Abstract
Glochidion eriocarpum is a shrub in the family Phyllanthaceae. The whole plant, stem bark, roots, and leaves are used for medicinal purposes by ethnic people in China to treat lacquer poison, convergence, diarrhea, dampness, and itching. As the intense research on chemical constituents, pharmacological activity and the active principles of G. eriocarpum have attracted the interest to the discovery of new drugs. This review summarizes the traditional uses of G. eriocarpum and its chemical constituents, pharmacological effects, and clinical applications with some suggestions for future research.
Access provided by Autonomous University of Puebla. Download chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
1 Introduction
Glochidion eriocarpum Champ. ex Benth. is a shrub in the family Phyllanthaceae (earlier included in Euphorbiaceae). The medicinal value of the genus Glochidion has attracted the interest of many scholars at home and abroad, and many patents have reported compounds from this genus for the treatment of certain diseases.
China is a rich country with abundant plant resources in the world. There are 37,500 plant species; 11,146 species of plants are used by people to treat diseases. Glochidion eriocarpum is a national plant in southwestern China and is widely used by many ethnic groups. The species is mainly distributed in China (Jiangsu, Fujian, Taiwan, Hunan, Guangdong, Hainan, Guangxi, Guizhou, Yunnan, etc.), Laos, Thailand, and Vietnam, growing on hillsides, valleys, or forest edges at an altitude of 130–1600 m (Luo and Sun 2013). Especially in China, the whole plant, root, and leaf of Glochidion eriocarpum are used for medicinal purposes. And it is commonly used to address hepatitis, intestinal diseases, diarrhea, urticaria, mastitis, toothache, menorrhagia, dysentery, skin eczema, and other diseases (Liu 2012). Thus, the medicinal value of the genus Glochidion has aroused the interest of many scholars at home and abroad. Some patents have reported that compounds from this genus were used to treat chronic and acute osteomyelitis, cirrhosis, chronic gastritis, hepatitis B, liver ascites, and malignant tumors. However, the scientific evidence of the abundant use value of this plant is still lacking. This paper summarizes various methods of utilizing this plant by Chinese people and chemical structure and pharmacological activities of Glochidion eriocarpum in the recent 10 years. We hope by systematically summarizing the research of the Glochidion eriocarpum we can further broaden the development and utilization prospects of the plant and provide clues and scientific theoretical basis for further research and development of the resource.
2 Folk Value of Glochidion eriocarpum
In China, Glochidion eriocarpum is a kind of important ethnic medicinal plant resource widely used by many people (Table 25.1). There are three ethnic medicinal formulas that record Glochidion eriocarpum for the treatment of gynecological inflammation, urinary stones, and detoxification. It can also be used as a dietary fiber in diet therapy. Studies have shown that Glochidion eriocarpum has anti-Helicobacter pylori (Zhang and Wang 2008) , which can be scientifically validated as a mechanism for treating stomach pain and gastric ulcer in Zhuang medicine. At the same time, they are used in other countries such as Vietnam for the treatment of asthma, enteritis, cholera, indigestion, rheumatism, etc. (Nhiem et al. 2012). In Laos, they were treated to treat postpartum recovery, anemia (dizziness, headache), mild puerperal fever, and abdominal pain (Vichith et al. 2011).
2.1 Chemical Constituents of Glochidion eriocarpum
There are 50 compounds isolated and identified from Glochidion eriocarpum, mainly quinones and glycosides extracted from the roots, stems, and leaves in addition to containing aromatic compounds, steroids, and other compounds.
2.1.1 Terpenoids
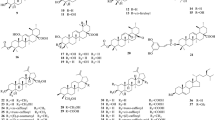
Terpenoids are the main components of the Glochidion eriocarpum, and they are ubiquitous in the plant kingdom which is the generic term for all isoprene polymers and their derivatives (Shi et al. 2012). Terpenoids have many biological activities, such as anticancer, anti-allergy, and anti-HIV (Chen and Li 2016), with important medicinal and economic value (Fu et al. 2003). Twenty-eight terpenoids, the highest proportion of Glochidion eriocarpum chemical constituents, and each part of the plant have contained terpenoids with good biological activities (Table 25.2, Fig. 25.1).
2.1.2 Glycoside Compounds
Glycosides are widely distributed in the roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and fruits of plants. It has the efficacy of eliminating phlegm and relieving cough (Liu et al. 2013), nourishing, treating rheumatism (Su 2016), lowering cholesterol, being anti-inflammatory and antibacterial (Peng et al. 2014) , improving immune regulation, being antitumor (Wang et al. 2014), and other effects. Glochidion eriocarpum contains 10 kinds of saponins and has good activity in improving human immunity (Table 25.3, Fig. 25.2).
2.1.3 Other Compounds
In addition to terpenoids and glycosides, the chemical components of Glochidion eriocarpum were also found: bergenin, steroids (β-sitosterol, stigmasterol), octadecanoic acid, tetradecyl ester, octanol, myristic acid, lauric acid, etc.
3 Pharmacological Activity
3.1 Antitumor Activity and Cytotoxic Activity
So far, the research on Glochidion eriocarpum in China and abroad has focused on its cytotoxic activity and antitumor activity, but there are few studies on new compounds and pharmacological activities. In 2009, two triterpenoid glochieriosides A and B from Glochidion eriocarpum were reported (Otsuka et al. 2000). The results showed that these two compounds have cytotoxic activity against four human cancer cells such as HL-60, HT-29, MCF-7, and SK-OV-3. Studies have shown that glochidonol exhibits strong cytotoxic activity on human breast cancer (MCF-7), lung cancer (NCI-H460), and prostate cancer (DU-145) (Bagalkotkar et al. 2011). Glochidone and lupeol have significant anti-malignant tumor growth effects and are very sensitive and have inhibitory effects on cancerous lung cells (Sakkrom et al. 2010). At the same time, glochidiol, lup-20(29)-ene-1α,23-diol, glochidone, and 3-epi-lupeol have cytotoxic effects on human hepatocellular carcinomas (Xiao et al. 2008). Further experiments showed that glochidonol and glochidiol have the effect of preventing the proliferation of malignant tumors, but lup-20(29)ene-3α,23-diol does not (Puapairoj et al. 2005) . In vivo experiments have shown that glochidiol has a strong inhibitory effect on mouse skin tumors (Tanaka et al. 2004).
3.2 Anti-inflammatory and Analgesic Effects
Phyllanthus urinaria was studied by Brazilians to show that its extract has analgesic effect. Chemical composition studies of P. urinaria extracts by chromatography and GC indicated that β-sitosterol, glochidonol, and glochidone were present in the extract (Catapan et al. 2001). Glochidone has significant antinociceptive effects on writhing and formalin tests (Krogh et al. 1999) suggesting that these compounds may have analgesic effects. Glochidion puberum extracts have significant anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects, and their effects may be related to the reduction of histamine content in the inflammation sites (Huang 2010). Glochidion eriocarpum may have the same effect.
3.3 Antioxidant Activity
Each extracted part of Glochidion puberum has a different in vitro antioxidant capacity (Hu et al. 2014). Pharmacological studies have shown that most of Glochidion species exhibit antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects. The dominant ingredient, lupin-type triterpenoids, has potential antitumor activity and antiviral effect. There are few studies on its chemical components and active ingredients in China. It is necessary to conduct in-depth research on the substance basis of its efficacy (Ganguly et al. 1968; Puapairoj et al. 2004) .
3.4 Others
Some patents have reported that some plants and their compounds of Glochidion can treat some diseases. For example, Glochidion puberum and its compound can treat chronic and acute osteomyelitis, chronic gastritis, hepatitis B, liver cirrhosis, liver ascites, and malignancy and assist in the treatment of hepatitis, intestinal diseases, diarrhea, and acute and chronic enteritis (Li 2007). Glochidion eriocarpum may contain the same chemical constituents as the Glochidion zylanicum root extract. The experiment shows that the water extract has inhibitory effect on Flavobacterium tegecticola (Sharma et al. 2010).
4 Conclusion
Glochidion eriocarpum is an ethnomedicinal plant in southwestern China. The study on its chemical composition and pharmacological effects can promote the standardization of Glochidion eriocarpum materials and provide theoretical guidance for its use, so as to further develop this ethnomedicine. So far, most of the 50 compounds extracted from Glochidion eriocarpum have good activity, and a small number of them are cytotoxic. They can be strengthened by structural modification and structure-activity relationship to discover new active lead compounds. However, the current research on the chemical composition of Glochidion eriocarpum mainly focuses on the component extraction and activity research; its activity, mechanism, and biosynthetic route and the development of ethnic medicine products need to be further explored; research on these can better develop the plant resources of Glochidion eriocarpum.
References
Bagalkotkar G, Tang SC, Khalivulla SI, Hamzah AS, Shaari K, Lajis NH, Stanslas J (2011) Isolation and cytotoxicity of triterpenes from the roots of Phyllanthus pulcher Wall. ex Müll.-Arg. (Euphorbiaceae). Afr J Pharm Pharmacol 5(2):183–188
Catapan E, Otuki M, Am Yunes R, Bresciani L, Ferreira J, Santos A, Cechinel-Filho V (2001) Pharmacological activity and chemical composition of callus culture extracts from selected species of Phyllanthus. Pharmazie 55(12):945–946
Chen JZ, Li CY (2016) Research progress on anti-HIV steroids in natural products. Asia-Pac Trad Med 12(7):54–59
Fu J, Wang Y, Qi XF (2003) Ecophysiological functions and economic value of terpenoids. J Northeast For Univ 31(6):59–62
Ganguly AK, Govindachari TR, Mohamed PA (1968) Chemical constituents of Glochidion hohenackeri. Tetrahedron 22(4):1513–1519
Hu DQ, Han ZX, Hu JH (2014) The screening of antioxidative active parts of plate leaves by hairy fruit. J Hubei Univ Trad Chin Med 16(4):51–54
Huang AJ (2010) An experimental study on the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of the extract from Glochidion puberum. J Hubei Inst Natl Med Sci 27(4):17–19
Hui WH, Li MM (1976) Lupene triterpenoids from Glochidion eriocarpum. Phytochemistry 15(4):23–26
Kiem PV, Thu VK, Yen PH, Nhiem NX, Tung NH, Cuong NX, Kang HK (2009) New triterpenoid saponins from Glochidion eriocarpum and their cytotoxic activity. Chem Pharm Bull 57(1):102–103
Krogh R, Kroth R, Berti C, Madeira AO, Souza MM, Cechinelfilho V, Yunes RA (1999) Isolation and identification of compounds with antinociceptive action from Ipomoea pes-caprae (L.) R. Br. Pharmazie 54(6):464–466
Li GY (2007) Two treatments of single Chinese medicine. Chin Naturopathy 15(1):22–23. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1007-5798.2007.01.027
Liu N (2012) Progress in studies on chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Glochidion, and the chemical constituents of Glochidion lanceolarium. Dissertation, Northwest Normal University
Liu Q, Li W, Zheng YN, Wu HF (2013) Research progress of three terpenoid saponins and their pharmacological activities in Platycodon grandiflorus. J Jilin Agric Univ 35(2):221–228
Luo YC, Sun QW (2013) Commonly used natural medicines in Guizhou Ethnic Groups, vol 2. Guizhou Sci Technol Press, Guiyang
Nhiem NX, Thu VK, Van KP, Van MC, Tai BH, Quang TH, Kang JI (2012) Cytotoxic oleane-type triterpene saponins from Glochidion eriocarpum. Arch Pharm Res 35(1):19–23
Otsuka H, Hirata E, Shinzato T, Takeda Y (2000) Isolation of lignan glucosides and neolignan sulfate from the leaves of Glochidion zeylanicum (Gaertn) A. Juss. Chem Pharm Bull 48(7):1084–1086
Peng SL, Zhang W, Li Y (2014) Research progress in the function and mechanism of Bupleurum saponin. J Jinlin Med Coll 35(1):66–68
Puapairoj P, Naengchomnong W, Kijjoa A, Pinto MM, Pedro M, Nascimento MS, Herz W (2005) Cytotoxic activity of lupane-type triterpenes from Glochidion sphaerogynum and Glochidion eriocarpum two of which induce apoptosis. Planta Med 71(3):208–213
Puapairoj P, Naengchomong W, Kijjoa A et al (2004) Cytotoxic activity of lupane-type triterpenes from Glochidion sphaerogynum and Glochidion eriocarpum. Planta Med 70(9):1234–1236
Sakkrom P, Pompimon W, Meepowpan P, Nuntasaen N, Loetchutinat C (2010) The effect of Phyllanthus taxodiifolius Beille extracts and its triterpenoids studying on cellular energetic stage of cancer cells. Am J Pharm Toxicol 5(3):139–144
Sharma JVC, Malleswari G, Rao JV, Muralibalaram V, Sangeetha R (2010) Antimicrobial activity of root extracts of Glochidion zylanicum. Int J Chem Sci 3(1):35–37
Shi RB, Jiang YY, Wang Z, Wang YY (2012) On the recent development of Chinese medicinal chemistry. J Beijing Univ Trad Chin Med 35(3):153–159
Su XF (2016) Extraction, purification and antioxidant activity of total flavonoids from Sambucus williamsii leaves. Shanxi Norm Univ 2(2):219–228
Tanaka R, Kinouchi Y, Wada S, Tokuda H (2004) Potential anti-tumor promoting activity of lupane-type triterpenoids from the stem bark of Glochidion zeylanicum and Phyllanthus flexuosus. Planta Med 70(12):1234–1235
Vichith L, De BHJ, Lars B (2011) Traditions and plant use during pregnancy, childbirth and postpartum recovery by the Kry ethnic group in Lao PDR. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed 7(1):14–15
Wang Y, Shao RG, Jiang JD, Wang Z (2014) Progress in research on mechanisms of antitumor effects of cardiac glycosides. Chin New Drugs J 27(6):677–681
Wang YM (2014) Studies on the chemical constituents and bioactivities of Gentiana dahurica and Glochidion eriocarpum. Kunming Bot 24(5):324–325
Wei XM (2001) Research on chemical constituents of Clinopodium urticifolium, Clerodendrum serratum and Glochidion eriocarpum. Lanzhou Univ 51(5):1043–1049
Xiao HT, Wang YH, Hao XY, Yang XS, Hao XJ (2008) Triterpenes from Glochidion coccineum and their cytotoxicity in vitro. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res 57(1):102–103
Zhang Y, Wang Y (2008) Screening study on the role of Chinese herbal medicine and Zhuang medicine in the treatment of Helicobacter pylori in Guangxi. Chin J Ethnomed Ethnopharm 17(10):19–20
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Key Laboratory of Ethnomedicine (Minzu University of China) of Ministry of Education of China (KLEM-ZZ201906), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31761143001, 31870316, 31161140345, and 31660083), Minzu University of China (Collaborative Innovation Center for Ethnic Minority Development, yldxxk201819), Ministry of Education of China, and State Administration of Foreign Experts Affairs of China (B08044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Zhang, B., Liu, S., Lei, Q., Zhou, J., Long, C. (2020). Phytochemical Constituents and Pharmacological Activities of a Traditional Medicinal Plant, Glochidion eriocarpum (Phyllanthaceae). In: Khasim, S.M., Long, C., Thammasiri, K., Lutken, H. (eds) Medicinal Plants: Biodiversity, Sustainable Utilization and Conservation. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-1636-8_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-1636-8_25
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-1635-1
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-1636-8
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)