Abstract
Lymphoid organs, in which antigen presenting cells (APCs) are in close proximity to T cells, are the ideal microenvironment for efficient priming and amplification of T-cell responses1. However, the systemic delivery of vaccine antigens into dendritic cells (DCs) is hampered by various technical challenges. Here we show that DCs can be targeted precisely and effectively in vivo using intravenously administered RNA-lipoplexes (RNA-LPX) based on well-known lipid carriers by optimally adjusting net charge, without the need for functionalization of particles with molecular ligands. The LPX protects RNA from extracellular ribonucleases and mediates its efficient uptake and expression of the encoded antigen by DC populations and macrophages in various lymphoid compartments. RNA-LPX triggers interferon-α (IFNα) release by plasmacytoid DCs and macrophages. Consequently, DC maturation in situ and inflammatory immune mechanisms reminiscent of those in the early systemic phase of viral infection are activated2. We show that RNA-LPX encoding viral or mutant neo-antigens or endogenous self-antigens induce strong effector and memory T-cell responses, and mediate potent IFNα-dependent rejection of progressive tumours. A phase I dose-escalation trial testing RNA-LPX that encode shared tumour antigens is ongoing. In the first three melanoma patients treated at a low-dose level, IFNα and strong antigen-specific T-cell responses were induced, supporting the identified mode of action and potency. As any polypeptide-based antigen can be encoded as RNA3,4, RNA-LPX represent a universally applicable vaccine class for systemic DC targeting and synchronized induction of both highly potent adaptive as well as type-I-IFN-mediated innate immune mechanisms for cancer immunotherapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Main
DCs initiate immune responses in lymphoid tissues upon early sensing of infectious pathogens5. Previous work aimed at gene delivery to DCs largely resorted to functionalization of nanoparticles with molecular ligands6,7,8. Antigen-encoding RNA formulations have been used for local9,10,11 and systemic injection in various RNA vaccine studies and resulted in antigen-specific T-cell responses, albeit with low antitumour activity12,13. We engineered RNA-containing nanoparticles differing in their molecular characteristics, for example, carrier composition, charge ratio (lipid to RNA ratio) and ionic conditions, and then analysed particle size, colloidal stability, RNA integrity, free RNA and zeta potential14. For in vivo testing, RNA nanoparticles encoding the reporter gene firefly luciferase (Luc-RNA) were injected intravenously (i.v.) into mice to assess biodistribution of the Luc signal. Whereas injection of naked Luc-RNA did not generate a reporter signal, several of the carrier–RNA formulations gave characteristic patterns of in vivo organ transfection, indicating protection and efficient translation of RNA (Extended Data Fig. 1a). Positively charged particles with higher in vitro transfection efficiencies compared to neutral or negatively charged compositions have previously been the focus of in vivo studies for nucleic acid delivery15,16. To systematically evaluate the effect of overall particle charge on in vivo targeting of DCs, which has remained unexplored to date, we varied lipid:RNA ratios. Cationic liposomes composed of the broadly used lipids DOTMA and DOPE formed colloidally stable nanoparticulate RNA-LPX of reproducible particle size (200–400 nm) and charge (Fig. 1a, Extended Data Fig. 1b) with positive as well as negative excess charge. Slightly positively charged and near-neutral RNA-LPX (positive to negative charge ratio from 2.5:1 to 1.8:2), in contrast, were unstable, forming large aggregates immediately after preparation. Positively charged Luc-RNA-LPX (charge ratio of 5:1), as typically used for gene delivery16, targeted Luc expression predominantly in the lungs of mice and less in the spleen (Fig. 1b). Surprisingly, gradual decrease of the cationic lipid content shifted Luc expression from the lungs towards the spleen. Near-neutral and slightly negative particles (for example, charge ratio of 1.7:2) provided an exclusively splenic signal (Fig. 1b). RNA-LPX of further lowered charge ratio (≤1.7:2) were medium-sized (∼200–320 nm), of low polydispersity, and were all expressed in the spleen. However, the transfection efficiency gradually declined with increasing negative charge, probably owing to increasing amounts of uncomplexed free RNA (Extended Data Fig. 1c). The unexpected selective targeting of negatively charged particles to the spleen prompted us to test various other well-characterized lipid compositions (for example, DOTAP, cholesterol). Irrespective of the lipids used, all particles with an excess negative charge exhibited pharmacologically suitable physicochemical properties (Extended Data Fig. 1d) and led to selective antigen expression in splenic cell populations (Extended Data Fig. 1e).
a, Particle size, polydispersity index (top) and zeta potential (bottom) (n = 3) of RNA-LPX constituted with DOTMA/DOPE liposomes and Luc-RNA at various charge ratios. b, Bioluminescence imaging of BALB/c mice (n = 3) after i.v. injection of Luc-LPX at various charge ratios. Pie charts show relative contribution of each organ to total signal. c, Particle size and polydispersity index of Luc-LPX either constituted freshly or stored at 4 °C followed by 24 h incubation at room temperature (top) and bioluminescence imaging of the spleens of BALB/c mice (n = 8, pooled from two experiments) after i.v. injection (bottom). d, Bioluminescence imaging after i.v. injection of Luc-LPX in CD11c-DTR mice (n = 3) depleted (depl.) of CD11c+ cells. e, Splenic localization of CD11c and Cy3 double-positive cells in BALB/c mice (n = 2) 1 h after i.v. injection of Cy3-labelled RNA-LPX. Scale bar, 100 μm. MZ, marginal zone; RP, red pulp; WP, white pulp. f, eGFP expression in splenic cell subsets of C57BL/6 mice (n = 3) 24 h after i.v. injection of eGFP-LPX by flow cytometry. g, Bioluminescence imaging of inguinal lymph nodes (LN), femur and tibia in BALB/c mice (n = 3) after i.v. injection of Luc-LPX. LDL, lower detection limit. h, Bioluminescence imaging of inguinal lymph nodes and ex vivo Luc assay of bone marrow (BM) single-cell suspensions after i.v injection of Luc-LPX in CD11c+ cell-depleted CD11c-DTR mice (n = 3). Significance was determined using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. Error bars, median (c, bottom), otherwise mean ± s.d.
For further characterization, we selected an RNA-LPX formulation with a charge ratio of 1.3:2, which effectively targeted RNA to the spleen (Extended Data Fig. 1f), formed monodisperse and stable particles (Fig. 1c, Extended Data Fig. 1g) and was fully resistant to degradation by mouse serum at 37 °C (Extended Data Fig. 1h). In CD11c-DTR mice (expressing diphtheria toxin receptor under control of the Cd11c promoter) depleted of CD11c+ cells before injection of this RNA-LPX, the reporter signal was almost undetectable in the spleen, indicating that APCs are the source of Luc expression (Fig. 1d).
We identified CD11c+ conventional (c)DCs in the marginal zone, and plasmacytoid (p)DCs and macrophages in the spleen as the cell subsets internalizing RNA-LPX by a set of experiments in which RNA-LPX with Cy3- or Cy5-labelled RNA or enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) was administered (Fig. 1e, f, Extended Data Fig. 2a, b).
The rate of RNA uptake was highest in macrophages (Extended Data Fig. 2a), whereas the highest eGFP transfection rate as measure for translation efficiency was observed in cDCs (Fig. 1f), indicating that DCs are more effective in cytoplasmic translocation and translation of RNA. Natural killer (NK), B and T cells, in contrast, did not exhibit relevant uptake. Concordant with the fact that the spleen, as the organ with the highest density of APCs, is known to be highly efficient in clearance of blood-borne pathogens, we found that i.v.-administered liposomal RNA was rapidly cleared from the blood within 1 h (Extended Data Fig. 2c).
Analysis of organs explanted after i.v. administration of RNA-LPX encoding Thy1.1 (enabling sensitive detection of Thy1.1+ transfected cells in Thy1.2 mice) or containing Cy5-labelled reporter RNA, revealed that not only APCs in the spleen are targeted. In the liver, we detected Cy5-labelled RNA in a small portion of cells, and Thy1.1 expression in CD11b+ macrophages (Extended Data Fig. 2d). Moreover, we detected Luc signals in lymph nodes from various body regions and in femur and tibia bone marrow (Fig. 1g, Extended Data Fig. 2e), as well as Cy5-labelled RNA and Thy1.1+CD11c+ cells in the bone marrow (Extended Data Fig. 2f). Again, depletion of CD11c+ cells before i.v. injection of Luc-LPX substantially reduced the reporter gene signal in these compartments (Fig. 1h).
We previously reported that DCs engulf naked RNA injected into lymph nodes by macropinocytosis17, which is constitutively active in immature DCs. RNA-LPX nanoparticles taken up by monocyte-derived human immature DCs almost completely co-localized with the macropinosome marker dextran (Extended Data Fig. 2g), whereas partial co-localization was observed with TLR7 and the early endosome marker EEA1 (Extended Data Fig. 2h). Moreover, rottlerin, a macropinocytosis inhibitor, and cytochalasin D, an inhibitor of phagocytosis and macropinocytosis, significantly inhibited RNA-LPX uptake by DCs in vitro (Extended Data Fig. 2i). Similarly, uptake of RNA-LPX was clearly reduced in vivo when lymph nodes were pre-injected with rottlerin (Extended Data Fig. 2j). DC maturation is known to prevent macropinocytosis18, whereas phagocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis remain unaffected19. Polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid (poly I:C)-matured DCs were unable to internalize Luc-RNA-LPX nanoparticles in vitro (Extended Data Fig. 2k). Similarly, in mice pre-treated with poly I:C before i.v. injection of RNA-LPX, the splenic Luc signal and reporter gene expression in CD8+ and CD8− cDCs were strongly reduced or completely lost (Extended Data Fig. 2l). Altogether, these findings identify macropinocytosis as the major uptake mechanism of RNA-LPX.
Investigating the biological effect of RNA-LPX in vivo, we found that a single i.v. injection of RNA-LPX encoding influenza virus hemagglutinin (HA), but not an empty control liposome carrier, induced maturation of splenic pDCs, CD8+ and CD8− cDCs, which upregulated activation markers CD40 and CD86 (Fig. 2a, left). Activated CD11c+ cells redistributed from the red pulp and marginal zone into the T-cell-rich white pulp within 6 h after i.v. injection of RNA-LPX (Extended Data Fig. 3a). NK, B, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were also strongly activated (Fig. 2a, middle), and a transient burst of serum IFNα peaking 6 h after RNA-LPX injection occurred (Fig. 2a, right). IFNα is typically produced in the context of RNA virus infections by APCs sensing dsRNA and ssRNA via endosomal TLR3 and TLR7, respectively, and is crucial for an efficient inflammatory, antiviral environment20. In Tlr7−/− mice, as compared to C57BL/6 wild-type mice, we found that splenocytes were moderately activated after i.v. injection of HA-LPX (Fig. 2b, left), and systemic IFNα release was not fully abrogated but significantly lower (Fig. 2b, right). By testing Tlr3−/−, Tlr4−/− and Tlr9−/− mice, we excluded the contribution of these TLR signalling pathways and of DNA or LPS contamination to RNA-LPX-mediated effects (Extended Data Fig. 3b).
a, b, Activation markers measured 24 h after i.v. injection of HA-LPX by in splenic immune cell subsets (n = 3 per time point) and kinetics of IFNα serum levels (n = 3 per time point) in wild-type (a) or Tlr7−/− (b) mice. c, IFNα serum levels in CD11c+ cell-depleted CD11c-DTR mice (n = 3) after i.v. injection of HA-LPX. d, Fraction of IFNα-expressing cells in splenic APC subsets after i.v. injection of HA-LPX in C57BL/6 and Ifnar1−/− mice (n = 3 per time point). e, Fraction of OVA-specific (left) and gp70-specific CD8+ T cells (right) within CD8+ T cells in blood after de novo priming of C57BL/6 mice (n = 5) and BALB/c mice (n = 5) immunized i.v. with OVA-LPX or gp70-LPX (day 0, 3, 8), respectively. f, Kinetics of OVA-specific CD8+ T cell frequencies within CD8+ T cells in blood after i.v. immunization of C57BL/6 mice (n = 5) with OVA-LPX. g, Fraction of OVA-specific CD8+ T cells within CD8+ T cells in blood of CD11c+ cell-depleted BM-chimaeric CD11c-DTR mice (n = 5) immunized i.v. with OVA-LPX (day 0, 3). Significance was determined using two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test (a, right, b, right, d), one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (d), and unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test (b, left, c, e, g). Error bars, mean ± s.d.
In C57BL/6 wild-type mice, expression of activation markers on cDCs, pDCs, NK cells, as well as B and T lymphocytes, increased continuously after i.v. injection of HA-LPX over a time period of 24 h. In C57BL/6 mice lacking IFNα receptor 1 (Ifnar1−/−) and in BALB/c mice pre-treated with an anti-IFNAR1 blocking antibody, cDC, pDC, and NK-cell activation was significantly impaired and restricted to the first 6 h, whereas no activation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and B cells occurred (Extended Data Fig. 3c–e). In CD11c-DTR mice depleted of CD11c+ cells before injection of HA-LPX, serum IFNα levels were markedly lower (Fig. 2c). These data support the role of type I IFN production and indicate that CD11c+ cells are the cellular source.
In C57BL/6 wild-type mice, splenic pDCs but not cDCs secreted IFNα immediately after RNA-LPX injection, which began to decrease 1 h after injection, whereas IFNα production by macrophages steadily increased over a period of 3 h (Fig. 2d). In Ifnar1−/− mice, however, IFNα secretion by pDCs was moderately reduced, whereas macrophages did not produce IFNα. Expression profiling of sorted cells showed that macrophages and pDCs upregulate distinct IFNα isoforms (Extended Data Fig. 3f). Selective depletion of pDCs in BDCA2-DTR mice (expressing diphtheria toxin receptor under control of the Bdca-2 promoter) or ablation of macrophages by pre-treatment with clodronate confirmed the role of these APC subsets for the TLR7-dependent biphasic IFNα production (Extended Data Fig. 3g).
Next, we studied antigen-specific T-cell stimulation upon vaccination. A single i.v. dose of HA-LPX induced strong proliferation of HA-specific T-cell receptor (TCR)-transgenic CD8+ and CD4+ T cells in blood, lymph nodes and spleen (Extended Data Fig. 3h). HA-specific T cells co-incubated with splenocytes from HA-LPX-treated mice ex vivo were strongly stimulated, indicating that HA-LPX delivered i.v. is efficiently internalized in vivo by splenocytes for functional antigen presentation (Extended Data Fig. 3i).
De novo priming of T-cell responses was analysed in C57BL/6 mice immunized with RNA-LPX encoding an ovalbumin epitope (OVA-LPX) and BALB/c mice immunized with gp70-LPX (an endogenous antigen of Moloney murine leukaemia virus integrated into the mouse genome). Three rounds of immunization with the respective RNA-LPX induced fully functional antigen-specific T cells reaching 30–60% of total CD8+ T cells (Fig. 2e, Extended Data Fig. 3j). Notably, repeated vaccination with RNA-LPX prevented the typical post-expansion T-cell retraction phase and high frequencies of antigen-specific T cells were maintained over several weeks (Fig. 2f). Concordantly, re-challenge of primed mice with OVA-LPX induced profound CD8+ T cell expansion, indicating the formation of memory cells (Fig. 2f, Extended Data Fig. 3k). Immune responses were not inducible in CD11c-DTR bone-marrow-chimaeric mice depleted of CD11c+ cells (Fig. 2g), whereas splenectomized mice vaccinated with RNA-LPX mounted a diminished but strong T-cell response, indicating the importance of APCs and the contribution of DCs in lymphoid tissues other than the spleen to RNA-LPX-mediated immunity (Extended Data Fig. 3l).
The prophylactic efficacy of RNA-LPX vaccines was assessed in two subcutaneous (s.c.) tumour models, B16-OVA and CT26: in both, immunization with OVA-LPX or gp70-LPX, respectively, led to complete and long-lasting protection upon tumour challenge, whereas all untreated mice died within less than 30 days (Fig. 3a).
a, Prophylactic efficacy in OVA-LPX immunized C57BL/6 (n = 6) challenged s.c. with B16-OVA melanoma and gp70-LPX immunized BALB/c mice (n = 5) challenged and rechallenged s.c. with CT26 colon carcinoma. b, B16F10-Luc growth (left) and tumour load in lungs (right) of B6 albino mice (n = 12) immunized i.v. with TRP-1-LPX, irrelevant (empty vector)-LPX or control (untreated). c, CT26-Luc growth and CT26 tumour load in lungs of BALB/c mice (n = 4–7) immunized i.v. with gp70-LPX. d, Survival of C57BL/6 mice (n = 10) with advanced s.c. TC-1-Luc tumours immunized i.v. with E6/E7-LPX or irrelevant (OVA)-LPX. e, Survival of BALB/c mice (n = 10) with i.v. CT26-Luc colon carcinoma tumours immunized i.v. with CT26-M90-LPX or irrelevant (OVA)-LPX. f, g, De novo priming in BALB/c mice (n = 3) immunized i.v. with gp70-LPX (day 0, 3, 8) and injected i.p. with anti-IFNAR1 antibody or isotype before each immunization. f, Fraction of gp70-specific CD8+ T cells within CD8+ T cells. g, Splenic CD8+ T cells upon in vitro restimulation with no (none), irrelevant (HA) or gp70 peptide. h, CT26 colon carcinoma load in lungs of BALB/c mice (n = 5) immunized i.v. with gp70-LPX and injected i.p. with anti-IFNAR1 antibody or isotype. Significance was determined using log-rank test (a, d, e), two-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test (b), and one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (g, h). Error bars, median with interquartile range (b), otherwise mean ± s.d.
Therapeutic efficacy was tested in several mouse tumour models. In a B16-OVA lung metastasis model, tumour-bearing C57BL/6 mice were immunized with three doses of OVA-LPX. The RNA-LPX-immunized mice cleared lung metastases completely and were free of tumours 20 days after the last immunization, whereas the lungs of mice immunized with control RNA exhibiting similar immune stimulatory properties were tumour-loaded (Extended Data Fig. 4a, b). In a lung metastases model with the melanocyte-differentiation antigen TRP-1 as vaccine target, strong CD8+ and CD4+ T-cell responses against this self-antigen were induced, and growing B16F10-Luc tumours were fully rejected (Fig. 3b, Extended Data Fig. 4c). Likewise, lung metastases derived from Luc-transduced or wild-type CT26 tumour cells were efficiently eradicated by vaccination with gp70-LPX (Fig. 3c, Extended Data Fig. 4d). Viral oncogenes and mutant neoepitopes are increasingly under investigation as clinically relevant vaccine-target classes. Vaccination with viral oncogene-coding E6/E7-LPX was successful at treating mice bearing advanced HPV16 E6- and E7-expressing TC-1 tumours and protected C57BL/6 mice against tumour re-growth (Fig. 3d, Extended Data Fig. 4e). All mice starting treatment on day 7 and 90% of mice that started on day 10 survived. We vaccinated BALB/c mice bearing established rapidly growing CT26 lung tumours with the MHC class II neoepitope CT26-M90, derived from the P154S mutation in the Aldh18a1 gene identified by exome sequencing21. This similarly led to efficient eradication of the lung tumours, highly significant long-term survival and protection from re-challenge, indicative of memory T-cell formation (Fig. 3e, Extended Data Fig. 4f).
To investigate the effect of RNA-LPX-induced IFNα on T cells, BALB/c mice were repeatedly immunized with gp70-LPX, but pre-treated either with an IFNAR1-blocking antibody or an isotype control before each immunization. Blocking IFNAR1 did not significantly affect expansion of gp70-specific CD8+ T cells in the blood and spleen (Fig. 3f). However, antigen-specific T cells primed under IFNAR1-blocking conditions failed to execute processes of pivotal effector function, such as secretion of granzyme B, IFNγ and tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFα), and mobilization of degranulation marker CD107a/b (Fig. 3g). In another experiment, BALB/c mice with metastases derived from CT26 cells were immunized repeatedly with gp70-LPX, each preceded by injection of anti-IFNAR1 antibody or isotype control. Under IFNAR1-blocking conditions, lung metastases were only partially reduced and substantial residual tumour burden remained, whereas the lung tumours in control mice were completely rejected (Fig. 3h). In conclusion, the ability of RNA-LPX to induce an IFNα response in lymphoid tissues appears to be critical for antigen-specific CD8+ T cells to acquire effector functions and execute potent in vivo anti-tumour activity.
These findings together with favourable outcomes of safety pharmacology studies with clinical grade material in mice and cynomolgus monkeys (Extended Data Table 1) encouraged the clinical translation of this concept.
A phase I dose-escalation trial with good manufacturing practise (GMP)-produced RNA-LPX vaccines encoding four tumour antigens (NY-ESO-1, MAGE-A3, tyrosinase and TPTE) for i.v. administration is currently recruiting patients with advanced malignant melanoma (NCT02410733). The first three patients were treated with a very low initial dose of RNA-LPX, followed by four weekly applications with moderately higher doses, but still below the absolute therapeutic dose levels used in mice (Extended Data Fig. 5a). All vaccine applications were well-tolerated with transient flu-like symptoms. All three patients had dose-dependent early release of IFNα and IP-10 (also known as CXCL10) peaking at 6 h (Fig. 4a), resembling the kinetics observed in mice (Fig. 2a). All patients developed de novo T-cell responses against the vaccine antigens. In patient 1, who had no T cells against NY-ESO-1 at baseline, cell counts of de novo induced NY-ESO-1-specific T cells four weeks after the last immunization reached the same range as those against immune-dominant HLA-class-I-restricted peptides from cytomegalovirus, Epstein–Barr and influenza viruses (Fig. 4b, Extended Data Fig. 5b). HLA-B35 NY-ESO-1 dextramer analysis of blood samples showed a rapid induction of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells within two weeks of starting treatment, increasing with subsequent vaccinations. Moreover, the pre-existing T-cell response against tyrosinase in this patient was augmented. Imaging before and after vaccination showed regression of a suspected metastatic thoracic lymph node lesion (data not shown). Patient 2, whose metastases were surgically removed before vaccination, experienced induction of CD4+ T-cell responses against NY-ESO-1 and MAGE-A3 (Extended Data Fig. 5c) and was tumour-free at the time of this report (seven months after the start of vaccination). In patient 3, a strong NY-ESO-1-specific HLA-Cw03-directed de novo T-cell response (Fig. 4c) and a weaker response against MAGE-A3 (Extended Data Fig. 5d) were induced. This patient previously received various treatments and had eight lung metastases at recruitment, which remained clinically and radiologically stable (data not shown).
a, Serum cytokines before (0 h) and after injection of intra-patiently escalated doses. b, c, T-cell responses against NY-ESO-1 and tyrosinase determined by restimulation with overlapping peptide mixtures or NY-ESO-1 epitopes (indicated with the amino acid position) in IFNγ ELISPOT and NY-ESO-1 specific MHC class I dextramer staining for patients 1 (b) and 3 (c). CEF, cytomegalovirus, Epstein–Barr and influenza viruses peptide pool; NM, not measured; PepMix, peptide mixture; pre-vac., pre-vaccination. d, Mechanism of action for RNA-LPX. Error bars, mean ± s.e.m.
In summary, our study provides insights into a novel class of systemically administered nanoparticulate RNA vaccines, which act by body-wide delivery of encoded antigens to APCs in the spleen, lymph nodes and bone marrow, and concomitant initiation of a strong type-I-IFN-driven immunostimulatory program (Fig. 4d). Systemic antigen targeting in lymphoid DCs is more potent than local vaccine delivery (Extended Data Fig. 6) and has large therapeutic potential. To our best knowledge, RNA-LPX vaccines are the first example of a clinically applied systemic nanoparticulate vaccine which accomplishes this aim. Whereas the current model involves functionalization of nanoparticles with molecular ligands that target DCs6,8, we show for the first time that precise DC targeting in lymphoid compartments can be accomplished using well-known lipid carriers such as DOTMA, DOTAP, DOPE and cholesterol, without functionalization, solely by adjusting negative net charge of the nanoparticles.
TLR7-driven type-I interferon release, the cellular source of which was unravelled in our study, appears to be essential for the full antitumour potency of this vaccine class, in contrast to previous reports that interferon counteracts locally applied RNA lipoplex vaccine responses10. Type I IFN as a key molecule in antigen-specific immunity against viral infections has further effects, for example, upregulation of MHC expression, promotion of maturation and cross-presentation in DCs22, and direct inhibition of regulatory T-cell functions23,24, which were not investigated in our study but may contribute to the antitumour efficacy of RNA-LPX. Our findings connect effective cancer immunotherapy with host pathogen-defence mechanisms. Mechanisms of antiviral host defence are important for survival, conserved in all vertebrates and evolutionarily optimized for high sensitivity and potency. RNA-LPX vaccines appear to mimic infectious non-self and thus mobilize concomitantly adaptive and innate antiviral mechanisms25,26. The i.v. delivery of RNA-LPX simulates a viraemic pathogen intrusion in the blood stream, and by reaching DCs in various lymphoid tissues, mobilizes the full T-cell repertoire for adaptive immune responses.
Our study shows profound expansion of effector T cells, even against self-antigens, and antitumour efficacy in various aggressively growing mouse tumour models induced by RNA-LPX. The dose-dependent IFNα response and stimulation of strong immune responses against self-antigens observed in the first cohort of patients supports the preclinically identified mode of action and strong potency of this approach in the clinical setting. RNA-LPX vaccines are fast and inexpensive to produce, and virtually any tumour antigen can be encoded by RNA. Thus, the nanoparticulate RNA immunotherapy approach introduced here may be regarded as a universally applicable novel vaccine class for cancer immunotherapy.
Methods
Mice
C57BL/6 mice, as well as Tlr3−/− and BDCA2-DTR mice27 bred on a C57BL/6 background, and BALB/c mice were purchased from the Jackson Laboratory and Charles River. C57BL/6BrdCrHsd-Tyrc (B6 albino) mice were purchased from Envigo EMS. C57BL/6 Ifnar1−/− mice28, derived from 129Sv Ifnar1−/− mice29 via backcrossing were a gift from J. Kirberg (Paul-Ehrlich-Institute). The following mice strains were provided from colleagues from the University Medical Center of the Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz: Rag2−/− TCR-HA mice transgenic for the influenza virus hemagglutinin A HA107-119 peptide-specific, I-Ed-restricted T cell receptor (TCR) (HA-TCRtg); BALB/c mice transgenic for the HA518-526 peptide-specific, H2-Kd-restricted TCR (CL4-TCRtg); and BALB/c Thy1.1+ mice from U. Hartwig, Tlr7−/− mice on a C57BL/6 background from H. J. Schild, CD11c-DTR30 and Tlr9−/− mice, both on a C57BL/6 background, by E. von Stebut-Borschitz, Tlr4−/− mice by K. Steinbrink. For prolonged ablation of CD11c+ cells, bone-marrow chimaeras were generated by reconstitution of lethally irradiated (9.5 Gy) C57BL/6 mice with bone marrow cells from CD11c-DTR mice. Age-matched (6–12 weeks) female animals were used throughout all experiments. Experimental group sizes were approved by the regulatory authorities for animal welfare after being defined to balance statistical power, feasibility and ethical aspects. All mice were kept in accordance with federal and state policies on animal research at the University of Mainz and BioNTech AG.
Tumour cell lines
B16-OVA is a murine B16F10 melanoma cell line expressing the chicken ovalbumin gene (OVA) containing the H2-Kb-restricted OVA257-264 epitope (SIINFEKL), which was a gift from U. Hartwig. CT26 (ATCC) is a murine colorectal cancer cell line endogenously expressing gp70 which is silent in most normal mouse tissues31. Luc-expressing CT26 (CT26-Luc) and B16F10 tumour cells (B16F10-Luc) were generated by lentiviral transduction. The Luc-expressing TC-1 tumour cell line (TC-1-Luc) derived from primary lung cells by immortalization and retroviral transduction with HPV16 E6 and E732 as well as Luc33 was obtained from E. Tartour (INSERM U970 PARCC) with the permission of T.-C. Wu (Johns Hopkins University). Master and working cell banks were generated immediately upon receipt, of which third and fourth passages were used for tumour experiments. Cells were tested for mycoplasma every three months. Reauthentication of cells was not performed after receipt.
RNA constructs and in vitro transcription
Plasmid templates for in vitro transcription of naked antigen-encoding RNAs were based on pSTI-A120 and pST1-MITD vectors34. pST1-MITD features a signal sequence for routeing to the endoplasmic reticulum and the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains for improved presentation of MHC class I and II epitopes. pST1-eGFP-A120 (eGFP), pST1-OVA-MITD (OVA), pST1-Influenza-HA-MITD (HA) and pST1-Luciferase-A120 (Luc) vectors were described previously34,35,36. The OVA construct encodes the H-2Kb-restricted, immunodominant epitope OVA257-264, and the HA construct contains a codon-optimized partial sequence of influenza HA (aa 60–285 fused to aa 517–527; influenza strain A/PR/8/34) designed to combine all major immunodominant MHC epitopes. pST1-Thy1.1 encodes the murine Thy1.1 protein. pST1-gp70-MITD encodes the H-2Ld-restricted peptide antigen AH1423-431 derived from Moloney murine leukaemia virus envelope glycoprotein 70 (gp70) with an amino acid substitution at position five (V/A; AH1-A5)37. pST1-E6-MITD and pST1-E7-MITD encode human papillomavirus (HPV) 16 full-length E6 and E738, respectively, and the sequence encoding the point-mutated 27-meric peptide CT26-M90 of ALDH18a1 was cloned into the pST1-MITD vector. pST1-TRP-1-MITD encodes murine tyrosinase-related protein 1 (TRP-1). pST1-empty-MITD does not encode a protein and was used as an irrelevant RNA control. RNA was generated by in vitro transcription as described previously39. For some experiments, Luc and Thy1.1 RNA was synthesized using 1-methyl-pseudouridine instead of uridine. Labelling of RNA with Cy3 or Cy5 was performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Amersham Biosciences), and of total uridine triphosphate (UTP), 15% were replaced with labelled UTP during in vitro transcription of the HA construct.
Liposomes
Liposomes with positive (cationic) net charge were used to complex RNA for the formation of RNA-LPX and comprised of the cationic lipid DOTMA (Merck & Cie) or DOTAP (Merck Eprova), and the helper lipid DOPE (Avanti Polar Lipids or Corden Pharma) or cholesterol (Sigma-Aldrich). Liposomes were produced either by protocols based on the thin film hydration method40,41 or by an adopted proprietary protocol based on the ethanol injection technique42. For the film method, stock solutions of the individual lipids were prepared in 99.5% ethanol at a concentration of approximately 10 mg ml−1 (exact concentrations controlled by HPLC), and appropriate amounts (volumes) of the stock solutions were mixed according to the intended lipid ratio. The solvent was evaporated and the obtained lipid film was dried for 1 h using a rotatory evaporator. The dry film was hydrated with RNase-free water by gently shaking to obtain a raw colloid with a total lipid concentration of approximately 6 mM which was left overnight at 4 °C for equilibration. For size adjustment, the dispersion was then extruded 10 times through polycarbonate membranes with 200 nm pore size using the LIPEX 10 ml extruder (Northern Lipids Inc.). The lipid concentration was measured by HPLC and adjusted by further addition of H2O to a fixed concentration of the cationic lipid.
RNA-LPX preparation and immunization
Lipoplex formation was performed with proprietary protocols, derived from extensive internal formulation development activities. The general procedures were derived from protocols for siRNA- and DNA-LPX preparation described elsewhere43. A diversity of formulations complexed with the reporter firefly luciferase (Luc)-encoding RNA was assembled, with liposomes comprising different cationic and helper lipids to create various lipid:RNA ratios, which defined the charge ratio and overall RNA-LPX net charge. The charge ratios were calculated from the number of positive charges represented by lipid-specific head groups (one positive charge per head group) and the number of negative charges represented by RNA nucleotides, that is, from the RNA phosphodiester groups (one negative charge per phosphodiester). For the calculation of the molar ratio between RNA and cationic lipid, a mean molar mass of 330 Da per nucleotide was assumed. RNA was provided as a HEPES-buffered solution at an RNA concentration of 1 mg ml−1. RNA-LPX were formed by diluting the RNA with H2O and 1.5 M NaCl solution followed by adding an appropriate amount of liposome dispersion to reach the selected charge ratio at a final NaCl concentration of 150 mM. RNA-LPX size (triplicates, from each measured ten technical replicates) and zeta potential (triplicates) were measured by photon correlation spectroscopy (PCS; 380 ZLS submicron particle/zeta potential analyser, PSS Nicomp). Uncomplexed RNA and RNA integrity were determined after isolation of total RNA by capillary gel electrophoresis (Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer, Agilent technologies) (2–7 replicates). For formulation screening studies, 20 μg RNA-LPX corresponding to 0.1 mg ml−1 RNA per mouse were injected i.v. into the retrobulbar venous plexus. For stability experiments, prepared RNA-LPX were pre-incubated with 50% syngeneic mouse serum for 30 min at room temperature or stored for 1, 2, 3 or 8 days at 4 °C and another 24 h at room temperature before injection. For immunological and tumour experiments, mice were immunized three times with 40 μg RNA LPX unless stated otherwise. The generation of memory T cells was verified by the recall response 42 days after the last immunization. Control mice received NaCl or remained untreated. Arrows in vaccination schemes indicate immunization.
Cryogenic transmission electron microscopy
Each sample was preserved in vitrified ice supported by holey carbon films on 400-mesh copper grids. Samples were prepared by applying a 3 μl drop of sample suspension to a cleaned grid, blotted away with a filter paper, and immediately proceeding with vitrification in liquid ethane. Grids were stored under liquid nitrogen until being transferred to the electron microscope for imaging. Electron microscopy was performed using a FEI Tecnai T12 electron microscope, operating at 120 keV equipped with a FEI Eagle 4k × 4k CCD camera. Vitreous ice grids were transferred into the electron microscope using a cryostage that maintains the grids at a temperature below −170 °C. Images of each grid were acquired at multiple scales to assess the overall distribution of the specimen. After identifying potentially suitable target areas for imaging at lower magnifications, pairs of high magnification images were acquired at nominal magnifications of 110,000× (0.10 nm per pixel), 52,000× (0.21 nm per pixel) and 21,000× (0.5 nm per pixel). The images were acquired at a nominal underfocus of −2 μm (110,000×), −4 μm (52,000×) and −4 μm (21,000×), and electron doses of ~10–24 e Å−2. Cryo-electron transmission microscopy measurements were performed at Nanoimaging Services, Inc.
Synthetic peptides
Peptides derived from gp70 (H2-Ld-restricted gp70423-431 AH1-A5 SPSYAYHQF), HA (H2-Kd-restricted HA518-526 IYSTVASSL), OVA (H2-Kb-restricted OVA257-264 SIINFEKL), TRP-1 (H2-Db-restricted TRP-1455–463 TAPDNLGYA; I-Ab-restricted TRP-1113-126 CRPGWRGAACNQKI), CT26-M90 (LHSGQNHLKEMAISVLEARACAAAGQS) and vesicular stomatitis virus nucleoprotein (H2-Kb-restricted VSV NP52-59 RGYVYQGL), NY-ESO-I (HLA-Cw03 NY-ESO-I91-102 YLAMPFATPMEA (patient 2, 3), NY-ESO-I96-104 FATPMEAEL (patient 2, 3); HLA-A31 NY-ESO-I53-62 ASGPGGGAPR; HLA-A02 NY-ESO-I157-165 SLLMWITQC (patient 3)), MAGE-A3 (HLA-A01 MAGE-A3168-176 EVDPIGHLY; HLA-Cw7 MAGE-A3212-220 EGDCAPEEK (patient 2); HLA-A02 MAGE-A3112-120 KVAELVHFL; HLA-B44 MAGE-A3167-176 MEVDPIGHLY; HLA-A02 MAGE-A3271-279 FLWGPRALV (patient 3)) and overlapping 15-mer peptide mixes for NY-ESO-I and tyrosinase (patient 1) were obtained from Jerini Peptide Technologies.
Tissue preparation
Peripheral blood was collected from the orbital sinus. Spleens and lymph nodes were stored in PBS (Life Technologies). Spleen single-cell suspensions were prepared in PBS by mashing tissue against the surface of a 70-μm cell strainer (BD Falcon) using the plunger of a 3-ml syringe (BD Biosciences). Erythrocytes were removed by hypotonic lysis. Lymph nodes were digested with collagenase D (1 mg ml−1; Roche) and passed through cell strainers. Bone marrow cells were flushed from femur and tibia bones, homogenized and filtered, before erythrocytes were removed by hypotonic lysis.
Flow cytometry
Monoclonal antibodies for extracellular staining included CD4, CD8, CD11b, CD40, CD45RA, CD49b, CD69, CD86, Ly6C, NK1.1, Thy1.1, Thy1.2 (BD Pharmingen), GR-1 (BioLegend), F4/80 (Invitrogen), CD11c, PDCA-1 (Miltenyi Biotec), CD62L, CD127, CD317 and Siglec H (eBioscience). Intracellular cytokine staining was performed with antibodies against IFNγ, TNFα and CD107a and CD107b (BD Pharmingen) and cross-reactive human granzyme B (Invitrogen) using the cytofix/cytoperm kit (BD Pharmingen), after stimulation of 2 × 106 splenocytes with 4 μg ml−1 gp70 AH1-A5 or irrelevant HA peptide in the presence of 20 μg ml−1 brefeldin A (Sigma), 40 μg ml−1 GolgiStop (BD Pharmingen) and CD107a and CD107b for 5 h at 37 °C. Intracellular IFNα (RMMA-1, R&D Systems) staining was performed using the fixation and permeabilization kit (eBioscience) after incubation of 2 × 106 splenocytes in the presence of 20 μg ml−1 brefeldin A (Sigma) for 5 h at 37 °C. Quantification of OVA-specific CD8+ T cells with H-2Kb/OVA257-264 tetramer (Beckman-Coulter) was previously described34, and CD8+ T cells recognizing gp70 AH1-A1 were detected with H-2Ld/AH1423-431 (SPSYVYHQF) tetramer kindly provided by the NIH tetramer core facility (Emory University Vaccine Center). Antigen-specific CD8+ T cells were determined five days after the last immunization. Viability was determined using 7-AAD (Sigma) or fixable viability dye (eBioscience). For patient samples, cryopreserved PBMC or freshly isolated PBMC (day 57) were stained for 10 min at room temperature in the dark with MHC dextramers (Immudex) bound to peptide (HLA-B35 NY-ESO-194-102 MPFATPMEA (patient 1), HLA-Cw03 NY-ESO-I92-100 LAMPPFATPM (patient 3). Cell surface markers CD3, CD8, CD16, CD14, CD19 (all BD Pharmingen) and CD4 (Biolegend) were subsequently stained along with DAPI (BD Biosciences) for 20 min at 4 °C in the dark. Antigen-specific CD8+ T cells were determined within the CD3+CD8+CD4− lineage− population. Flow cytometric data were acquired on a FACSCanto II or, for patient samples, an LSR Fortessa SORP flow cytometer (both BD Biosciences) and analysed with FlowJo 7.6.5 software (Tree Star). For cell sorting, splenocytes were pre-enriched by simultaneous magnetic depletion of T and B cells using MACS magnetic microbeads coated with CD3 or CD19 antibodies and MACS columns (Miltenyi Biotec). cDCs (F4/80−CD11chi), pDCs (F4/80−CD11cint PDCA-1hi) and macrophages (F4/80hi) were then sorted on a FACSAria cell sorter (BD Biosciences) according to their surface marker expression. Purities of sorted populations: cDCs, 97.8%; pDCs, 99.7%; macrophages, 98.9%.
Immunofluorescence staining
Immuofluorescence was performed as previously described21. For colocalization studies with CD11c+ cells, 8-μm sections of cryconserved spleens were stained. Sections were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for 10 min at room temperature in the dark, blocked using PBS supplemented with 1% BSA, 5% mouse serum, 5% rat serum and 0.02% Nonident for 1 h at room temperature in the dark. Fluorescence-labelled CD11c antibody (clone N418, BioLegend) was used to stain sections overnight at 4 °C, followed by nuclear staining with Höchst (Sigma). Uptake of Cy3-RNA-LPX by CD11c+ cells was revealed by visualization of CD11c- and Cy3-double-positive cells. Immunofluorescence images were acquired using an epifluorescence microscope (ApoTome, Zeiss).
For biodistribution studies of Cy5-labelled RNA-LPX in the spleen and liver, cryconserved organs were cut and 6-μm sections were fixed in 4% PFA for 10 s at room temperature in the dark, followed by nuclear staining with DAPI (Sigma). Immunofluorescence images were acquired using an epifluorescence microscope (Axio Scan.Z1, Zeiss). For in vitro uptake and colocalization studies with Cy3-labelled RNA-LPX, treated human monocyte-derived DCs were fixed in 4% PFA for 10 min at room temperature in the dark, blocked using PBS supplemented with 0.5% BSA, 0.01% saponin, 5% mouse serum and 5% goat serum for 1 h at room temperature in the dark. Primary antibody staining with TLR7 (polyclonal, Novus) and EEA1 (polyclonal, Cell signaling) was followed by secondary antibody (anti-rabbit IgG, Jackson ImmunoResearch) and Höchst (Sigma) staining. Immunofluorescence images were acquired using a confocal microscope (SP8 Leica). For the quantification of RNA-Cy3-LPX uptake by DCs in absence or presence of inhibitors, images were acquired using an epifluorescence microscope (ApoTome, Zeiss). The area (as pixel square) of Cy3+ particles in individual cells was quantified as selected threshold areas using Fiji ImageJ 1.49.
Ex vivo luciferase assay
Single-cell suspensions were prepared from the bone marrow of femur and tibia bones from mice 6 h after injection of 100 μg Luc-RNA-LPX and 5 × 106 cells were plated in 96-well Nunc white plates (Thermo Scientific). Cell suspensions were treated with the equal volume of Bright-Glo luciferin reagent (Promega), incubated for 3 min on a microplate shaker and bioluminescence was measured with an Infinite M200 plate reader (Tecan) with an integration time of 1 s. Background luminescence measured in cells obtained from untreated mice were within the range of 15 ± 5 counts per second.
In vitro uptake studies
For uptake and maturation studies with whole blood, 30 μl fresh whole blood were coincubated with 2 × 105 freshly generated human monocyte-derived immature DCs pre-treated with 50 μg ml−1 poly I:C for 40 h at 37 °C or left untreated and transfected with 0.2 μg Luc-LPX. After incubation for 20 h at 37 °C, luciferase assay was performed as described above. For colocalization and uptake inhibition studies, freshly generated human monocyte-derived immature DCs (2.5 × 105 or 5 × 105) were plated on poly-l-lysine-coated 12-mm cover slips or chamber slides (Nunc) and incubated overnight at 37 °C. Cells were transfected with 0.8 or 1.25 μg Cy3-labelled RNA-LPX for 10 min and washed thoroughly with medium to remove extracellular RNA-LPX. For colocalization studies, cells were co-transfected with RNA-LPX and 1 mg ml−1 FITC-labelled dextran (70,000 kDa, ThermoFisher) and fixed directly after washing. For costaining with EEA1 and TLR7, cells were incubated for another 30 min before fixation. For inhibition studies, cells were treated with 10 μM cytochalasin D44 (Sigma) for 3 h or 10 μM Rottlerin45 (Sigma) for 1 h (inhibitors present during transfection) before transfection, and fixed directly after washing. All conditions were performed in duplicates.
Bioluminescence imaging
Uptake and translation of Luc-RNA were evaluated by in vivo bioluminescence imaging using the Xenogen IVIS Spectrum imaging system (Caliper Life Sciences). Unless stated otherwise, an aqueous solution of l-luciferin (250 μl, 1.6 mg; BD Biosciences) was injected intraperitoneally 6 h after i.v. injection of 20 μg Luc-RNA-LPX (ex vivo lymph nodes and bone marrow imaging: 24 h after i.v. injection of 100 μg). Emitted photons from live animals or extracted tissues were quantified 10 min later with an exposure time of 1 min. Regions of interest (ROI) were quantified as average radiance (photons s−1 cm−2 sr−1, represented by colour bars) (IVIS Living Image 4.0).
Ex vivo fluorescence measurements
Upon organ retrieval, individual tissues were homogenized in 500 μl PBS using Lysis Matrix D tubes and the MP Biomedicals FastPrep-24 5G Instrument. Lysed tissues were directly subjected to fluorescence measurements for Cy5 (excitation, 650 nm; emission, 680 nm) using a standard fluorescence reader (Tecan Reader, Software i-control).
Enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) assay
As described previously21, 5 × 105 freshly isolated splenocytes were incubated in a microtiter plate (Merck Millipore) coated with anti-IFNγ antibody (10 μg ml−1, AN18, Mabtech) in the presence of 2 μg ml−1 peptide for 18 h at 37 °C, and cytokine secretion was detected with anti-IFNγ antibody (1 μg ml−1 R4-6A2, Mabtech). For analysis of T-cell responses in peripheral blood, PBMC were isolated via density gradient centrifugation, pooled and restimulated with 2 μg/ml peptide. From each biological replicate, three technical triplicates were performed. For ex vivo ELISPOT assay from patient samples (patient 1 and 3), cryopreserved peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) or freshly isolated PBMC (day 57) were used. Cryopreserved PBMC were thawed, resuspended in CTS OpTimizer T Cell Expansion serum-free medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and left for 2–5 h at 37 °C before performing the assay. For in vitro stimulation (IVS) before ELISPOT (patient 2), cryopreserved PBMC were thawed in a 37 °C water bath and immediately transferred into CTL-Wash serum-free wash buffer (Cellular Technology). CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were purified using CD4 or CD8 microbeads (Miltenyi Biotec) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Positive fractions were resuspended at 1 × 106 cells ml−1 in DMEM (ThermoFisher Scientific) containing 10% AB-human serum (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and left overnight at 37 °C before performing the assay. Negative fractions were resuspended in RPMI (Thermo Fisher Scientific) containing 5% human serum, 0.5% penicillin-streptomycin 1× MEM non-essential amino acids and 1 mM Sodium Pyruvate (all from Thermo Fisher Scientific) and left to rest overnight at room temperature before being electroporated with RNA encoding vaccine antigens (BioNTech). Electroporated APCs were left to rest for 3 h at 37 °C, followed by irradiation at 15 Gy. CD4+/CD8+ effectors and electroporated and irradiated APCs were coincubated at an effector:target ratio of 2:1. One day after starting the IVS, fresh culture medium was added together with 10 U ml−1 IL-2 (Proleukin 2, Novartis Pharma) and 5 ng ml−1 IL-15 (Peprotech). IL-2 was added once again at the same concentration 7 days after setting up the IVS cultures, and the cultures were incubated for another 4 days. During incubation, IVS cultures were checked microscopically and fresh medium was added if necessary. ELISPOT was performed after 11 days of stimulation (50,000 cells per well). On multiscreen filter plates (Merck Millipore) coated with antibodies specific for IFNγ (1-D1K, Mabtech), 3 × 105 PBMC were stimulated with overlapping peptides covering the whole length of the vaccine antigens (PepMix, JPT Peptide Technologies) or a mixture of HLA-class-I-restricted peptides from cytomegalovirus, Epstein–Barr and influenza viruses (CEF pool, JPT Peptide Technologies) for 16–20 h at 37 °C. Plates were sequentially incubated with biotin-conjugated secondary anti-IFNγ antibody (7-B6-1, Mabtech) and ExtrAvidin-Alkaline Phosphatase (Sigma-Aldrich) before cytokine secretion was detected by adding BCIP/NBT substrate (Sigma-Aldrich). For each patient, technical triplicates were performed. Plates were scanned and analysed using the ImmunoSpot Series S5 Versa ELISPOT Analyzer (S5Versa-02-9038), ImmunoCapture software 6.3 and ImmunoSpot software 5.0.3 (all Cellular Technology Ltd).
Depletion and blocking experiments
For depletion of CD11c+ cells, CD11c-DTR mice were treated i.p. with 4 ng g−1 body weight (bone marrow chimaeras: 8 ng g−1 body weight) diphtheria toxin diluted in 200 μl PBS 12 h before RNA-LPX administration (depletion efficiency of CD11c+DTR+ cells: >97.2%). CD11cint pDCs are hardly affected by depletion in CD11c-DTR mice46. For depletion of pDCs, BDCA2-DTR mice were treated i.p. with 4.5 ng g−1 body weight diphtheria toxin diluted in 200 μl PBS (depletion efficiency of CD11b−CD11cintSiglec-HhiLy6Chi pDCs: >97.2%). Macrophages were depleted by administration of 50 mg kg−1 body weight of clodrolip47 (4.46 mg ml−1 clodronate formulated with 16 mM POPC and 14 mM cholesterol) in PBS i.p. 12 h before RNA-LPX administration (depletion efficiency of F4/80+CD11b+CD11cint macrophages: >96.3%). Depletion of CD11c+ cells, pDCs and macrophages was specific, other cells were not affected. In some experiments, 100 μg anti-IFNAR1 blocking antibody (MAR1-5A3, BioXCell) or IgG1 isotype control (MOPC-21, BioXCell) diluted in 200 μl PBS were applied i.p. 1 h before RNA-LPX injection.
Cellular uptake, splenocyte activation, in vivo cytokine secretion
Mice were injected i.v. with 40 μg Cy3- or Cy5-labelled RNA-LPX or 80 μg eGFP RNA-LPX and spleens were recovered 1 h (Cy3, Cy5) or 24 h later (eGFP). For splenocyte activation and cytokine secretion, mice were injected i.v. with 40 μg HA RNA-LPX. Unless stated otherwise, splenocytes were prepared 24 h after injection to measure median fluorescence intensity of CD40, CD86 and CD69 expression on immune cell subsets. Serum was collected and production of IFNα was determined from samples stored at −20 °C (pan-IFNα ELISA kit, PBL assay science). For patient samples, serum was stored at −80 °C and IFNα and IP-10 levels were determined using the pan-IFNα ELISA kit (PBL assay science) and ECLIA multiplex assay (Meso Scale Discovery), respectively. Patient samples were measured in duplicates. Quantification of RNA in blood was performed by quantitative RT–PCR using antigen sequence-specific primers (IMGM Laboratories).
In vivo proliferation assay
Splenocytes (1 × 107) from BALB/c Thy1.2+ CL4-TCR-transgenic mice labelled with 1 μM carboxyfluorescein diacetate, succinimidyl ester (CFSE, Invitrogen) were adoptively transferred into BALB/c Thy1.1+ mice and immunized i.v. with 40 μg HA-RNA-LPX 18 h after transfer. Controls received Thy1.2+ CL4-TCR-transgenic CD8+ T cells but were not immunized. Four days after immunization, peripheral blood, splenocytes and LN cells were stained for Thy1.2+CD8+ T cells and proliferation analysed by flow cytometry.
Tumour models
Protective immunity: BALB/c or C57BL/6 mice were immunized repetitively with 40 μg RNA-LPX. After the last immunization, 2 × 105 CT26 or B16-OVA tumour cells, respectively, were inoculated s.c. into the flanks of mice. Therapeutic immunity: 1 × 105 TC-1 tumour cells were inoculated s.c. and mice were immunized three times with 40 μg RNA-LPX (for E6/E7, 20 μg each). Tumour sizes were measured unblinded with a caliper every three to four days for calculating tumour volumes using the equation (a2 × b)/2 (a, width; b, length). Animals were euthanized when exhibiting signs of impaired health or when the length of the tumour exceeded 15 mm. Metastasis models: 2 × 105 CT26, CT26-Luc (immunization with CT26-M90 RNA-LPX: 5 × 105), B16-OVA or 3 × 105 B16F10-Luc tumour cells were injected i.v. and immunizations were initiated on day four after tumour inoculation. In some experiments, 1 mg of anti-IFNAR1 blocking antibody (MAR1-5A3, BioXCell) or IgG1 isotype control (MOPC-21, BioXCell) diluted in 200 μl PBS were applied i.p. 6 h before RNA-LPX injection. CT26-Luc and B16F10-Luc tumour growth kinetics were determined unblinded by bioluminescence in vivo imaging. Mice were randomized based on their average radiance values (ANOVA-P method, Daniel’s XL Toolbox V6.53). When exhibiting impaired breathing, mice were killed and tumour burden was quantified unblinded after intratracheal ink (85 ml H2O, 15 ml ink, two drops of ammonia water) injection (this step was omitted for B16-OVA model) and fixation with Fekete’s solution (5 ml 70% ethanol, 0.5 ml formalin, and 0.25 ml glacial acetic acid)48. After 2–6 h, tumour lesions were bleached whereas normal lung tissue remained stained.
Clinical trial design
The study protocol was approved by the relevant authority and ethics committee. The study was conducted in accordance with all applicable laws, regulations and in agreement with the ICH-GCP guidelines and the Declaration of Helsinki (Fortaleza 2013). Written informed consent from all patients was obtained before enrolment. For patient treatment, tumour antigen encoding RNA-LPX were prepared from GMP-manufactured components (BioNTech) in a dedicated pharmacy under GMP. Patients were injected i.v. with weekly escalating doses of RNA-LPX encoding antigens NY-ESO-149, tyrosinase50, MAGE-A351 and TPTE52 (1.9, 3.6 or 7.2 μg RNA-LPX of each antigen; see vaccination schemes in Extended Data Fig. 5a). Blood samples were obtained for cytokine measurements on day 1, 8 and 15 (0 (pre-vaccination), 2, 6, 24 h after each vaccination), for ELISPOT and MHC class I dextramer staining on day 0 (pre-vaccination), 15, 22, 29, 57. Blood samples for T-cell monitoring were obtained before vaccination on the respective vaccination day.
Statistical analyses and data presentation
All results are expressed as mean ± s.d., mean ± s.e.m. or median with or without interquartile range as indicated. Biological replicates were used in all experiments unless stated otherwise. Unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test was used for comparison of two groups. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed when more than two groups were compared, and when determined significant (P < 0.05), multiple comparisons were performed using Tukey’s post-hoc test. Two-way ANOVA was performed when both time and treatment were compared, and when significant (P < 0.05) multiple comparisons were performed using Bonferroni post-hoc tests or Dunnett’s post-hoc test (Fig. 3b). Survival benefit was determined with the log-rank test. All statistical analyses were performed with GraphPad PRISM 6.01. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001. In all experiments, representative images, dot plots and histograms are shown. Values below detection limit are marked with <LDL (lower detection limit). No statistical methods were used to pre-determine sample size for animal or other experiments.
Change history
07 June 2016
The competing financial interests statement did not display correctly online when this paper was first published; this has been corrected and the statement is now available.
References
Zinkernagel, R. M. et al. Antigen localisation regulates immune responses in a dose- and time-dependent fashion: a geographical view of immune reactivity. Immunol. Rev. 156, 199–209 (1997).
Stetson, D. B. & Medzhitov, R. Type I interferons in host defense. Immunity 25, 373–381 (2006).
Boczkowski, D., Nair, S. K., Snyder, D. & Gilboa, E. Dendritic cells pulsed with RNA are potent antigen-presenting cells in vitro and in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 184, 465–472 (1996).
Sahin, U., Karikó, K. & Türeci, Ö. mRNA-based therapeutics—developing a new class of drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 13, 759–780 (2014).
Banchereau, J. & Steinman, R. M. Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature 392, 245–252 (1998).
Tacken, P. J., de Vries, I. J. M., Torensma, R. & Figdor, C. G. Dendritic-cell immunotherapy: from ex vivo loading to in vivo targeting. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 7, 790–802 (2007).
Phua, K. K. L. Towards targeted delivery systems: ligand conjugation strategies for mRNA nanoparticle tumor vaccines. J. Immunol. Res. 680620 (2015).
Mitragotri, S., Burke, P. A. & Langer, R. Overcoming the challenges in administering biopharmaceuticals: formulation and delivery strategies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 13, 655–672 (2014).
Brito, L. A. et al. A cationic nanoemulsion for the delivery of next generation RNA vaccines. Mol. Ther. 22, 2118–2129 (2014).
Pollard, C. et al. Type I IFN counteracts the induction of antigen-specific immune responses by lipid-based delivery of mRNA vaccines. Mol. Ther. 21, 251–259 (2013).
Zhou, W. Z. et al. RNA melanoma vaccine: induction of antitumor immunity by human glycoprotein 100 mRNA immunization. Hum. Gene Ther. 10, 2719–2724 (1999).
Hess, P. R., Boczkowski, D., Nair, S. K., Snyder, D. & Gilboa, E. Vaccination with mRNAs encoding tumor-associated antigens and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor efficiently primes CTL responses, but is insufficient to overcome tolerance to a model tumor/self antigen. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 55, 672–683 (2006).
Perche, F. et al. Enhancement of dendritic cells transfection in vivo and of vaccination against B16F10 melanoma with mannosylated histidylated lipopolyplexes loaded with tumor antigen messenger RNA. Nanomedicine 7, 445–453 (2011).
Blanco, E., Shen, H. & Ferrari, M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 33, 941–951 (2015).
Lee, E. R. et al. Detailed analysis of structures and formulations of cationic lipids for efficient gene transfer to the lung. Hum. Gene Ther. 7, 1701–1717 (1996).
Liu, Y. et al. Factors influencing the efficiency of cationic liposome-mediated intravenous gene delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 15, 167–173 (1997).
Diken, M. et al. Selective uptake of naked vaccine RNA by dendritic cells is driven by macropinocytosis and abrogated upon DC maturation. Gene Ther. 18, 702–708 (2011).
Sallusto, F., Cella, M., Danieli, C. & Lanzavecchia, A. Dendritic cells use macropinocytosis and the mannose receptor to concentrate macromolecules in the major histocompatibility complex class II compartment: downregulation by cytokines and bacterial products. J. Exp. Med. 182, 389–400 (1995).
Platt, C. D. et al. Mature dendritic cells use endocytic receptors to capture and present antigens. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 4287–4292 (2010).
Diebold, S. S., Kaisho, T., Hemmi, H., Akira, S. & Reis e Sousa & C. Innate antiviral responses by means of TLR7-mediated recognition of single-stranded RNA. Science 303, 1529–1531 (2004).
Kreiter, S. et al. Mutant MHC class II epitopes drive therapeutic immune responses to cancer. Nature 520, 692–696 (2015).
Le Bon, A. et al. Cross-priming of CD8+ T cells stimulated by virus-induced type I interferon. Nat. Immunol. 4, 1009–1015 (2003).
Bacher, N. et al. Interferon-α suppresses cAMP to disarm human regulatory T cells. Cancer Res. 73, 5647–5656 (2013).
Zitvogel, L., Galluzzi, L., Kepp, O., Smyth, M. J. & Kroemer, G. Type I interferons in anticancer immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 15, 405–414 (2015).
Janeway, C. A. Jr The immune system evolved to discriminate infectious nonself from noninfectious self. Immunol. Today 13, 11–16 (1992).
Janeway, C. A. Jr & Medzhitov, R. Innate immune recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 20, 197–216 (2002).
Swiecki, M., Gilfillan, S., Vermi, W., Wang, Y. & Colonna, M. Plasmacytoid dendritic cell ablation impacts early interferon responses and antiviral NK and CD8+ T cell accrual. Immunity 33, 955–966 (2010).
Kamphuis, E., Junt, T., Waibler, Z., Forster, R. & Kalinke, U. Type I interferons directly regulate lymphocyte recirculation and cause transient blood lymphopenia. Blood 108, 3253–3261 (2006).
Müller, U. et al. Functional role of type I and type II interferons in antiviral defense. Science 264, 1918–1921 (1994).
Jung, S. et al. In vivo depletion of CD11c+ dendritic cells abrogates priming of CD8+ T cells by exogenous cell-associated antigens. Immunity 17, 211–220 (2002).
Huang, A. Y. et al. The immunodominant major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted antigen of a murine colon tumor derives from an endogenous retroviral gene product. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93, 9730–9735 (1996).
Lin, K.-Y. et al. Treatment of established tumors with a novel vaccine that enhances major histocompatibility class II presentation of tumor antigen. Cancer Res. 21–26 (1996).
Chuang, C.-M., Monie, A., Wu, A. & Hung, C.-F. Combination of apigenin treatment with therapeutic HPV DNA vaccination generates enhanced therapeutic antitumor effects. J. Biomed. Sci. 16, 49 (2009).
Holtkamp, S. et al. Modification of antigen-encoding RNA increases stability, translational efficacy, and T-cell stimulatory capacity of dendritic cells. Blood 108, 4009–4017 (2006).
Kreiter, S. et al. Increased antigen presentation efficiency by coupling antigens to MHC class I trafficking signals. J. Immunol. 180, 309–318 (2008).
Kuhn, A. N. et al. Phosphorothioate cap analogs increase stability and translational efficiency of RNA vaccines in immature dendritic cells and induce superior immune responses in vivo. Gene Ther. 17, 961–971 (2010).
Slansky, J. E. et al. Enhanced antigen-specific antitumor immunity with altered peptide ligands that stabilize the MHC-peptide-TCR complex. Immunity 13, 529–538 (2000).
Kenter, G. G. et al. Vaccination against HPV-16 oncoproteins for vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia. N. Engl. J. Med. 361, 1838–1847 (2009).
Kreiter, S. et al. Simultaneous ex vivo quantification of antigen-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses using in vitro transcribed RNA. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 56, 1577–1587 (2007).
Bangham, A. D., Hill, M. W. & Miller, N. G. A. in Methods in Membrane Biology (ed. Korn, E. D. ) 1–68 (Springer US, 1974).
Duzgunes, N. in Methods in Enzymology (Academic Press Inc, 2009).
Batzri, S. & Korn, E. D. Single bilayer liposomes prepared without sonication. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 298, 1015–1019 (1973).
Barichello, J. M., Ishida, T. & Kiwada, H. Complexation of siRNA and pDNA with cationic liposomes: the important aspects in lipoplex preparation. Methods Mol. Biol. 605, 461–472 (2010).
Racoosin, E. L. & Swanson, J. A. Macrophage colony-stimulating factor (rM-CSF) stimulates pinocytosis in bone marrow-derived macrophages. J. Exp. Med. 170, 1635–1648 (1989).
Sarkar, K., Kruhlak, M. J., Erlandsen, S. L. & Shaw, S. Selective inhibition by rottlerin of macropinocytosis in monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Immunology 116, 513–524 (2005).
Bar-On, L. & Jung, S. Defining in vivo dendritic cell functions using CD11c-DTR transgenic mice. Methods Mol. Biol. 595, 429–442 (2010).
Aichele, P. et al. Macrophages of the splenic marginal zone are essential for trapping of blood-borne particulate antigen but dispensable for induction of specific T cell responses. J. Immunol. 171, 1148–1155 (2003).
Wexler, H. Accurate identification of experimental pulmonary metastases. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 36, 641–645 (1966).
Chen, Y. T. et al. A testicular antigen aberrantly expressed in human cancers detected by autologous antibody screening. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 1914–1918 (1997).
Brichard, V. et al. The tyrosinase gene codes for an antigen recognized by autologous cytolytic T lymphocytes on HLA-A2 melanomas. J. Exp. Med. 178, 489–495 (1993).
Gaugler, B. et al. Human gene MAGE-3 codes for an antigen recognized on a melanoma by autologous cytolytic T lymphocytes. J. Exp. Med. 179, 921–930 (1994).
Simon, P. et al. Functional TCR retrieval from single antigen-specific human T cells reveals multiple novel epitopes. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2, 1230–1244 (2014).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank M. Holzmann, R. Roth, U. Schmitt, M. Brkic, A. König, C. Worm, N. Krimmel, A.-K. Thiel, C. Bender, M. Suchan, A.-L. Popa, P. Bezerra Gomes, S. Herbert, M. Lux, D. Wintergerst, V. Bischoff, R. Krishna, Y. Hajime, J. Groß, A. Spruss, M. Erdeljan, S. Wöll, T. Bukur, H. Muramatsu and M. Baiersdörfer for technical support, NIH Tetramer Core Facility for providing gp70 MHC class I tetramer, A. Kong for critical reading, A. Kemmer-Brück, D. Schwarck, S. Bolte for clinical operations support and K. Kariko for advice. This work was supported by the technology innovation program of the Rhineland Palatinate government, the InnoTop program, the CI3 Cutting Edge Cluster Funding of the German Ministry of Technology (BMBF) and the Collaborative Research Group 1066 of Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG). L.M.K. was funded by the Graduate School of Immunotherapy 1043 of DFG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
U.S. was responsible for conception and experimental strategy of the study. Formulation development was performed by H.H. and P.L. Design and analysis of the experiments were done by L.M.K, M.D., H.H., S.K, M.M. and D.F. supported by K.C.R. and F.V. L.M.K, M.D., M.M., D.F., K.C.R., A.S., F.V., Y.H., Ho.He, C.G. and M.V. performed the experiments and acquired the data. C.L., J. H., J.D., A.N.K., J.B., R.J., S.H., S.G., E.D., R.R. and S.A. were involved in design, implementation or laboratory analyses of the clinical study. L.M.K., M.D., Ö.T. and U.S. interpreted the data and drafted the manuscript. C.H. supported the revision of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
U.S., H.H, M.M., D.F., K.C.R, C.G., Ho.He, Y.H., M.V., A.N.K., J.B., E.D., J.D., R.J. and S.H. are employees at BioNTech AG (Mainz, Germany). M.D. and S.K. are working as consultants for BioNTech AG (Mainz, Germany). U.S., L.M.K., M.D., H.H., S.K., D.F., M.M. and K.C.R. are inventors on patents and patent applications related to this study. U.S. and C.H are stock owners, C.H. is advisor and supervisory board member and U.S. is management board member of BioNTech AG. All other authors have no potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Reviewer Information: Nature thanks O. Farokhzad, C. G. Figdor, C. Melief, L. Zhang and the other anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Extended data figures and tables
Extended Data Figure 1 Physicochemical characteristics and biological activity of RNA-LPX constituted from different lipids at various charge ratios.
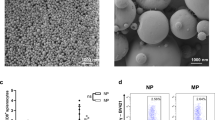
a, Bioluminescence imaging of Luc expression in BALB/c mice 6 h after i.v. injection of different transfection reagents and controls: PBS (n = 3), 60 μg Luc-RNA alone (n = 3), 25 μg Luc-RNA complexed with TransMessenger (Qiagen) (n = 3), 5 μg Luc-RNA complexed with Viromer RED (Lipocalyx) (n = 3). b, Cryo-TEM images of Luc-LPX constituted at a positive:negative ((+):(−)) charge ratio of 1.3:2 with DOTMA/DOPE liposomes. Scale bar, 100 nm. c, Fraction of uncomplexed RNA in Luc-LPX preparations constituted at different charge ratios with DOTMA/DOPE liposomes determined by capillary gel electrophoresis (n = 2–7). d, Particle size, polydispersity index (left) and zeta potential (right) (n = 3) of RNA-LPX constituted with Luc-RNA and differently constituted liposomes at various charge ratios. e, Bioluminescence imaging of BALB/c mice (n = 3) after i.v. injection of Luc-LPX constituted with different liposomes at various charge ratios corresponding to d. Pie charts show relative contribution of each organ to total signal. f, Relative biodistribution of Luc expression in explanted organs of BALB/c mice (n = 3) after i.v. injection of Luc-LPX constituted with DOTMA/DOPE liposomes at a charge ratio of (+):(-) of 1.3:2 or Luc-RNA alone. g, Luc expression in human immature DCs transfected with 5 μg Luc-LPX constituted freshly or stored after constitution for indicated time periods at 4 °C (left) or room temperature (right). RNA-LPX tested in duplicates (stored) or quadruplets (fresh). Each bar represents triplicates. h, Particle size (upper left) and percentage of RNA integrity (upper right) of Luc-LPX (n = 1) incubated in 50% mouse serum for indicated time periods at 37 °C. Bioluminescence imaging of Luc expression in BALB/c mice (n = 5) after i.v. injection of Luc-LPX preincubated in 50% mouse serum for 30 min at 37 °C (lower left and right). NM, not measured. Error bars, median with interquartile range (h), otherwise mean ± s.d.
Extended Data Figure 2 Biodistribution and cellular uptake mechanism of RNA-LPX vaccines.
a, Uptake of Cy5-labelled RNA in splenic cell subsets of C57BL/6 mice (n = 3) 1 h after i.v. injection of 40 μg Cy5-labelled RNA-LPX. b, Localization of CD11c and Cy3 double-positive cells in the spleen of BALB/c mice (n = 2) 1 h after i.v. injection of 40 μg Cy3-labelled RNA-LPX. Nuclear staining in blue. Scale bar,100 μm. c, Half-life of RNA-LPX in circulation analysed by quantitative RT–qPCR in male and female C57BL/6 mice (n = 5 per time-point) after injection of 60 μg RNA-LPX constituted with NY-ESO-I, tyrosinase, MAGE-A3 and TPTE RNA (15 μg each). d, Localization of Cy5+ (upper left) or Thy1.1+ cells (lower left) in spleen and liver of BALB/c mice (n = 5) determined by microscopy or flow cytometry 1 h or 20 h after i.v. injection of 40 μg Cy5-labelled RNA-LPX or 40 μg 1-methyl-pseudouridine-modified Thy1.1-LPX, respectively. Nuclear staining in blue. Scale bar, 50 μm (top), 20 μm (bottom). Biodistribution of Cy5 signal in homogenized organs of BALB/c mice (n = 2) (right). Note the signal in the liver is overestimated in this analysis owing to the strong signal in the gall bladder, probably reflecting biliary secreted free dye. e, Bioluminescence imaging of lymph nodes of BALB/c mice (n = 3) 18 h after i.v. injection of 40 μg 1-methyl-pseudouridine-modified Luc-LPX. ax, axillary; ing, inguinal; mand, mandibular. f, Flow cytometry analysis of Cy5 and Thy1.1 expression in CD11c+ cells in the bone marrow of C57BL/6 mice (n = 3) 1 h or 20 h after i.v. injection of 40 μg Cy5-labelled RNA-LPX or 40 μg 1-methyl-pseudouridine-modified Thy1.1-LPX, respectively. g, h, Localization of Cy3-labelled RNA in human immature DCs after co-transfection of 1.25 μg Cy3-labelled RNA-LPX at a charge ratio of (+):(−) of 1.3:2 and 3:1 with dextran (g) or of 1.3:2 after staining for TLR7 or EEA1 (h). Nuclear staining in blue. Scale bar, 10 μm. i, Visualization and quantification of inhibited uptake of positively as well as negatively charged Cy3-labelled RNA-LPX in human immature DCs pretreated with rottlerin or cytochalasin D. Scale bar, 10 μm. j, Bioluminescence imaging of lymph nodes of BALB/c mice (n = 3) injected intranodally with 10 μM rottlerin in 10 μl PBS 15 min before i.v. injection of 80 μg Luc-LPX. k, Luminescence assay of whole blood enriched or not enriched with human immature DCs pretreated with poly I:C or not (control) before transfection with Luc-LPX at a charge ratio of 1.3:2. WB, whole blood. l, Poly-I:C-induced maturation determined by CD86 expression (left), bioluminescence imaging (middle) and eGFP expression in splenic cDC subsets (right) upon injection of BALB/c mice (n = 3) with 50 μg poly I:C i.p. 12 h before i.v. injection of 20 μg Luc-LPX or 80 μg eGFP-LPX, respectively. Significance was determined using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test (d, lower left, f, l, middle) and one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (i–k, l, right). Error bars, mean ± s.e.m. (k) or mean ± s.d. otherwise.
Extended Data Figure 3 Systemic TLR7- and IFNAR-dependent activation of APCs and effector cells, IFNα production and strong expansion of fully functional antigen-specific T cells induced by RNA-LPX vaccines.
a, Localization of splenic CD11chi cells at baseline (top) and 6 h after i.v. injection of 40 μg HA-LPX (bottom) into BALB/c mice (n = 2). Nuclear staining in blue. Scale bar, 100 μm. RP, red pulp; WP, white pulp. b–e, Activation marker expression in splenic cell subsets and kinetics of IFNα serum levels after i.v. injection of mice (n = 3 per time point) with HA-LPX in Tlr3−/−, Tlr4−/− and Tlr9−/− mice (b), in Ifnar1−/− mice (c, d), or in BALB/c mice treated with 100 μg anti-IFNAR1 antibody or isotype i.p. 1 h before i.v. injection of HA-LPX (e). Ab, antibody. f, mRNA levels of IFNα isoforms in sorted splenic APC subsets of C57BL/6 mice (n = 3) 1 h after i.v. injection of HA-LPX determined by qRT–PCR. Data expressed as log2-fold change, as compared to control animals. g, IFNα serum levels after i.v. injection of HA-LPX in BDCA2-DTR mice (n = 3 per time point) depleted (depl) of pDCs (left) and in C57BL/6 mice (n = 3 per time point) depleted of macrophages (right). h, CFSE proliferation profile of HA-specific CD4+ T cells in lymphoid compartments of BALB/c Thy1.1+ mice (n = 3) after adoptive transfer of HA-specific Thy1.2+ HA-TCR-transgenic CD4+ T cells and subsequent immunization with HA-LPX or control (untreated). Fraction of proliferated cells indicated. tg, transgenic. i, Priming of naive HA-specific CD8+ T cells ex vivo. BALB/c (n = 3) mice were immunized with 80 μg HA-LPX, irrelevant (eGFP)-LPX or NaCl (control). Splenocytes were prepared 12 h later and co-incubated with CFSE-labelled CL4-TCR-transgenic CD8+ T cells isolated using MACS magnetic microbeads coated with CD8 antibodies at an effector:target ratio of 1:6. Four days later, proliferation profiles were analysed by flow cytometry. Numbers indicate the percentage of proliferated cells. j, Fraction of cytokine-secreting CD8+ T cells within CD8+ T cells in the spleen upon de novo priming in C57BL/6 mice (n = 5) immunized i.v. (day 0, 3, 8) with OVA-LPX after in vitro restimulation with no (none), irrelevant VSV (irrelevant) or OVA peptide and intracellular cytokine staining (top). Spleen ex vivo ELISPOT assay upon de novo priming in BALB/c mice (n = 5) immunized i.v. (day 0, 3, 8) with gp70-LPX. Stimulation with no (none), irrelevant HA (irrelevant) or gp70 peptide (lower left). gp70-specific cytotoxicity in vivo (lower right). BALB/c mice (n = 5) were immunized i.v. (day 0, 3, 8) with 40 μg gp70-LPX. Naive splenocytes were labelled with 0.5 or 5 μM CFSE and pulsed with peptide (6 μg ml−1) five days after the last immunization, and target cells (2 × 107) were adoptively transferred into immunized recipients i.v. (irrelevant HA-loaded CFSElow:gp70-loaded CFSEhigh = 1:1). Recipient splenocytes were analysed by flow cytometry 18 h after transfer, and antigen-specific lysis was determined: specific lysis (%) = (1 − (percentage of cells pulsed with gp70/percentage of cells pulsed with HA)) × 100). k, Expression of memory markers CD127 and CD62L in gp70-specific, CD44+CD8+ T cells compared to non-specific CD8+ T cells in blood (day 19) and spleen (day 67) of BALB/c mice (n = 3) after priming with gp70-LPX (day 0, 7, 14). l, Fraction of gp70-specific CD8+ T cells within total CD8+ T cells in blood, bone marrow and lymph nodes determined by MHC class I tetramer staining after de novo priming of splenectomized BALB/c mice (n = 5–7) immunized with gp70-LPX (day 0, 7) or left untreated (control). Significance was determined using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test (b left, c), two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test (b right, g) and one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (j, l). Error bars, mean ± s.d.
Extended Data Figure 4 Potent antitumour immunity and rejection of advanced aggressively growing tumours in mice conferred by RNA-LPX vaccines.
a, B16-OVA melanoma load in lungs of C57BL/6 mice (n = 8) immunized i.v. (days 4, 7, 11) with OVA-LPX or irrelevant (eGFP)-LPX. b, Expression of activation markers measured 24 h after i.v. injection of 40 μg irrelevant (empty vector)-LPX, eGFP-LPX or OVA-LPX by flow cytometry in splenic immune cell subsets (n = 3) and IFNα serum levels (n = 3) 6 h after injection in C57BL/6 mice. c, Bioluminescence signal of tumours in different groups before immunization and on day 25 (upper left), tumour load and lung weights (upper right) and TRP-1-specific CD8+ and CD4+ T-cell responses in spleens of control (untreated), irrelevant (empty vector)-LPX and TRP-1-LPX-immunized B6 albino mice (n = 12) on day 25 detected by ELISPOT assay (bottom), depicted in Fig. 3b. d, Bioluminescence imaging of CT26-Luc carcinoma in BALB/c mice (n = 4–7) depicted in Fig. 3c (left). e, TC-1-Luc tumour growth in C57BL/6 mice (n = 10) (left), depicted in Fig. 3d, and remission of established advanced TC-1-Luc tumours in C57BL/6 mice (n = 10) immunized i.v. with 40 μg E6/E7-LPX (day 13, 20, 27) (right). f, Survival of BALB/c mice rechallenged with CT26-Luc colon carcinoma cells on day 109, depicted in Fig. 3e. Significance was determined using one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (c), two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test (d), paired two-tailed Student’s t-test (f, right), unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test (f, far right), and log-rank test (f, left). Error bars, median with interquartile range (d), mean ± s.d. otherwise.
Extended Data Figure 5 Clinical application of RNA-LPX vaccines and de novo priming and amplification of patient T-cell responses against encoded vaccine antigens.
a, Vaccination scheme and monitoring for patients 1–3. b, Antigen-specific T-cell responses against NY-ESO-1 and tyrosinase determined by restimulation with overlapping peptide mixtures in IFNγ ELISPOT for patient 1. c, Antigen-specific T-cell responses against NY-ESO-1 and MAGE-A3, determined by post-IVS IFNγ ELISPOT assay at indicated days for patient 2. Values are corrected for background (no peptide). d, Antigen-specific T-cell responses against NY-ESO-I and MAGE-A3, determined by ex vivo IFNγ ELISPOT assay at indicated days for patient 3. Numbers in ELISPOT data indicate the amino acid position of each epitope. Significance was determined using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. Error bars, mean ± s.e.m.
Extended Data Figure 6 Comparison of i.v. and s.c. routes for RNA-LPX administration in the context of T-cell priming and biodistribution of RNA-LPX upon s.c. administration.
Fraction of OVA-specific CD8+ T cells within CD8+ T cells on day 13 in blood after de novo priming of C57BL/6 mice (n = 5) immunized i.v. with OVA-LPX (day 0, 3, 8) (left). Biodistribution of Luc expression 24 h after s.c. injection of Luc-LPX in BALB/c mice (n = 3) (right). Signal can only be observed at the injection site and the draining lymph node. Significance was determined using one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Error bars, mean ± s.d.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kranz, L., Diken, M., Haas, H. et al. Systemic RNA delivery to dendritic cells exploits antiviral defence for cancer immunotherapy. Nature 534, 396–401 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature18300
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature18300
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Nucleic acid-based drugs for patients with solid tumours
Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology (2024)
-
Natural long-chain saturated fatty acids doped LNPs enabling spleen selective mRNA translation and potent cancer immunotherapy
Nano Research (2024)
-
mRNA nanodelivery systems: targeting strategies and administration routes
Biomaterials Research (2023)
-
Passive, active and endogenous organ-targeted lipid and polymer nanoparticles for delivery of genetic drugs
Nature Reviews Materials (2023)
-
Engineering nanomaterial physical characteristics for cancer immunotherapy
Nature Reviews Bioengineering (2023)