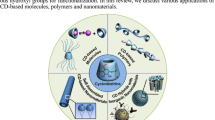
Abstract
Supramolecular hybrid inorganic nanocomposites, as a burgeoning type of hybrid nanomaterials, have been prepared by anchoring macrocyclic organic molecules and supramolecules onto inorganic nanoscaffolds. Macrocyclic organic molecules, such as crown ethers, cryptands, calixarenes, cucurbiturils, pillararene, and cyclodextrins, have frequently been used as building blocks for supramolecular hybrid inorganic materials. These macrocyclic molecules anchoring onto the surface of inorganic nanomaterials particularly act as the valid host molecules that one or more “guest” molecules can bind to a “host” cavity reversibly. Among the various macrocyclic molecules, native and modified cyclodextrins (CDs) have long been recognized as the host molecules with inherent hydrophobic internal cavity and hydrophilic external surface in host-guest chemistry ; therefore, much attention of CDs has attracted in the construction of supramolecular hybrid inorganic nanomaterials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rekharsky MV, Inoue Y (1998) Complexation thermodynamics of cyclodextrins. Chem Rev 98(5):1875–1918
Szejtli J (1998) Introduction and general overview of cyclodextrin chemistry. Chem Rev 98(5):1743–1754
Khan AR, Forgo P, Stine KJ, D'Souza VT (1998) Methods for selective modifications of cyclodextrins. Chem Rev 98(5):1977–1996
Prochowicz D, Kornowicz A, Lewiński J (2017) Interactions of native cyclodextrins with metal ions and inorganic nanoparticles: fertile landscape for chemistry and materials science. Chem Rev 11(7):13461–13501
Kasprzak A, Poplawska M (2018) Recent developments in the synthesis and applications of graphene-family materials functionalized with cyclodextrins. Chem Commun 54(62):8547–8562
Zhou J, Yu GC, Huang FH (2017) Supramolecular chemotherapy based on host-guest molecular recognition: a novel strategy in the battle against cancer with a bright future. Chem Soc Rev 46(22):7021–7053
Georgakilas V, Otyepka M, Bourlinos AB, Chandra V, Kim N, Kemp KC, Hobza P, Zboril R, Kim KS (2012) Functionalization of graphene: covalent and non-covalent approaches, derivatives and applications. Chem Rev 112(11):6156–6214
Guo YJ, Guo SJ, Ren JT, Zhai YM, Dong SJ, Wang EK (2010) Cyclodextrin functionalized graphene nanosheets with high supramolecular recognition capability: synthesis and host-guest inclusion for enhanced electrochemical performance. ACS Nano 4(7):4001–4010
Liu JL, Leng XY, Xiao Y, Hu CG, Fu L (2015) 3D nitrogen-doped graphene/β-cyclodextrin: host-guest interactions for electrochemical sensing. Nanoscale 7(28):11922–11927
Guo YJ, Guo SJ, Li J, Wang EK, Dong SJ (2011) Cyclodextrin-graphene hybrid nanosheets as enhanced sensing platform for ultrasensitive determination of carbendazim. Talanta 84(1):60–64
Zhang M, Zhang H, Zhai XC, Yang X, Zhao HT, Wang J, Dong AJ, Wang ZY (2017) Application of beta-cyclodextrin-reduced graphene oxide nanosheets for enhanced electrochemical sensing of the nitenpyram residue in real samples. New J Chem 41(5):2169–2177
Liang WT, Rong YQ, Fan LF, Dong WJ, Dong QC, Yang C, Zhong ZH, Dong C, Shuang SM, Wong WY (2018) 3D graphene/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin nanocomposite as an electrochemical chiral sensor for the recognition of tryptophan enantiomers. J Mater Chem C 6(47):12822–12829
Yang L, Fan S, Deng G, Li Y, Ran X, Zhao H, Li CP (2015) Bridged β-cyclodextrin-functionalized MWCNT with higher supramolecular recognition capability: the simultaneous electrochemical determination of three phenols. Biosens Bioelectron 68:617–625
Ul AA, Qin YH, Howlader MMR, Hu NX, Deen MJ (2018) Electrochemical sensing of acetaminophen using multi-walled carbon nanotube and β-cyclodextrin. Sens Actuator B-Chem 254:896–909
Zarei K, Fatemi L, Kor K (2015) Stripping voltammetric determination of nicardipine using β-cyclodextrin incorporated carbon nanotube-modified glassy carbon electrode. J Anal Chem 70(5):615–620
Le HTN, Jeong HK (2017) Enhanced supramolecular recognition capability of γ cyclodextrin-graphite oxide-carbon nanotube composite. Electrochim Acta 250:259–266
Liu ZG, Xue Q, Guo YJ (2017) Sensitive electrochemical detection of rutin and isoquercitrin based on SH-β-cyclodextrin functionalized graphene-palladium nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 89:444–452
Wang C, Li T, Liu Z, Guo Y, Li C, Dong C, Shuang S (2016) An ultra-sensitive sensor based on β-cyclodextrin modified magnetic graphene oxide for detection of tryptophan. J Electroanal Chem 781:363–370
Dong SQ, Bi Q, Qiao CD, Sun YM, Zhang X, Lu XQ, Zhao L (2017) Electrochemical sensor for discrimination tyrosine enantiomers using graphene quantum dots and β-cyclodextrins composites. Talanta 173:94–100
Jie O, Zhu Y, Yong K, Ma J (2015) Graphene quantum dots/β-cyclodextrin nanocomposites: a novel electrochemical chiral interface for tryptophan isomer recognition. Electrochem Commun 60:60–63
Lei P, Zhou Y, Zhang G, Zhang Y, Zhang C, Hong S, Yang Y, Dong C, Shuang S (2019) A highly efficient chiral sensing platform for tryptophan isomers based on a coordination self-assembly. Talanta 195:306–312
Zaidi SA (2017) Facile and efficient electrochemical enantiomer recognition of phenylalanine using β-Cyclodextrin immobilized on reduced graphene oxide. Biosens Bioelectron 94:714–718
Upadhyay SS, Kalambate PK, Srivastava AK (2017) Enantioselective analysis of moxifloxacin hydrochloride enantiomers with graphene-β-cyclodextrin-nanocomposite modified carbon paste electrode using adsorptive stripping differential pulse Voltammetry. Electrochim Acta 248:258–269
Li Y, Gao Y, Li YA, Liu SY, Zhang H, Su XG (2014) A novel fluorescence probing strategy based on mono-6-(2-aminoethylamino)-6-deoxy-β-cyclodextrin functionalized graphene oxide for the detection of amantadine. Sens Actuator B-Chem 202:323–329
Zor E, Saglam ME, Alpaydin S, Bingol H (2014) A reduced graphene oxide/α-cyclodextrin hybrid for the detection of methionine: electrochemical, fluorometric and computational studies. Anal Methods 6(16):6522–6530
Mondal A, Jana NR (2012) Fluorescent detection of cholesterol using β-cyclodextrin functionalized graphene. Chem Commun 48(58):7316–7318
Zhou SH, Xu HB, Gan W, Yuan QH (2016) Graphene quantum dots: recent progress in preparation and fluorescence sensing applications. RSC Adv 6(112):110775–110788
Mondal S, Purkayastha P (2016) α-Cyclodextrin functionalized carbon dots: pronounced photoinduced electron transfer by aggregated nanostructures. J Phys Chem C 120(26):14365–14371
Lin ZY, Kuo YC, Chang CJ, Lin YS, Chiu TC, Hu CC (2018) Highly sensitive sensing of hydroquinone and catechol based on β-cyclodextrin-modified carbon dots. RSC Adv 8(35):19381–19388
Shao D, Sheng G, Chen C, Wang X, Nagatsu M (2010) Removal of polychlorinated biphenyls from aqueous solutions using β-cyclodextrin grafted multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Chemosphere 79(7):679–685
Salipira KL, Mamba BB, Krause RW, Malefetse TJ, Durbach SH (2008) Cyclodextrin polyurethanes polymerised with carbon nanotubes for the removal of organic pollutants in water. Water SA 34(1):113–118
Wei L, Jiang X, Chen X (2014) A novel method of synthesizing cyclodextrin grafted multiwall carbon nanotubes/iron oxides and its adsorption of organic pollutant. Appl Surf Sci 320:764–771
Sinha A, Jana NR (2015) Separation of microcystin-LR by cyclodextrin-functionalized magnetic composite of colloidal graphene and porous silica. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(18):9911–9919
Mphahlele K, Onyango MS, Mhlanga SD (2015) Adsorption of aspirin and paracetamol from aqueous solution using Fe/N-CNT/β-cyclodextrin nanocomopsites synthesized via a benign microwave assisted method. J Environ Chem Eng 3(4):2619–2630
Siriviriyanun A, Tsai YJ, Voon SH, Kiew SF, Imae T, Kiew LV, Looi CY, Wong WF, Lee HB, Chung LY (2018) Cyclodextrin- and dendrimer-conjugated graphene oxide as a nanocarrier for the delivery of selected chemotherapeutic and photosensitizing agents. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl 89:307–315
Iannazzo D, Mazzaglia A, Scala A, Pistone A, Galvagno S, Lanza M, Riccucci C, Ingo GM, Colao I, Sciortino MT, Valle F, Piperno A, Grassi G (2014) β-Cyclodextrin-grafted on multiwalled carbon nanotubes as versatile nanoplatform for entrapment of guanine-based drugs. Colloid Surf B-Biointerfaces 123:264–270
Srinivasarao M, Low PS (2017) Ligand-targeted drug delivery. Chem Rev 117(19):12133–12164
Yang Y, Zhang YM, Chen Y, Zhao D, Chen JT, Liu Y (2012) Construction of a graphene oxide based noncovalent multiple nanosupramolecular assembly as a scaffold for drug delivery. Chem Eur J 18(14):4208–4215
Hu Z, Wang C, Zhao F, Xu XR, Wang SH, Yu L, Zhang D, Huang YD (2017) Fabrication of a graphene/C60 nanohybrid via γ-cyclodextrin host-guest chemistry for photodynamic and photothermal therapy. Nanoscale 9(25):8825–8833
Zhang YM, Cao Y, Yang Y, Chen JT, Liu Y (2014) A small-sized graphene oxide supramolecular assembly for targeted delivery of camptothecin. Chem Commun 50(86):13066–13069
Liang WT, Huang Y, Lu DT, Ma XW, Gong T, Cui XD, Yu BF, Yang C, Dong C, Shuang SM (2019) β-Cyclodextrin–hyaluronic acid polymer functionalized magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposites for targeted photo-chemotherapy of tumor cells. Polymers 11(1):133–148
Wei GC, Dong RH, Wang D, Feng L, Dong SL, Song AX, Hao JC (2014) Functional materials from the covalent modification of reduced graphene oxide and β-cyclodextrin as a drug delivery carrier. New J Chem 38(1):140–145
Ko NR, Nafiujjaman M, Lee JS, Lim HN, Lee YK, Kwon IK (2017) Graphene quantum dot-based theranostic agents for active targeting of breast cancer. RSC Adv 7(19):11420–11427
Dong HQ, Li YY, Yu JH, Song YY, Cai XJ, Liu JQ, Zhang JM, Ewing RC, Shi DL (2013) A versatile multicomponent assembly via β-cyclodextrin host-guest chemistry on graphene for biomedical applications. Small 9(3):446–456
Wang CL, Li B, Niu WF, Hong SS, Saif B, Wang SB, Dong C, Shuang SM (2015) β-Cyclodextrin modified graphene oxide-magnetic nanocomposite for targeted delivery and pH-sensitive release of stereoisomeric anti-cancer drugs. RSC Adv 5(108):89299–89308
Boncel S, Herman AP, Budniok S, Jedrysiak RG, Jakobik-Kolon A, Skepper JN, Mueller KH (2016) In vitro targeting and selective killing of T47D breast cancer cells by purpurin and 5-fluorouracil anchored to magnetic CNTs: nitrene-based functionalization versus uptake, cytotoxicity, and intracellular fate. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 2(8):1273–1285
An-Hui L, Salabas EL, Ferdi S (2010) Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew Chem Int Ed 46(8):1222–1244
Sophie L, Delphine F, Marc P, Alain R, Caroline R, Luce VE, Muller RN (2008) Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem Rev 108(6):2064–2110
Zhu J, Jiang HE, Xiaoyan DU, Ruihua LU, Huang L, Xia GE (2011) A facile and flexible process of β-cyclodextrin grafted on Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles and host-guest inclusion studies. Appl Surf Sci 257(21):9056–9062
Wang CL, Huang LZ, Song SM, Saif B, Zhou YH, Dong C, Shuang SM (2015) Targeted delivery and pH-responsive release of stereoisomeric anti-cancer drugs using β-cyclodextrin assembled Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 357:2077–2086
Zhou YH, Sun LL, Wang HX, Liang WT, Yang J, Wang L, Shuang SM (2016) Investigation on the uptake and release ability of β-cyclodextrin functionalized Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles by methylene blue. Mat Chem Phys 170:83–89
Wang HX, Zhou YH, Guo YJ, Liu WJ, Dong C, Wu YH, Li SD, Shuang SM (2012) β-Cyclodextrin/Fe3O4 hybrid magnetic nano-composite modified glassy carbon electrode for tryptophan sensing. Sensors Actuators B Chem 163(1):171–178
Zhang Y, Wang W, Li Q, Yang QB, Li YX, Du JS (2015) Colorimetric magnetic microspheres as chemosensor for Cu2+ prepared from adamantane-modified rhodamine and β-cyclodextrin-modified Fe3O4@SiO2 via host-guest interaction. Talanta 141:33–40
Helal AS, Mazario E, Mayoral A, Decorse P, Losno R, Lion C, Ammar S, Hemadi M (2018) Highly efficient and selective extraction of uranium from aqueous solution using a magnetic device: succinyl-β-cyclodextrin-APTES@maghemite nanoparticles. Environ Sci Nano 5(1):158–168
Cai KY, Li JH, Luo Z, Hu Y, Hou YH, Ding XW (2011) β-Cyclodextrin conjugated magnetic nanoparticles for diazepam removal from blood. Chem Commun 47(27):7719–7721
Kong L, Yan LL, Qu Z, Yan NQ, Li L (2015) β-Cyclodextrin stabilized magnetic Fe3S4 nanoparticles for efficient removal of Pb(II). J Mater Chem A 3(30):15755–15763
Chen X, Rao JA, Wang J, Gooding JJ, Zou G, Zhang QJ (2011) A facile enantioseparation for amino acids enantiomers using β-cyclodextrins functionalized Fe3O4 nanospheres. Chem Commun 47(37):10317–10319
Sun ZB, Cui GJ, Li HZ, Liu Y, Tian YX, Yan SQ (2016) Multifunctional optical sensing probes based on organic-inorganic hybrid composites. J Mat Chem B 4(31):5194–5216
Wu YP, Zuo F, Zheng ZH, Ding XB, Peng YX (2009) A novel approach to molecular recognition surface of magnetic nanoparticles based on host-guest effect. Nanoscale Res Lett 4(7):738–747
Jiang JJ, Lin XY, Ding D, Diao GW (2018) Enzyme-free homogeneous electrochemical biosensor for DNA assay using toehold-triggered strand displacement reaction coupled with host-guest recognition of Fe3O4@SiO2@ β-CD nanocomposites. Biosens Bioelectron 114:37–43
Munoz J, Gonzalez-Campo A, Riba-Moliner M, Baeza M, Mas-Torrent M (2018) Chiral magnetic-nanobiofluids for rapid electrochemical screening of enantiomers at a magneto nanocomposite graphene-paste electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 105:95–102
Wang W, Zhang Y, Yang QB, Sun MD, Fei XL, Song Y, Zhang YM, Li YX (2013) Fluorescent and colorimetric magnetic microspheres as nanosensors for Hg2+ in aqueous solution prepared by a sol-gel grafting reaction and host-guest interaction. Nanoscale 5(11):4958–4965
Badruddoza AZM, Tay ASH, Tan PY, Hidajat K, Uddin MS (2011) Carboxymethyl-β-cyclodextrin conjugated magnetic nanoparticles as nano-adsorbents for removal of copper ions: synthesis and adsorption studies. J Hazard Mater 185(2–3):1177–1186
Badruddoza AM, Bhattarai B, Suri RPS (2017) Environmentally friendly β-cyclodextrin-ionic liquid polyurethane-modified magnetic sorbent for the removal of PFOA, PFOS, and Cr(VI) from water. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(10):9223–9232
Mu B, Kang YR, Wang AQ (2013) Preparation of a polyelectrolyte-coated magnetic attapulgite composite for the adsorption of precious metals. J Mater Chem A 1(15):4804–4811
Guo ZQ, Li Y, Pan SH, Xu JZ (2015) Fabrication of Fe3O4@cyclodextrin magnetic composite for the high-efficient removal of Eu(III). J Mol Liq 206:272–277
Fuhrer R, Herrmann IK, Athanassiou EK, Grass RN, Stark WJ (2011) Immobilized β-Cyclodextrin on surface-modified carbon-coated cobalt nanomagnets: reversible organic contaminant adsorption and enrichment from water. Langmuir 27(5):1924–1929
Gong T, Zhou YH, Sun LL, Liang WT, Yang J, Shuang SM, Dong C (2016) Effective adsorption of phenolic pollutants from water using β-cyclodextrin polymer functionalized Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. RSC Adv 6(84):80955–80963
Duan ZB, Ding XC, Wang Y, Zhu LJ, Xia DH (2018) A new strategy for fuel desulfurization by molecular inclusion with copper(II)-β-cyclodextrin@SiO2@Fe3O4 for removing thiophenic sulfides. Energy Fuel 32(11):11421–11431
Sinha A, Basiruddin SK, Chakraborty A, Jana NR (2015) β-Cyclodextrin functionalized magnetic mesoporous silica colloid for cholesterol separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(2):1340–1347
Guo J, Wang NJ, Peng L, Wu JJ, Ye QQ, Feng AC, Wang ZP, Zhang C, Xing XH, Yuan JY (2016) Electrochemically-responsive magnetic nanoparticles for reversible protein adsorption. J Mat Chem B 4(22):4009–4016
Deng XJ, Li WB, Ding GS, Chen XP (2018) Enantioselective separation of RS-mandelic acid using β-cyclodextrin modified Fe3O4@SiO2/Au microspheres. Analyst 143(11):2665–2673
Yang X, Song X, Zhu H, Cheng C, Yu H, Zhang H (2018) Novel smart polymer brushes modified magnetic graphene oxide for highly efficient chiral recognition and enantioseparation of tryptophan enantiomers. ACS Appl Bio Mat 1(4):1074–1083
Luo Z, Cai K, Hu Y, Li J, Ding X, Zhang B, Xu D, Yang W, Liu P (2012) Redox-responsive molecular nanoreservoirs for controlled intracellular anticancer drug delivery based on magnetic nanoparticles. Adv Mater 24(3):431–435
Lee JH, Chen KJ, Noh SH, Garcia MA, Wang H, Lin WY, Jeong H, Kong BJ, Stout DB, Cheon J, Tseng HR (2013) On-demand drug release system for in vivo cancer treatment through self-assembled magnetic nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Edit 52(16):4384–4388
Hong SS, Li ZB, Li CZ, Dong CA, Shuang SM (2018) β-Cyclodextrin grafted polypyrrole magnetic nanocomposites toward the targeted delivery and controlled release of doxorubicin. Appl Surf Sci 427:1189–1198
Zhou J, Yang Y, Zhang CY (2015) Toward biocompatible semiconductor quantum dots: from biosynthesis and bioconjugation to biomedical application. Chem Rev 115(21):11669–11717
Denis D, Shu-Han H, Nikodem T, Reinhoudt DN, Jurriaan H, Velders AH, Julius Vancso G (2010) Fabrication and luminescence of designer surface patterns with β-cyclodextrin functionalized quantum dots via multivalent supramolecular coupling. ACS Nano 4(1):137–142
Palaniappan K, Hackney SA, Liu J (2004) Supramolecular control of complexation-induced fluorescence change of water-soluble, β-cyclodextrin-modified CdS quantum dots. Chem Commun 23(23):2704–2705
Li H, Han C (2008) Sonochemical synthesis of cyclodextrin-coated quantum dots for optical detection of pollutant phenols in water. Chem Mater 20(19):6053–6059
Shang ZB, Hu S, Wang Y, Jin WJ (2011) Interaction of β-cyclodextrin-capped CdSe quantum dots with inorganic anions and cations. Luminescence 26(6):585–591
Duran GM, Contento AM, Rios A (2015) Continuous method incorporating β-cyclodextrin modified CdSe/ZnS quantum dots for determination of ascorbic acid. Anal Methods 7(8):3472–3479
Hu T, Na W, Xu Y, Su X (2017) Sensitive fluorescence detection of ATP based on host-guest recognition between near-infrared β-Cyclodextrin-CuInS2 QDs and aptamer. Talanta 165:194–200
Geng S, Lin SM, Liu SG, Li NB, Luo HQ (2016) A new fluorescent sensor for detecting p-nitrophenol based on β-cyclodextrin-capped ZnO quantum dots. RSC Adv 6(89):86061–86067
Freeman R, Finder T, Bahshi L, Willner I (2009) β-cyclodextrin-modified CdSe/ZnS quantum dots for sensing and chiroselective analysis. Nano Lett 9(5):2073–2076
Durán GM, Abellán C, Contento AM, Ríos Á (2017) Discrimination of penicillamine enantiomers using β-cyclodextrin modified CdSe/ZnS quantum dots. Microchim Acta 184(3):815–824
Han C, Li H (2010) Chiral recognition of amino acids based on cyclodextrin-capped quantum dots. Small 4(9):1344–1350
Wei YL, Li HH, Hao HY, Chen YX, Dong C, Wang GF (2015) β-Cyclodextrin functionalized Mn-doped ZnSquantum dots for the chiral sensing of tryptophan enantiomers. Polym Chem 6(4):591–598
Jie Z, Yun L, Zhang Z, Sha Y, Jian T, Wei L, Tang W (2016) Cyclodextrin-clicked silica/CdTe fluorescent nanoparticles for enantioselective recognition of amino acids. Nanoscale 8(10):5621–5626
Dreaden EC, Alkilany AM, Huang X, Murphy CJ, El-Sayed MA (2012) The golden age: gold nanoparticles for biomedicine. Chem Soc Rev 41(7):2740–2779
Alvarez J, Liu J, Román E, Kaifer AE (2000) Water-soluble platinum and palladium nanoparticles modified with thiolated β-cyclodextrin. Chem Commun 13:1151–1152
Zhao Y, Huang Y, Zhu H, Zhu Q, Xia Y (2016) Three-in-one: sensing, self-assembly, and cascade catalysis of cyclodextrin modified gold nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 138(51):16645–16654
Aswathy B, Avadhani GS, Suji S, Sony G (2012) Synthesis of β-cyclodextrin functionalized gold nanoparticles for the selective detection of Pb2+ ions from aqueous solution. Front Mater Sci 6(2):168–175
Wang J, Kong LT, Guo Z, Xu JY, Liu JH (2010) Synthesis of novel decorated one-dimensional gold nanoparticle and its application in ultrasensitive detection of insecticide. J Mater Chem 20(25):5271–5279
Wang M, Su K, Cao J, She Y, Wang Y (2018) “Off-On” non-enzymatic sensor for malathion detection based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer between β-cyclodextrin@Ag and fluorescent probe. Talanta 192:295–300
Qi M, Song JP, Zhang SF, Wang MF, Yong G, Dong C (2016) Colorimetric detection of riboflavin by silver nanoparticles capped with β-cyclodextrin-grafted citrate. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 148:66–72
Liu C, Lian J, Liu Q, Xu C, Li B (2016) β-Cyclodextrin-modified silver nanoparticles as colorimetric probes for the direct visual enantioselective recognition of aromatic α-amino acids. Anal Methods 8(29):5794–5800
Stiles PL, Dieringer JA, Shah NC, Van Duyne RP (2008) Surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy. Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto, Calif) 1:601–626
Teng H, Fei M, Qi L (2009) Facile synthesis and one-dimensional assembly of cyclodextrin-capped gold nanoparticles and their applications in catalysis and surface-enhanced raman scattering. J Phys Chem C 113(31):13636–13642
Dickson J, Geckeler KE (2009) Surfactant-directed multiple anisotropic gold nanostructures: synthesis and surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Langmuir the Acs J Surfaces Colloids 25(22):13224–13231
Teng H, Fei M, Limin Q (2010) Controlled synthesis of dendritic gold nanostructures assisted by supramolecular complexes of surfactant with cyclodextrin. Langmuir 26(10):7582–7589
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this entry
Cite this entry
Liang, W., Shuang, S. (2019). Cyclodextrin Hybrid Inorganic Nanocomposites for Molecular Recognition, Selective Adsorption, and Drug Delivery. In: Liu, Y., Chen, Y., Zhang, HY. (eds) Handbook of Macrocyclic Supramolecular Assembly . Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-1744-6_17-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-1744-6_17-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-13-1744-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-13-1744-6
eBook Packages: Springer Reference Chemistry and Mat. ScienceReference Module Physical and Materials ScienceReference Module Chemistry, Materials and Physics