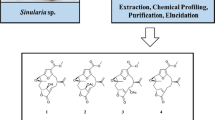
Two new phthalate derivatives, N1-(2-aminoethyl)-N2-isopentylphthalamide (1) and N1-isobuty-N2-tridecylphthalamide (2), were isolated from the marine sponge Haliclona sp. The structures of the new isolates were elucidated on the basis of extensive spectroscopic analysis and by comparison of the data with those of related secondary metabolites.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Previous chemical investigation of the genus Haliclona (order Haplosclerida, family Haliclonidea) has displayed the presence of many bioactive secondary metabolites [1]. In our study of bioactive compounds from a Haliclona sp. collected from South China Sea, some secondary metabolites of this specimen have been reported [1,2,3]. Further search for bioactive metabolites from this specimen has led to the isolation of two new phthalate derivatives, N1-(2-aminoethyl)-N2-isopentylphthalamide (1) and N1-isobuty-N2-tridecylphthalamide (2) (Fig. 1). Herein we describe the isolation and structure elucidation of the new isolates.
Compound 1 was obtained as a white powder and had the molecular formula C15H23N3O2 as deduced from the HR-ESI-MS mass spectrum (found [M + H]+ at m/z 278.1865, calcd [M + H]+, 278.1869). The NMR data of 1 revealed the presence of two Me groups, four sp3 CH2 groups, one sp3 CH group, four sp2 CH groups, and four quaternary sp2 C-atoms. The aromatic region of the NMR spectrum of 1 displayed the presence of a 1,2-disubstitued aromatic ring at δ 7.36 (1H, d, J = 8.5 Hz), 7.32 (1H, dd, J = 8.5, 6.8 Hz), 7.30 (1H, dd, J = 8.0, 6.8 Hz), and 7.28 (1H, d, J = 8.0 Hz), together with two carbonyl resonances at _C 170.1 and 169.2, confirming the phthalate characteristic of the molecule [4, 5].
The gross structure was determined by the aid of COSY and HMBC experiments (Fig. 1). The 1H-1H COSY spectrum displayed three fragments of H-2/H-3/H-4/H-5, H-3′/H-4′, and H-3″/H-4″/H-5″/H-6″ or H-7″. These data, together with the key HMBC correlations from H-2 to C-1′, H-3′ to C-1′, H-5 to C-1″, and H-3″ to C-1″, established the whole structure as N1-(2-aminoethyl)-N2-isopentylphthalamide (1).
Compound 2, a white powder, was established as C25H42N2O2 based on the NMR and HR-ESI-MS data (found [M + H]+ at m/z 403.3320, calcd [M + H]+, 403.3325). The NMR data of 2 revealed the presence of three Me groups, 13 sp3 CH2 groups, one sp3 CH group, four sp2 CH groups, and four quaternary sp2 C-atoms. The presence of a 1,2-disubstitued aromatic ring in 2 was revealed by four proton signals at δH 7.30 (1H, d, J = 8.7 Hz), 7.29 (1H, dd, J = 8.7, 6.7 Hz), 7.23 (1H, dd, J = 8.3, 6.7 Hz), and 7.20 (1H, d, J = 8.3 Hz). These proton resonances, together with two carbonyl resonances at δC 171.0 and 169.4, indicated that 2 possessed a phthalate moiety [4, 5]. In addition, the NMR and the signal for fragmentation in the ESI-MS/MS data of m/z 183 [M – C12H15N2O2]+ indicated the presence of 13 aliphatic carbon chain ((CHx)12CH3) in the structure.
The molecular framework was established by 1H–1H COSY and HMBC correlations (Fig. 1). The comprehensive analysis of the 1H–1H COSY correlations of 2 established the spin systems of H-2/H-3/H-4/H-5, H-3′/H-4′/H-5′ or H-6′, H-3″/H-4″, and H-12″/H-13″. These data, together with the key HMBC correlations from H-2 to C-1′, H-3′ to C-1′, H-5 to C-1″, and H-3″ to C-1″, established the whole structure as N1-isobuty-N2-tridecylphthalamide (2).
Experimental
General Experimental Procedures. NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker AV 500 MHz NMR spectrometer with TMS as internal standard (Bruker, Bremen, Germany). HR-ESI-MS data were obtained from a Bruker Maxis mass spectrometer (Bruker, Bremen, Germany). ESI-MS/MS data were obtained with a Thremo LCQ-DECA-XP LC-MS spectrometer. Semipreparative HPLC was performed on a Hitachi L-2400 HPLC system using a YMC ODS-H80 column (250 × 10 mm i.d., 4 μm) coupled to an Alltech ELSD 800 detector with the flow-splitter valve (Parker: NS) set at a split ratio of 20:1 (collector: detector). The silica gel GF254 used for TLC was supplied by the Qingdao Marine Chemical Factory, Qingdao, China. Spots were detected on TLC under UV light or by heating after spraying with 5% H2SO4 in EtOH. All solvent ratios are measured v/v.
Animal Material. The sponge was collected in July 2005, off the coast of Hainan Island, China. The specimen was identified as Haliclona sp. by Dr. Kyung Jin Lee. A voucher specimen (0507003) was deposited at the Guangdong Key Laboratory of Marine Materia Medica, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, CAS.
Extraction and Isolation. The sponge Haliclona sp. (20 kg, wet) was extracted with ethanol (95%). Ethanol was evaporated in vacuo to afford a syrupy residue, which was suspended in distilled water and fractionated successively with CHCl3 and n-butanol. The n-butanol soluble portion (7.21 g) was subjected to reversed-phase flash column chromatography (YMC Gel ODS-A, 60 Å, 230 mesh) using EtOH–H2O (from 90:10 to 20:80) as eluent, giving 24 fractions (A–Z). Fraction B (6.2 g) was subjected to column chromatography using MeOH–H2O (from 0 to 1:1) as eluent to afford 24 subfractions. Fraction B3-4 (155.0 mg) was subjected to column chromatography using MeOH–H2O (from 0 to 6:94) as eluent to afford 2 (3.1 mg). Fraction B3-5 (640 mg) was subjected to column chromatography using CHCl3–MeOH (from 0 to 7:3) as eluent to afford 15 fractions; then the B3-5-2 was subjected to column chromatography using CHCl3–MeOH (from 0 to 95:5) as eluent to afford 1 (2.9 mg).
N 1-(2-Aminoethyl)- N 2-isopentylphthalamide (1). White powder. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CD3OD, δ, ppm, J/Hz): 7.36 (1H, J = 8.5, H-2), 7.32 (1H, dd, J = 8.5, 6.8, H-3), 7.30 (1H, dd, J = 8.0, 6.8, H-4), 7.28 (1H, d, J = 8.0, H-5), 3.19 (2H, t, J = 8.2, H-3′), 2.98 (2H, t, J = 8.2, H-4′), 2.96 (2H, t, J = 8.1, H-3″), 1.70 (2H, m, H-5″), 1.56 (2H, m, H-4″), 0.90 (3H, d, J = 6.5, H-7″), 0.89 (3H, d, J = 6.5, H-6″). 13C NMR (125 MHz, CD3OD, δ, ppm): 170.1 (C-1′), 169.2 (C-1″), 135.2 (C-1), 134.3 (C-6), 132.2 (C-3), 130.4 (C-4), 127.1 (C-2), 126.7 (C-5), 55.6 (C-4′), 42.1 (C-3′), 40.3 (C-3″), 34.3 (C-4″), 29.3 (C-5″), 22.9 (C-6″), 22.5 (C-7″). HR-ESI-MS m/z 278.1865 [M + H]+, calcd 278.1869).
N 1-Isobuty- N 2-tridecylphthalamide (2). White powder. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CD3OD, δ, ppm, J/Hz): 7.30 (1H, J = 8.7, H-2), 7.29 (1H, dd, J = 8.7, 6.7, H-3), 7.23 (1H, dd, J = 8.3, 6.7, H-4), 7.20 (1H, d, J = 8.3, H-5), 2.98 (2H, t, J = 8.1, H-3″), 2.96 (2H, t, J = 8.2, H-3′), 2.15 (2H, m, H-4′), 1.60 (2H, m, H-4″), 1.20–1.57 (16H, overlapping, H-5″–12″), 0.93 (3H, d, J = 6.7, H-5′), 0.91 (3H, d, J = 6.7, H-6′), 0.84 (3H, d, J = 6.3, H-13″). 13C NMR (125 MHz, CD3OD, δ, ppm): 170.0 (C-1′), 169.4 (C-1″), 134.1 (C-1), 133.5 (C-6), 131.3 (C-3), 130.1 (C-4), 126.2 (C-2), 125.8 (C-5), 47.3 (C-3′), 39.3 (C-3″), 31.3 (C-4″), 30.6 (C-4′), 23.5 (C-5′), 22.9 (C-6′), 31.9–19.2 (8C, overlapping, C-5″–12″), 14.2 (C-13″). HR-ESI-MS m/z 403.3320 [M + H]+, calcd 403.3325.
References
B. Wang, Y. C. Lin, Y. N. Chen, and R. M. Huang, Nat. Prod. Commun., 9, 471 (2014).
B. Wang, K. J. Lee, S. Zhang, J. H. Jung, and Y. H. Liu, Chem. Nat. Compd., 45, 137 (2009).
B. Wang, J. Dong, X. F. Zhou, K. J. Lee, R. M. Huang, S. Zhang, and Y. H. Liu, Z. Naturforsch., 64c, 143 (2009).
M. Saleem, M. Nazir, N. Akhtar, P. A. Onocha, N. Riaz, A. Jabbar, M. S. Ali, and N. Sultana, J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res., 11, 974 (2009).
K. S. Satyan, A. Prakash, R. P. Singh, and R. S. Srivastava, Planta Med., 61, 293 (1995).
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong (No. 2016A030313151) and the Science and Technology Plan Projects of Shenzhen City (No. JCYJ20140414160300581).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Khimiya Prirodnykh Soedinenii, No. 4, July–August, 2018, pp. 615–616.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Zhou, H., Gao, C. et al. Two New Phthalate Derivatives from the Marine Sponge Haliclona sp.. Chem Nat Compd 54, 726–728 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-018-2455-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-018-2455-3