sephadex LH-20 (Pharmacia Co. Ltd., Sandwich, UK) and silica gel (200–300 and 300–400 mesh, Qingdao Marine Chemical Factory, Qingdao, China) were used for column chromatography (CC). Silica gel (GF254) for TLC were supplied by the Qingdao Marine Chemical Factory in China. All solvents used were of analytical grade (Guangzhou, China).
Plant Material. The plant material was collected from Danzhou, Hainan Province, China and was identified by Prof. Caijuan Zheng, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hainan Normal University, Haikou, China. A voucher specimen (No. HZ202109) has been deposited at the key laboratory of tropical medicinal resource chemistry of ministry of education, college of chemistry and chemical engineering, Hainan Normal University.
Extraction and Isolation. The air-dried Sargassum polycystum (1.5 kg) were powdered and extracted three times with 95% EtOH (each for 7 days) at room temperature. The crude extract was suspended in water and extracted successively with petroleum ether (PE) and ethyl acetate (EtOAc). The petroleum ether extract (20.0 g) was subjected to column chromatography (CC) on silica gel, eluting with PE–EtOAc (40:1, 20:1, 15:1, 10:1, 8:1, 5:1, 2:1, 1:1) to yield eight fractions (Frs. 1–8). Fraction 6 (200 mg) was further subjected over silica gel column (PE–EtOAc, 8:1) and subjected to Sephadex LH-20 (PE–CHCl3–MeOH, 2:1:1), and then purified by semipreparative HPLC eluted with MeOH–H2O (70:30) to yield compound 1 (1.5 mg). Repeated chromatography of Fr. 3 (355 mg) was used over a silica gel column (PE–EtOAc, 10:1→1:10) to yield compound 2 (4 mg).
Spheciospongone C (1), yellowish oil; \({\left[\mathrm{\alpha }\right]}_{\mathrm{D}}^{20}\) –12.0° (c 1.0, CH3OH). UV (MeOH, λmax, nm): 272, 208. IR (KBr, νmax, cm–1): 3516, 2900, 1668, 1457, 1169. 1H and 13C NMR data (CD3OD), see Table 1. HR-ESI-MS m/z 281.1392 [M – H]– (calcd for C15H21O5, 281.1394).
Fucosterol (2), white powder. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, δ, ppm, J/Hz): 5.34 (1H, br.d, J = 5.2, H-6), 5.17 (1H, q, J = 6.7, H-28), 3.51 (1H, m, H-3), 2.18 (1H, m, H-25), 1.60 (3H, d, J = 6.7, H-29), 1.00 (3H, s, H-19), 0.96 (3H, d, J = 1.4, H-21), 0.68 (3H, s, H-18). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3, δ, ppm): 37.4 (C-1), 31.9 (C-2), 71.9 (C-3), 42.40 (C-4), 140.8 (C-5), 121.8 (C-6), 31.6 (C-7), 32.0 (C-8), 50.3 (C-9), 36.6 (C-10), 21.2 (C-11), 39.9 (C-12), 42.5 (C-13), 56.9 (C-14), 24.5 (C-15), 28.4 (C-16), 55.9 (C-17), 12.0 (C-18), 19.5 (C-19), 36.5 (C-20), 18.9 (C-21), 35.4 (C-22), 25.8 (C-23), 147.1 (C-24), 34.9 (C-25), 22.3 (C-26), 22.4 (C-27), 115.7 (C-28), 13.3 (C-29). ESI-MS m/z 411.3 [M – H]– [14].
References
C. K. Zeng, Algae of China, Science Press, Beijing, 2000.
S. H. Xu, L. S. Ding, M. K. Wang, S. L. Peng, and X. Liao, Chin. J. Org. Chem., 22 (2), 138 (2002).
Y. J. Wu, H. Q. Gao, Y. X. Wang, Z. T. Peng, Z. Q. Guo, Y. X. Ma, R. F. Zhang, M. W. Zhang, Q. Wu, J. Xiao, and Q. P. Zhong, J. Food Sci., 87, 968 (2022).
M. F. Nazarudin, N. H. Alias, S. Balakrishnan, W. N. I. W. Hasnan, N. A. I. N. Mazli, M. I. Ahmad, I. M. Yasin, A. Isha, and M. Aliyu, Molecules, 26, 5216 (2021).
X. Q. Luo, X. G. Wang, and Z. B. Yang, Chem. Bioengin., 24 (6), 64 (2007).
P. Matanjun, S. Mohamed, N. M. Mustapha, and K. Muhammad, J. Appl. Phycol., 21 (1), 75 (2009).
Q. Y. Liu, Q. Y. Meng, and Z. H. Liu, Acad. J. Guangdong Coll. Pharm., 19 (4), 336 (2003).
P. Matanjun, S. Mohamed, K. Muhammad, and N. M. Mustapha, J. Med. Food, 13 (4), 792 (2010).
M. Motshakeri, M. Ebrahimi, Y. M. Goh, P. Matanjuna, and S. Mohamed, J. Sci. Food Agr., 93 (7), 1772 (2013).
V. Erulan, P. Soundarapandian, G. Thirumaran, and G. Ananthan, Ame-Eur. J. Agric. Environ. Sci., 6 (4), 392 (2009).
J. F. Liu, E. Y. Xie, S. L. Sun, and J. B. Zhang, Ocean Deve Managemen, 11, 71 (2012).
M. Shibagaki, S. Shibata, and H. Kanekoa, Agric. Biol. Chem., 45 (12), 2911 (1981).
D. Liu, M. J. Xu, L. J. Wu, Z. W. Deng, and W. H. Lin, J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res., 11 (9), 811 (2009).
Y. Sun, G. F. Ding, and Y. F. Xu, Oceanologia Et Limnologia Sinica, 48 (3), 640 (2017).
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 220RC593), the Key Research and Development Program of Hainan Province (No. ZDYF2021SHFZ270), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 32160108 and 41866005), Key Science and Technology Program of Hainan Province (No. ZDKJ202008), and the Innovation Platform for Academicians of Hainan Province Specific Research Fund of The Innovation Platform for Academicians of Hainan Province (No. YSPTZX202030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Khimiya Prirodnykh Soedinenii, No. 3, May–June, 2023, pp. 428–430.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, M., Gong, YB., Chen, Y. et al. A New Sesquiterpene from the Brown Algae Sargassum polycystum. Chem Nat Compd 59, 505–507 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-023-04036-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-023-04036-1