Abstract
An effective two-spin density matrix (TSDM) for a pair of spin-1/2 degree of freedom, residing at a distance of R in a spinfull Fermi sea, can be obtained from the two-electron density matrix following the framework prescribed in Oh and Kim (Phys Rev A 69:054305, 2004. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.69.054305). We note that the single-spin density matrix (SSDM) obtained from this TSDM for generic spin-degenerate systems of free fermions is always pinned to the maximally mixed state, i.e. \((1/2) \ {\mathbb {I}}\), independent of the distance R, while the TSDM confirms to the form for the set of maximally entangled mixed state (the so-called X-state) at finite R. The X-state reduces to a pure state (a singlet) in the \(R\rightarrow 0\) limit, while it saturates to an X-state with the largest allowed value of von-Neumann entropy of \(2 \ln 2\) as \(R\rightarrow \infty \) independent of the value of chemical potential. However, once an external magnetic field is applied to lift the spin-degeneracy, we find that the von-Neumann entropy of SSDM becomes a function of the distance R between the two spins. We also show that the von-Neumann entropy of TSDM in the \(R\rightarrow \infty \) limit becomes a function of the chemical potential and it saturates to \(2 \ln 2\) only when the band in completely filled unlike the spin-degenerate case. Finally, we extend our study to include spin–orbit coupling and show that it does effect these asymptotic results. Our findings are in sharp contrast to previous works, which were based on continuum models owing to physics which stem from the lattice model.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
In recent years, significant effort has gone into developing understanding of quantum condensed matter system from a quantum information perspective [1,2,3,4,5,6]. One of the key ingredients that has been used to characterize quantum many-body systems is quantum “entanglement" which has no classical counterpart [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14], and a variety of idea involving von-Neumann entropy, concurrence [15], and mutual information [16, 17] have been introduced to quantify the amount of entanglement in them. In particular, quantum many-body systems comprising of indistinguishable particles have been studied extensively using such tools [18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28] and the phenomenon of quantum phase transition in such system has all been characterized using these ideas [12, 29,30,31].
However, finding exact many-body states in case of fermions is a formidable task in general except for mean field theories where an exact Green’s function approach can be used for systematic investigation. The framework of probing non-interacting fermionic systems in terms of density matrices was laid down by Dirac [32], Lowdin [33, 34]. Vederal [35] studied spin correlation of two electrons, located at different positions in terms of entanglement in a system of non-interacting fermions, which Kim et al. [36] then explored further. It was shown in [36] that for a continuum model of free fermions in three-dimensions, the entropy of two spin degrees of freedom (TSDM) varies with the distance R between them and it saturates to its maximum value of \(2 \ln 2\) as \(R\rightarrow \infty \). However, the single-spin density matrix (SSDM) obtained by partial tracing the TSDM is always found to be maximally mixed (von-Neumann entropy being \(\ln 2\)) and hence is independent of the distance R between the two spins. We show that, once the fermions are placed on a lattice and an external magnetic field is applied to break the spin degeneracy, the entropy of SSDM starts to depend upon the distance R between the two spins. Moreover, the saturation value of entropy of TSDM in the \(R\rightarrow \infty \) limit is no longer \(2 \ln 2\) rather it depends upon the chemical potential of the system. These features are indicative of physics beyond what is studied in 36, i.e. effects that can not be captured by a spin degenerate Fermi sea for a continuum model. Motivated from this fact we study a spin correlation encoded in TSDM and SSDM using this framework given in Ref. [36] for a one-dimensional spinfull Fermionic chain, which is subjected both Zeeman field and spin–orbit field, as a function of the chemical potential.
The remainder of this article is organized as follows: In Sect. 2, we introduce our 1D lattice model and define TSDM including both Zeeman and Rashba spin–orbit coupling (RSOC) interaction terms and analyse the TSDM entropy for the case where both terms are zero. In Sect. 3, we study the case where only the Zeeman coupling (\(B\ne 0\) and \(\lambda =0\)) is present. We examine the variation of entropy of TSDM as well as SSDM as a function of the chemical potential. In Sect. 4, we first study entanglement in the presence of the RSOC term alone followed by the case where both terms are present (\(B, \lambda \ne 0\)). Finally, Sect. 5 is dedicated to conclusion and discussion.
2 Model and method
We begin with the 1D tight-binding model Hamiltonian in real space, which takes the following form:
while \(c_{i}\)s and \(c^{\dagger }_{i}\)s at site ‘i’ are the creation and annihilation operators, t is the hopping parameter, B and \(\lambda \) are the Zeeman and RSOC strengths, respectively. Within our analysis, the value of B and \(\lambda \) has been chosen in terms of the hopping parameter t, which is fixed to \(t=1\). Also, the distance scale R is set in terms of the lattice spacing a, throughout our analysis.
We consider periodic boundary condition (PBC) and work in momentum space to obtain the single-particle spectrum. The corresponding dispersion relation \(E_{\pm }(k) = -2 t \cos (k a)\pm \sqrt{B^{2} + 4 \lambda ^{2} \sin ^{2}(k a)} \) defines two bands with the following eigen-functions,
with \(L = Ma\). Here a is the lattice constant. Also, \(e^{- i \theta _{k}} = |Z|/Z \), where Z is defined as \(Z = B + 2i \lambda \sin (ka)\).
In an earlier work, Löwdin proposed the idea of fundamental invariant [34] employing which density matrix of any order for a given many-body wave-function can be obtained and written as follows:
where \(x= (r, \sigma )\) denotes position and spin quantum number of electron, and \(\sigma = (\uparrow / \downarrow )\) represents up and down components of \(\phi _{\pm ,k}(r)\). Using the fundamental invariant, one can write elements of two particle density matrix as [33, 34]
Here, superscripts (1) and (2) denote one- and two-particle density matrix elements, respectively. Since our model consists of two bands and therefore have two different Fermi momenta \(k_{f}^{-}\) (for lower band) and \(k_{f}^{+}\) (for upper band), for any arbitrary chemical potential denoted as \(\delta \). The single particle density matrix elements in Eq. (4), namely \(\rho ^{(1)}(x,x')\), can then be defined as:
where Fermi momenta \(k_{f}^{-}\) and \(k_{i}\) can be obtained from the relation \(\mu = E_{-}(k)\) and momentum \(k_{f}^{+}\) from the relation \(\mu = E_{+}(k)\). Temperature is assumed to be zero in our entire analysis. Therefore, the mean occupation number at each momentum below the Fermi level is unity. Since our objective in this article is to study the entanglement of the spin degrees of freedom, we obtain TSDM using Eq. (4). We also consider diagonal elements of space density matrix: \(r_{1}= r_{1}'\) and \(r_{2}= r_{2}'\) to compare with the earlier results [35, 36] and have physical interpretation of elements with \(\sigma =\sigma '\) as probabilities [32, 34]. Hence, we define generic element of TSDM \(\rho ^{(2)}_{\sigma _{1},\sigma _{2};\sigma _{1}',\sigma _{2}'}\) using Eq. (4) as
where each single particle density matrix can be written in terms of spin–orbital wave function \(\phi _{\pm ,k}(r)\) using Eq. (5). We thus obtain the full TSDM in basis \(\{|\uparrow \uparrow \rangle ,|\uparrow \downarrow \rangle ,|\downarrow \uparrow \rangle ,|\downarrow \downarrow \rangle \}\) using Eqs. (5) and (6) as,
In Eq. (7), N is the normalization constant and is equal to inverse of sum of the diagonal elements, i.e. \(1/N= 4m^{2}- 2G^{2}_{r} - H_{r}H^{*}_{r} - K_{r}K^{*}_{r}\). Also, \(m = \sum _{|k|=k_{i}}^{k_{f}^{-}} 1+ \sum _{|k|=0}^{k_{f}^{+}} 1\); \(A= \sum _{|k|=k_{i}}^{k_{f}^{-}} e^{i \theta _{k}}- \sum _{|k|=0}^{k_{f}^{+}} e^{i \theta _{k}}\) and the functions \(G_{r} =\sum _{|k|=k_{i},0}^{k_{f}^{-},k_{f}^{+}} e^{{i k (r_{1}-r_{2})}}\), \(H_{r} =\sum _{|k|=k_{i}}^{k_{f}^{-}} \ e^{i \theta _{k}} \ e^{{i k (r_{1}-r_{2})}} - \sum _{|k|=0}^{k_{f}^{+}} \ e^{i \theta _{k}} \ e^{{i k (r_{1}-r_{2})}}\) and \(K_{r} =\sum _{|k|=k_{i}}^{k_{f}^{-}} \ e^{i \theta _{k}} \ e^{{i k (r_{2}-r_{1})}} - \sum _{|k|=0}^{k_{f}^{+}} \ e^{i \theta _{k}} \ e^{{i k (r_{2}-r_{1})}}\). It can be checked that the model parameters \(G_{r}\), \(K_{r}\) and \(H_{r}\) are functions of distance scale \(R = |r_{1}- r_{2}|\) where R defines the distance between the two electrons located at sites \(r_{1}\) and \(r_{2}\). It should be noted that the functions A, \(K_{r}\) and \(H_{r}\) are such that they are zero when there is no spin-distinguishing terms, i.e. \(B=\lambda =0\). Henceforth, we use the term “spin-pair" to denote the pair of spins in the TSDM. We now define the filling of the system by imposing the following constraint equation in the mean field level given by:
where \(\delta \) carries the information about average filling at each lattice site i and fixes the chemical potential.
We first consider the case when both \(B=0\) and \(\lambda =0\). This corresponds to \(k_{f}^{-}=k_{f}^{+}\) and \(k_{i}=0\). This in turn leads to double degeneracy of the eigenspectrum. As a result, the spin-distinguishing functions in the expression of TSDM (Eq. (7)) reduce to \(A=H_{r}=K_{r}=0\). Hence, the TSDM in Eq. (7) reads as:
The TSDM, given by Eq. (9), only represents a pair of spin-1/2 degrees of freedom residing at a distance R from each other and the entropy corresponding to this density matrix indicates the entanglement of two spins with the rest of the Fermi sea. The two spin states in Eq. (9) are known as maximally entangled mixed states or popularly known as “X- states" [37]. In Fig. 1, we illustrate the behaviour of entropy \(S_{ab}\), corresponding to the TSDM \(\rho _{12}^{(2)}\), as a function of distance R between them for various fillings \(\delta \) ranging from (0.1–0.6). For \(R\rightarrow 0\) entropy \(S_{ab}\rightarrow 0\) implying a complete decoupling of the spin-pair from the rest of the Fermi sea. In fact, the TSDM reduces to a spin-singlet. However, in the large R limit entropy \(S_{ab}\) approaches the asymptotic value of \(2 \ln 2\) independent of \(\delta \) though the rate (\(d S_{ab}/d R \) ) at which it reaches asymptotic value is greater for larger value of \(\delta \). Note that \(2 \ln 2 \) is the maximum value of allowed entropy for a pair of spin-1/2 and corresponding states having this maximum value are known as “2-entangled states" [38,39,40,41].
(Color online) The variation of entropy (in the units of \(\ln 2\)) for the case \(B=\lambda =0\) is depicted as a function of distance \(R= |r_{1}- r_{2}|\) for different filling \(\delta \), starting from \(\delta =0.1\) (yellow) to \(\delta =0.6\) (cyan). The number of sites has been taken to be \(M= 500\) for this plot as well as all the plots that follow
3 Zeeman field and entropy reduction
In this section, we analyse the case where only \(B \ne 0\). This lifts the spin degeneracy and breaks the time reversal symmetry. We find that when \(B \ne 0\) and RSOC term \(\lambda =0\), then the factor \(e^{i \theta _{k}}=1\), which results in following constraints on the functions in TSDM (Eq. (7)): \( H_{r} = K_{r} = H^{*}_{r} = K^{*}_{r}\). The un-normalized TSDM \(\rho ^{(2)}_{12}\) then reduces to:
where we have left the factor \(1/(2 L)^{2}\). We now compute the entropy corresponding to this TSDM for different chemical potentials. We begin by filling the lower energy band represented by the dispersion relation \( E_{-}(k) = -2 t \cos (k a) - \sqrt{B^{2} + 4 \lambda ^{2} \sin ^{2}(k a)} \). In this case, the functions in TSDM can be further simplified as: \(G_{r} = H_{r}\) and \(A=m\). Therefore, the TSDM is a pure state given by the triplet \(|\psi _{t_{1}}\rangle = |00\rangle \) (where \(|0\rangle \) is one of the eigenstate of Pauli-x matrix) and is independent of R as expected.
(Color online) a This diagram demonstrates the variation of entropy (denoted as \( S_{ab}/\ln 2\)) of the TSDM \(\rho _{12}^{(2)}\) (Eq. (10)) as a function of distance \(R= |r_{1}- r_{2}|\) for different filling \(\delta \), starting from \(\delta =0.1\) (yellow) to \(\delta =0.6\) (cyan). Here we choose \(B=0.4\) and RSOC term \(\lambda =0\). B is chosen in terms of the hopping parameter t. b Variation of entropy of SSDM is shown. c Corresponding fillings in the band structure are included. d MI for different fillings \(\delta \) as a function of the distance between the two spins
(Color online) Fidelities of TSDM in Eq. (10) with the spin- singlet \(|\psi _{s}\rangle \) and three triplets \(|\psi _{t_{1}}\rangle \), \(|\psi _{t_{2}}\rangle \) and \(|\psi _{t_{3}}\rangle \) are illustrated, respectively, in a, b, c and d for varying chemical potential \(\mu \). The vertical red dashed line represents the value of chemical potential \(\mu \) (\(\delta \approx 0.3\)) for which the fermions start to fill the upper band. Value of magnetic field is \(B=0.4\) and of RSOC parameter is \(\lambda =0\)
However, when we fill the upper band \(E_{+}(k)\) with electrons having opposite spin polarization w.r.t. the lower band, then the above-mentioned relations, namely \(G_{r} = H_{r}\) and \(A=m\), do not hold, leading to a TSDM which is a mixed state (Fig. 2a). This implies that now the spin-pair is entangled with the rest of the Fermi sea. We analyse this entanglement as a function of distance R and chemical potential \(\mu \), where \(\mu \) is tuned by varying the filling fraction \(\delta \). It is interesting to note that even when we add a single electron in the upper band (\(\delta \approx 0.3\)) while the lower band is partially filled, TSDM undergoes a triplet \(|\psi _{t_{1}}\rangle = |00\rangle \) to singlet \(|\psi _{s}\rangle = (1/\sqrt{2}) \ ( |10\rangle - |01\rangle )\) transition in case \(R =0\) as clear from Fig. 3a–d, where the four fidelities \(F_{s}\) and \(F_{t_{i}}\)s are defined as: \(F_{s} = {\langle {\psi _{s}}|} \rho _{12}^{(2)} |\psi _{s}\rangle \) and \(F_{t_{i}} = {\langle {\psi _{t_{i}}}|} \rho _{12}^{(2)} |\psi _{t_{i}}\rangle \). Here, the density matrix \(\rho _{12}^{(2)}\) is the TSDM (normalized) in Eq. (10) and \(|\psi _{t_{1}}\rangle = |00\rangle \), \( |\psi _{t_{2}}\rangle =(1/\sqrt{2}) \ ( |10\rangle + |01\rangle )\) and \(|\psi _{t_{3}}\rangle = |11\rangle \). This transition exemplifies remarkable sensitivity of the entropy to the degeneracy of fermionic states with opposite spins. Moreover, in sharp contrast to the study of spin degenerate-free fermionic continuum model in [36] and the spin-degenerate case on the lattice model here (\(B, \lambda = 0\)), the saturating value of entropy of TSDM in large R limit has strong dependence on the filling fraction \(\delta \). This saturating value can never reach the maximum entropy value of \( 2 \ln 2\), unless all the states in the two bands are filled, i.e. \(\delta =2\) (Fig. 2a). In this case, all four states, namely singlet and triplets, have equal occupancy, i.e four fidelities \(F_{s}\) and \(F_{t_{i}}\)s are equal to 1/4 independent of the value of the distance R, other than when \(R=0\) (i.e. two spins at the same site).
Another feature, which is in contrast to the results in [36], is the tunability of the entropy of a single spin with the rest of the Fermi sea by the chemical potential and distance R, in the presence of magnetic field. In order to examine this, we again consider a situation where the lower band is partially filled and the upper band is empty. In this case, the normalized reduced SSDM \(\rho _{1} \) turns out to be a pure state and reads as \(\rho _{1} = (1/2) \ ({\mathbb {I}} - \sigma _{x})\), where \(\sigma _{x}\) is a Pauli-x matrix. To explore the single-spin entropy behaviour as the upper band \(E_{+}(k)\) is filled, we first note that the constraints on the functions in the TSDM change as: \( H_{r} = K_{r} = H^{*}_{r} = K^{*}_{r}\), though the factor \(e^{i \theta _{k}}=1\) remains unchanged. These constraints, in turn, simplify the normalized SSDM \(\rho _{1}\), which acquires the following form:
It is evident that the SSDM \(\rho _{1}\) (Eq. (11)) above, depends upon the distance between the two spins via TSDM \(\rho ^{(2)}_{12}\). More interestingly, \(\rho _{1}\) is not a pure state anymore rather a maximally mixed state when the distance between the spins is zero i.e., \(R =|r_{1}-r_{2}|=0\). The off-diagonal elements in the expression of \(\rho _{1}\) in this case, turns out to be zero as \(G_{r} = m\) and \(H_{r}= A\), relations still hold when two spins are located at the same site within the chain. Also, since the \(\textrm{Tr}(\rho ^{(2)})\) = \(2 (m^{2}- A^{2})/(2L)^{2}\), each of the diagonal elements becomes 1/2. We now focus on the profile of entropy in the large R limit and is depicted in Fig. 2b. Note that when the chemical potential \(\mu \) lies in the lower band \(E_{-}(k)\), the entropy corresponding to SSDM is zero and independent of the distance R (see Fig. 2b with filling values \(\delta =0.1\) and \(\delta =0.2\)). However, when we start to fill the upper band \(E_{+}(k)\) as well, we observe that entropy of SSDM saturates to nonzero value which increases upon increasing the filling values from \(\delta =0.3\) to \(\delta =0.6\) and finally saturates to the maximum value of \( \ln 2\) when both the bands are completely filled. The corresponding fillings in the band structure are indicated in Fig. 2c.
(Color online) In a we depict the variation of entropy of the TSDM as a function of distance for various filling starting from yellow (\(\delta =0.1)\) to the cyan (\(\delta =0.6)\). In b, we show the variation of SSDM as a function of distance R for fillings (\(\delta =0.1\)–0.6), respectively. c The spectrum of our 1D chain along with different fillings \(\delta \) is shown in c. The spatial dependence of MI is sketched in the d. See text for discussion. We choose \(\lambda =1.0\), \(B=0.4\) for all the panels
Now we investigate the degree of correlation between the two spins in TSDM by studying mutual information (MI), which is defined as \(\textrm{MI} = 2 S(\rho _{1})-S(\rho ^{(2)}_{12})\). Here S(X) denotes the entropy of a given density matrix X. Note that MI is zero for the product state of two spins (hence uncorrelated), but it can also be zero while \(S(\rho _{1})= 1/2 \ S(\rho ^{(2)}_{12})\), i.e. when the total entropy follows an addition law of individual entropies and in this case also spins are uncorrelated. In Fig. 2d, we demonstrate the MI variation as a function of distance R for various fillings ranging from \(\delta =0.1\) to \(\delta =0.6\). We find that MI is a monotonically decreasing function of distance R for the fillings \(\delta =0.3\)–0.6 and identically zero for \(\delta =0.1-0.2\). Note that the corresponding behaviour of the entropies is non-monotonic with respect to the filling factor \(\delta \). As before, when we fill only the lower energy band \(E_{-}(k)\), MI is zero as TSDM is a pure state which is also a product state in this case. However, once we put a single electron in the upper band \(E_{+}(k)\), MI attains the maximum value of \(2 \ln 2\) at \(R = 0\). Interestingly, as the distance between the two spins R is increased, MI decays monotonically to zero again in large R limit. Although both the single spin (represented by SSDM) and two spins (represented by TSDM), that have been taken into consideration, are highly entangled with the rest of the Fermi sea and are maximally entangled in case \(\delta =2\), there is no correlation between the two spins in the spin-pair for large distance R.
4 Rashba SOC and Zeeman field
In this section, we first turn off the Zeeman term i.e., \(B=0\) and assumes only RSOC \(\lambda \ne 0\). This implies that there is a double degeneracy owing to the time-reversal symmetry at \(k=0\). The factor \(e^{\pm i \theta _{k}} = \pm i\) for \(B = 0\) implies \(e^{ i \theta _{-k}} = e^{- i \theta _{k}}\). Hence, the constraints on the functions within the TSDM are: \(A=0; H_{r}= -K_{r} = H^{*}_{r} = - K^{*}_{r}=0\). Moreover, the functions m and \(G_{r}\) remain invariant, leading to TSDM, which has exactly the same functional form as given in Eq. (9), i.e. retains the same functional form of “X-state", which is not the case for \(B \ne 0\) and \(\lambda =0\) as discussed in Sect. 3. Moreover, as discussed the entropy of a single spin is again reduced to its maximum value of \(\ln 2\) independent of R and chemical potential. Therefore, it is apparent that even in presence of nonzero \(\lambda \), the entropy of TSDM as well as SSDM remains unchanged, i.e. are matching with the case where both \(B =0, \lambda =0\). However, once we switch on the Zeeman term \(B \ne 0\) as well, the resulting TSDM do not confine to the form of “X-states" and is given by Eq. (7). The entropy corresponding to TSDM is depicted in Fig. 4a. In the limiting case \(R=0\), TSDM is yet a pure state independent of filling fraction \(\delta \). In order to find which pure state TSDM is in when \(R=0\) we write the entropy of a single spin in the presence of both B and \(\lambda \). The SSDM \(\rho _{1}\) (un-normalized) for this case can be written as:
the entropy reaches maximum value of \(\ln 2\) when distance \(R=|r_{1}-r_{2}|=0\). This confirms the fact that TSDM not a product state, rather a maximally entangled state. It should be noted that when the chemical potential is such that only the lower band is filled, i.e. \(\delta \) ranging from 0.1to0.5, still the TSDM is not a triplet \(|\psi _{t_{1}}\rangle \), unlike the case where only \(B \ne 0\) and \(\lambda =0\) in Sect. 3. In fact, we find that TSDM turns out to be a singlet state \(|\psi _{s}\rangle \). Another interesting observation to note is that the entropy of SSDM oscillates with a decaying envelope, as a function of distance R, owing to the competition of Zeeman term B and the RSOC term \(\lambda \). Finally, in Fig. 4d we demonstrate the behaviour of \(\mathrm MI\) as a function of distance R for various fillings ranging from \(\delta =0.1\) to \(\delta =0.6\). We observe that for filling \(\delta =0.1\)–0.5, i.e. when the chemical potential lies in the lower band, MI is maximum at \(R=0\) and gradually suppressed over distance in a monotonic decaying fashion unlike the case discussed in Sect. 3 where MI is identically zero independent of R when only the lower band is filled. Moreover, as we increase the filling gradually, \(\mathrm MI\) exhibits faster decay rate over distance, which implies that the correlations between the individual spin in the spin-pair and the rest of Fermi sea grow stronger as the depth of the Fermi sea is increasing and hence the faster decay.
(Color online) Entropy of SSDM \( S_{a}/\ln 2\) demonstrated in the plane of magnetic field B and RSOC \(\lambda \) in the three panels a, b and c, where the distance R has been set to 0, 2 and 10, respectively. Here blue colour corresponds to a SSDM which is a pure state, whereas red denotes a SSDM which is a maximally mixed state (\(\mathrm ln~2\)) state. We choose the filling fraction \(\delta \) to be \(\delta =0.3\) in all the three panels
5 Conclusion and discussion
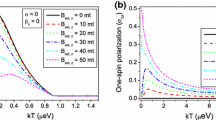
To conclude, we employ spin density matrix approach proposed by Kim et al. ([36]) to analyse the many-body fermionic states of a 1-D lattice model in the presence of magnetic field and RSOC. In contrast to their study, we find that SSDM is a function of the distance between the two spins in the spin-pair once the magnetic field is turned on. Moreover, TSDM cannot get maximally entangled, i.e entropy is \( 2 \ln 2\) with the rest of the Fermi sea in the large R limit (\(R \rightarrow \infty \)), unless both the bands are completely filled. Note that this is also in sharp contrast to the case in [36], where the energy spectrum is unbounded above and has no well-defined sense of filling fraction and hence the related physics does not exist in their continuum model. Finally, for the case where only magnetic field is present, we also note the fact that even when we add a single electron in the upper band, while the lower band is partially filled, SSDM entropy undergoes a sharp transition (corresponds to triplet to singlet transition of TSDM ) in the limit \(R =0\) (see Fig. 5a). This entropy transition persists for small distance corresponding to few lattice sites and for large R as well, though the sharpness is reduced (see Fig. 5b, c). It is also evident from Fig. 5 that when \(B=0\), SSDM entropy \(S_{a}\) is independent of the strength of RSOC like it was in the case studied in [36].
We should also point out that main interest in our article is prominently restricted to the examination of entanglement of the spin degrees of freedom of two electrons living on a lattice under the influence of rest of the Fermi sea and subsequently to briefly discuss the correlations in the form of mutual information as well. Since mutual information is not a complete quantification of all possible correlations, which might exist in bipartite systems, complete analysis of correlation requires further analysis of full correlation matrices [42]. As far as practical realization of our system is concerned RSOC \(\lambda \) between the nearest neighbour sites in one-dimensional lattice can be engineered in an optical lattice system [43]. In the fermionic system, entanglement negativity and Rényi entanglement entropy [44] recently proposed as an excellent tool for measuring entanglement between two subsystems connected to an environment. For a direct experimental measurement, we also propose a spin-polarized STM tip at each site of the lattice and measure the spin orientation and population as a function of the magnetic field B and \(\lambda \). Based on this, it is very convenient to realize the (B-\(\lambda \)) phase diagram in the one-dimensional lattice, engineered on optical systems.
Data availability
The data sets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Zeng, B., Chen, X., Zhou, D.L., Wen, X.G.: Quantum Information Meets Quantum Matter. Springer, Berlin (2019)
Amico, L., Fazio, R., Osterloh, A., Vedral, V.: Entanglement in many-body systems. Rev. Mod. Phys. 80, 517 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.80.517
Shi-Jian, G., Tian, G.-S., Lin, H.-Q.: Ground-state entanglement in the x x z model. Phys. Rev. A 71, 052322 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.71.052322
Shi-Jian, G., Deng, S.-S., Li, Y.-Q., Lin, H.-Q.: Entanglement and quantum phase transition in the extended hubbard model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 086402 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.93.086402
Larsson, D., Johannesson, H.: Entanglement scaling in the one-dimensional hubbard model at criticality. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 196406 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.196406
Vidal, J.: Concurrence in collective models. Phys. Rev. A 73, 062318 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.73.062318
Horodecki, R., Horodecki, P., Horodecki, M., Horodecki, K.: Quantum entanglement. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 865 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.81.865
O’connor, K.M., Wootters, W.K.: Entangled rings. Phys. Rev. A 63, 052302 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.63.052302
Arnesen, M.C., Bose, S., Vedral, V.: title Natural thermal and magnetic entanglement in the 1d heisenberg model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 017901 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.87.017901
Wang, X.: Entanglement in the quantum heisenberg xy model. Phys. Rev. A 64, 012313 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.64.012313
Osborne, T.J., Nielsen, M.A.: Entanglement in a simple quantum phase transition. Phys. Rev. A 66, 032110 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.66.032110
Osterloh, A., Amico, L., Falci, G., Fazio, R.: Scaling of entanglement close to a quantum phase transition. Nature 416, 608–610 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/416608a
Vidal, G., Latorre, J.I., Rico, E., Kitaev, A.: Entanglement in quantum critical phenomena. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 227902 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.90.227902
Glaser, U., Büttner, H., Fehske, H.: Entanglement and correlation in anisotropic quantum spin systems. Phys. Rev. A 68, 032318 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.68.032318
Wootters, W.K.: Entanglement of formation of an arbitrary state of two qubits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 2245 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.80.2245
Vedral, V.: Mean-field approximations and multipartite thermal correlations. New J. Phys. 6, 22 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/6/1/022
Gu, S.J., Sun, C.P., Lin, H.Q.: Universal role of correlation entropy in critical phenomena. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 41, 025002 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1088/1751-8113/41/2/025002
Schliemann, J., Cirac, J.I., Kuś, M., Lewenstein, M., Loss, D.: Quantum correlations in two-fermion systems. Phys. Rev. A 64, 022303 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.64.022303
Wiseman, H.M., Vaccaro, J.A.: Entanglement of indistinguishable particles shared between two parties. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 097902 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.91.097902
Ghirardi, G.C., Marinatto, L.: General criterion for the entanglement of two indistinguishable particles. Phys. Rev. A 70, 012109 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.70.012109
Zanardi, P.: Quantum entanglement in fermionic lattices. Phys. Rev. A 65, 042101 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.65.042101
Shi, Yu.: Quantum entanglement of identical particles. Phys. Rev. A 67, 024301 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.67.024301
Friis, N., Lee, A.R., Bruschi, D.E.: Fermionic-mode entanglement in quantum information. Phys. Rev. A 87, 022338 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.87.022338
Benatti, F., Floreanini, R., Marzolino, U.: Entanglement in fermion systems and quantum metrology. Phys. Rev. A 89, 032326 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.89.032326
Debarba, T., Vianna, R.O., Iemini, F.: Quantumness of correlations in fermionic systems. Phys. Rev. A 95, 022325 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.95.022325
Iemini, F., Debarba, T., Vianna, R.O.: Quantumness of correlations in indistinguishable particles. Phys. Rev. A 89, 032324 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.89.032324
Majtey, A.P., Bouvrie, P.A., Valdés-Hernández, A., Plastino, A.R.: Multipartite concurrence for identical-fermion systems. Phys. Rev. A 93, 032335 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.93.032335
Gigena, N., Rossignoli, R.: Bipartite entanglement in fermion systems. Phys. Rev. A 95, 062320 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.95.062320
Islam, R., Ma, R., Preiss, P.M., Eric Tai, M., Lukin, A., Rispoli, M., Greiner, M.: Measuring entanglement entropy in a quantum many-body system. Nature 528, 77–83 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature15750
Yuan, H.Y., Yung, M.-H.: Thermodynamic entanglement of magnonic condensates. Phys. Rev. B 97, 060405 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.97.060405
Demokritov, S.O., Demidov, V.E., Dzyapko, O., Melkov, G.A., Serga, A.A., Hillebrands, B., Slavin, A.N.: Bose–Einstein condensation of quasi-equilibrium magnons at room temperature under pumping. Nature 443, 430–433 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05117
Dirac, P.A.M.: Note on the interpretation of the density matrix in the many-electron problem. Math. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 27, 240–243 (1931). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0305004100010343
Löwdin, P.-O.: Quantum theory of many-particle systems. i. Physical interpretations by means of density matrices, natural spin-orbitals, and convergence problems in the method of configurational interaction. Phys. Rev. 97, 1474 (1955). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.97.1474
Löwdin, P.-O.: Quantum theory of many-particle systems. ii. Study of the ordinary Hartree–Fock approximation. Phys. Rev. 97, 1490 (1955). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.97.1490
Vedral, V.: Entanglement in the second quantization formalism. Centr. Eur. J. Phys. 1, 289–306 (2003). https://doi.org/10.2478/BF02476298
Oh, S., Kim, J.: Entanglement of electron spins of noninteracting electron gases. Phys. Rev. A 69, 054305 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.69.054305
Verstraete, F., Audenaert, K., De Moor, B.: Maximally entangled mixed states of two qubits. Phys. Rev. A 64, 012316 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.64.012316
Scott, A.J.: Multipartite entanglement, quantum-error-correcting codes, and entangling power of quantum evolutions. Phys. Rev. A 69, 052330 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.69.052330
Facchi, P., Florio, G., Parisi, G., Pascazio, S.: Maximally multipartite entangled states. Phys. Rev. A 77, 060304 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.77.060304
Arnaud, L., Cerf, N.J.: Exploring pure quantum states with maximally mixed reductions. Phys. Rev. A 87, 012319 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.87.012319
Sudevan, S., Das, S.: N-qubit states with maximum entanglement across all bipartitions: a graph state approach (2022). arXiv:2201.05622
Alipour, S., Tuohino, S., Rezakhani, A.T., Ala-Nissila, T.: Unreliability of mutual information as a measure for variations in total correlations. Phys. Rev. A 101, 042311 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.101.042311
Zhang, S., Cole, W.S., Paramekanti, A., Trivedi, N.: Spin–orbit coupling in optical lattices. In: Annual Review of Cold Atoms and Molecules, pp. 135–179 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1142/9789814667746_0003
Cornfeld, E., Sela, E., Goldstein, M.: Measuring fermionic entanglement: entropy, negativity, and spin structure. Phys. Rev. A 99, 062309 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.99.062309
Acknowledgements
A.V.V. acknowledges the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Govt. of India, for financial support. S.D. would like to acknowledge the MATRICS grant (Grant No. MTR/ 2019/001 043) from the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) for funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The first two authors, S.J. and A.V.V., have contributed equally to this work.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jana, S., Varma, A.V., Saha, A. et al. Non-local spin entanglement in a fermionic chain. Quantum Inf Process 21, 374 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-022-03718-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-022-03718-z