Abstract
A novel bacterium, designated strain APA_H-1(4)T, was isolated from the saline−alkaline soil, Zhaodong, Heilongjiang Province, China. Phenotypic and chemotaxonomic analyses, and whole-genome sequencing were used to determine the taxonomic position of the strain. Phylogenetic analysis indicated that the isolate belongs to the genus Oceanobacillus, and showed the highest sequence similarity to O. damuensis KCTC 33146T (98.35%, similarity) and ‘O. massiliensis’ DSM 24644 (98.32%). The average nucleotide identity values between strain APA_H-1(4)T and other members of the genus Oceanobacillus were lower than 82% recommended for distinguishing novel prokaryotic species. The digital DNA−DNA hybridization values of strain APA_H-1(4)T with O. damuensis KCTC 33146T and ‘O. massiliensis’ DSM 24644 were 13.60 and 17.60%, respectively. Cells of strain APA_H-1(4)T were Gram-staining positive, motile, aerobic, spore-forming rods (0.5–0.7 × 1.8–2.6 μm) with flagella. The growth was found to occur optimally at 37 °C. The whole-cell hydrolysate contained meso-diaminopimelic acid as the diagnostic cell wall diamino acid. The main detected polar lipids consisted of diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylglycerol, an unidentified phospholipid and an unidentified polar lipid. The predominant respiratory quinone was identified as menaquinone-7 (MK-7). The major cellular fatty acid (>10%) was anteiso-C15:0. The G + C content of the genomic DNA was determined to be 38.4% based on the draft genome sequence. Based on the comparative analysis of polyphasic taxonomic data, strain APA_H-1(4)T represents a novel species of the genus Oceanobacillus, for which the name Oceanobacillus saliphilus sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is APA_H-1(4)T (=GDMCC 1.2239T = KCTC 43254T).
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
The genus Oceanobacillus belongs to the family Bacillaceae within the phylum Bacillota, and it is a large taxonomic entity that was firstly described by Lu et al. [1] with Oceanobacillus iheyensis as the type species. The members of the genus Oceanobacillus are widely distributed in various habitats, such as seawater [2], chironomid egg mass [3], saline−alkali soil [4], salt lakes [5], fermented polygonum indigo [6], the skin of rainbow trout [7] and other environments. All strains of this genus are Gram-staining positive, rod-shaped, motile bacteria and extremely halotolerant or halophilic. At the time of writing, the genus comprised 28 species with validly published names (https://lpsn.dsmz.de/genus/oceanobacillus). The saline−alkaline soils located in Heilongjiang Province of China are the representatives of naturally occurring salt and alkali environment. Isolating the pure cultures of strains obtained from saline alkaline soils can help us better understand the ‘microbial dark matter’ [8,9,10]. The species isolated from saline alkaline habitats have been studied in depth because of their ecological significance and potential applications for the biotechnological and industrial purposes [11,12,13]. During a study on the cultivable microbial diversity of saline−alkaline soils in Heilongjiang, a novel strain designated as APA_H-1(4)T was isolated and has now been shown to represent a novel species of the genus Oceanobacillus. The present study was conducted to establish the taxonomic position of strain APA_H-1(4)T.
Methods and Materials
Bacterial Isolation and Cell Growth
Sample was collected from saline−alkaline soil, located in Zhaodong (46°01′44.1″N, 125°50′05.9″E), China. Strain APA_H-1(4)T was isolated using the standard dilution plate method on APA medium [14]. After incubating for one week at 37 °C, colonies were picked and re-streaked several times to obtain axenic cultures, and then stored as glycerol suspensions (20%, w/v) concentration at −80 °C for further use. Biomass for chemical and molecular studies was obtained by cultivation on APA medium at 37 °C for 3–10 days. O. damuensis KCTC 33146T [4] and ‘O. massiliensis’ DSM 24644 [15] were used as reference strains, and they were cultured under the optimum conditions as appropriate for specific comparative tests.
Molecular Characterization
The extraction of genomic DNA was carried out according to our previously standardized protocol [16]. 16S rRNA gene was amplified using the bacterial universal primers 27F (5′-AGAGTTTGATCMTGGCTCAG-3′) and 1492R (5′-GGYTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3′). The PCR amplicon was sequenced by Sangon Biotech (Guangzhou, China). The obtained 16S rRNA gene sequence was compared with available sequences of cultured species at EzBioCloud server [17]. The 16S rRNA gene sequences of strain APA_H-1(4)T and related type strains were aligned using ClustalW [18]. Phylogenetic trees were constructed on MEGA version X [19] using neighbor-joining [20], maximum-likelihood [21] and maximum-parsimony [22] methods. The stability of relationships was assessed by performing bootstrap analyses with 1000 replications [23]. The genome of the strain APA_H-1(4)T was sequenced using the Illumina HiSeq X platform at Majorbio (Shanghai, China). The paired-end reads were assembled using SOAPdenovo (v2.04). The completeness and contamination of strain APA_H-1(4)T genome were calculated using CheckM [24]. Average nucleotide identity (ANI) among the genomes of the genus Oceanobacillus was calculated using the pyANI with blast method [25]. The digital DNA–DNA hybridization (dDDH) analysis was performed using the DSMZ Genome-to-Genome Distance Calculator platform (http://ggdc.dsmz.de/distcalc2.php) [26]. Phylogenomic tree was constructed according to the methods of [8, 9]. The DNA G + C content was determined from the genomic sequences. Genome sequences were annotated using the KEGG databases and Prokka [27, 28].
Physiology and Morphology
The morphological properties of the strain APA_H-1(4)T were observed by transmission electron microscopy (JEM-1400FLASH; JEOL). The presence of endospores was investigated using the Schaeffer−Fulton staining method [29]. Cell motility was tested by the development of turbidity in a tube containing semi-solid APA medium. The Gram-staining reaction was performed by the Burke method [29] and the results were confirmed by the KOH test [30]. The growth was tested at temperatures ranging from 4 to 65 °C (4, 15, 20, 29, 37, 45, 55, 65 °C) on APA medium by incubating the cultures for 10 days. The ability of the strain to grow at different pH values (6.0–13.0, at intervals of 1.0 pH unit using the buffer system described by [31] and NaCl concentrations (0–20%, w/v) was examined on APA medium at 37 °C for 10 days. Catalase activity was detected by the formation of bubbles on the addition of a drop of 3% (v/v) H2O2, while oxidase activity was determined by observing color shift with oxidase reagent (bioMerieux, SA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Hydrolysis of cellulose, starch and Tweens (20, 40, 60 and 80), milk peptonization and coagulation, H2S production, methyl red and Voges−Proskauer tests were performed as described by Smibert and Krieg [32]. The determination of other enzyme activities and biochemical characteristics were used API ZYM and API 20NE systems (bioMérieux) and substrate utilization was tested using Biolog GEN III Micro plate according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Antibiotic susceptibility tests were performed on APA medium containing 2% (w/v) NaCl using discs impregnated with various antimicrobial compounds.
Biochemical Characteristics
Biomass for chemical characteristics was obtained by cultivation on APA medium containing 2% NaCl at 37 °C. Analysis of amino acids of whole-cell hydrolysate was performed according to the procedures described by Lechevalier and Lechevalier [33] and Hasegawa et al. [34]. Polar lipids were extracted as described by Minnikin et al. [35] and examined by two-dimensional TLC on 10 × 10 cm silica gel G60 plates (Merck). The polar lipid profile was identified using the described procedures [36, 37]. Menaquinones were isolated according to Collins et al. [38] and separated by HPLC [39]. The biomass for fatty acid analysis was harvested when the population quantity was half of maximum value. For fatty acid analysis, strain APA_H-1(4)T was cultured on APA medium containing 2% NaCl at 37 °C for 3 days. Cellular fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) profiles were determined by GC (7890B; Agilent) according to the standard protocol of the Microbial Identification System (Sherlock Version 6.2; MIDI database: TSBA6).
Results and Discussion
Molecular Characteristics
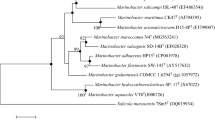
An almost complete 16S rRNA gene sequence (1591 bp) of strain APA_H-1(4)T was obtained. The GenBank accession number for the 16S rRNA gene of strain APA_H-1(4)T was ON077165. Analyses of the 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain APA_H-1(4)T using the EzBioCloud server showed that they were moderately related to O. damuensis KCTC 33146T (98.35%, similarity) and ‘O. massiliensis’ DSM 24644 (98.32%). 16S rRNA gene-based phylogeny using the neighbor-joining method (Fig. 1 and Fig. S3) showed strain APA_H-1(4)T form a clade with O. damuensis KCTC 33146T, ‘O. massiliensis’ DSM 24644 and O. endoradicis py1294T. The stabilities of trees were further confirmed by maximum-likelihood and maximum-parsimony methods (Fig. S1 and Fig. S2). The affiliation of the strain APA_H-1(4)T to the genus Oceanobacillus was also supported by the phylogenomic tree (Fig. 2) based on the concatenated alignment of 120 marker genes. The completeness and contamination of the genome of strain APA_H-1(4)T were 100.00 and 1.61%, respectively. The genome had a total of 4082 genes, including 3985 protein-coding genes, 13 rRNA genes and 84 tRNA genes. The most abundant KEGG function pathway in strain APA_H-1(4)T was carbohydrate metabolism, followed by overview and amino acid metabolism (Table S2). Amino acids (e.g., glutamine, glutamate and proline) are widely distributed compatible solutes in prokaryotes [40]. The accumulation of compatible solutes can be beneficial for halophilic microorganisms to overcome osmotic pressure in high salt environment [41]. According to the annotation results of the KEGG automatic annotation server (KAAS), strain APA_H-1(4)T contains glutamine biosynthesis genes (glnA and GLUL) and proline biosynthesis genes (proB and proC), which can enhance the ability of cells to withstand high osmotic pressure. The genomic DNA G + C content of strain APA_H-1(4)T was 38.44%. The ANI values between strain APA_H-1(4)T and O. damuensis KCTC 33146T (GenBank accession no. GCA_001618145.1) and ‘O. massiliensis’ DSM 24644 (GenBank accession no. GCA_000285495.1) were 81.82% and 76.43%, respectively. The dDDH values of strain APA_H-1(4)T with O. damuensis KCTC 33146 T and ‘O. massiliensis’ DSM 24644 were 13.60 and 17.60%, respectively. These data supported the finding that strain APA_H-1(4)T represents a different genomic species of the genus Oceanobacillus. O. damuensis KCTC 33146T, ‘O. massiliensis’ DSM 24644, were used as reference strains.
Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on the 16S rRNA gene sequences of strain APA_H-1(4)T and its closest relatives. Effusibacillus lacus DSM 27172T was selected as the outgroup. Bootstrap values are shown at the branch points. A number at nodes are bootstrap percentages based on the 1000 replications, only values > 50% are shown at branch points. Asterisks denote topologies that were also recovered in trees generated with the maximum-likelihood and maximum-parsimony methods. Bar, 0.02 substitutions per nucleotide position
The phylogenomic tree based on the 120 marker genes showing the relationship of strain APA_H-1(4)T with representative members of the genus Oceanobacillus. Effusibacillus lacus DSM 27172T (SLZX00000000) was selected as the outgroup. Bootstrap values are shown at the branch points. Bar, 0.1 substitutions per nucleotide position
Physiology and Morphology
Strain APA_H-1(4)T was Gram-staining positive, motile, aerobic and can produced oval terminal endospores. Cells were rods with a width of 0.5–0.7 μm and a length of 1.8–2.6 μm (Fig. S4). The growth of strain APA_H-1(4)T was observed in a wide range of temperature 4–55 °C with optimal growth at 37 °C. The pH range for growth was pH 7.0–10.0 with an optimum pH (8.0–9.0). The NaCl tolerance was up to 15.0% (w/v) with optimal growth at 2–10% NaCl (w/v). The strain APA_H-1(4)T was positive for the production of catalase, while strain APA_H-1(4)T was negative for oxidase, nitrate reduction, milk peptonization and coagulation, methyl red and Voges−Proskauer test. H2S was not produced. Tweens (20, 40, 60 and 80) and cellulose were hydrolyzed, but gelatin and starch were not. Differential characteristics of strain APA_H-1(4)T and the closely related type strains are listed in Table 1. The detailed physiological characteristics of the strain are given in the species description and all negative traits of strain APA_H-1(4)T observed with commercial kits, including API ZYM, API 20 NE and Biolog Gen III were listed in Table S3.
Biochemical Characteristics
Cell wall amino acids of strain APA_H-1(4)T contained meso-diaminopimelic acid as the diagnostic diamino acid. The phospholipids consisted of diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylglycerol, an unidentified phospholipid and an unidentified polar lipid (Fig. S5). The respiratory quinone was identified as menaquinone-7 (MK-7), and the cellular fatty acid profile contained anteiso-C15:0 (66.02%) as the major fatty acid, anteiso-C17:0 (9.91%) iso-C16:0 (6.31%), iso-C14:0 (5.60%), C16:0 (5.14%) and iso-C15:0 (2.15%) as minor fatty acids.
Conclusion
Based on the phenotypic, genotypic, phylogenetic and chemotaxonomic data, strain APA_H-1(4)T belongs to the genus Oceanobacillus. Furthermore, the analyses of 16S rRNA gene sequences, ANI values, dDDH values and other properties, notably, enzyme activities, the sensitivity to antibiotics and utilization of carbon sources and nitrogen sources, indicate that strain APA_H-1(4)T could be distinguished from the species of O. damuensis KCTC 33146T and ‘O. massiliensis’ DSM 24644. Based on the data described above, strain APA_H-1(4)T represents a novel species of the genus Oceanobacillus, for which the name Oceanobacillus saliphilus sp. nov. is proposed.
Description of Oceanobacillus saliphilus sp.nov.
Oceanobacillus saliphilus (sa.li’phi.lus. L. masc. n. sal, salt; Gr. masc. adj. philos, loving; N.L. masc. adj. saliphilus, loving salt).
Gram-staining positive, motile, aerobic, spore-forming rods (0.5–0.7 × 1.8–2.6 μm) with flagella. Endospores are ellipsoid and terminally positioned. Colonies are circular, smooth, and creamy yellow. Growth occurs at 4–55 °C (optimum 37 °C), at pH 7.0–10.0 (optimum pH 8.0–9.0) and in the presence of 0–15% (w/v) NaCl (optimum 2–10% NaCl). Positive for the production of catalase. Negative for the oxidase, nitrate reduction, H2S production, milk peptonization and coagulation, methyl red and Voges−Proskauer test. Tweens (20, 40, 60 and 80) and cellulose are hydrolyzed, but gelatin, starch are not. In the GEN III Microplate (Biolog) system, the following substrates can be utilized: acetoacetic acid, acetic acid, formic acid, glucuron-amide, 3-methyl-glucose, D-mannose, D-fructose, D-galactose, D-fucose, D-galacturonic acid, D-glucuronic acid, L-fucose and L-rhamnose, α-D-glucose. According to the API ZYM, cystine arylamidase, esterase (C4), leucine arylamidase, naphthol-AS-BI-phosphohydrolase, valine arylamidase, α-chymotrypsin, α-glucosidase and β-glucuronidase are positive. In the API 20NE test, positive for glucosidase and galactosidase. Sensitive to amikacin, ampicillin, bacitracin, chloramphenicol, erythromycin, furantoin, kanamycin, norfloxacin, rifampicin, sulfamethoxazole, streptomycin, tetracycline, tobramycin. The polar lipids are diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylglycerol, an unidentified phospholipid and an unidentified polar lipid. The major fatty acid (>10%) is anteiso-C15:0. The predominant menaquinone is MK-7. The whole-cell hydrolysates contain meso-diaminopimelic acid as the diagnostic diamino acid. The genomic DNA G + C content is 38.44%.
The type strain is APA_H-1(4)T(=GDMCC 1.2239T = KCTC 43254T), isolated from saline−alkaline surface soil (0–10 cm), Zhaodong, Heilongjiang Province, China.
The GenBank accession numbers for 16S rRNA gene sequence and draft genome sequence of the strain APA_H-1(4)T are ON077165 and JALCZU000000000, respectively.
References
Lu J, Nogi Y, Takami H (2001) Oceanobacillus iheyensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a deep-sea extremely halotolerant and alkaliphilic species isolated from a depth of 1050 m on the Iheya Ridge. FEMS Microbiol Lett 205:291–297
Ouyang YC, Xiang WZ, Wang GH (2015) Oceanobacillus bengalensis sp. nov., a bacterium isolated from seawater of the Bay of Bengal. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 108:1189–1196
Raats D, Halpern M (2007) Oceanobacillus chironomi sp. nov., a halotolerant and facultatively alkaliphilic species isolated from a chironomid egg mass. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:255–259
Long XF, Ye RY, Zhang S, Liu B, Zhang YQ, Zeng Z, Tian YQ (2015) Oceanobacillus damuensis sp. nov. and Oceanobacillus rekensis sp. nov., isolated from saline alkali soil samples. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 108:731–739
Zhu WY, Yang L, Shi YJ, Mu CG, Wang Y, Kou YR, Yin M, Tang SK (2020) Oceanobacillus halotolerans sp. nov., a bacterium isolated from salt lake in Xinjiang province, north-west China. Arch Microbiol 202:1545–1549
Hirota K, Aino K, Nodasaka Y, Yumoto I (2013) Oceanobacillus indicireducens sp. nov., a facultative alkaliphile that reduces an indigo dye. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:1437–1442
Yumoto I, Hirota K, Nodasaka Y, Nakajima K (2005) Oceanobacillus oncorhynchi sp. nov., a halotolerant obligate alkaliphile isolated from the skin of a rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss), and emended description of the genus Oceanobacillus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1521–1524
Jiao JY, Liu L, Hua ZS, Fang BZ, Zhou EM, Salam N, Hedlund BP, Li WJ (2021) Microbial dark matter coming to light: challenges and opportunities. Natl Sci Rev 8:nwaa280
Jiao JY, Fu L, Hua ZS, Liu L, Salam N, Liu PF, Lv AP, Wu G, Xian WD, Zhu Q, Zhou EM, Fang BZ, Oren A, Hedlund BP, Jiang HC, Knight R, Cheng L, Li WJ (2021) Insight into the function and evolution of the Wood-Ljungdahl pathway in Actinobacteria. ISME J 15:3005–3018
Marcy Y, Ouverney C, Bik EM, Lösekann T, Ivanova N, Martin HG, Szeto E, Platt D, Hugenholtz P, Relman DA, Quake SR (2007) Dissecting biological “dark matter” with single-cell genetic analysis of rare and uncultivated TM7 microbes from the human mouth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(29):11889–11894
Hyun DW, Whon TW, Kim JY, Kim PS, Bae JW (2015) Genomic analysis of the moderately haloalkaliphilic bacterium Oceanobacillus kimchii strain x50(t) with improved high-quality draft genome sequences. J Microbiol Biotechnol 25(12):1971–1976
Hagaggi N (2020) Studies on the extremo-lipase produced by the halotolerant Oceanobacillus iheyensis strain QCS. Novel Res Microbiol J 4(4):907–920
Kavita K, Singh VK, Mishra A, Jha B (2014) Characterisation and anti-biofilm activity of extracellular polymeric substances from Oceanobacillus iheyensis. Carbohyd Polym 101:29–35
Wang S, Sun L, Wei D, Salam N, Fang BZ, Dong ZY, Hao XY, Zhang MY, Zhang Z, Li WJ (2021) Nesterenkonia haasae sp. nov., an alkaliphilic actinobacterium isolated from a degraded pasture in Songnen Plain. Arch Microbiol 203:959–966
Roux V, Million M, Robert C, Magne A, Raoult D (2013) Non-contiguous finished genome sequence and description of Oceanobacillus massiliensis sp. nov. Stand Genomic Sci 9:370–384
Li WJ, Xu P, Schumann P, Zhang YQ, Pukall R, Xu LH, Stackebrandt E, Jiang CL (2007) Georgenia ruanii sp. nov., a novel actinobacterium isolated from forest soil in Yunnan (China) and emended description of the genus Georgenia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1424–1428
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S, Lim J, KimY SH, Chun J (2017) Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database 16S rRNA and whole genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613–1617
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specifc gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35(6):1547–1549
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Tamura K, Nei M (1993) Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol Biol Evol 10:512–526
Nei M, Kumar S (2000) Molecular evolution and phylogenetics. Oxford University Press, New York
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Parks DH, Imelfort M, Skennerton CT, Hugenholtz P, Tyson GW (2015) CheckM: assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res 25(7):1043–1055
Pritchard L, Glover RH, Humphris S, Elphinstone JG, Toth KL (2016) Genomics and taxonomy in diagnostics for food security: soft-rotting enterobacterial plant pathogens. Anal Methods 8:12–24
Meier-Kolthof JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform 14:60
Kanehisa M, Sato Y, Kawashima M, Furumichi M, Tanabe M (2016) KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein annotation. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D457-462
Seemann T (2014) Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 30(14):2068–2069
Murray RG, Doetsch RN, Robinow CF (1994) Determinative and cytological light microscopy. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RG, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC, pp 21–41
Baron EJ, Finegold SM (1990) Bailey and Scott’s diagnostic microbiology, 8th edn. Mosby, St. Louis
Xu P, Li WJ, Tang SK, Zhang YQ, Chen GZ, Chen HH, Xu LH, Jiang CL (2005) Naxibacter alkalitolerans gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel member of the family ‘Oxalobacteraceae’ isolated from China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1149–1153
Smibert R, Krieg NRM (1994) Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RG, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC, pp 607–654
Lechevalier MP, Lechevalier HA (1970) Chemical composition as a criterion in the classification of aerobic actinomycetes. Int J Syst Bacteriol 20:435–443
Hasegawa T, Takizawa M, Tanida S (1983) A rapid analysis for chemical grouping of aerobic actinomycetes. J Gen Microbiol 29:319–322
Minnikin DE, O’Donnell AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M, Schaal A, Parlett JH (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241
Collins MD, Jones D (1980) Lipids in the classification and identification of coryneform bacteria containing peptidoglycans based on 2, 4-diaminobutyric acid. J Appl Bacteriol 48:459–470
Minnikin DE, Collins MD, Goodfellow M (1979) Fatty acid and polar lipid composition in the classification of Cellulomonas, Oerskovia and related taxa. J Appl Bacteriol 47:87–95
Collins MD, Pirouz T, Goodfellow M, Minnikin DE (1977) Distribution of menaquinones in actinomycetes and corynebacteria. J Gen Microbiol 100:221–230
Tamaoka J, Katayama-Fujimura Y, Kuraishi H (1983) Analysis of bacterial menaquinone mixtures by high performance liquid chromatography. J Appl Bacteriol 54:31–36
Empadinhas N, Costa MS (2008) Osmoadaptation mechanisms in prokaryotes: distribution of compatible solutes. Int Microbiol 11:151–161
Ventosa A, Nieto JJ, Oren A (1998) Biology of moderately halophilic aerobic bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62(2):504–544
Funding
This research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFD1500300) and the National Science and Technology Fundamental Resources Investigation Program of China (2021FY100900). WJL and SW were also supported by Introduction project of high-level talents in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WJL, SW and LXC designed the research and project outline. SW isolated the bacterium. JYJ and LL performed the genomic data analysis. YTOY, MML, APL and ZTL performed the deposition, physiological and chemotaxonomic experiments. YTOY drafted the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
OuYang, YT., Li, MM., Lv, AP. et al. Oceanobacillus saliphilus sp. nov., Isolated from Saline−Alkali Soil in Heilongjiang Province, China. Curr Microbiol 79, 301 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-022-02997-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-022-02997-0