Abstract
During angiogenesis, growing neovessels must effectively navigate through the tissue space as they elongate and subsequently integrate into a microvascular network. While time series microscopy has provided insight into the cell activities within single growing neovessel sprouts, less is known concerning neovascular dynamics within a large angiogenic tissue bed. Here, we developed a time-lapse imaging technique that allowed visualization and quantification of sprouting neovessels as they form and grow away from adult parent microvessels in three dimensions over cubic millimeters of matrix volume during the course of up to 5 days on the microscope. Using a new image acquisition procedure and novel morphometric analysis tools, we quantified the elongation dynamics of growing neovessels and found an episodic growth pattern accompanied by fluctuations in neovessel diameter. Average elongation rate was 5 μm/h for individual vessels, but we also observed considerable dynamic variability in growth character including retraction and complete regression of entire neovessels. We observed neovessel-to-neovessel directed growth over tens to hundreds of microns preceding tip-to-tip inosculation. As we have previously described via static 3D imaging at discrete time points, we identified different collagen fibril structures associated with the growing neovessel tip and stalk, and observed the coordinated alignment of growing neovessels in a deforming matrix. Overall analysis of the entire image volumes demonstrated that although individual neovessels exhibited episodic growth and regression, there was a monotonic increase in parameters associated with the entire vascular bed such as total network length and number of branch points. This new time-lapse imaging approach corroborated morphometric changes in individual neovessels described by us and others, as well as captured dynamic neovessel behaviors unique to days-long angiogenesis within the forming neovascular network.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Angiogenesis is the formation of new blood vessel segments from existing parent vessels [1] in which sprouting neovessels advance through the complex stromal environment until they connect with other vessel segments, thereby completing a new perfusion circuit. Sprouting angiogenesis is a spatially complex, temporally dynamic biological process. Initially, an endothelial cell sprouts out from the parent vessel wall. A combination of migration and proliferation of endothelial cells leads to the elongation and advancement of the sprouted neovessel, which can reach millimeters in length. However, the details of this process are poorly understood. A single endothelial cell at the advancing end of the growing neovessel (called a tip cell), in coordination with the trailing endothelial cells (or stalk cells), is thought to guide the neovessel as it advances [2]. Unlike the stalk cells, the tip cell must simultaneously anchor to, yet deform, the nascent matrix system to enable the advancement of the neovessel. This deformation involves an active matrix remodeling process involving local structural degradation, matrix synthesis, and matrix deformation [3–6]. It is unclear whether interactions between stalk cells and matrix are also important aspects of the angiogenesis process. While there is considerable information regarding the genes, molecules, and cell activities that regulate angiogenesis, very little is known how this complex biological system is integrated.
Visualization of growing neovessels and matrix in three dimensions (3D) over time has provided invaluable insight into this dynamic process [4]. This 4D imaging approach (3D plus time) can provide direct observation of neovessels sprouting and advancing, along with matrix deformation. However, the approach is technically challenging, and applications to date for studying angiogenesis in vitro have focused on imaging small spatial volumes for relatively short periods of time. Although sprouting angiogenesis involves small structures, as individual neovessels are typically microns in diameter, the neovessels advance across a macroscopic scale of millimeters to centimeters in 3D tissue spaces over a relatively slow time frame (hours to days), and the resulting microvascular networks in organ and tissue culture models of sprouting angiogenesis often occupy many cubic millimeters of space [6–9]. Observation of tips of neovessels requires a small field of view, which complicates the visualization of larger fields of view in the macroscale tissue space. The relatively slow nature of neovessel growth requires an imaging approach that maintains the viability of the angiogenic culture over long periods of time. Finally, the 3D nature of the neovessels and stromal environment in physiologically relevant tissue and cell culture models complicates image acquisition, not only due to compromised optical performance, but also due to spatial registration, as the site may undergo arbitrary deformation due to vessel traction forces.
This manuscript presents an imaging system, culture model, and analysis pipeline that enables the visualization of angiogenic sprouting in a 3D stromal environment over cubic millimeters of physical space during many days of culture using multiphoton time-lapse microscopy, allowing visualization of thousands of neovessel segments in the network while still providing the spatial resolution to identify and track individual neovessel sprouts. Using this process, we have captured the dynamic behavior of neovessel sprouting and advancement in a 3D organ culture model of angiogenesis while simultaneously imaging the collagen matrix [9–11]. Neovessel behavior included frequent changes in the direction of tip cell orientation, repeated neovessel advancement and retraction, episodic elongation of neovessels when advancing, collagen fibril alignment and condensation coincidental with neovessel advancement, and tip cell “handshaking” during inosculation of two neovessels. Quantitative morphometric analysis of the entire image domain over time demonstrated that measurements of the size and complexity of the overall microvascular network, which typically consisted of thousands of neovessel segments, continued to increase nearly monotonically despite the apparent stochastic behavior exhibited by individual neovessel sprouts.
Materials and methods
Materials
Low-glucose Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium (DMEM), F12 nutrient, and gentamicin (25 mg/l) were obtained from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA). DMEM and F12 were combined in 1:1 ratio. Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO) provided transferrin (100 mg/ml), insulin (10 mg/l), sodium selenite (2.7 mg/l), putrescine (17 mg/l), progesterone (6.6 mg/l), and bovine serum albumin (BSA) (105 mg/l). Type I rat tail collagen was supplied by BD Biosciences (San Jose, CA), and recombinant human vascular endothelial growth factor (rhVEGF, 100 µg/l)) was obtained from Peprotech (Rocky Hill, NJ). Worthington Biochemical (Lakewood, NJ) provided clostridial collagenase. The Rat Resource and Research Center (University of Missouri) provided the SD-EGFP rats (SD-Tf(UBC-EGFP)2BalRrrc, Strain # 65) [12].
Microvessel isolation
We employed a 3D in vitro model of angiogenesis involving neovessel sprouting from intact microvessel elements [6, 9, 10, 13, 14]. Microvessel fragments were isolated from epididymal fat pads harvested from male rats heavier than 350 g, as described previously [10], and the study was approved by the University of Arizona Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. The fat pads were minced into ~1-mm3 pieces and then subjected to limited digestion with 2 mg/ml Clostridium collagenase in Dulbecco’s divalent-cation-free phosphate-buffered saline (DCF-PBS) containing 2 mg/ml BSA at 37 °C for 8 min. The solution was immediately diluted with L-15 media containing 2 % fetal bovine serum to halt digestion and then centrifuged. The pellet was washed twice and re-suspended in L-15 media with 2 % serum. Subsequently, the suspension was filtered through 350- and 30-µm sterile nylon filters. The 30-µm filter was transferred to a sterile Petri dish and washed with L-15 media to suspend the fragments. The solution was analyzed for number of microvessels and centrifuged to obtain a pellet of microvessel fragments. While on ice, type I rat tail collagen was mixed with water and concentrated DMEM to obtain a 3 mg/ml collagen and 1X DMEM solution. This solution was neutralized to ~pH 7.4 with 1 N NaOH. The microvessels were immediately re-suspended in collagen at a concentration of 30,000 fragments/ml. The resulting mixture of microvessels and liquid collagen was poured into molds and allowed to polymerize, as described below.
Preparation of vascularized cultures
The collagen and vessel preparations were poured into polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) molds containing a stainless steel mesh frame (56 wires per inch, 316 stainless steel, 0.004″ diameter) that served as an anchor. The mesh was washed thoroughly and cut into strips that were three wires wide. The mesh was then curved into an 11-mm-diameter circular frame, overlapping and crimping the ends. Alternatively, the mesh was bent to construct a 22 × 32 mm rectangle, for rectangular constructs (Suppl. Fig. 1). We assembled the circular shaped steel mesh ring and the circular PTFE molds (interior diameter of 15 mm) in a 60-mm plastic Petri dish. This configuration allowed for a planar equally constrained growth model (circular constrained (CC) model). The long-axis-constrained (LAC) cultures were assembled with a rectangular PTFE mold (opening 26 × 9 mm) that had a notch cut into its side so that it fit over the rectangular mesh (Suppl. Fig. 1) [5]. This configuration held the culture across the short sides.
Five hundred microliters of collagen–microvessel suspension was added to the PTFE and mesh molds. Collagen was polymerized at room temperature for 5 min. Then, the culture was transferred to a 37° 5 % CO2 incubator where the gel was fully polymerized for 20 min. PTFE molds were then removed from the constructs, and serum-free media (DMEM/F-12 with SATO components, transferrin, insulin, and vascular endothelial growth factor) was added to the culture. The cultures were incubated for 48 h before imaging began. A duplicate culture remained in the incubator during imaging as a growth control sample.
On stage incubation
Cultures were imaged on an upright multiphoton microscope, using a high NA water immersion objective (XLUMPlanFl, 20X/0.95 W, Olympus). The objective lens was soaked in a bath of 70 % ethanol and then allowed to evaporate dry. A stage-top incubator maintained the cultures during imaging (NU-UW5D, Tokai Hit, Fujinomiya, Japan) (Suppl. Fig. 1 top). The incubator consisted of a heated glass stage, a water bath, a heated glass top with opening for objective, a silicone gasket skirt on the objective to cover the opening in the incubator top, an objective heater, a line for CO2 gas, and a controller for all of the components. The stage was heated to 38 °C, the water bath to 34 °C, and the objective heater was set to 39.5 °C and the top heater to 43 °C to prevent condensation. A premixed 95 % air and 5 % CO2 gas were passed through the water bath and into the chamber at a rate of 150 ml/min. A pump system was added to maintain a constant level in the water bath and to counteract any evaporation that occurred. Solid perfusion tubes were used for daily flushing of media in the culture. Two tubes were allowed for syringe access to the removal of media, addition of a fresh media wash, removal of the wash, and replacement of media to the culture.
Imaging parameters
A Trimscope I microscope (LaVision BioTec, Bielefeld, Germany), the ImSpector software package (LaVision), and a titanium sapphire laser (Ti:Saph) (Chameleon Ultra, Coherent, Glasgow, Scotland) were used to acquire image data. The microscope was fitted with a triple port with three PMTs to collect light from the sample through the objective lens, and a double transmission port holding two PMTs and a photodiode for light through the condenser lens. SHG and fluorescence were imaged with two gallium arsenide PMTs (H7422-40, Hamamatsu, Japan) and the transmitted laser light was recorded with a silicone photodiode. The Ti:Saph laser operated at 780 nm. A 405-nm dichroic mirror separated SHG and EGFP fluorescence. SHG was collected through a 377/50-nm band-pass filter, and EGFP fluorescence was collected through a 550/88-nm band-pass filter. To adjust for attenuation due to the optical properties of the sample, we adjusted the laser power with an automatic increase from 40 to 80 mW during the z-scan.
A mosaic array of 3D image stacks was acquired to provide an overall 3D image dataset with dimensions 2.0 × 2.0 × 0.9 mm. The mosaic consisted of a 5 × 5 grid of 400-µm square stacks, where each stack consisted of 301 slices in the z-direction, incremented by 3 µm. We scanned each 400-µm field of view at a resolution of 510 × 510 pixels, with an 800-Hz line frequency. These settings allowed the entire volume to be imaged every 2 h.
The sample was placed on the stage, and the x- and y-coordinates of the approximate center of the gel were identified. The top of the gel was identified at these coordinates, and the z-location was zeroed. The positional limits for imaging along the x- and y-directions were set to ±800 µm. We set the z-range to state at 100 µm and end at 1000 µm below the sample surface. Image acquisition was paused after approximately 24 h to change the media. At this time, the objective was retracted from the culture, and the media was changed. We then reset the stage to the original x- and y-coordinates and identified the top of the gel again. This location served as the new z-coordinate zero. This processes reduced the effect of collagen gel contraction in z-direction.
Image processing
For processing of data MATLAB (MathWorks, Natick, USA), the Image Processing Toolbox and publically shared MATLAB functions and custom programs were used. The image files were assembled from each slice in each stack into data stacks for each time point and channel using HDF file format (Suppl. Fig. 2). The intensity range in each channel and time point was assessed to compute an appropriate global scaling for conversion from 16 to 8 bit. Standard max–min scaling is inappropriate for two-photon data due to hyper-intense signals from lipid-rich vacuoles. The SHG data were square-root-transformed, as signal intensity is nonlinearly dependent on collagen density. Fluorescence intensity was also square-root-transformed, as this preserves low-intensity signals. Noise in the SHG channel was reduced using a median filter and in the fluorescence channel with a Wiener filter (Suppl. Fig. 2).
We analyzed the spatial sensitivity of the system and found that it varied over time and with depth due to laser drift and nonlinear signal production. The 60th percentile of the SHG signal in a 100 × 100 × 50 µm subregion was computed as a measure of spatial sensitivity. Collagen, the source of the SHG signal, is uniformly present throughout the sample. We interpolated an intensity correction matrix from these data and applied it to the SHG and fluorescence channels. Background in the fluorescence channel originated from collagen autofluorescence as well as out-of-focus two-photon fluorescence. We subtracted the background from the EGFP signal by first thresholding the EGFP signal from fragments and sprouts through a multistep process that included edge and noise detection. We used signals not originating from fragments and sprouts to interpolate the background throughout the image stack. For visualization of the microvessels and sprouts, we thresholded fluorescence using a similar approach as for background estimation. Our large data stacks have only a small fraction of voxels containing signal from EGFP, and noise in the remaining voxels affected the rendering quality. The computation of thresholds also allowed the removal of small independent noncellular particles in the volume datasets. We corrected drift of the imaged sample manually for each time point to create movies and time series visualization using a custom program written in MATLAB. Image co-registration software assisted the manual process. 3D rendering occurred on a down-sampled dataset and on full resolution regions of interest (ROI) on a subset of the scanned depth that included features present at all time points.
Data storage and transfer
To overcome the limitations of microscopy software addressable memory space, each frame was stored in a single file, keeping minimal data in memory and minimizing storage of microscope metadata in the image files. Since we stopped imaging daily to change culture medium, we used this opportunity to initiate data transfer of the previous day’s data to external storage. We accumulated more than a million files and more than 500 GB of data per experiment. Because transfer of small files is highly inefficient, we compressed the raw data for each imaging interval into a single archive file and transferred it to a storage server (Suppl. Fig. 2). For sharing of the data among multiple investigators, a data grid software solution was employed (iRODS.org, Data Intensive Cyber Environments Center) allowing transfer of large files through multiple connections at inter-institutional speeds of up to 20–30 MB/s.
Visualization and analysis of 4D image data
Visualization was accomplished using FluoRender [15, 16] (http://www.sci.utah.edu/software/fluorender.html). Morphometric analysis was performed using Amira (FEI, Hillsboro, Oregon) and WinFiber3D (http://mrl.sci.utah.edu/software/winfiber3d). Details of the 3D morphometric analysis can be found in our previous publications [5, 9, 17]. Briefly, the processed image datasets for the cellular fluorescence channel were skeletonized at each time point, and these skeletonizations were analyzed using WinFiber3D to determine total vascular length (length of all line segments within the dataset, i.e., the contour length of the network), total number of branch points (sites of branching and anastomosis), and end points (vessel-free ends). These data were normalized by the imaged volume at each time point to account for contraction during the imaging process.
Since in-plane contraction of the gel was minimal in the CC experiments due to the boundary constraint, we were able to identify all vascular components associated with an individual microvessel fragment over time in the successive skeletonizations. Four initial fragments were selected randomly at the first time point, and the total length of all vascular elements connected to these initial fragments was measured at each time point and normalized by the vascular length of the entire culture. This provided the percentage of vascular length that can be associated with these initial fragments.
Results
Our previous findings from experiments examining angiogenesis suggested that there is a dynamic interplay between the neovessel and the surrounding bulk 3D stroma [8, 9, 11]. To better elucidate this putative dynamic behavior, we performed 5D microscopy (3D, time, and multichannel) of growing neovessels sprouting from parent microvessels in a simple 3D collagen-I matrix. Because we desired to visualize individual neovessels simultaneously with collagen fibril organization (and possible other tissue components) over a large field of view, we developed an onstage ex vivo system (Suppl. Fig. 1), facilitating the use of nonlinear optical microscopy via two-photon-excited fluorescence and second harmonic generation (SHG). This enabled us to visualize neovessel activity in three dimensions, using either a ubiquitously expressed GFP fluorescence reporter or endogenous cell signals, while simultaneously capturing the SHG signal from collagen fibrils to visualize matrix architecture [11]. Finally, mosaic arrays of these different signals were collected over time and assembled into a 5D image dataset, permitting a completely new physical and temporal assessment of neovessel–matrix dynamics (Fig. 1). Neovessel sprouting and growth were imaged over the course of 5 days starting after an initial two-day lag period after culture setup. Twenty-five individual, adjacent image stacks, encompassing an area of approximately 4 mm2 of culture, were acquired every 2 h. Neovessel sprouting and growth were fairly uniform across the imaged volume (Fig. 2). Incubation conditions in the commercial stage-top culture chamber (Suppl. Fig. 1) matched routine ex vivo culturing of isolated microvessels [10] and resulted in comparable neovessel growth between the stage-top and routine culture (Suppl. Fig. 3).
Summary of the imaging and analysis protocol used in the study, and the generalized findings related to neovessel activity. Top row: schematic of the time-lapse acquisition involved an iterative process of twenty-five fields of view simultaneously recording SHG signals from collagen and fluorescence from EGFP in a mosaic fashion every 2 h. Raw image data were transferred to an open-source storage server and processed off-line. Bottom Rows: cartoons of the three main dynamic processes observed in the angiogenesis ex vivo system emphasizing the neovessel growth activities and collagen fibril restructuring associated with the growing neovessels
Full field of view of microvessel culture undergoing sprouting and neovessel formation during 5 days of incubation. Numbers indicated the time points in hours after start of microscopy. Green: EGFP; black: collagen SHG; bottom: minimum projection of laser transmission resembling a phase contrast image. Scale bar 250 microns. Red square illustrates region of interest for subsequent figures. Neovessels formed uniformly throughout the culture. (Color figure online)
Angiogenic growth over the entire imaged volume appeared to advance in time relatively monotonically. Examining the morphometric data based on the skeletonizations of the entire neovessel network for the circular constrained construct, both normalized total vascular length and normalized branch points increased steadily throughout the CC experiment with seemingly asymptotic behavior after 100 h (Fig. 3a, b). Normalized end points steadily decreased over the time series experiment (Fig. 3c). Morphometric data from the LAC experiment exhibited the same trends (data not shown).
Morphometric data measured over the entire imaged domain of one of the circular constrained datasets. a Total vascular length, representing the sum of the length of all neovessel segments. b Total number of branch points (sites of branching and anastomosis). c Total number of end points (vessel-free ends). Morphometric data were normalized by the volume of the imaged domain to account of contraction during the time series experiment. Discontinuity of the dashed line illustrates culture media change
In contrast, detailed examination of individual neovessel behavior demonstrated that there was considerable local variability during this 5-day period (Suppl. Movies 4 and 5). Most notably, some neovessels retracted or regressed completely while others continued to elongate and advance. The percentage of normalized total vascular length associated with a particular initial microvessel fragment was collected throughout the time series for four randomly selected initial fragments from the skeletonization of the same circular constrained dataset (Fig. 4a). Vascular length tended to oscillate throughout time as neovessels transitioned between periods of elongation and regression (Fig. 4b, c). The percentage of total vascular length for an individual fragment increased the most when the fragment was able to inosculate with an existing vascular network, as seen as large jumps in the vascular length data for Fragments 1 and 3 (Fig. 4b). The length of the other two fragments (Fragments 2 and 4) simply oscillated around their starting length and did not anastomose before the end of the culture time, and therefore, vascular length associated with these fragments remained low (Fig. 4c). At the end of the time series, the majority of vascular length (~70 %) was associated with a single interconnected vascular network (Fig. 4d) that Fragments 1 and 3 joined around 100 h (Fig. 4b). Animation of the skeletonization for a single neovessel segment over time further demonstrated the dynamics of neovessel regression and direction change (Suppl. Movie 5).
Morphometric data for selected individual microvessel fragments as obtained from the skeletonized vascular networks. a The percentage of total vascular length that was connected to an individual microvessel fragment was calculated for four randomly selected initial fragments. b–d Vascular length percentage tended to oscillate over time as neovessels transitioned between periods of elongation and regression. Fragments 1 and 3 inosculated to the predominate vascular network forming within the construct, which eventually accounted for roughly 70 % of total vascular length (b, e), while Fragments 2 and 4 simply oscillated throughout time and did not experience any significant anastomosis events and remained unconnected to the majority of vascular perfusion within the construct (c)
To verify our skeleton-based measurements of neovessel dynamics and to rule out that the apparent regression events could be an artifact of the skeletonization algorithm, we tracked the length, branching, and inosculation of six individual neovessel fragments in the high-resolution field of interest by hand (Fig. 5). These measurements verified the complex behavior that was illustrated in the skeletonizations. In particular, individual neovessel growth rates ranged from 2 to 12 μm/h, with an average growth rate of 5.3 ± 3.0 μm/h (Mean ± SD). This overall growth rate included periods of retraction, with neovessels shortening at a rate of 10.4 ± 2.3 μm/h (Mean ± SD) when it occurred. As is often observed during cell migration over a surface, there was a continuous fluctuation of neovessel tip cell filopodia formation and retraction. The neovessel tip often contained two advancing filopodia (time point 60 in Fig. 6a), with one eventually serving as the main guiding tip while the other regressed. Occasionally, both filopodia persisted, leading to the formation of a bifurcation (Fig. 5, trace for Neovessel 1). While not exhaustively examined, we did not observe the formation of three branches from a single neovessel tip. Frequently, individual neovessels, even those with substantial length, also regressed (Suppl. Movie 4). During retraction, the neovessel would either regress all the way back to the parent microvessel (regression) or only part-way back. In one example, the partial regression resulted in the tip cell advancing in a new direction once growth began again (time points 72–84 in Fig. 6a). Once a sprout formed from the parent microvessel (which often occurred at the microvessel ends) and persisted, growth and advancement was episodic and accompanied by additional fluctuations in neovessel diameter. New forward extensions were relatively narrow as compared to the diameter of the adjacent stalk region of the neovessel. However, over the next hours, a bulk of the stalk cell cytoplasm would quickly move forward, eventually followed by the normalization of the neovessel diameter across the newly advanced region. This process repeated as the tip extended forward and the neovessel elongated.
Length tracings of individual growing neovessels indicating total neovessel length (y-axis) over time (x-axis) over a 5-day period. Neovessel 1 is the tracing of the neovessel illustrated in Fig. 6. Advancement of the sprouts is episodic with phases of growth punctuated by retraction (rapid, brief shortening) or regression (shortening without further growth)
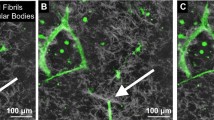
a Sequential (left–right, top–bottom) still frames from time-lapse movie of angiogenesis highlighting neovessel sprouting and growth activities via the EGFP channel for microvessel sprouts. Numbers in the top-right indicate acquisition time relative to the beginning of acquisition in hours. Notable features of the growing neovessel include sprout to body formation (44–52 h), tip cell filopodia (60 and 64 h), sprout advancement and retraction (72–80 h), changes in growth direction (84 h), and the directed growth toward inosculation with adjacent neovessel sprouts (94–104 h). While clearer in the Suppl. Movie 4, neovessel diameters fluctuated as the neovessel advanced, reflecting possible redistribution of cytoplasm. The solid and open arrows point to two different advancing neovessels. Representative time points were selected for this figure. b SHG channel of the time points illustrated in Fig. 6a. We only rendered frames over a depth of 10 μm at the sprout tip. The location of the sprout tip is illustrated with the green arrow. White arrows point to locations of collagen fibril recruitment, condensation, or deposition. An aster-like fibril cluster served as stalk cell anchor (44–52). Fibrils were recruited behind the advancing sprout to surround it (68–72). Fibril reorientation occurred ahead of the advancing tip cell in frames 84–94. We observed unilateral condensation of fibrils at the stalk segment at the inside of the curved neovessel (102,104). (Color figure online)
Due to its ordered, repetitive character, collagen fibrils and fibers can generate second harmonic signal in the matrix [18, 19]. Based on this SHG signal, we found the fibrillar architecture of the collagen supporting the ex vivo microvessel system to be complex, containing variations in fibrillar density and aster-like fibril clusters (Fig. 6b and Suppl. Movie 6). Additional collagen structural features appeared at and/or nearby the advancing neovessel: collagen densification was present along the parent microvessels and the stalk portions of the neovessels (Fig. 6b). The extent of condensation varied, sometimes forming a dense “cocoon” of collagen and sometimes forming a loose mesh around the neovessel. The degree of collagen fibril condensation at the neovessel surface varied, which was neither present along the entire neovessel length nor on all neovessels. Once formed, the collagen layers around the neovessels often persisted. Additionally, we observed a fan-like organization of collagen fibrils extending forward from the advancing neovessel tip (time points 84–94 in Fig. 6b). This was consistent with similar observations during static assessment of the ex vivo microvessel cultures [11]. Furthermore, it appeared that these collagen fibrils at the neovessel tip eventually contributed to the layer of collagen surrounding the advancing neovessel, presumably remaining as the neovessel advanced through the fan “structure” (Fig. 6b). As previously noted [11], the collagen mesh surrounding the stalk portion of the neovessel became more condensed toward the inner side of a curved neovessel (time points 100–104 in Fig. 6b).
We commonly witnessed inosculation between two growing neovessels. In an inosculation sequence, growing neovessels located each other over a distance of tens to hundreds of microns (time points 84–104 in Fig. 6a, Suppl. Fig. 7A and Suppl. Movie 8). As the two neovessels destined to inosculate grew in length, they appeared to advance directly toward each other with minimal random tip directional changes (Fig. 6a). Early in the actual inosculation event, side-by-side alignment of the two neovessel tips was followed by a formal connection and normalization of neovessel diameters (time points 98–114 in Fig. 7, Suppl. Movie 8). Finally, the similar mesh-like condensation of collagen that occurred along the length of a growing neovessel also appeared at the inosculation site (time points 102–104 in Fig. 6b). Beside tip-to-tip inosculation (Fig. 6, Suppl. Fig. 7A), we also observed tip-to-parent vessel inosculation (Suppl. Fig. 7B) and neovessel branching where both branches inosculated (Suppl. Fig. 7C).
Still frames of a higher magnification volume rendered and rotated relative to the view in Fig. 2 (from the 2-o’clock direction) highlighting the inosculation event between two growing neovessels. The rendered images clearly show two neovessels approached each other and joining tip to tip. The inosculation event involved an initial side-by-side alignment or “handshaking” of the two respective neovessel tips followed by an apparent redistribution of cytoplasm along the length of the newly derived neovessel segment
Previously, we have shown that constraining the boundaries in our ex vivo microvessel system resulted in anisotropic alignment of the neovessel network due to cell-induced traction forces [5, 9, 13]. In addition to circular constrained cultures, long-axis-constrained ex vivo cultures were anchored on the two, short opposite ends while the long sides of the culture were not anchored and free to deform (Fig. 8 and Suppl. Fig. 1). In the long-axis-constrained cultures, neovessels aligned perpendicular to the direction of deformation. Coincidently, collagen fibrils within the matrix also aligned in the same orientation as the neovessels. In our previous studies, neovessels were grown for a specified time period, fixed and then assessed at a single time point. Repeating these experiments using our 4D imaging system enabled us to visualize the temporal sequence of neovessel growth in a deforming collagen gel environment (Fig. 8, Suppl. Movies 9 and 10). Neovessel alignment and matrix deformation happened coordinately (Fig. 8). Interestingly, growing neovessels became oriented soon after sprouting from the parent microvessel and persisted in this new direction as deformation became more pronounced.
Temporal and spatial changes in the orientation of neovessels in cultures constrained on all axes (circular constrained) or only along one axis (long-axis-constrained). Shown are 2D projections of rendered 5 × 5 image stack arrays acquired 6 h and 4 days after imaging was started. The red boxes indicate the regions of the cultures shown at higher magnification in the bottom row. Collagen fibril structure is not shown. The axis of constraint in the LA constrained culture is from top to bottom. (Color figure online)
Discussion
The experimental model used in our study involves the isolation and culture of adult, mammalian microvessels that retain the cells, matrix, and structure of normal microvessels in vivo [10]. In this system, neovessels spontaneously sprout from the intact, parent microvessel in a manner analogous to what is thought to occur in vivo [20]. Furthermore, the neovasculature that arises from the parent microvessels in this model recapitulates all of the post-angiogenesis vascular activities necessary to form a mature, stable, and functional microcirculation when implanted [13, 20–22]. The sprouting activity we observed mirrored that described by others in different model systems including the zebrafish larva [23, 24], the chick embryo [25], the rodent eye [26, 27], the explanted aorta culture [28, 29], and other cell-based analyses examining sprouting endothelial cell–matrix interactions [4, 30, 31]. In these published studies, an emphasis was placed on the cell dynamics of and localized matrix effects on the growing sprout, often utilizing high-resolution time-lapse over short time periods. In contrast, we characterized extended neovessel growth (over millimeters) as well as neovessel guidance and inosculation with the long-term goal of understanding how global tissue mechanics influences neovascular outcomes during neovascularization. Similar processes can be observed in the zebrafish larva and chick embryo [23, 25]. However, in contrast to these embryo systems, angiogenesis in our ex vivo microvessel model occurs in a less structured tissue environment lacking predetermined spatial and temporal cues.
We have used this in vitro model of angiogenesis in the past to define a neovessel–matrix interplay such that tissue mechanics influence neovessel growth, which in turn influences the local matrix properties, which in turn changes the compliance of the matrix to deformation [5–7, 9, 32]. With our 5D imaging approach, we monitored angiogenesis from initial neovessel sprouting to the formation of a complex 3D neovascular network in a 4-mm3 matrix volume over the course of several days of culture. The global neovessel behavior observed in these onstage, time-lapse experiments mimicked that observed in these previous static microvessel experiments. However, in the present study, we observed considerable heterogeneity in neovessel growth rate, elongation, retraction, and directional change across the entire angiogenic bed, which was not detected in the previous, static-based experiments. Angiogenic growth was far more temporally dynamic than we anticipated based on standard, single time point analyses and even previous time series analyses by others. Perhaps, most surprising was the prevalent retraction of neovessels. We expected to observe tip retraction, in which the tip cell extends forward and then pulls back, analogous to the exploratory behavior of migrating cells. However, there was clear evidence that entire neovessels, many of which were tens of microns long, partially or completely disappeared due to regression. This observed oscillatory neovessel growth and regression behavior hints at a possible new dynamic of control during angiogenesis. Given the time frame of changes, it is unlikely that regression is caused by a collapse of angiogenic factor gradients or exhaustion of some external signal. This, combined with the relative absence of parenchyma that might produce changing signals, suggests that neovessel regression during angiogenesis may be intrinsic to the neovessel, possibly reflecting a stochastic component to the growth process.
Interestingly, neovessel diameters also fluctuated as the neovessel advanced. Others have described a similar phenomenon in shorter, more time-resolved time-lapse studies in other model tissues and attributed these diameter changes to the movement of endothelial cells up and down the neovessel sprout [2, 28]. Undoubtedly, these sprout-cell dynamics are occurring in the neovessels in our system. Possibly, these changes might also reflect the redistribution of cytoplasm and the nucleus secondary to changes in tension along the neovessel. Such tension must be present as the free end of the tip cell extends forward, pulling on the adjacent yet less mobile stalk cells. Advancement of the stalk cell(s) toward the pulling tip cell would lessen this tension and associated cell deformation, allowing the cytoplasm to redistribute. Perhaps, these same mechanical forces are involved in initiating neovessel retraction. Given that cells exist in a state of balanced tension with the extracellular matrix, perturbation of which can lead to profound changes in cell phenotype and behavior [33, 34], then retraction may reflect a neovascular response to some aspect of this cellular tension state. A similar dynamic may also cause the changes in the direction of neovessel growth we observed.
Previously, through SHG imaging, we have shown that bright, dense collagen is layered along the parent microvessels due to collagen polymerization occurring at the time the culture is established [11]. From the time-lapse data, it appears that this condensed collagen persists on the parent microvessel over the 5 days that we monitored angiogenesis. Similar collagen layers composed as a mesh-like collagen covering also appeared on growing neovessels. However, the neovessel-associated fibrillar collagen appeared only after the neovessels had elongated. It appeared that the neovessel-associated collagen was derived from fibrils already present within the bulk matrix. Previously, we described the appearance of fan-like arrays of collagen fibrils extending ahead of the advancing neovessels [11]. We observed those same tip-associated fibril fans in the time-lapse data, which appeared to form coordinately with neovessel advancement.
Not unexpectedly, we often observed the inosculation of growing neovessels in the ex vivo cultures; our previous experience with this angiogenesis model indicated that an interconnected network of neovessels forms. We observed connections forming via interactions between tip cells of growing neovessels. In tip-to-tip inosculation, the two neovessel tips moved alongside each other, forming an overlap between the tip cells prior to fusion. This occurred even if the two tips were approaching each other at oblique angles and not head-on. This is somewhat different than the pattern observed between vascular precursor cells and growing neovessel tips in an implant model in which the connections between host neovessels and the assembling engineered neovasculature involve a “tap and wrap” activity [35]. Tips of joining neovessels sometimes bifurcated, with one extension of the tip cell making a connection with the partner neovessel tip and the second extension continuing on to lead further neovessel elongation. This fascinating activity resulted in a branch point, which, at times, leads to a three-way or even four-way intersection (Suppl. Fig. 7C). While we clearly observed tip-to-tip connections between neovessels mediated by tip cells, there were examples where the tip of a growing neovessel appeared to interact with the stalk of a neighboring neovessel (Suppl. Fig. 7D), particularly in areas of high neovessel density. It was difficult to determine whether that interaction involved filopodia extending from the stalk cell as the amount of cytoplasmic GFP in such fine cell extensions was small. Similarly, growing neovessels interacted with the remnants of parent microvessels. It is not clear whether this indicates that angiogenic neovessels can interact directly with stable, mature microvessels in vivo, as the parent microvessels in our ex vivo system have lost the rigorous vessel wall structure after the many days in culture. Regardless of the types of nature of the connections, clearly neovessels are capable of inosculating with each other during angiogenesis, forming an immature microvascular network.
Our time-lapse data revealed that neovessels are capable of locating each other in a directed fashion. From the time-lapse datasets, it even appeared that a growing neovessel in one case (Fig. 7; Suppl. Movie 4) made a course correction that eventually resulted in its inosculation with another neovessel. This change in direction occurred at a relatively long distance from its eventual connecting partner. The absence of any significant “wandering” by the neovessel tips as they approached each other suggests that there is an active process through which neovessels sense and move toward each other. The possibility that this can occur over some distance entertains the idea of a gradient of a soluble factor. VEGF gradients have been implicated in guiding angiogenic sprouting by establishing tip and stalk cell hierarchy [2, 29]. But whether or not factor gradients external to the individual neovessels exist in our simplified ex vivo culture system, that lacks an organized parenchyma or stromal cells which might serve as an attracting point source, remains to be determined. There are cells that have left the microvessel walls and migrated throughout the collagen stroma. Some or all of these cells are likely producing angiogenic factors that may serve to guide individual neovessels. However, we did not observe neovessels systematically growing toward individual “stromal” cells, suggesting that angiostatic gradients are not being established. Whether these factors are playing an angiokinetic role (stimulate angiogenesis with guiding tip cells) is not clear, but probable. It seems unlikely, also, that the tips of the growing neovessels are producing an attractant for other neovessel tips as such a factor gradient would also act to attract the very neovessel releasing the factor. The orientation of growing neovessels in response to matrix deformation constraints suggests that mechanical properties of the matrix may be a strong determinant. Given that we observe considerable neovessel-dependent matrix remodeling in our system and growing neovessels track along aligned matrix fibrils [9], it is likely that neovessels can locate each other via matrix tracks or patterns of matrix compliance, perhaps created by the growing neovessels themselves.
Recently, others have described a role for macrophages in facilitating sprout-to-sprout connections in pre- and perinatal angiogenesis [36]. While we suspect that macrophages are present in our ex vivo microvessel cultures (the amoeboid-like cells in the stroma), we did not observe nonvascular cells involved in the inosculation events. In the embryo, ~80 % of the inosculation events appeared to not require a macrophage chaperone [36]. Therefore, it is possible that macrophages could be involved in some of the inosculation events in our ex vivo angiogenesis system, but at a frequency too low to be readily observed.
While there is a relative paucity of parenchymal cells, we know that a variety of cells types directly associated with the microvessel wall are included in the isolate used in our model. We have shown [20] that during the angiogenesis sprouting phase, which is the focus of this current manuscript, alpha-actin-positive perivascular/mural cells migrate off of the parent microvessel into the stromal space and do not associate with the endothelial cell-based neovessel sprout. They do re-associate during post-angiogenesis maturation as the new network hemodynamically revises and remodels. We also suspect that mesenchymal stem cells (i.e., pericytes) and tissue macrophages are associated with the isolated microvessels and also migrate into the stroma (see the spindly cells that are rapidly moving throughout the stroma in the supplemental time-lapse videos). Recently, others have described a role for macrophages in facilitating sprout-to-sprout connections in pre- and perinatal angiogenesis [36]. Undoubtedly, these different vascular-associated stromal cell types are producing angiogenic factors in our model system. However, via the 3D visualization over time, none of these cells appear to serve as attraction points to the growing neovessels (i.e., they are not leading the growing neovessel) nor is there any apparent organization of these cells such that they could create a zone of elevated angiogenic factors (i.e., a multicellular point source).
Our quantitative analysis focused primarily on global behavior of the vessel network. For example, we have shown the continued formation of vessel network connections throughout our culture time (Fig. 3), because the number of vessel end points is continuously decreasing while the number of branch points and normalized vessel length came to a plateau after 100 h of incubation. We have shown on multiple fragments the regression, redirections, and retraction behavior; however, a more detailed analysis would be necessary to compute the average number of bifurcations formed per sprout or the distribution of total growth, regression, and redirection for all sprouting segments. Such analysis could be further supported by techniques that automatically adjust for sample-drift in the microscope (which optimizes the number of continuously observed fragments) as well as a processing pipeline that easily tracks a large number of sprouting vessel sections.
In conclusion, we developed and applied an advanced 4D imaging protocol to visualize the spatial and temporal dynamics of sprouting angiogenesis and interactions with the extracellular matrix, which may be particularly useful in constructing computational models of angiogenesis. The 4D analysis of adult angiogenesis has revealed to us, and enabled a means by which to answer, new questions related to the mechanisms underlying angiogenesis including how the interplay between growing neovessel and stromal matrix structure mediates neovessel advancement and navigation through the stromal space.
References
Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2011) Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature 473(7347):298–307. doi:10.1038/nature10144
Jakobsson L, Franco CA, Bentley K, Collins RT, Ponsioen B, Aspalter IM, Rosewell I, Busse M, Thurston G, Medvinsky A, Schulte-Merker S, Gerhardt H (2010) Endothelial cells dynamically compete for the tip cell position during angiogenic sprouting. Nat Cell Biol 12(10):943–953
Lu P, Takai K, Weaver VM, Werb Z (2011) Extracellular matrix degradation and remodeling in development and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a005058
Lee PF, Yeh AT, Bayless KJ (2009) Nonlinear optical microscopy reveals invading endothelial cells anisotropically alter three-dimensional collagen matrices. Exp Cell Res 315(3):396–410. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2008.10.040
Underwood CJ, Edgar LT, Hoying JB, Weiss JA (2014) Cell-generated traction forces and the resulting matrix deformation modulate microvascular alignment and growth during angiogenesis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 307(2):H152–H164. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00995.2013
Krishnan L, Hoying JB, Nguyen H, Song H, Weiss JA (2007) Interaction of angiogenic microvessels with the extracellular matrix. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293(6):H3650–H3658
Edgar LT, Hoying JB, Utzinger U, Underwood CJ, Krishnan L, Baggett BK, Maas SA, Guilkey JE, Weiss JA (2014) Mechanical interaction of angiogenic microvessels with the extracellular matrix. J Biomech Eng 136(2):021001. doi:10.1115/1.4026471
Edgar LT, Underwood CJ, Guilkey JE, Hoying JB, Weiss JA (2014) Extracellular matrix density regulates the rate of neovessel growth and branching in sprouting angiogenesis. PLoS ONE. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0085178
Krishnan L, Underwood CJ, Maas S, Ellis BJ, Kode TC, Hoying JB, Weiss JA (2008) Effect of mechanical boundary conditions on orientation of angiogenic microvessels. Cardiovasc Res 78(2):324–332
Hoying JB, Boswell CA, Williams SK (1996) Angiogenic potential of microvessel fragments established in three-dimensional collagen gels. Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 32(7):409–419
Kirkpatrick ND, Andreou S, Hoying JB, Utzinger U (2007) Live imaging of collagen remodeling during angiogenesis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 292(6):H3198–H3206
Lois C, Hong EJ, Pease S, Brown EJ, Baltimore D (2002) Germline transmission and tissue-specific expression of transgenes delivered by lentiviral vectors. Science 295(5556):868–872. doi:10.1126/science.1067081
Chang CC, Krishnan L, Nunes SS, Church KH, Edgar LT, Boland ED, Weiss JA, Williams SK, Hoying JB (2012) Determinants of microvascular network topologies in implanted neovasculatures. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 32(1):5–14. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.238725
Nunes SS, Krishnan L, Gerard CS, Dale JR, Maddie MA, Benton RL, Hoying JB (2010) Angiogenic potential of microvessel fragments is independent of the tissue of origin and can be influenced by the cellular composition of the implants. Microcirculation 17(7):557–567
SCI Institute (2014) FluoRender: an interactive rendering tool for confocal microscopy data visualization. Scientific Computing and Imaging Institute (SCI), Salt Lake City
Wan Y, Otsuna H, Chien C-B, Hansen C (2009) An interactive visualization tool for multi-channel confocal microscopy data in neurobiology research. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 15(6):1489–1496
Edgar LT, Sibole SC, Underwood CJ, Guilkey JE, Weiss JA (2013) A computational model of in vitro angiogenesis based on extracellular matrix fibre orientation. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng 16(7):790–801. doi:10.1080/10255842.2012.662678
Williams RM, Zipfel WR, Webb WW (2005) Interpreting second-harmonic generation images of collagen I fibrils. Biophys J 88(2):1377–1386. doi:10.1529/biophysj.104.047308
Bal U, Andresen V, Baggett B, Utzinger U (2013) Intravital confocal and two-photon imaging of dual-color cells and extracellular matrix mimics. Microsc Microanal 19(1):201–212. doi:10.1017/S1431927612014080
Nunes SS, Greer KA, Stiening CM, Chen HY, Kidd KR, Schwartz MA, Sullivan CJ, Rekapally H, Hoying JB (2010) Implanted microvessels progress through distinct neovascularization phenotypes. Microvasc Res 79(1):10–20
Nunes SS, Rekapally H, Chang CC, Hoying JB (2011) Vessel arterial-venous plasticity in adult neovascularization. PLoS ONE 6(11):e27332. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0027332
Shepherd BR, Chen HY, Smith CM, Gruionu G, Williams SK, Hoying JB (2004) Rapid perfusion and network remodeling in a microvascular construct after implantation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 24(5):898–904. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000124103.86943.1e
Isogai S, Lawson ND, Torrealday S, Horiguchi M, Weinstein BM (2003) Angiogenic network formation in the developing vertebrate trunk. Development 130(21):5281–5290. doi:10.1242/dev.00733
Yu PC, Gu SY, Bu JW, Du JL (2010) TRPC1 is essential for in vivo angiogenesis in zebrafish. Circ Res 106(7):1221–1232. doi:10.1161/Circresaha.109.207670
le Noble F, Fleury V, Pries A, Corvol P, Eichmann A, Reneman RS (2005) Control of arterial branching morphogenesis in embryogenesis: go with the flow. Cardiovasc Res 65(3):619–628. doi:10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.09.018
Peebo BB, Fagerholm P, Traneus-Rockert C, Lagali N (2011) Time-lapse in vivo imaging of corneal angiogenesis: the role of inflammatory cells in capillary sprouting. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52(6):3060–3068. doi:10.1167/Iovs.10-6101
Murakami T, Suzuma K, Takagi H, Kita M, Ohashi H, Watanabe D, Ojima T, Kurimoto M, Kimura T, Sakamoto A, Unoki N, Yoshimura N (2006) Time-lapse imaging of vitreoretinal angiogenesis originating from both quiescent and mature vessels in a novel ex vivo system. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47(12):5529–5536. doi:10.1167/Iovs.06-0373
Arima S, Nishiyama K, Ko T, Arima Y, Hakozaki Y, Sugihara K, Koseki H, Uchijima Y, Kurihara Y, Kurihara H (2011) Angiogenic morphogenesis driven by dynamic and heterogeneous collective endothelial cell movement. Development 138(21):4763–4776. doi:10.1242/Dev.068023
Gerhardt H, Golding M, Fruttiger M, Ruhrberg C, Lundkvist A, Abramsson A, Jeltsch M, Mitchell C, Alitalo K, Shima D, Betsholtz C (2003) VEGF guides angiogenic sprouting utilizing endothelial tip cell filopodia. J Cell Biol 161(6):1163–1177. doi:10.1083/jcb.200302047
Korff T, Augustin HG (1999) Tensional forces in fibrillar extracellular matrices control directional capillary sprouting. J Cell Sci 112(Pt 19):3249–3258
Ma X, Schickel ME, Stevenson MD, Sarang-Sieminski AL, Gooch KJ, Ghadiali SN, Hart RT (2013) Fibers in the extracellular matrix enable long-range stress transmission between cells. Biophys J 104(7):1410–1418. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2013.02.017
Edgar LT, Underwood CJ, Guilkey JE, Hoying JB, Weiss JA (2014) Extracellular matrix density regulates the rate of neovessel growth and branching in sprouting angiogenesis. PLoS ONE 9(1):e85178. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0085178
Mammoto T, Mammoto A, Ingber DE (2013) Mechanobiology and developmental control. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 29:27–61. doi:10.1146/annurev-cellbio-101512-122340
Ingber DE (2002) Mechanical signalling and the cellular response to extracellular matrix in angiogenesis and cardiovascular physiology. Circ Res 91(10):877–887. doi:10.1161/01.Res.0000039537.73816.E5
Cheng G, Liao S, Wong HK, Lacorre DA, di Tomaso E, Au P, Fukumura D, Jain RK, Munn LL (2011) Engineered blood vessel networks connect to host vasculature via wrapping-and-tapping anastomosis. Blood 118(17):4740–4749. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-02-338426
Fantin A, Vieira JM, Gestri G, Denti L, Schwarz Q, Prykhozhij S, Peri F, Wilson SW, Ruhrberg C (2010) Tissue macrophages act as cellular chaperones for vascular anastomosis downstream of VEGF-mediated endothelial tip cell induction. Blood 116(5):829–840. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-12-257832
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by NIH Grants R01HL077683 and S10RR023737. We thank Richard A. Cordova (Ironwood Ridge High School, Tucson Arizona) for registering datasets and selecting regions of interests for visualization. He also contributed to the vessel length measurements. Nathan Galli (SCI Institute, University of Utah) provided the artwork in Fig. 1. The developers of the FluoRender software were supported by National Institutes of Health (NIH) Grant R01GM098151. Carlos Lois (California Institute of Technology) developed the ubiquitous EGFP expressing transgenic rat that was provided by the RRRC (University of Missouri).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental Figure 1
(PPTX 205 kb)
Supplemental Figure 2
(PPTX 69 kb)
Supplemental Figure 3
(PPTX 568 kb)
Supplemental Movie 4
(MPG 7050 kb)
(MP4 2629 kb)
Supplemental Movie 6
(MPG 11416 kb)
Supplemental Figure 7A
(PPTX 2115 kb)
Supplemental Figure 7B
(PPTX 1474 kb)
Supplemental Figure 7C
(PPTX 1938 kb)
Supplemental Figure 7D
(PPTX 1258 kb)
Supplemental Movie 8
(MPG 3020 kb)
Supplemental Movie 9A
(MPG 16790 kb)
Supplemental Movie 9B
(MPG 9604 kb)
Supplemental Movie 10A
(MPG 16142 kb)
Supplemental Movie 10B
(MPG 7812 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Utzinger, U., Baggett, B., Weiss, J.A. et al. Large-scale time series microscopy of neovessel growth during angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 18, 219–232 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-015-9461-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-015-9461-x