Abstract
This study examines the relationship between green human resource management and environmental performance using green employee empowerment and organizational citizenship behavior for the environment. It also evaluates the moderating role of environmental knowledge between green human resource management and green employee empowerment, which was not discussed in previous studies—the research data was collected from Pakistani hotel industry employees using a cross-sectional process method. The total number of employees who completed the questionnaire was 360, out of which 237 were considered valid as these responses were used for further partial least square analysis. The study's findings revealed that green human resource management practices directly correlate with environmental performance. Furthermore, the results shed light on green employee empowerment and organizational citizenship behavior for the environment with moderation by environmental knowledge and individual green values to motivate employees to achieve sustainability leading toward ecological performance. This study supports theoretical contributions using the ability, motivation, and opportunity and sports value framework theories. In addition, our outcomes contribute to the literature by incorporating the moderation role of environmental knowledge between green human resource management and green employee empowerment. The study provides implications for green human resource management practices and sustainable environmental performance to top management and policymakers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
The tourism industries worldwide are the primary source of the nation's income, particularly in developed and developing countries (Bank 2012). The tourism industry of Pakistan has been positively increasing in terms of revenue and generated good profits through it (Economics 2019). According to the trend, the enterprises will increase further and create more income in terms of tourism (Times 2019). The tourism industry has faced the challenges of employee turnover, a big problem for enterprises worldwide (Kenneth 2016). According to Catio (2020), the strategies of management that show investment opportunities and workers' progress can play a significant role in reducing employee turnover. Generally, as in other countries of the world, the tourism industry of Pakistan also has many organizations, such as transportation, restaurants, hotels, resorts, etc. The most selected organization was hotels, as they are overgrowing in the environment (Yusoff et al. 2020; Jahanger et al. 2022). Human resource management (HRM) is significant because it inspires the employees as they are involved in the initiatives of a green environment and are associated with the company's vision (Renwick et al. 2013; Yang and Usman 2021; Roscoe et al. 2019). The activities of green human resource management (GHRM) are essential to creating awareness among the employees related to the environment to inspire them to perform actions to keep the environment free from pollution (Zaid et al. 2018; Usman and Makhdum 2021; Zhang et al. 2019). Le et al. (2021) describe the influence of green human resource management on the environment's friendly eco behavior and performance.
According to Jackson and Seo (2010), organizations implement green human resource management activities regarding the policies that lead to environmental sustainability. Empowerment of employees EE increases the performance of the job through work regarding efficiency and effectiveness (Ren et al. 2020). The employees who try to achieve their goals use empowerment; then it is said to be green employee empowerment (GEE). The green plans include recycling office furniture, efficient energy appliances, double-sided photocopies, and the recycling process. In this way, the organizations achieve their goals with the practices of GEE. The managers provide the support and feedback to empower the employees to help them act related to green tasks (Daily and Huang 2001; Tariq et al. 2016). Tariq et al. (2016) explain that the empowerment of employees related to green practices improves an organization's commitment and production level. Therefore, the empowered employees show better performance related to their duties and do organization citizenship behavior environment (OCBE) (Boiral, 2009). According to Sinaga and Nawangsari (2019), an individual's voluntary actions to improve the environment are known as organizational citizenship behavior environment. These individual actions can be compared to providing information to prevent workplace pollution and offering alternatives to cut waste. The organization's citizenship behavior environment is personal conduct chosen on purpose and directed toward items that advance the business's goals and environmental improvement. According to Paillé and Boiral (2013) describes, the three crucial describable extents to the quantity of the organizational citizenship behavior environment are named eco-initiatives and eco-management civic. The management at the top plays an essential role as they have the freedom to impact an organization’s environmental performance (Hambrick and Quigley 2014; Singh and El-Kassar 2019). Research has investigated the measurement and evaluation of a corporation’s environmental performance for many years (Dias-Sardinha and Reijnders 2005; Intisar et al. 2020; Searcy et al. 2016).
The present study contributes to the influence of green human resources management in many conducts. First, in this study, we described the relationship of green employee empowerment as a mediation function between the two variables of green human resource management and organizational citizenship behavior. The practices of green human resource management have a direct link with green employee empowerment, which positively creates employee organizational citizenship behavior and leads to environmental performance. Our study tends to explain the moderation effect of a variable like individual green values (IGV) and environmental knowledge concerning relation with green employee empowerment and organizational citizenship behavior, which leads to ecological performance. The individual values and knowledge about the environment increase commitment and develops the relationship between green employee empowerment and employee's organizational citizenship behavior leading directly toward ecological performance. Third, in previous studies, two variables such as environmental knowledge and environmental performance were neglected this study has added these two variables as these variables need to be studied. The issue of the environment is significant to be investigated more. The organizations could reach the care-maintained sustainability level and carry out environment-friendly employee behavior. The organization is always expected to advance its performance in terms of the environment (Kim et al. 2019).
The purpose of the study is to fill the gaps not studied previously as it incorporates the potential variables/factors such as (i.e., green human resource management, green employee empowerment, individual green values, environmental knowledge, organizational citizenship behavior, and environmental performance). These variables are the key to providing the solution to environmental issues. These variables significantly affect employee behaviors and attitudes as they act as a role model in designing the good policies of the organization.
Literature review
Theoretical foundation
The present study used theories that support the theoretical model—the ability, motivation, and opportunity (AMO) and Sport value framework (SVF) Theory. The AMO theory renders human resource management activities directly interrelated to performance (Jiang et al. 2012), opportunity, motivation, and ability (Appelbaum et al. 2000). The theory of AMO describes the human resource management activities which improve an institution's wealth and improve competencies. This theory affects workers' flexible behaviors (Shen et al. 2018). The theory of AMO activities significantly influences employees' discretionary conduct (Ashraful et al. 2021). The human resource management social process describes that human resource management activities affect several workers in their workplaces regarding their behavior and attitudes through social and psychological practices (Jiang et al. 2012). The second theory supporting the model is SVF which describes workplace behaviors and how it affects individual standards as Chou (2014) explains that personal environmental beliefs have a substantial effect on the worker's ecological conduct, so the theory of AMO supports the conceptual model of the research through the combination of three AMO element’s ability, motivation, and opportunity which create environmental knowledge and green employee empowerment which will lead toward improvement in environmental performance.
Relationship between green HRM and green employee empowerment
Green human resource management is one of the fundamental problems within organizations and has become an essential strategy for increasing competition worldwide (Nawangsari and Sutawidjaya 2019). Green employee empowerment is one of the crucial elements to accomplishing the organization’s objectives related to the green goals (Tariq et al. 2016). Gutowski et al. (2005) explain some of the significant benefits related to encouraging green worker’s the benefits are the commitment of upper level, satisfaction related to the work, improvement in work excellence, and self-esteem (Renwick et al. 2013) explains that for a sustainable environment many institutions may use human resources activities as a relation with the environment. For example, by providing training to the workers and participation programs, the institutions may increase workers' inspiration for social and economic welfare related to employee empowerment. Therefore, it shows the following relationship between green human resources management and green employee empowerment:
H1
Green HRM is positively related to green employee empowerment GEE.
Moderating the role of environmental knowledge
Environmental knowledge discusses an individual's knowledge in terms of the environment and the problem nearby it, such as the problems of deforestation, sea contamination, and other significant issues in the background. The previous studies tend to explain the association between environmental knowledge and the beliefs of consumers (Dahlbo et al. 2017). Value-Belief-Norm (VBN) theory shows a logical relationship that environmental knowledge influences green human resource management and green employee empowerment and performs a moderation function between two variables. Knowledge regarding the environment is a significant and external factor. The theory of VBN makes it logical to describe the importance of environmental knowledge as it positively influences both variables. Therefore, this hypothesis tends to explain the relationship between two variables. One of the most important aspects is that knowledge of the environment is essential for the employees in making decisions. However, the employees in the organizations ignore such conditions where they feel shunned by the organization (Otto and Pensini 2017). The following hypothesis shows that:
H2
Environmental knowledge moderates the relationship between GHRM and GEE.
Relationship between green employee empowerment and OCBE
Furthermore, Pinzone et al. (2016) describe that when employees are involved in decision-making concerning environmental issues, they are enthusiastic about applying to volunteer activities to improve the environment. The empowerment of green employees involves. Hard work recognition, opportunities for promotion, the procedure of good job appraisal, and good behavior of superiors are the essential activities for the implementation and development that leads toward making the employees go green within the organization and perform well (Amrutha and Geetha 2020). Tang et al. (2017) have highlighted that enunciating a solid vision of the environment and spreading the information through different communication channels guides the employees to be involved in the initiatives of the domain. A recent study examined that there is a direct link between organizational citizenship behavior environment and employee empowerment that influences green activities. The study showed that empowerment and individual green values are the essential aspects influencing the employee's organizational citizenship behavior environment (Hameed et al. 2021). Organizations must use green human resource management practices to ensure that organizational citizenship behavior environment inspires employees to act sustainably. Therefore, it is hypothesized that:
H3
Green employee empowerment GEE is positively related to OCBE.
Relationship between OCBE and environmental performance
Organizational citizenship behavior environment is intended for those activities that are not a requirement in terms of an individual's job if they are willing to protect the critical environment from the counterproductive belongings of business processes. Kim et al. (2019) describe that organizational citizenship behavior environment contribution is essential in promoting environmental performance. The involvement of employees is necessary to address the challenges of the environment and also inspire them to determine the organization's citizenship behavior environment as it is considered a critical strategy in terms of the organization as it demonstrates the positive results related to increasing environmental performance (Anwar et al. 2020; Tian and Robertson 2019). The hypothesis that organizational citizenship behavior environment is an essential predictor of ecological performance is recognized by the involvement of the employees in the activities of the environment in terms of their job requirements and how it enables the organizational to improve its environmental efficiency (Yusoff et al. 2020). As organizational citizenship behavior environment incorporates a diversity of behavior related to the environment, it is essential to describe that employee's environmental behavior has a positive influence on their environmental performance and also has a significant effect on their environmental performance in many ways (Kim et al. 2019; Luu 2019; Hussain et al. 2022). As organizational citizenship behavior environment provides help in terms of many objectives related to the environment, it needs to be considered an opportunity to improve environmental performance (Bishop et al. 2017). Many reasons justify that environmental performance is an essential aspect of enhancing the organizational citizenship behavior environment. As for the literature review related to environmental performance, many examples show their link with each other. For instance, by involving the organizational environmental committee (Stewart and Tyler 2019; Usman and Radulescu 2022), organizational citizenship behavior environment can improve the environmental performance related to eco-civic management (Boiral et al. 2018; Dangelico and Environment 2015). Likewise, organizational citizenship behavior environment, as an element of low energy or recycling consumption, expands environmental performance by avoiding preventable resources (Anwar et al. 2020). The organizational citizenship behavior environment also deals with employees' pro-environmental voluntary actions during their routine activities and plays a vital role in establishing environmental performance. Therefore, it is hypothesized that:
H4
OCBE is positively related to environmental Performance.
Mediating role of green employee empowerment
The conceptual model shows how green human resource management activities have a direct effect on green employee empowerment as it describes the activities of green human resource management that have a direct influence on the psychological behavior of the employees (Hameed et al. 2020a). Employees contribute to environmental performance when they are authorized through the practices of green human resource management. According to the studies, it was found that employees, when they receive benefits and incentives, tend to feel grateful and show green behavior toward the organization (Hameed et al. 2020b). It tends to describe the significant role of green employee empowerment as mediation among organization citizenship behavior environment workers and green human resource management activities. Social exchange theory explains that workers who feel green employee empowerment by promising human resources activities feel grateful and actively engage in organizational citizenship behavior environment. The green human resource management activities improve workers' participation in green practices, inspiration, and consciousness, resulting in workers' empowerment to green objectives. Workers get inspired when empowerment feelings keep increasing, and they show their discretion behavior. The conceptual model shows that green employee empowerment has a mediation influence on workers' organization citizenship behavior environment by green human resource management (Jiang et al. 2012). Ultimately, the conceptual model framework shows that green employee empowerment performs the mediator function between green human resource management and workers' organizational citizenship behavior environment. Based on the previous studies, the following hypothesis is proposed:
H5
Green employee empowerment mediates the relationship between GHRM and OCBE.
The Moderating role of individual green values
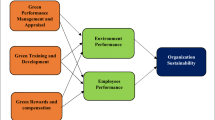
According to Yong et al. (2019), the research study focuses on individual values in forecasting the efficacy of green human resource management practices to increase employee behavior. The methods of green human resource management can be an indicator in an organization to value the sustainability and environment, and individual responses to those indicators (Luu 2019; Usman and Balsalobre-lorente 2022). Previously, green values were found to strengthen the relationship between green human resource management and employees regarding environmental passion (Gilal et al. 2019) and green citizenship behavior and psychological climate (Dumont et al. 2017b). Further research shows unpredictable answers regarding employees' individual values (Boiral et al. 2015). The individual green value is a conditional variable, and it positively affects the behavior and attitudes of employees (Hameed et al. 2020b; Low 2013). Looking at the research that describes individual green values, it is proposed that personal green values have an essential function as moderation between two variables representing the bond between green employee empowerment and the organizational citizenship behavior environment of employees as individual green values perform the role of moderation between two factors. The following hypothesis is proposed (Fig. 1):
H6
Individual green values moderates the relationship between GEE and OCBE.
Materials and methods
Sample design and data collection
The research data was collected from employees of the tourism sector from hotels. The total population of this study includes four central 5-star hotel employees in Lahore, Pakistan, Pearl continental hotel, Avari hotel, Royal Swiss, and park lane hotel, from which the data were collected from employees to measure the green human resource management practices. The respondents provided the answers based on their experience with the green human resource management practices concerning five options Likert scales from strongly agree to disagree. The measures were produced concerning the literature (Tilikidou 2007) through which the scales were developed. The research data was collected through an online questionnaire that addressed the variables of the research. A self-administered questionnaire method is used to collect data from the tourism industry using the simple random technique. This technique is beneficial as it contains the data from a different population group and provides the complete information required to obtain data (Saunders et al. 2009). The research data based on a questionnaire was taken from 360 respondents, of which 237 were valid responses for data analysis.
Measurement of variables
The green human resource management practices scale was taken from previous research studies (Dumont et al. 2017a). The response was based on their experience on five major points from Strongly Agree to disagree. Green employee empowerment was a significant aspect of the scale of employee psychological empowerment to judge its perspectives (Spreitzer 1995). The process of green employee empowerment measures work-related factors that involve green behavior and jobs. The variable environmental knowledge was restrained according to the method (Gatersleben et al. 2002). The respondents provided their answers to asked questions about the significant environmental issues. The individual green values variable was measured using the three main items (Chou 2014) to describe the scale of the personal environment. This scale was measured through the hierarchy of (1 = strongly agree to = strongly disagree).
An example could be, "I feel a personal obligation to do whatever I can to prevent environmental degradation.” The scales were measured using the questionnaire. Organization citizenship behavior environment, the scale was measured by (Boiral and Paillé, 2012) as it was developed to observe the behaviors of the employees regarding the improvement of the environment. These scales were introduced by (Raineri and Paillé, 2016). The variable environmental performance tends to describe the practices of the domain. This scale was measured through a qualitative study (Yusof and Jamaludin 2013), representing the good's reliability and validity.
Results and discussion
To generate a result of data analysis for correlation and expressive statistics, we used SPSS data analysis. This study used Smart PLS and structural equation modeling (SEM) to find accurate results for the structural equation, which are commonly used when we do SEM, and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). The screening process involves descriptive statistics, correlations, normality, multicollinearity, multivariate outliers, and missing values analysis.
Reliability analysis
Reliability refers to the inter-item consistency of the scales. Reliability can be measured easily with the help of the inter-item correlation and alpha coefficients to study the significant importance of the variables. Table 1 shows that the reliability analysis is calculated by assessing the importance of Cronbach's alpha coefficients. The reliability data of this research study show the coefficient alpha values are 0.71, 0.75, 0.95, 0.82, 0.72, and 0.75. These values show the reliability of the data.
Correlation analysis
Table 2 shows the correlation that exists between the variables. The above correlation matrix classifies that green human resource management has a significant positive correlation with Individual green Values (r = 0.61, p < 0.05). However, green human resource management has no negative correlation with any variables. Also, green human resource management has a Positive significant correlation with green employee empowerment (r = 0.80, p < 0.5), environmental knowledge (r = 0.82, p < 0.5), organization citizenship behavior environment (r = 0.83, p < 0.5), and environmental performance (r = 0.52, p < 0.5), it shows that green human resource management is more correlated to individual green values as compared to the other variables.
Common bias method
The common method bias (CMB) was used to explore the significant aspects of the measure of statically and procedural work described by (Podsakoff et al. 2003). The data was collected from the employees and supervisors for procedural measures assessment. It was made clear to ensure the confidentiality of participants who responded to the questionnaire. The primary factor singular factor, the human singular factor, which refers to joint common factor analysis, was used to assess the reliability (Guide and Ketokivi 2015). The results of factor human single tend to describe that the variables are divided into four essential elements. The common factor analysis single-factor does not show any illustration that fits the model appropriately. In the current study, no threat of CMB was taken related to common latent factors (Podsakoff et al. 2003). The primary variance inflation factor refers to indicators (VIF) to assess multicollinearity. The research by (Hair et al. 2006) describes that the value of VIF needs to be below 5. The scores of VIF range from 1.04 to 1.67, which reflects the multicollinearity absence problem.
Measurement model assessment
The measurement model was assessed with the help of loading in the concurrent validity table. It includes significant factors like composite reliability and the extract of average variance extract. In Table 1, the factor loading values exceed the recommended matter, which is 0.60. The importance of composite reliability has also exceeded the recommended value of 0.70. Significant values of the average variance extract (AVE) show that their values also exceed the recommended 0.50 (Hair et al. 2016). The items below recommended values of the factor loadings were deleted to have their weights more minor than the required value (< 0.050). Similarly, the Heterotrait-Monotriat ratio (HTMT) describes the measurement of discriminate validity. Table 2 tends to show the significant value cut of 0.85 major aspects explained by (Kline 2011), which represents that in case the values remain more minor than the 0.85.
Structural model assessment
To assess the hypothesis, the structure modeling was used in the tourism industry after confirming the validation and reliability of the model by evaluating model measurement. To describe the model's relationship, the standard error path coefficient t-values in terms of the collected data. The path coefficient value presents how the hypothesis supports or does not support it. The important process in Smart PLS-3 used is the bootstrapping procedure to assess the structural model's reliability in assessing moderation effects. According to Table 3, environmental knowledge has the significant relationship with green employee empowerment (β = 0.485, t = 4.705; LL = 0.299, UL = 0.634) therefore H1 is supported. Besides this, Green employee empowerment it has positive and significant association with organization citizenship behavior environment (β = 0.492, t = 7.879; LL = 0.568, UL = 0.852) shows that H2 is supported. However, it was found that green human resource management is significantly associated to Green employee empowerment (β = 0.494, t = 4.77; LL = 0.341, UL = 0.676), therefore H3 is supported. Environmental knowledge performs major function of moderation between green human resource management and green employee empowerment (β = 0.014, t = 0.565; LL = 0.018, UL = 0.063) so it shows H4 is supported. The findings also revealed that there is a significant relationship between organization citizenship behavior environment and environmental performance (β = 0.96, t = 103.83; LL = 0.944, UL = 0.973) thus H5 is supported. Individual green values is significantly has the relationship with organization citizenship behavior environment (β = 0.288, t = 3.159; LL = 0.119, UL = 0.414) therefore H6 is supported. The green employee empowerment performs mediation function (β = 0.342, t = 3.887; LL = 0.218, UL = 0.504) thus H7 is supported.
Discussion and findings
The previous research paper focused on the role of green human resource management in managing the environment (Ren et al. 2020; Renwick et al. 2013). This research paper aims to describe the relationship between green human resource management and environmental performance with the moderation role performed by environmental knowledge and how it links mediation for green employee empowerment and organizational citizenship behavior environment in the hotel industry of Pakistan. Also, through the help of SVF theory, we explained that environmental knowledge performs a moderation function between green human resource management and green employee empowerment, and individual green values perform a moderation function between green employee empowerment and organization citizenship behavior environment of employees. This research's primary output is to investigate how green employee empowerment performs a mediation function between two variables, green human resource management, and organizational citizenship behavior environment, of employees and leads to better environmental performance. The research study describes green employee empowerment as the significant psychological process between the two variables of green human resource management and organizational citizenship behavior environment of an employee as described in the research conducted in the past (Jiang et al. 2012; Renwick et al. 2013). The study examines how environmental knowledge moderates the outcome of green human resource management and green employee empowerment and how individual green values moderates the effect of green employee empowerment and organization citizenship behavior environment on employees, leading to environmental performance. This research explains how the core relationship between two variables, green employee empowerment, and organizational citizenship behavior environment, of employees becomes much more potent when the employees' green is high. The theory of SVF (Edwards 1996) describes that when employees show positive behavior, it will result in the similarity between organizational values and employees' performance. The theory also explains the moderating roles of individual green values and environmental performance and their influences on the different variables to describe the green behavior of employees (Chou 2014; Dumont et al. 2017a). The primary outcome is to describe the moderation effect of environmental knowledge, which previous researchers and environmental performance ignored. Also, examining the mediation role of green employee empowerment is a positively essential part through which green human resource management influences organization citizenship behavior environment of employees and leads to environmental performance.
Conclusion
The research study concludes that green human resource management practices hinge as an essential antecedent of green employee empowerment and organization citizenship behavior environment of employees in the context of the hotel industry of Pakistan to escalate environmental performance. The analytical findings of this study revealed that green human resource management has a direct relationship; furthermore, the secondary outcome environmental recital facilitating variables and green employee empowerment, organization citizenship behavior environment, environmental knowledge, and individual green values. The hypothesis of this study is based upon (AMO) and (SVF) theories or theory that green employee empowerment, organization citizenship behavior environment, environmental knowledge, and individual green values signify the relationship between green human resource management and ecological performance. The analysis of the current study confirmed that green human resource management practices directly impact environmental performance. Additionally, green employee empowerment, organization citizenship behavior environment, environmental knowledge, and individual green values augment ecological performance to reduce water pollution, air emission, energy usage, and consumption of risky materials that affect the environment. Finally, the study revealed the moderating effect of individual green values and environmental knowledge for enhanced environmental performance.
Implications of the study
This research study's results significantly contribute to the human resource management literature regarding environmental management. Firstly, this study shows the basis of organizational citizenship behavior environment and the critical relationship between green human resource management and environmental performance. In this way, the present study contributes that the hotel's environmental performance can be further improved through greening related to human resource management. Secondly, environmental apprehension is mandatory for pro-environmental behavior (Han et al. 2019; Ke et al. 2022). In terms of our knowledge, we have seen essential aspects of mediating the effect of employee Green Employee Empowerment in the relationship between green human resource management and environmental performance. Therefore, the present study relates green human resource management to the context of environmental performance in the hotel industry. This study describes that when employees become anxious about the environment, they focus more on adopting green behavior, protecting the natural environment, and achieving environmental performance. The third and important aspect is the number of studies showing an essential link between green employee empowerment and environmental performance (Han et al. 2019; Stanwick and Stanwick 1998). Thus, our research links green human resource management and environmental performance through green employee empowerment in the hotel industry context. It shows by having green employee empowerment, the employees contribute more toward improving their performance.
Practical implications
This research study provides different practical impacts on organizations, groups, and practitioners. In terms of empowering the human resource managers, the organizations need to involve them in green human resource management activities because they are responsible for implementing the organization’s core vision in the management environment. From the perspective of employees, the organizations need to encourage them and authorize them to freely perform the main tasks involved in the work activity to contribute more to the green values of the organization. Another element is that the organizations need to provide proper training to their employee to make them able to become aware of green values and green conceptions in the workplace. Through the help of this training provided to the employees, they could further improve their skills, and they can achieve the management goals by applying the concepts of green values in the organization. The organization needs to appreciate the green behavior of the employees (Dumont et al. 2017a) and turn this behavior into activities like compensation and pay, opportunities for promotion further inspire them to remain involved in the green practices through which the employees would become able to play their parts in the achievement of the purpose of the organization.
Limitations and future directions
The study of research has some limitations that give information to future researchers for their research. The organization of our research study was the tourism industry of Pakistan in the area of Lahore. However, the activities of multinational corporations result from the origin country's effect (Ferner 1997). The research data we collected was cross-sectional data from the tourism industry employees. The administrators in this research have rated the organizational citizenship behavior environment of employees that influences CMB and minimizes its effects (Podsakoff 2003). To further assess the problem of CMB, the research study describes the use of longitudinal activities to determine the green behavior of employees with the help of activities of green human resource management. In this study, our Theoretical model describes the variable green employee empowerment as a mediator. However, future research can research psychological and social concepts such as organizational pride as a variable (Jones 2010) and human capital and perspectives of motivation (Jiang et al. 2012). The previous research examined the influence of green human resource management on individual and green organizations. Research needs to be done on the impact of green human resource management on non-green behavior and the attitudes that need to be examined. It is a suggestion for the future researcher to research by describing how green human resource management influences the non-green effects in the light of behavior and attitudes. Exploring these studies will help increase the knowledge and contribute significantly to the outcome of the green employee organization.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are variability from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Amrutha V, Geetha S (2020) A systematic review on green human resource management: Implications for social sustainability. J Clean Prod 247:119131
Anwar N, Mahmood NHN, Yusliza MY, Ramayah T, Faezah JN, Khalid WJ (2020) Green human resource management for organisational citizenship behaviour towards the environment and environmental performance on a university campus. J Clean Prod 256:120401
Appelbaum E, Bailey T, Berg P, Kalleberg AL, Bailey TA (2000) Manufacturing advantage: why high-performance work systems pay off. Cornell University Press, Cornell
Ashraful AM, Niu X, Rounok NJ, Science S (2021) Effect of green human resource management (GHRM) overall on organization’s environmental performance: the mediating role of green employee empowerment. Int J Res Bussiness Soc Sci 10(4):99–116
Bank W (2012) Transformation through tourism: development dynamics past, present and future: The World Bank Washington, DC
Bishop JW, Govindarajulu N, Daily B (2017) Perceptions of environmental and quality performance and employee support: The role of OCB and OCBE. Paper presented at the academy of management proceedings
Boiral O, Paillé P (2012) Organizational citizenship behaviour for the environment: measurement and validation. J Bus Ethics 109(4):431–445
Boiral O, Talbot D, Paillé P (2015) Leading by example: a model of organizational citizenship behavior for the environment. Bus Strateg Environ 24(6):532–550
Boiral O, Raineri N, Talbot DJ (2018) Managers’ citizenship behaviors for the environment: a developmental perspective. J Bussiness Ethics 149(2):395–409
Catio M (2020) Manajemen sumber daya manusia. Indigo Media, Mumbai
Chou C-J (2014) Hotels’ environmental policies and employee personal environmental beliefs: interactions and outcomes. Tour Manage 40:436–446
Dahlbo H, Aalto K, Eskelinen H, Salmenperä HJ, consumption. (2017) Increasing textile circulation—consequences and requirements. Sustain Prod Consump 9:44–57
Daily BF, Huang SC (2001) Achieving sustainability through attention to human resource factors in environmental management. Int J Operat Prod Manag 21(12):1539–1552
Dangelico RM, Environment T (2015) Improving firm environmental performance and reputation: the role of employee green teams. Bussiness Strat Environ 24(8):735–749
Dias-Sardinha I, Reijnders L (2005) Evaluating environmental and social performance of large Portuguese companies: a balanced scorecard approach. Bus Strateg Environ 14(2):73–91
Dumont J, Shen J, Deng X (2017a) Effects of green HRM practices on employee workplace green behavior: the role of psychological green climate and employee green values. Hum Resour Manag 56(4):613–627
Dumont J, Shen J, Deng XJH (2017) Effects of green HRM practices on employee workplace green behavior: the role of psychological green climate and employee green values. Hum Resour Manag 56(4):613–627
Economics Trading (2019) Tourism Malaysia revenues.
Edwards JR (1996) An examination of competing versions of the person-environment fit approach to stress. Acad Manag J 39(2):292–339
Ferner A (1997) Country of origin effects and HRM in multinational companies. Hum Resour Manag J 7(1):19
Gatersleben B, Steg L, Vlek C (2002) Measurement and determinants of environmentally significant consumer behavior. Environ Behav 34(3):335–362
Gilal FG, Ashraf Z, Gilal NG, Gilal RG, Channa NAJCSR, Management E (2019) Promoting environmental performance through green human resource management practices in higher education institutions: a moderated mediation model. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag 26(6):1579–1590
Guide Jr VDR, & Ketokivi M (2015) Notes from the Editors: Redefining some methodological criteria for the journal⋆. Wiley Online Library, Hoboken.
Gutowski T, Murphy C, Allen D, Bauer D, Bras B, Piwonka T, Wolff E (2005) Environmentally benign manufacturing: observations from Japan, Europe and the United States. J Clean Prod 13(1):1–17
Hair JF Jr, Hult GTM, Ringle C, Sarstedt M (2016) A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). Sage publications, Thousand Oaks
Hair JF, Black W, Babin B, Anderson RE & Tatham RL (2006) Multivariate data analysis sixth edition pearson education. New Jersey, 42–43.
Hambrick DC, Quigley TJ (2014) Toward more accurate contextualization of the CEO effect on firm performance. Strateg Manag J 35(4):473–491
Hameed Z, Khan IU, Islam T, Sheikh Z, Naeem RM (2020a) Do green HRM practices influence employees’ environmental performance? Int J Manpow 41(7):1061–1079
Hameed Z, Khan IU, Islam T, Sheikh Z, Naeem RM (2020) Do green HRM practices influence employees’ environmental performance? Int J Manp 41(7):1061–1079
Hameed Z, Naeem RM, Hassan M, Naeem M, Nazim M, Maqbool AJIJ (2021) How GHRM is related to green creativity? A moderated mediation model of green transformational leadership and green perceived organizational support. Int J Manpow 43(3):595–613
Han H, Yu J, Kim W (2019) Environmental corporate social responsibility and the strategy to boost the airline’s image and customer loyalty intentions. J Travel Tour Mark 36(3):371–383
Hussain Y, Abbass K, Usman M, Rehan M, Asif M (2022) Exploring the mediating role of environmental strategy, green innovations, and transformational leadership: the impact of corporate social responsibility on environmental performance. Environ Sci Pollut Res 423:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20922-7
Intisar RA, Yaseen MR, Kousar R, Usman M, Makhdum MSA (2020) Impact of trade openness and human capital on economic growth: a comparative investigation of Asian countries. Sustainability 12(7):2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12072930
Jackson SE, Seo J (2010) The greening of strategic HRM scholarship. Org Manag J 7(4):278–290
Jahanger A, Usman M, Balsalobre-Lorente D (2022) Linking institutional quality to environmental sustainability. Sustain Dev 30(6):1–17
Jiang K, Lepak DP, Hu J, Baer JC (2012) How does human resource management influence organizational outcomes? a meta-analytic investigation of mediating mechanisms. Acad Manag J 55(6):1264–1294
Jones DA (2010) Does serving the community also serve the company? Using organizational identification and social exchange theories to understand employee responses to a volunteerism programme. J Occup Organ Psychol 83(4):857–878
Ke J, Jahanger A, Yang B, Usman M, Ren F (2022) Digitalization, financial development, trade, and carbon emissions; implication of pollution haven hypothesis during globalization mode. Front Environ Sci 211:873880. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.873880
Kenneth N (2016) Malaysia’s hospitality industry—What are the talent challenges
Kim YJ, Kim WG, Choi H-M, Phetvaroon KJIJ, oHM (2019) The effect of green human resource management on hotel employees’ eco-friendly behavior and environmental performance. Int J Hosp Manag 76:83–93
Kline RB (2011) Convergence of structural equation modeling and multilevel modeling In: The SAGE handbook of innovation in social research methods. SAGE Publications Ltd, Thousand Oaks. pp. 562–589
Low KP (2013) Value matters or do values really make a difference. Educ Res 4(4):330–339
Luu TT (2019) Building employees’ organizational citizenship behavior for the environment: the role of environmentally-specific servant leadership and a moderated mediation mechanism. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag 31(1):406–426
Nawangsari, L. C., & Sutawidjaya, A. H. (2019). How the green human resources management (GHRM) process can be adopted for the organization business. Paper presented at the 1st International Conference on Economics, Business, Entrepreneurship, and Finance (ICEBEF 2018).
Otto S, Pensini P (2017) Nature-based environmental education of children: environmental knowledge and connectedness to nature, together, are related to ecological behaviour. Glob Environ Change 47:88–94
Paillé P, Boiral O (2013) Pro-environmental behavior at work: Construct validity and determinants. J Environ Psychol 36:118–128
Pinzone M, Guerci M, Lettieri E, Redman T (2016) Progressing in the change journey towards sustainability in healthcare: the role of ‘Green’HRM. J Clean Prod 122:201–211
Podsakoff N (2003) Common method biases in behavioral research: a critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J Appl Psychol 885(879):1037
Podsakoff PM, MacKenzie SB, Lee J-Y, Podsakoff NP (2003) Common method biases in behavioral research: a critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J Appl Psychol 88(5):879
Raineri N, Paillé P (2016) Linking corporate policy and supervisory support with environmental citizenship behaviors: the role of employee environmental beliefs and commitment. J Bus Ethics 137(1):129–148
Ren S, Tang G, Jackson SE (2020) Effects of green HRM and CEO ethical leadership on organizations’ environmental performance. Int J Manpow 42(6):961–983
Renwick DW, Redman T, Maguire S (2013) Green human resource management: a review and research agenda. Int J Manag Rev 15(1):1–14
Roscoe S, Subramanian N, Jabbour CJ, Chong T (2019) Green human resource management and the enablers of green organisational culture: enhancing a firm’s environmental performance for sustainable development. Bus Strateg Environ 28(5):737–749
Saunders M, Lewis P, Thornhill A (2009) Research methods for business students. Pearson education, Noida
Searcy C, Dixon SM, Neumann WP (2016) The use of work environment performance indicators in corporate social responsibility reporting. J Clean Prod 112:2907–2921
Shen J, Dumont J, Deng X (2018) Employees’ perceptions of green HRM and non-green employee work outcomes: the social identity and stakeholder perspectives. Group Org Manag 43(4):594–622
Sinaga SA, Nawangsari LC (2019) The effect of green recruitment, green training on employee performance in pt tru using organization citizenship for environment as mediation variable. Dinas Int J Manag Sci 1(2):204–216
Singh SK, El-Kassar A-N (2019) Role of big data analytics in developing sustainable capabilities. J Clean Prod 213:1264–1273
Spreitzer GM (1995) Psychological empowerment in the workplace: dimensions, measurement, and validation. Acad Manag J 38(5):1442–1465
Stanwick PA, Stanwick SD (1998) The relationship between corporate social performance, and organizational size, financial performance, and environmental performance: an empirical examination. J Business Ethics 17:195–204
Stewart J, Tyler ME (2019) Bridging organizations and strategic bridging functions in environmental governance and management. Int J Water Resour Dev 35(1):71–94
Tariq S, Jan FA, Ahmad MS (2016) Green employee empowerment: a systematic literature review on state-of-art in green human resource management. Qual Quant 50(1):237–269
Tian Q, Robertson JL (2019) How and when does perceived CSR affect employees’ engagement in voluntary pro-environmental behavior? J Bussiness Ethics 155(2):399–412
Tilikidou I (2007) The effects of knowledge and attitudes upon Greeks’ pro-environmental purchasing behaviour. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag 14(3):121–134
Times, N. S. (2019). Tourism industry expected to generate RM192bil in 2020.
Usman M, Balsalobre-Lorente D (2022) Environmental concern in the era of industrialization: can financial development, renewable energy and natural resources alleviate some load? Energy Pol 162:112780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2022.112780
Usman M, Makhdum MSA (2021) What abates ecological footprint in BRICS-T region? Exploring the influence of renewable energy, non-renewable energy, agriculture, forest area and financial development. Renew Energy 179:12–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.07.014
Usman M, Radulescu M (2022) Examining the role of nuclear and renewable energy in reducing carbon footprint: does the role of technological innovation really create some difference? Sci Total Environ 841:156662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156662
Yang B, Usman M (2021) Do industrialization, economic growth and globalization processes influence the ecological footprint and healthcare expenditures? Fresh insights based on the STIRPAT model for countries with the highest healthcare expenditures. Sustain Prod Consum 28:893–910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2021.07.020
Yong JY, Yusliza MY, Fawehinmi OO (2020) Green human resource management: A systematic literature review from 2007 to 2019. Benchmarking Int J 27(7):2005–2027
Yusof ZB, Jamaludin M (2013) Green approaches of Malaysian green hotels and resorts. Proc Soc Behav Sci 85:421–431
Yusoff YM, Nejati M, Kee DMH, Amran A (2020) Linking green human resource management practices to environmental performance in hotel industry. Glob Bus Rev 21(3):663–680
Zaid AA, Jaaron AA, Bon AT (2018) The impact of green human resource management and green supply chain management practices on sustainable performance: an empirical study. J Clean Prod 204:965–979
Zhang Y, Luo Y, Zhang X, Zhao JJS (2019) How green human resource management can promote green employee behavior in China: a technology acceptance model perspective. Sustainability 11(19):5408
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.R.: Conceptualization, introduction, software, methodology, interpreted results. K.A.: Conceptualization, formal analysis, visualization, results interpretation, writing-original draft preparation. Y.H.: validation, writing-original draft preparation and review and editing. M.U.: Conceptualization, visualization, project administration, results interpretation, conclusion, revised draft, finalizes manuscript and review and editing. M.S.A.M.: Literature review, supervision, writing-original draft preparation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Sivakumar Durairaj.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rehan, M., Abbass, K., Hussain, Y. et al. Green human resource management in Pakistan tourism industry: Moderating role of environmental knowledge and individual green values. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 21, 2505–2516 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-05136-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-05136-9