Abstract
A Gram-stain negative, rod-shaped, facultative anaerobic, motile bacterial strain, designated TP187T, was isolated from a seamount near the Yap Trench in the tropical western Pacific. Phylogenetic analysis based on the 16S rRNA gene sequence showed that strain TP187T is related to members of the genus Vibrio and has high 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity with the type strains of Vibrio chagasii (97.3%) and Vibrio gallaecicus (97.1%). Sequence similarities to all other type strains of current species of the genus Vibrio were below 97%. The polar lipids profile was found to contain diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylglycerol, an aminophospholipid, two aminolipids, four phospholipids and eleven unidentified polar lipids. Ubiquinone Q-8 was detected as the predominant quinone. The genomic DNA G + C content of strain TP187T was determined to be 43.7 mol%. In addition, the maximum values of in silico DNA–DNA hybridization (isDDH) and average nucleotide identity (ANI) between strain TP187T with V. chagasii LMG 21353T were 22.40 and 77.50% respectively. Both values are below the proposed cutoff levels for species delineation, i.e. 70 and 95%, respectively. Combined data from phenotypic, phylogenetic, isDDH and ANI data demonstrated that the strain TP187T is representative of a novel species of the genus Vibrio, for which we propose the name Vibrio profundi sp. nov. (type strain TP187T = KACC 18555T = CGMCC 1.15395T).
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
The genus Vibrio belongs to the family Vibrionaceae (Baumann and Baumann 1984) and members of the genus Vibrio are widespread in aquatic environments (Huq and Colwell 1995, Thompson et al. 2004). Vibrio cholera is the type species of the genus Vibrio and is a free-living aquatic bacterium that interacts with and infects a variety of organisms. Members of the genus Vibrio are typically Gram-stain negative, halophilic, chemoorganotrophic bacteria, which have facultatively fermentative metabolism. They contain ubiquinone-8 as the main respiratory quinone and C16:0 as their predominant fatty acid. At the time of writing, more than 120 species are recognised in the genus Vibrio (http://www.bacterio.net/vibrio.html).
In this study, we report the characterisation of a novel bacterium of the genus Vibrio isolated from a deep-sea seamount, for which we propose the name Vibrio profundi sp. nov. (type strain TP187T = KACC 18555T = CGMCC 1.15395T).
Materials and methods
Isolation of the bacterial strain and culture conditions
Strain TP187T was isolated from a coral, which was collected from a seamount (tentatively named the Yap-3 seamount; 8°51′N, 137°40′E at a depth of 2030 m) near the Yap Trench by the submersible remotely operated vehicle (ROV) Faxian (Discovery) during the seamount cruise of the R/V Kexue (Science) in the tropical western Pacific in 2014 (Zhang et al. 2016, 2017; Liu et al. 2017a, b; Wang et al. 2018). The coral sample was washed immediately with sterile saline solution (0.8%) and appropriate dilutions were then plated on Marine agar 2216 (MA, Difco) at 20 °C. After incubation at 20 °C for 2 weeks on the ship, single colonies were selected and sub-cultured on MA to achieve purity. One of the pure cultures was designated TP187T. The strain was routinely cultured on MA at 25 °C and stored as a suspension in skim milk (10%, w/v) at –80 °C. Vibrio gallaecicus DSM 23502T and Vibrio chagasii LMG 21353T were obtained from DSMZ and LMG for comparison as reference strains and routinely grown on MA at 25 °C.
Phenotypic determination
Cell morphology was investigated using a transmission electron microscope (JEM-1400, JEOL). Gram-staining was tested by using the bioMérieux Gram stain kit. The nitrate reduction, indole production, citrate, methyl red and Voges–Proskauer tests were done according to Dong and Cai (2001). Degradation of casein, starch, Tween 60, Tween 80, carboxymethyl cellulose, alginic acid, agar and chitin were tested on MA plates supplemented with appropriate substrates as described by Margesin et al. (2003). Hydrolysis of DNA was tested on DNAse agar (Oxoid, CM0321) prepared in sterile seawater. Growth under anaerobic conditions was examined after 7 days of incubation at 25 °C in an anaerobic jar (containing Anaerocult A (Merck) to produce anaerobic conditions) on MA supplemented with 20 mM NaNO3 and 10 mM NaNO2.
Physiological and biochemical characteristics and enzyme activities were determined using API 20 NE, API 20 E and API ZYM kits (bioMérieux) at 25 °C according to the manufacturers’ instructions except that the NaCl concentration was adjusted to 2.0% in all tests and cell suspensions for inoculation were prepared in sterile seawater. API ZYM panels were analysed after 4 h at 25 °C and API 20 NE and API 20 E panels after 7 days at 25 °C, except nitrate reduction and indole production, which were analysed after 48 h. Growth at 4, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 37 and 40 °C was assessed on MA and in marine broth 2216 (MB; BD). Salt tolerance tests, growth at different temperatures and pH range were performed as described Wang et al. (2018).
Chemotaxonomic characterisation
For fatty acid methyl ester analysis, strain TP187T and the two reference strains were grown on MA at 25 °C for 3 days. All three strains shared similar growth behaviour and a sufficient amount of cells of comparable physiological age could be harvested from the third streak quadrant of the MA plates after cultivation under the applied conditions. The fatty acid methyl esters were extracted and prepared according to the standard protocol of the Sherlock Microbial Identification System (MIDI, version 6.1) (Sasser 1990), using the data bank TSBA40 for identification. Respiratory quinones were extracted according to Altenburger et al. (1996) and were analysed by HPLC (Stolz et al. 2007). The polar lipid profile was analysed by the TLC methods of Tindall (1990a, b).
Phylogenetic analyses
DNA was extracted and purified as described by Sambrook and Russell (2001). The 16S rRNA gene was amplified, cloned and sequenced according to a previous protocol (Zhang et al. 2006, 2011). Multiple sequence alignments were performed using the clustalw program integrated in the MEGA version 6 (Tamura et al. 2013).
The MLSA was performed using five housekeeping genes, pyrH (uridylate kinase),
recA (recombination-repair protein), rpoD (polymerase sigma factor), gapA (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) and topA (topoisomerase I). These housekeeping genes were amplified by PCR and sequenced as described by Sawabe et al. (2007) (Supplementary Table S1). The sequences of these genes were compared with the sequences available from GenBank using the BLASTN program. The phylogenetic trees were reconstructed using the neighbour-joining (NJ; Saitou and Nei 1987) and maximum-likelihood (ML; Felsenstein 1981) methods in MEGA version 6. The topologies of the phylogenetic trees were determined using bootstrap analyses based on 1000 replicates.
Genome sequencing
The draft genomes of strain TP187T and the two reference strains V. gallaecicus DSM 23502T and V. chagasii LMG 21353T were sequenced using an Illumina NovaSeq PE150 at the Beijing Novogene Bioinformatics Technology Co., Ltd. Reads of each data set were filtered, and high quality paired-end reads were assembled using the SOAP denovo (Li et al. 2008, 2010).
DNA–DNA relatedness
Both the in silico DNA–DNA hybridization (isDDH) and the average nucleotide identity (ANI) values were used to determine the similarity of TP187T with its two closely related type strains of the genus Vibrio. isDDH similarity was calculated using the GGDC web server (http://ggdc.dsmz.de/), with 70% similarity as the standard threshold for the bacterial species boundary (Meier-Kolthoff et al. 2013). The ANI values was calculated using the EzBioCloud web (https://www.ezbiocloud.net/tools), with the 95% cut-off value suggested for the bacterial species boundary (Yoon et al. 2017).
Results and discussion
Cells of strain TP187T were observed to be motile by a polar flagellum and rod-shaped (Supplementary Fig. S1). Cells were observed to be Gram-stain negative, catalase positive and oxidase positive. Strain TP187T is able to grow on LB medium and requires Na+ for growth. Strain TP187T can hydrolyse aesculin, gelatin, DNA, Tween 60, Tween 80, casein, chitin and starch, but not urea, carboxymethyl cellulose and alginic acid. The strain shows distinctive phenotypic features that discriminates it from closely related members of the genus Vibrio as shown in Table 1. Strain TP187T was found to be positive for alkaline phosphatase, esterase lipase (C8), leucine arylamidase, valine arylamidase, acid phosphatase, α-glucosidase, nitrate reduction, indole production, glucose fermentation, assimilation of d-maltose, mannitol, potassium gluconate, trisodium citrate and malic acid; fermentation of glucose, mannitol, melibiose and amygdalin. The strain is negative for cystine arylamidase, trypsin, α-chymotrypsin, α-galactosidase, β-galactosidase, β-glucosidase, β-glucuronidase, N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase, α-fucosidase, α-mannosidase, arginine dihydrolase, lysine dihydrolase, ornithine dihydrolase, H2S production, urease, tryptophan deaminase, assimilation of d-mannose, L-arabinose, capric acid, adipic acid and phenylacetic acid; and fermentation of inositol, sorbitol, rhamnose and sucrose. The polar lipids profile was found to contain diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylglycerol, an aminophospholipid, two aminolipids, four phospholipids and eleven unidentified polar lipids (Supplementary Fig. S2). The quinone system of strain TP187T was found to consist predominantly of ubiquinone-8 (92.6%) and also traces of ubiquinone-7 (7.4%). The predominant cellular fatty acids were identified as C16:0 and summed feature 3 (composed of iso-C15:0 2-OH and/or C16:1ω7c) (Supplementary Table S2).
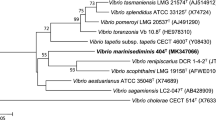
The 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain TP187T was obtained (GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession number KT900237). On the basis of pairwise comparisons of 16S rRNA gene sequences using the latest version of EzTaxon-e, strain TP187T has high 16S rRNA gene sequence similarities with the type strains of Vibrio chagasii (97.3%) and Vibrio gallaecicus (97.1%). The phylogenetic tree constructed using the NJ algorithm (Saitou and Nei 1987) revealed that strain TP187T clusters with the members of the genus Vibrio and forms a coherent cluster with V. gallaecicus CECT 7244T (Fig. 1). The phylogenetic tree for concatenated sequences of the five housekeeping genes constructed with the maximum-likelihood method confirmed the clustering of strain TP187T and representatives of the genus Vibrio and again forms a coherent cluster with V. gallaecicus (Fig. 2). The pyrH, gapA and topA gene sequences of V. gallaecicus DSM 23502T have been deposited as MK840790, MK840792 and MK840795.
Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree, based on 16S rRNA gene sequence data, showing the phylogenetic position of strain TP187T among other members of the genus Vibrio. Bootstrap values (%) are based on 1000 replicates and are shown for branches with more than 50% support. Alteromonas macleodii DSM 6062T was used as an outgroup. GenBank accession numbers of 16S rRNA sequences are given in parentheses. Bar, 0.01 substitutions per nucleotide position
Maximum-likelihood tree using multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA) based on the concatenated partial sequences of recA (665 bp), pyrH (316 bp), gapA (767 bp), rpoD (883 bp) and topA (677 bp) of strain 187T and representatives of the genus Vibrio and other genera. Enterovibrio norvegicus CAIM 430T and Grimontia hollisae ATCC 33564T were used as outgroup. Bootstrap values (> 50%) are shown at the nodes. Bar, 0.05 substitutions per nucleotide position
Sequence scaffolds of the draft genomes of strains TP187T, V. gallaecicus DSM 23502T and V. chagasii LMG 21353T have been deposited at DDBJ/ENA/GenBank under the accession numbers RZIS00000000,SZXU00000000 and SZQG00000000, respectively. The DNA G + C content of strain TP187T determined from the genome sequence is 43.7 mol%, which is within the range observed for other members of the genus Vibrio.
The OrthoANI values of TP187T with the two closely related type strains of the genus Vibrio were ≤ 77.50% ANI (Table 2). These values are far lower than the 95% ANI cut-off value suggested for the bacterial species boundary (Chun and Rainey 2014). Likewise the isDDH with the two closely related type strains of the genus Vibrio were ≤ 23.0, again below the standard threshold for the bacterial species boundary (Meier-Kolthoff et al. 2013). These result strongly support the conclusion that TP187T is a novel species of the genus Vibrio.
On the basis of physiological, chemotaxonomic characteristics, phylogenetic analysis, isDDH and ANI data, it is proposed that strain TP187T represents a novel species belonging to the genus Vibrio, for which the name Vibrio profundi sp. nov. is proposed.
Description of Vibrio profundi sp. nov.
Vibrio profundi (pro.fun′di. L. gen. n. profundi, of/from the depths of the sea).
Cells are Gram-stain negative, oxidase positive, catalase positive and rod-shaped, 1.3–1.9 µm long and 0.8–1.2 µm wide. Motile by a flagellum. Colonies on MA are white, smooth, raised with entire margins and circular. Requires Na+ for growth. Growth occurs in media with 0.5–6% (w/v) NaCl (optimum 2–3%). Grows at 4–37 °C but not at 40 °C on MA (optimum growth at 22–25 °C). The pH for growth is 6.0–8.5, with the optimum pH 6.5–7.5. The polar lipids profile contains diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylglycerol, an aminophospholipid, two aminolipids, four phospholipids and eleven unidentified polar lipids. The predominant cellular fatty acids are C16:0 and summed feature 3 (composed of iso-C15:0 2-OH and/or C16:1ω7c). Ubiquinone Q-8 is the predominant quinone. The genomic DNA G + C content of the type strain is 43.7 mol%.
The type strain, TP187T (= KACC 18555T = CGMCC 1.15395T), was isolated from a coral, which was collected from a seamount (tentatively named as Yap-3 seamount) (8°51′N, 137°40′E at a depth of 2030 m) near the Yap Trench in the tropical western Pacific. The GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession numbers for the draft genome and recA, pyrH, gapA, rpoD, topA and16S rRNA gene sequences of strain TP187T are RZIS00000000, MK840788, MK840789, MK840791, MK840793, MK840794 and KT900237.
References
Altenburger P, Kämpfer P, Makristathis A, Lubitz W, Busse HJ (1996) Classification of bacteria isolated from a medieval wall painting. J Biotechnol 47:39–52
Baumann P, Baumann L (1984) Genus II. Photobacterium Beijerinck 1889, 401AL. In: Krieg NR, Holt JG (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 1. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 539–545
Chun J, Rainey FA (2014) Integrating genomics into the taxonomy and systematics of the Bacteria and Archaea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:316
Dong XZ, Cai MY (eds) (2001) Determinative manual for routine bacteriology. Scientific Press, Beijing (English translation)
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Huq A, Colwell RR (1995) Vibrios in the marine and estuarine environments. J Mar Biotechnol 3:60–63
Li R, Li Y, Kristiansen K, Wang J (2008) SOAP: short oligonucleotide alignment program. Bioinformatics 24:713–714
Li R, Zhu H, Ruan J, Qian W, Fang X, Shi Z, Li Y, Li S, Shan G, Kristiansen K, Li S, Yang H, Wang J, Wang J (2010) De novo assembly of human genomes with massively parallel short read sequencing. Genome Res 20:265–272
Liu J, Sun YW, Zhang DD, Li SN, Zhang DC (2017a) Oceanisphaera marina sp. nov. isolated from a deep-sea seamount. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1996–2000
Liu J, Sun YW, Li SN, Zhang DC (2017b) Thalassotalea profundi sp. nov. isolated from a deep-sea seamount. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:3739–3743
Margesin R, Gander S, Zacke G, Gounot AM, Schinner F (2003) Hydrocarbon degradation and enzyme activities of cold-adapted bacteria and yeasts. Extremophiles 7:451–458
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk H-P, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinformatics 14:60
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sambrook J, Russell DW (eds) (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. Technical note 101. Newark, DE: MIDI Inc
Sawabe T, Kita-Tsukamoto K, Thompson FL (2007) Inferring the evolutionary history of vibrios by means of multilocus sequence analysis. J Bacteriol 189:7932–7936
Stolz A, Busse HJ, Kämpfer P (2007) Pseudomonas knackmussii sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:572–576
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 130:2725–2729
Thompson FL, Iida T, Swings J (2004) Biodiversity of vibrios. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 68:403–431
Tindall BJ (1990a) Lipid composition of Halobacterium lacusprofundi. FEMS Microbiol Lett 66:199–202
Tindall BJ (1990b) A comparative study of the lipid composition of Halobacterium saccharovorum from various sources. Syst Appl Microbiol 13:128–130
Wang Q, Sun YW, Liu J, Zhang DC (2018) Rheinheimera marina sp. nov. isolated from a deep-sea seamount. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68:266–270
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Lim J, Kwon S, Chun J (2017) A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 110:1281–1286
Zhang D-C, Wang H-X, Liu H-C, Dong X-Z, Zhou P-J (2006) Flavobacterium glaciei sp. nov., a novel psychrophilic bacterium isolated from the China No. 1 glacier. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:2921–2925
Zhang DC, Redzic M, Schinner F, Margesin R (2011) Glaciimonas immobilis gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of the family Oxalobacteraceae isolated from alpine glacier cryoconite. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:2186–2190
Zhang DC, Liu YX, Huang HJ, Wu J (2016) Pseudoalteromonas profundi sp. nov., isolated from a deep-sea seamount. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:4416–4421
Zhang DC, Liu YX, Huang HJ (2017) Novosphingobium profundi sp. nov. isolated from a deep-sea seamount. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 110:19–25
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Senior User Project of RV KEXUE (KEXUE2019G09), the Science & Technology Basic Resources Investigation Program of China (2017FY100804) and the Open Fund of Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Marine Ecological Environment and Disaster Prevention and Mitigation under contract No. 201802. We are grateful for Center for Ocean Mega-Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D-C Zhang designed the project and took samples. N-X Zhang performed lab work, N-X Zhang and N–H Qiao analysed data and wrote the manuscript. D-C Zhang revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, NX., Zhang, DC. & Qiao, NH. Vibrio profundi sp. nov., isolated from a deep-sea seamount. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 112, 1603–1610 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-019-01286-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-019-01286-4