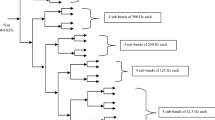
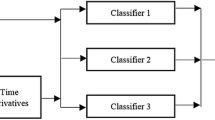
Abstract
Phoneme parameter extraction framework based on spectral and cepstral parameters is proposed. Using this framework, the phoneme signal is divided into frames and Hamming window is used. The performances are evaluated for recognition of Lithuanian vowel and semivowel phonemes. Different feature sets without noise as well as at different level of noise are considered. Two classical machine learning methods (Naive Bayes and Support Vector Machine) are used for classifying each problem, separately. The experiment results show that cepstral parameters give higher accuracies than spectral parameters. Moreover, cepstral parameters give better performance compared to spectral parameters in noisy conditions.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Korvel, G., Kostek, B.: Examining feature vector for phoneme recognition. In: Proceeding of IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology, ISSPIT 2017, Bilbao, Spain (2017). https://drive.google.com/open?id=1ugidXH_qNO9LRWTnkJU6Mbrk4AfTonGw
Eringis, D., Tamulevičius, G.: Improving speech recognition rate through analysis parameters. Electr. Control Commun. Eng. 5(1), 61–66 (2014)
Kostek, B., Piotrowska, M., Ciszewski, T., Czyzewski, A.: Comparative study of self-organizing maps vs subjective evaluation of quality of allophone pronunciation for non-native english speakers. In: Audio Engineering Society Convention, p. 143 (2017)
Fastl, H., Zwicker, E.: Psychoacoustics: Facts and Models. Springer Series in Information Sciences, 3rd edn. Springer, Heidelberg (2007)
Schuller, B.R., Steidl, S., Batliner, A., Burkhardt, F., Devillers, L., Müller, C., Narayanan, S.: Paralinguistics in speech and language - state-of-the-art and the challenge. Comput. Speech Lang. 27(1), 4–39 (2009)
Eyben, F., Scherer, K.R., Schuller, B.W., Sundberg, J., Andre, E., Busso, C., Devillers, L.Y., Epps, J., Laukka, P., Narayanan, S.S., Truong, K.P.: The geneva minimalistic acoustic parameter set (GeMAPS) for voice research and affective computing. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 7(2), 190–202 (2016)
Boersma, P.: Praat, a system for doing phonetics by computer. Glot Int. 5(9/10), 341–347 (2002)
Matsumoto, M., Hori, J.: Classification of silent speech using support vector machine and relevance vector machine. Appl. Soft Comput. 20, 95–102 (2014)
Bojanic, M., Crnojevic, V., Delic, V.: Application of neural networks in emotional speech recognition. In: 2012 11th Symposium on Neural Network Applications in Electrical Engineering (NEUREL), pp. 223–226. IEEE (2012)
Sadjadi, S.O., Pelecanos, J., Zhu, W.: Nearest neighbor based i-vector normalization for robust speaker recognition under unseen channel conditions. In: Fifteenth Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Singapore, pp. 1860–1864 (2014)
Kotsiantis, S.B.: Supervised machine learning: a review of classification techniques. Informatica 31, 249–268 (2007)
Metallinou, A., Katsamanis, A., Narayanan, S.: A hierarchical framework for modeling multimodality and emotional evolution in affective dialogs. In: IEEE International Conference on IEEE Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 2401–2404 (2012)
Vasuki, P., Aravindan, C.: Improving emotion recognition from speech using sensor fusion techniques. In: IEEE Region 10 Conference, TENCON, pp. 1–6 (2012)
Rabiner, L., Juang, B.H.: Fundamental of Speech Recognition. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River (1933)
Rao, K.S., Vuppala, A.K.: Speech Processing in Mobile Environments, Springer Science & Business Media, Heidelberg (2014)
Pyž, G., Šimonytė, V., Slivinskas, V.: Developing models of lithuanian speech vowels and semivowels. Informatica 25(1), 55–72 (2014)
Rabiner, L.R., Schafer, R.W.: Introduction to Digital Speech Processing. Now Publishers Inc., Breda (2007)
LIEPA Homepage. https://www.raštija.lt/liepa/about-project-liepa/7596
Refaeilzadeh, P., Tang, L., Liu, H.: Cross-validation. In: Encyclopedia of Database Systems, pp. 532–538 (2009)
Ghosh, J.K., Delampady, M., Samanta, T.: An Introduction to Bayesian Analysis: Theory and Methods, 1st edn. Springer Science Business Media, LLC, New York (2006)
Palaniappan, R., Sundaraj, K., Sundaraj, S.: A comparative study of the svm and k-nn machine learning algorithms for the diagnosis of respiratory pathologies using pulmonary acoustic signals. BMC Bioinf. 15, 1–8 (2014)
Hegde, S., Achary, K.K., Shetty, S.: Feature selection using fisher’s ratio technique for automatic speech recognition. Int. J. Cybern. Inf. (IJCI) 4(2) (2015). https://doi.org/10.5121/ijci.2015.4204
Korvel, G., Kostek, B.: Voiceless stop consonant modelling and synthesis framework based on MISO dynamic system. Arch. Acoust. 3(42), 375–383 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1515/aoa-2017-0039
Acknowledgment
This research is funded by the European Social Fund under the No 09.3.3-LMT-K-712 “Development of Competences of Scientists, other Researchers and Students through Practical Research Activities” measure.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Korvel, G., Kurasova, O., Kostek, B. (2019). Comparative Analysis of Spectral and Cepstral Feature Extraction Techniques for Phoneme Modelling. In: Choroś, K., Kopel, M., Kukla, E., Siemiński, A. (eds) Multimedia and Network Information Systems. MISSI 2018. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 833. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-98678-4_48
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-98678-4_48
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-98677-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-98678-4
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)