Abstract
A novel Gram-stain-negative, motile, and facultative anaerobic coccus, strain ChDC F240T was isolated from human subgingival dental plaque of a gingivitis lesion. The phylogenetic analysis based on the 16S ribosomal RNA gene (16S rDNA) sequence showed that the strain belonged to the genus Lautropia. 16S rDNA of strain ChDC F240T had the highest similarity to that of Lautropia mirabilis ATCC 51599T (98.8%). Major cellular fatty acids of strain ChDC F240T were C16:0 (43.9%) and C16:1ω6C/C16:1ω7C (38.1%). Draft genome of the strain was 3,834,139 bp in length and the G+C content was 65.0 mol%. Average nucleotide identity and genome-to-genome distance values between strain ChDC F240T and L. mirabilis ATCC 51599 T were 81.99% and 28.50% (26.1–30.9%), respectively. These results reveal that strain ChDC F240T is a novel species within the genus Lautropia, for which the name Lautropia dentalis sp. nov. is proposed; type strain is ChDC F240T (= KCOM 2505T = JCM 33297T).
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
The genus Lautropia is Gram-stain-negative and facultative anaerobic coccus. It was isolated from a human oral cavity [6]. Lautropia mirabilis has been the only Lautropia sp. till date (https://www.bacterio.net/lautropia.html). Six strains of L. mirabilis were isolated from human saliva sampled from the back of the tongue [6]. This species was also isolated from the sputum of a patient with cystic fibrosis [2] and from the oral cavities of human immunodeficiency virus-infected children [13].
Strain ChDC F240T was isolated from the human subgingival dental plaque of a gingivitis lesion in right maxillary first molar of a male from the Republic of Korea in 2003. According to polyphasic taxonomic characterization, strain ChDC F240T represents a novel species of the genus Lautropia.
Materials and Methods
Bacterial Strain and Culture Conditions
Strain ChDC F240T was grown on tryptic soy agar (TSA; BD Difco Laboratories, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) plate supplemented with 0.5% yeast extract, 0.05% cysteine HCl–H2O, 0.5 mg/ml hemin, and 2 μg/ml vitamin K1 (TSA-YCHVk) [4] at 37 °C in an anaerobic chamber (Bactron I, Sheldon Manufacturing Inc., Cornelius, OR, USA) under 10% H2, 5% CO2, and 85% N2.
Phylogenetic Analysis
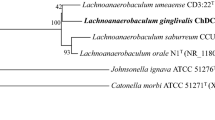
The 16S ribosomal RNA gene (16S rDNA) strain ChDC F240T was cloned and sequenced using PCR and the dideoxy chain termination method as described previously [8]. 16S rDNA sequences of type strains of L. mirabilis and other bacterial species were obtained from GenBank (Fig. 1). Multiple sequences were aligned using the CLUSTAL W algorithm and sequence similarities were calculated using the MegAlign program (DNAStar Lasergene™ 8.0, DNAStar Inc., Madison, WI, USA) [4]. Evolutionary distance was calculated according to the Kimura two-parameter model [9] and phylogenetic trees were constructed by the neighbor-joining method [14] in MEGA 6.06 software [15]. Stability of the phylogenetic trees was assessed by bootstrap analysis [5] of 1000 replicates.
Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on 16S rDNA sequences of strain ChDC F240T and type strains of related species. Stability of the tree was assessed using bootstrap analysis of 1000 replicates with MEGA version 6.06 [15]. Bar = 0.01 changes per nucleotide position. GenBank accession numbers of 16S rDNA sequences of strains were given in parenthesis
Genome Sequence
Genomic DNA of strain ChDC F240T was prepared using the phenol–chloroform extraction method as described previously [4]. The genomic DNA sequencing of the strain was carried out using the Illumina Hiseq 2500 platform by the next-generation sequencing service of the Macrogen Inc. (Seoul, Korea). Two libraries of 350 bp paired-end and 8 kb mate-pair were constructed and sequenced which generated approximately 1127 Mb (294.0×) with 11,160,068 read and 321 Mb (83.9×) with which 3,834,139 reads, respectively. The de novo assembly was performed by SPAdes (https://bioinf.spbau.ru/spades) [1]. All gaps among the scaffolds were filled by GapCloser (https://soap.genomics.org.cn/soapdenovo.html) [11]. Error correction was performed by Pilon (https://platanus.bio.titech.ac.jp/platanus-assembler) [7]. Genome annotation was conducted using the NCBI Prokaryotic Genome Annotation Pipeline through the NCBI Genome Submission Portal (GenomeSubmit at https://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov) [16]. The genome sequence of strain ChDC F240T was deposited at GenBank (Accession Number: RRUE01000000).
Pairwise Genome Comparisons
Average nucleotide identity (ANI) and genome-to-genome (GGD) analyses were performed to discriminate strains ChDC F240T from L. mirabilis at the species level as previously described [10, 12]. GenBank accession number of L. mirabilis ATCC 51599T was NZ_AEQP00000000.1, which was downloaded from GenBank (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome).
Morphological, Physiological, and Chemotaxonomic Characterization and Biochemical Analysis
Cell shape and size were determined under a field-emission scanning electron microscope (S-4800, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan) as previously described [4].
Flagella were stained using Leifson stain solution (1.2% basic fuchsin, 0.75% sodium chloride, and 1.5% tannic acid) and methylene blue as previously described [3]. Light microscope image was taken using a CX43 Biological Microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan).
Optimal growth conditions of strain ChDC F240T that depended on the temperature, pH, and NaCl concentration were investigated as previously described with minor modifications [4]. Briefly, growth at different temperatures (25–55 °C at intervals of 5 °C and 37 °C) and various pH values (5–9.5 at intervals of 0.5) were determined on TSB-YCHVk agar medium for three days in an anaerobic condition. Growth at various NaCl concentrations was assessed in the TP-YCHVk agar medium containing 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5% (w/v) NaCl (pH 7 at 37 °C) for three days in an anaerobic condition.
The cellular fatty acids composition was determined using the MIDI/Hewlett Packard Microbial Identification System (MIDI, Microbial ID, Newark, DE, USA) as previously described [4].
API 20NE and GNI systems (bioMerieux, Marcy-l'Etoile, France) were used to analyze biochemical traits of strain ChDC F240T according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Results and Discussion
Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rDNA revealed that strain ChDC F240T belonged to the genus Lautropia (Fig. 1). Stability of the resulting tree was confirmed by maximum likelihood and minimum evolution methods (Supplementary Fig S1). 16S rDNA sequence of strain ChDC F240T had the highest similarity to that of L. mirabilis ATCC 51599T (98.8%, Supplementary Table S1). Draft genome size of strain ChDC F240T was 3,834,139 bp in length, which was longer than that of L. mirabilis ATCC 51599T (3,137,198 bp). The average G+C content of the strain was 65.0 mol%, similar to those of the strains of L. mirabilis (65.4–65.3 mol%) [6]. ANI and GGD values between strain ChDC F240T and L. mirabilis ATCC 51599T were 81.99% and 28.50% (26.1–30.9%), respectively. Considering that threshold values of ANI and GGD for bacterial species classification were 95–96% and 70%, respectively [10, 12], these finding reveal that strain ChDC F240T is a novel species belonging to the genus Lautropia.
The cellular fatty acid profile of strain ChDC F240T revealed that C16:0 (43.9%) and C16:1ω6C/C16:1ω7C (38.1%) were predominant (Table 1). Cellular fatty acid composition of strain ChDC F240T was similar to those of the strains of L. mirabilis (Table 1).
Flagella staining result revealed that strain ChDC F240T possessed lophotrichous flagella (Supplementary Fig. S2).
API 20NE and GNI test results were summarized in Supplementary Tables S2 and S3, respectively. Strain ChDC F240T could be discriminated by the urease activity and acid production from d-glucose from L. mirabilis (Table 2).
Based on these results, strain ChDC F240T represented a novel species of the genus Lautropia, for which the name Lautropia dentalis is proposed.
Description of Lautropia dentalis sp. nov.
Lautropia dentalis de'n.ta.lis. L. n. dens dentis, a tooth; L. fem. suff. -alis, suffix denoting pertaining to; N.L. fem. adj. dentalis, pertaining to teeth.
Colonies grown on TSA-YCHVk agar are opaque, crisp, and convex with irregular margins. They spread to diameters of sizes that ranged from 0.04 to 0.8 mm after three days at 37C. Cells are Gram-stain-negative, facultative anaerobic, motile, and spherical bacteria with a typical cell size of 2.09 ± 0.75 μm in diameter. Temperature range for their growth was 25–37 °C (optimum: 30–37 °C). The pH range for their growth was 6.5–8.5 (optimum; 7.5). Growth occurred in the presence of 0–1% (w/v) NaCl (optimum: 0.05%). In the API 20NE system, positive reaction is reduction of nitrates to nitrites. From the GNI test results, glutamyl arylamidase and γ-glutamyl-transferase are present. Acid is produced from d-mannitol, d-maltose, and sucrose. The Ellman test is positive. Major cellular fatty acids are C16:0 and C16:1ω6C/C16:1ω7C.
Type strain ChDC F240T (= KCOM 2505T = JCM 33297T) was isolated from human subgingival dental plaque of a gingivitis lesion in the Republic of Korea. The G+C content of type strain is 65.0 mol%.
References
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS, Lesin VM, Nikolenko SI, Pham S, Prjibelski AD, Pyshkin AV, Sirotkin AV, Vyahhi N, Tesler G, Alekseyev MA, Pevzner PA (2012) SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol 19:455–477. https://doi.org/10.1089/cmb.2012.0021
Ben Dekhil SM, Peel MM, Lennox VA, Stackebrandt E, Sly LI (1997) Isolation of Lautropia mirabilis from sputa of a cystic fibrosis patient. J Clin Microbiol 35(4):1024–1026
Breakwell DP, Moyes RB, Reynolds J (2009) Differential staining of bacteria: flagella stain. Curr Protoc Microbiol Appendix 3:Appendix 3G. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780471729259.mca03gs15
Cho E, Park SN, Lim YK, Shin Y, Paek J, Hwang CH, Chang YH, Kook JK (2015) Fusobacterium hwasookii sp. nov., isolated from a human periodontitis lesion. Curr Microbiol 70:169–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-014-0692-7
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Gerner-Smidt P, Keiser-Nielsen H, Dorsch M, Stackebrandt E, Ursing J, Blom J, Christensen AC, Christensen JJ, Frederiksen W, Hoffmann S, Holten-Andersen W, Ying UT (1994) Lautropia mirabilis gen. nov., sp. nov., a gram-negative motile coccus with unusual morphology isolated from the human mouth. Microbiology 140(Pt7):1787–1797
Kajitani R, Toshimoto K, Noguchi H, Toyoda A, Ogura Y, Okuno M, Yabana M, Harada M, Nagayasu E, Maruyama H, Kohara Y, Fujiyama A, Hayashi T, Itoh T (2014) Efficient de novo assembly of highly heterozygous genomes from whole-genome shotgun short reads. Genome Res 24:1384–1395. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.170720.113
Kim HS, Lee DS, Chang YH, Kim MJ, Koh S, Kim J, Seong JH, Song SK, Shin HS, Son JB, Jung MY, Park SN, Yoo SY, Cho KW, Kim DK, Moon S, Kim D, Choi Y, Kim BO, Jang HS, Kim CS, Kim C, Choe SJ, Kook JK (2010) Application of rpoB and zinc protease gene for use in molecular discrimination of Fusobacterium nucleatum subspecies. J Clin Microbiol 48:545–553. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.01631-09
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Lee I, Kim YO, Park SC, Chun J (2016) OrthoANI: An improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:1100–1103. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.000760
Luo R, Liu B, Xie Y, Li Z, Huang W, Yuan J, He G, Chen Y, Pan Q, Liu Y, Tang J, Wu G, Zhang H, Shi Y, Liu Y, Yu C, Wang B, Lu Y, Han C, Cheung DW, Yiu SM, Peng S, Xiaoqian Z, Liu G, Liao X, Li Y, Yang H, Wang J, Lam TW, Wang J (2012) SOAPdenovo2: an empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. Gigascience 1:18 (Erratum in: Gigascience (2015) 4:30)
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform 14:60. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-60
Rossmann SN, Wilson PH, Hicks J, Carter B, Cron SG, Simon C, Flaitz CM, Demmler GJ, Shearer WT, Kline MW (1998) Isolation of Lautropia mirabilis from oral cavities of human immunodeficiency virus-infected children. J Clin Microbiol 36(6):1756–1760
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst197
Tatusova T, DiCuccio M, Badretdin A, Chetvernin V, Nawrocki EP, Zaslavsky L, Lomsadze A, Pruitt KD, Borodovsky M, Ostell J (2016) NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res 44:6614–6624. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw569
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (2017M3A9B8065844), in part by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (2018R1A2B5002239), and in part by the KRIBB Research Initiative Program funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
DPD number: TA00934. GenBank accession number of 16S rRNA gene for strain ChDC F240T: MK748163. GenBank accession number of genome for strain ChDC F240T: RRUE01000000.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
284_2019_1761_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplementary material 1 (DOCX 42 kb) Supplementary Fig S1. Maximum likelihood (A) and the minimum evolution (B) phylogenetic trees based on 16S rDNA sequences of strain ChDC F240T and type strains of related species. Stability of phylogenetic trees was assessed by bootstrap analysis of 1,000 replicates with MEGA version 6.06 [15]. Bars indicate 0.01 (A) or 0.01 (B) changes per nucleotide position. GenBank accession numbers of 16S rDNA sequences of strains were given in parenthesis.
284_2019_1761_MOESM2_ESM.pptx
Supplementary material 2 (PPTX 1234 kb) Supplementary Fig S2. Flagella were stained using Leifson stain solution and methylene blue. Light microscope image was taken using a CX43 Biological Microscope. Arrows indicate the flagella. Original magnification: ×1,000. Bar = 30 μm.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, Y.K., Park, SN., Lee, WP. et al. Lautropia dentalis sp. nov., Isolated from Human Dental Plaque of a Gingivitis Lesion. Curr Microbiol 76, 1369–1373 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-019-01761-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-019-01761-1