Abstract
A new topology for solar photovoltaic (PV) energy conversion system is used in this paper. Various topologies are available nowadays which have several problems associated with using several blocks and in its performance analysis of the system from the stability point of view like DC-DC converter, low-frequency transformer, maximum power point tracking [MPPT] block, unfold circuit like push-pull circuit, etc. New types of topology for solar photovoltaic energy conversion systems have been shown which bypass the MPPT separate block units, unfold circuit, low-frequency transformer. By the use of current-controlled inverter integration of MPPT along with the DC-DC to AC conversion takes place inside a single block which reduces the number of blocks helping in getting a simple transformation block for the stability analysis. With the help of Phase Locked Loop (PLL) quadrature axis voltage can set to zero so that only direct axis voltage is used which corresponds to a single PI controller which again reduces one set point type tracking controller. Currents which are injected into the grid contains harmonics, THD generated form inverter is approximately 10% only, which can be further reduced by 5% by using simple suitable LC filter. MATLAB simulation depicts the whole work.
Access provided by Autonomous University of Puebla. Download conference paper PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
- Current controlled inverter
- Phase-locked loop
- Integrated maximum power point tracking
- Set-point controller
1 Introduction
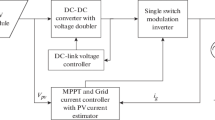
MPPT controller (DC-DC circuit) can be of any type either isolated or non-isolated type. It ensures the load line attributes with respect to PV terminals so that maximum power can be drawn from the photovoltaic cell. An old topology that includes various blocks like separate MPPT block, DC-DC converter (Buck–Boost), Unfold circuit, push–pull circuit, low-frequency transformer is used. In the new topology, DC-DC converter and unfolding circuit are replaced by a single power stage block called current controlled inverter. Low-frequency transformer which is present at the right side is shifted to the high-frequency side, i.e. into the dc-dc converter. Low frequency transformer is bulky to use in this circuit. Isolation of transformer from the circuit is necessary from any type of discharging of currents which leads to shock, for this flyback converter topology is used which is an isolated version of buck-boost topology. DC-DC converter is eliminated by the use of current-controlled inverter. Inverter is doing current control with the help of inductor current which is actually being pumped into the grid is being controlled, then the MPPT algorithm can be used for the terminal currents of the photovoltaic panel. The stability analysis of the terminal voltage can be seen in [1–3], similarly the terminal voltage of the photovoltaic can be measured and the power that is obtained can be pass through the maximum power point tracking algorithm. The output of the reference current for the inverter will be appropriately modulated in such a way that the desired current flows through it and maximum power will be achieve from the photovoltaic panel [4]. In [5, 6], the simulink model of hybrid system can be observed and also in this way this topology works, where is only one power stage which is coming between the photovoltaic module and the grid (Figs. 1 and 2).
2 Three-Phase Grid Connection
The three-phase inverter, there are six gates (let we are using IGBT or MOSFET, for this six gate drive terminals are required, gate drive is getting the control signal from PWM block for RYB phases [7]. Now the input to the PWM will be control signals coming from the output of controllers. Now, to control the inductor current that is being pumped into the grid. Again, with the help of a comparator an Ig reference can be compared. Now, it compare current with the value of ig reference and then pass it to the controller block it could be PI controller. Each phase of the three phases are need to compare and control the output of controllers which will give it to the PWM block. So let us say each of the controllers is connected to PWM. Currents are sensed compared with a reference and based on the error the controller output will send the signal to the PWM which compares with the triangle carrier and then appropriately gives the PWM drive to each of the arms of the inverter with proper energy management [8]. These references \(i_{\text{gR}}^{*}\), \(i_{\text{gY}}^{*}\), \(i_{\text{gB}}^{*}\) are obtained from the MPPT algorithm. All the three currents are sensed by using a hall sensor or alternatively resistive shunt and differential amplifiers, instrumentation amplifiers can be used but hall sensor is better because it is contactless and has large bandwidth. VT and IT are measured by another hall sensor for MPPT block. Input to MPPT is VT and IT and output are \(i_{\text{gR}}^{*}\), \(i_{\text{gY}}^{*}\), \(i_{\text{gB}}^{*}\) (These are sinusoidal values).
3 Controller
However there are lots of drawbacks in this particular type of the circuit, first of all, the references \(i_{\text{gR}}^{*}\), \(i_{\text{gY}}^{*}\), \(i_{\text{gB}}^{*}\) are sinusoidal. They are not DC or setpoint value. The controller becomes a tracking controller it is no longer a setpoint controller reference current signal and feedbacks current signal all are AC sinusoidal in general.
Tracking controller needs to handle large signal deviation as the consequence the B.W of tracking controller will be lower compared to a similar setpoint controller, if \(i_{\text{gR}}^{*}\) and feedback signal have DC. So, design of tracking controller will be much more complex compare to a set point controller and DC to DC converter in power system [9]. It can also able to achieve intra cycle dynamics if one user setpoint controller but for the tracking controller only integral cycle dynamics can be achieved. Another problem is here three separate controllers one for each phase and the dynamics are coupled, so fining the three controllers simultaneously will become difficult as the dynamics are coupled. So those issues should be short out for the controller for three-phase photovoltaic grid-connected inverters [10] in the control methodology.
4 Current Controlled Inverter
Input to PWM is reference Va, Vb, Vc (as desired) which will be compare with the carrier triangle which PWM has and then generate the necessary PWM signals (pulse). For the gate drive to switch ON and OFF accordingly and supply a voltage here such that ia, ib, ic flows according to this control such that error just before PT is zero. Now to define ρ, angle between the d axis and α axis so that both coordinate systems rotates synchronously. α, β coordinate system has current space vector id get aligned along the current space vector that is iq is equal to zero because id is aligned itself along grid current. We use Va, Vb, Vc voltage waveforms to obtain ρ then id and iq will be such that it will be with the respect to the voltage space vector as the d-axis and it has an advantage. Let we take angle ρ between Vα and α axis also Vg is not along Vd and Vq is not equal to zero. Then we get some error the PT activates and PI controller will work in such a way that error to PI tends to zero. Then Vq is equivalent to \(V_{\text{q}}^{*}\) which is equal to zero and d-axis will go and aligned along Vg voltage space vector and such a value of ρ (ρ will increase while aligning) will come up because of control action such that Vq is equal to zero here. In this way, ρ gives the value of difference between dq axis and αβ coordinate system such that d-axis aligned along the voltage space vector.
So, it becomes a robust mechanism because it is a close loop system and then there is PI component that has a history in it which will have a filtering effect on harmonics, surges, spikes, and uncertainties. So by incorporating this modification into our entire three phase grid-connected inverter block diagram, it will be a completely workable solution like other PV inverters used in [11, 12]. So we modify ρ-generation block.
5 SPWM (Unipolar PWM Technique)
According to IEEE—5/19/992-for household appliances total harmonic distortion (THD) is less than five percent. So we can just attach a simple AC filter like LC filter in order to reduce harmonics which is injected into the grid without using complex AC filter also we can make THD less than five percent or by using base works as a filter. This can be achieved by using a sinusoidal PWM technique in which we should use less filter (Fig. 3).
6 Detailed Comparisons of Older Photo-Voltaic Conversion Topology with Respect to New One
Various topologies are available in the past in which separate DC-DC converter [9] which can be of any type of isolated or non-isolated type are present whose work is just to match load line to the PV terminals in such a way that maximum power [13, 14] can be drawn from the PV cell. Unfolding circuit which is basically a two-way switch type which switches ON alternatively can be replaced by a more popular bridge stage which is decoupled from the isolating stage. In the new topology, DC-DC converter and unfolding stage are replaced by a single power stage which is called the inverter. This leads to an increase in the efficiency of this model. Power transformer is of low frequency which is bulky, heavy, and expensive, so in this electronic model, the transformer is shifted to DC-DC converter so that it can work as high switching frequency which thereby reduces its weight, size, and works with increased efficiency. System becomes more compact. This leads to transformerless interface. In this high-frequency isolation flyback converter topology which is the isolated version of the buck-boost topology that can handle the entire first quadrant of the curve of the PV module is used. Further, improve on this topology by the use of current-controlled inverter, DC-DC converter is eliminated which is doing the job of maximum power point tracking. MPPT is done by the current-controlled inverter [15] itself, there is inductor current which is pumped into the grid is being controlled, then the maximum point algorithm is used for the terminal currents and the terminal voltage of the PV panel are measured and power that is obtained is pass through the maximum power point tracking algorithm..
7 Proposed Model of PV Energy Conversion System in MATLAB
See Fig. 4.
8 Simulated Result
See Fig. 5.
9 Parameters with Different Rated Values Used
See Table 1.
10 Conclusion
Setpoint controllers only two have been used (while we need three for AC tracking type controller). Working with DC values is easy because it is difficult to compare changing values of magnitude of AC which is changing with respect to time with the reference values for comparison. MPPT is integrated into the invertors by removing the DC-DC converter and power block is simple (just has one power stage) so that the analysis from the stability point of view becomes easy and the efficiency of the model is increased. Robust Phase Locked Loop (PLL) based on ρ determination is done as the current is injected into the grid via current terminals contain harmonics. So getting ρ we converted current terminals into voltage terminals with the help of proper transformation. In PLL open-loop becomes closed-loop by doing certain modifications, in this way it becomes robust a robust mechanism there is proportional-integral (PI) component there is history in it which will filtering the effect on harmonics, surges and spikes.
References
IEEE TF Report (1982) Proposed terms and definitions for power system stability. IEEE Trans Power Appart Syst PAS-101:1894–1897
Banerjee A, Mukherjee V, Ghoshal SP (2013) Modeling and seeker optimization based simulation for intelligent reactive power control of an isolated hybrid power system. Swarm Evol Comput 13:85–100
Kundur P et al (2004, Aug) Definition and classification of power system stability IEEE/CIGRE joint task force on stability terms and definitions. IEEE Trans Power Syst 19(3):1387–1401. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRS.2004.825981
Dinga Z, Houa H, Yua G, Hub E, Duana L, Zhaoc J (2019) Performance analysis of a wind solar hybrid power generation system. Elsevier
Onara OC, Uzunoglua M, Alama MS (2018) Modeling, control and simulation of an autonomous wind turbine/photovoltaic/fuel cell/ultra-capacitor hybrid power system. Elsevier
Tsai HL, Tu CS, Su YJ (2008) Development of generalized photovoltaic model using MATLAB/Simulink. In: Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering and Computer Science (WCECS’08), San Francisco, USA, 22–24 Oct 2008
Figueres E, Garcera G, Sandia J et al (2009) Sensitivity study of the dynamics of three-phase photovoltaic inverters with an LCL grid filter. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 706–717
Dali M, Belhadj J, Roboam X (2010) Hybrid solar–wind system with battery storage operating in grid-connected and standalone mode: control and energy management–experimental investigation. Energy 35(6):2587–2595
Banaei M, Ardi H, Alizadeh R et al (2014) Non-isolated multi-input-single output DC/DC converter for photovoltaic power generation systems. IET Power Electron 7(11):2806–2816
Kroutikova N, Hernandez-Aramburo C, Green T (2007) State-space model of grid-connected inverters under current control mode. IET Electr Power Appl 1(3):329–338
Fazeli M, Ekanayake J, Holland P et al (2014) Exploiting PV inverters to support local voltage—A small-signal model. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 29(2):453–462
Fortunato M, Giustiniani A, Petrone G et al (2008) Maximum power point tracking in a one-cycle controlled single-stage photovoltaic inverter. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 55(7):2684–2693
Patel H, Agarwal V (2008) Maximum power point tracking scheme for PV systems operating under partially shaded conditions. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 55(4):1689–1698
Noguchi T, Togashi S, Nakamoto R (2002) Short-current pulse-based maximum-power-point tracking method for multiple photovoltaic-and converter module system. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 49(1):217–223
Feng J, Wang H, Xu J et al (2017) A three-phase grid-connected microinverter for AC photovoltaic module applications. IEEE Trans Power Electron
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Maurya, S., Banerjee, A. (2020). A New Topology for Photo Voltaic Energy Conversion System. In: Mallick, P.K., Meher, P., Majumder, A., Das, S.K. (eds) Electronic Systems and Intelligent Computing. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 686. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-7031-5_59
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-7031-5_59
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-7030-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-7031-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)