Abstract
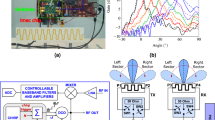
In this research work, we are locating the moving objects or targets inside a building. It is sensor technology, and standoff distance outstandingly increases for the classical urban battlefield. In this study, a thermal image has to be developed based on cross-range vs down range mechanism; these tracks the moving targets with a video frame rate. This mechanism had to design based on S-band frequency and TDMA-MIMO antenna array. The continuous wave modulating scheme acquires the image and display at the frame rate of 10.80 Hzs. The maximum allowed range is 20 m concrete wall and thickness of 20 cm. This modern system can locate humans either in moving or in standing positions, behind 20 m thickness of the concrete wall. The results challenging the present technologies and outperforms the performance metrics.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Charvat, G.L.: A low-power radar imaging system. PhD dissertation, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Michigan State University, East Lansing, Michigan, August 2007
Charvat, G.L., Kempel, L.C., Rothwell, E.J., Coleman, C., Mokole, E.J.: An Ultrawideband (UWB) switched-antenna-array radar imaging system. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Phased Array Systems and Technology (2010)
Ralston, T.S., Marks, D.L., Carney, P.S., Boppart, S.A.: Real-time interferometric synthetic aperture microscopy. Opt. Express 16(4), 2555–2569 (2008)
Charvat, G.L., Kempel, L.C., Rothwell, E.J., Coleman, C., Mokole, E.L.: A through-dielectric radar imaging system. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 58(8), 2594–2603 (2010)
T.S. Ralston, G.L. Charvat, and J.E. Peabody, “Real-Time Through-Wall Imaging using an Ultrawideband Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) Phased-Array Radar Sys-tem,” Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Phased Array Systems and Technology, pp. 551–558, 2010.
Charvat, G.L., Ralston, T.S., Peabody, J.E.: A through-wall real-time MIMO radar sensor for use at stand-off ranges. MSS Tri-Services Radar Symposium, Orlando, Florida (2010)
Carrara, W.G., Goodman, R.S., Majewski, R.M.: Spotlight synthetic aperture radar signal processing algorithms. Bos-ton: Artech House (1995)
Marchand, P.R.H.: Penetration losses in construction materials and buildings. MIT Lincoln Laboratory Project Report TR-ACC-1, Rev. 1, 19 July 2006
Vo, B.N., Ma, W.K.: The Gaussian mixture probability hypothesis density filter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 54(11), 4091–4101 (2006)
Syahrim, N., Anwar, N.: Multiple line cracks in concrete material. Int. J. Hum. Technol. Interact. 2 (2018)
Kaushal, S., Singh, D.: Sensitivity analysis of microwave UWB radar for TWI system. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 12(19), 8665–8675 (2017)
Liang, F., et al.: Through the wall imaging of human vital signs based on UWB MIMO bioradar. Progress Electromagnet. Res. C 87, 119–133 (2018)
Gennarelli, G., Soldovieri, F.: Radar imaging through cinderblock walls: Achievable performance by a model-corrected linear inverse scattering approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 52(10), 6738–6749 (2014)
Miao, Z., Kosmas, P.: Cmpact of information loss on reconstruction quality in microwavetomography for medical imaging. Diagnostics 8(52), 1–15 (2018)
Nawawi, J., Sahrani, S., Anak, K., Ping, H.: Automated scaling region of interest with iterativeedge preserving in forward-backward time-stepping. Progress Electromagnet. Res. 67, 177–188 (2018)
Joseph, E.J., et al.: Integration of image segmentation method in inverse scattering for braintumour detection. Progress Electromagnet. Res. 61, 111–122 (2017)
Ping, K.H., Ng, S.W., Yong, G., Rajaee, N.: Elliptic filter and iterative inversion method forburied object detection applications. Appl. Mech. Mater. 833, 164–169 (2016)
Elizabeth, M.A.P., Hong Ping, K.A., Rajaee, N.B., Moriyama, T.: Chebyshev filter applied to an inversion technique for breast tumour detection. Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol.4(5), 1–9 (2015)
Yong, G., et al.: Profile reconstruction utilizing forward-backward time-stepping with the integration of automated edge-preserving regularization technique for object detection applications. Progress Electromagnet. Res. M 54, 125–135 (2017)
Jamali, N.H., Anak, K., Ping, H., Sahrani, S.: Image reconstruction based on combination of inverse scattering technique and total variation regularization method. Indonesian J. Electric. Eng. Comput. Sci. 5(3), 569–576 (2017)
Xu, K., Zhong, Y., Chen, X., Lesselier, D.: A fast integral equation based method for solving electromagnetic inverse scattering problems with inhomogeneous background. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 66(8), 4228–4239 (2018)
Gorji, A.B., Zakeri, B.: Time-reversal through-wall microwave imaging in rich scattering environment based on target initial reflection method time-reversal through-wall microwave imaging in rich scattering. Appl. Comput. Electromagn. Soc. J. 30, 625–637 (June 2015)
Selesnick, I., Rizzo, J., Rucker, J., Hudson, T.: A nonlinear generalization of the Savitzky-Golayfilter and the quantitative analysis of saccades. J. Vis. 9, 1–15 (2017)
Liu, Y., Dang, B., Li, Y., Lin, H., Ma, H.: Applications of Savitzky-Golay filter for seismicrandom noise reduction. Acta Geophys. 64(1), 101–124 (2016)
Liang, X., Deng, J., Zhang, H., et al.: Ultra-wideband impulse radar through-wall detection of vital signs. Sci. Rep. 8, 13367 (2018)
Kebe, M., Gadhafi, R., Mohammad, B., Sanduleanu, M., Saleh, H., Al-Qutayri, M.: Human vital signs detection methods and potential using radars: a review. Sensors 20, 1454 (2020)
Liang, S.D.: Sense-through-wall human detection based on UWB radar sensors. Signal Process. 126, 117–124 (2016)
Gu, C., Li, C.: Assessment of human respiration patterns via noncontact sensing using doppler multi-radar system. Sensors 15, 6383–6398 (2015)
Lazaro, A., Girbau, D., Villarino, R.: Techniques for clutter suppression in the presence of body movements during the detection of respiratory activity through UWB radars. Sensors 14, 2595–2618 (2014)
Chuantao, L., et al.: A method for remotely sensing vital signs of human subjects outdoors. Sensors 15, 14830–14844 (2015)
Duan, Z., Liang, J.: Non-contact detection of vital signs using a UWB radar sensor. IEEE Access 7, 36888–36895 (2019)
Liang, X., Lv, T., Zhang, H., Gao, Y., Fang, G.: `Through-wall human being detection using UWB impulse radar. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2018(1), 1–17 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13638-018-1054-0
Yoo, S., Chung, S., Seol, D., Cho, S.H.: Adaptive clutter suppression algorithm for detection and positioning using IR-UWB Radar. In: 2018 9th International Conference on Ultrawide band and Ultrashort Impulse Signals (UWBUSIS), Odessa, pp. 40–43 (2018)
Pardhu, T., Kumar, V.: Reduction of Clutter using TWI Ultra-wide band Imaging. Int. J. Ultra-Wideband Commun. Syst. 3(2), 101–105 (2015)
Pardhu, T., Kumar, V.: An investigation of human identification behind the wall. J. Adv. Res. Dyn. Control Syst. 10(5), 122–129 (2018)
Pardhu, T., Kumar, V.: Implementation of TWI using UWB RADAR Signals. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Applications of Soft Computing Techniques in Engineering & Technology , Supported by IET (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Thottempudi, P., Dasari, V.S.C.B., Sista, V.S.P. (2022). Recognition of Moving Human Targets by Through the Wall Imaging RADAR Using RAMA and SIA Algorithms. In: Mandal, J.K., De, D. (eds) Advanced Techniques for IoT Applications. EAIT 2021. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 292. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-4435-1_53
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-4435-1_53
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-4434-4
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-4435-1
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)