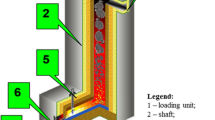
Abstract
The treatment of waste materials is a social and economic problem that has grown rapidly over the last few decades. Relatively simple solutions such as landfill depository and ocean dump sites are no more an option due to the sheer volume of the waste material generated and their long-term negative impact on the environment. The problem is compounded by the wide variety of the waste material generated by our society ranging from municipal solid waste to hazardous industrial waste and low-level radioactive waste. In this chapter, a brief introduction provides some statistics on the volume and composition of waste materials generated across the world and different waste classifications that are commonly used. This is followed by a review of current waste treatment technologies for three broad groups of waste materials, namely:
-
Municipal solid waste materials
-
Industrial waste materials
-
Low-level radioactive waste materials
In each of these groups, attention is given to the unique role thermal plasma technology can play for the safe and reliable treatment of the waste material and niche opportunities for the recovery of valuable products from the waste. In a field as vast and diversified as waste treatment, it is unrealistic to attempt to treat it in an exhaustive manner in a single chapter. Emphasis is therefore given to providing typical examples of some of the leading technologies developed over the past few decades with adequate references for further information.
Emil Pfender died before publication of this work was completed.
E. Pfender: deceased.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AC:
-
Alternating current
- ACW:
-
Asbestos-containing waste
- ASR:
-
Automobile shredder residue
- BF:
-
Blast furnace
- BOF:
-
Basic oxygen furnace
- CFC:
-
Chlorofluorocarbon
- CFC-11:
-
Trichlorofluoromethane, CFCl3
- CFC-113:
-
Trichlorotrifluoroethane, C2F3Cl3
- CFC-114:
-
Dichlorotetrafluoroethane, C2F4Cl2
- CFC-115:
-
Chloropentafluoroethane, C2F5Cl
- CFC-12:
-
Dichlorodifluoromethane, CF2Cl2
- CFD:
-
Converter flue dust
- CMP:
-
Center for materials production
- CP:
-
Compressor
- CPCB:
-
Central Pollution Control Board
- CPI:
-
Chemical process industries
- DC:
-
Direct current
- DENOX:
-
Nitrogen oxide removal system
- DREs:
-
Destruction and removal efficiencies
- EAF:
-
Electric arc furnace
- EDF:
-
Electricité de France
- EDM:
-
Engineering development model
- EPA:
-
Environmental Protection Agency
- EPI:
-
Electroplating industry
- EPRI:
-
Electric Power Research Institute
- EW:
-
Electronic waste
- GHG:
-
Greenhouse gases
- HCFC-134a:
-
Tetrafluoroethane, CH2FCF3
- HCFC-22:
-
Chlorodifluoromethane, CHClF2
- HEPA:
-
High-efficiency particulate arrestance
- HLW:
-
High-level liquid waste
- HPS:
-
Hot plating sludge
- HSW:
-
Hospital solid waste
- HTS:
-
High-temperature shift
- HW:
-
Hazardous waste
- HWM:
-
Hazardous waste materials
- IET:
-
Integrated environmental technology
- IPGCC:
-
Integrated plasma gasification combined cycle
- IWM:
-
Industrial waste materials
- IWT:
-
Industrial waste treatment
- LD:
-
Linz-Donawitz
- LHS:
-
Left-hand side
- LLRW:
-
Low-level radioactive materials
- LLW:
-
Low-level nuclear waste
- LNG:
-
Liquefied natural gas
- LTS:
-
Low-temperature shift
- MSW:
-
Municipal solid waste
- MW:
-
Medical waste
- NMP:
-
Nonmetallic product
- ODSs:
-
Ozone-depleting substances
- PACT:
-
Plasma-arc centrifugal treatment
- PAG:
-
Plasma-arc gasification
- PAHWTS:
-
Plasma-arc hazardous waste treatment system
- PAWDS:
-
Plasma-arc waste destruction system
- PCB:
-
Printed circuit boards
- PCBs:
-
Polychlorinated biphenyls
- PCC:
-
Post-combustion chamber
- PCDDs:
-
Polychlorinated dibenzodioxins
- PCDFs:
-
Polychlorinated dibenzofurans
- PE:
-
Polyethylene
- PEC:
-
Plasma Energy Corporation
- PEM:
-
Plasma-enhanced melter
- PET:
-
Polyethylene terephthalate
- PGM:
-
Platinum group metals
- PMW:
-
Paper mill waste
- POM:
-
Prescription-only medicines
- PP:
-
Polypropylene
- PPC:
-
Primary processing chamber
- PS:
-
Polystyrene
- PSA:
-
Pressure swing adsorption
- PSW:
-
Plastic solid waste
- PVC:
-
Polyvinyl chloride
- RDF:
-
Refuse-derived fuel
- RF:
-
Radio frequency
- RHS:
-
Right-hand side
- RSF:
-
Rotary salt furnace
- SCR:
-
Selective catalytic reduction
- SEER:
-
Specific electrical energy requirement
- SER:
-
Specific energy requirement
- SLRG:
-
Soda lime recycled glass
- SPME:
-
Solid-phase microextraction system
- SSW:
-
Sewage sludge waste
- TA:
-
Transferred arc
- TBP:
-
Tributylphosphate
- TPD:
-
Ton per day
- TPT:
-
Thermal plasma technology
- WEEE:
-
Waste electrical and electronic equipment
- WGS:
-
Water-gas shift
- WM:
-
Waste materials
- WPT:
-
Waste-processing technologies
- WSAP:
-
Water-stabilized arc plasma
- WtE:
-
Waste-to-energy
References
An’shakov AS, Faleev VA, Danilenko AA, Urbakh EK, Urbakh AE (2007) Investigation of plasma gasification of carbonaceous technogeneous wastes. Thermophys Aeromech 14:607–616
Arena U (2012) Process and technological aspects of municipal solid waste gasification. A review. Waste Manag 32:625–639
Barton TG (1979) Problem waste disposal by plasma heating. Int Recycl Congress Berlin 1:733–736
Barton TG, Mordy JA (1984) The destruction of halogenated organic chemicals by plasma pyrolysis. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 62(8):976–978
Barton NY et al (1987) Plasma pyrolysis waste destruction. US Patent 4,644,877
Benocci R, Bonizzoni G, Sindoni E (eds) (1995) Thermal plasmas for hazardous waste treatment. In: Proceedings of the international school of plasma physics. World Scientific, Hackensack
Bhada-Tata P, Hoornweg D (2012) What a waste a global review of solid waste management. Urban Development Series Knowledge Papers, 15. World Bank
Botes A (2017) South African waste management tire fee to generate million per year to promote tire recycling
Bouvier A, Justin L (1990) R&D at EDF into the industrial applications of plasma generators. In Solonenko OP, Fedorchenko AI (eds) Plasma jets in the development of new materials. VSP Utrecht, The Netherlands
Bowyer J, Fernholz K (2010) Plasma gasification: an examination of the health, safety, and environmental records of established facilities. Dovetail Partners
Buckson M (2007) Turning garbage into power, an environmental dream becomes a real business. The Ottawa Construction News, January, pages C1–C8
Byun Y, Cho M, Woo Chung J, Namkung W, Lee HD, Jang SD, Kim Y-S, Lee J-H, Lee C-R, Hwang S-M (2011) Hydrogen recovery from the thermal plasma gasification of solid waste. J Hazard Mater 190:317–323
Byun Y, Cho M, Hwang S-M, Chung J (2012) Thermal plasma gasification of municipal solid waste (MSW), Chapter 7. In: Gasification for practical applications. Intech
Chand S, Paul B, Kumar M (2016) Sustainable approaches for LD slag waste management in steel industries: a review. Metallurgist 60(1–2):116–128
Circeo LJ, Martin RC Jr, Smith ME (2007) Achieving “zero waste” with plasma arc technology, transparencies. Georgia Tech Research Institute
Clean Energy Center (1995) CFCs destroying demonstration plant. Cat. N. PMD357 ‘95, Tokyo Japan Cat. No
Cretenot D et al (1990) Waste destruction by plasma. In: Proceedings of 1st international EPRI plasma symposium, May
Cubas ALV, Machado M d M, Dutra AR d A, Moecke EHS, Fiedler HD, Bueno P (2015) Final treatment of spent batteries by thermal plasma. J Environ Manag 159:202–208
Cuchet JM, Luycs P, De Goeyse A, Braeckeveldt M (2007) The HRA-solarium project: processing of historical waster on the BelgoProcess site (Belgium). In: Proceedings of 11th international conference on environmental remediation and radioactive waste management ICEM07-7026, Sept 2-6 Bruges, Belgium
Czajczynska D, Anguilano L, Ghazal H, Krzyzynska R, Reynolds AJ, Spencer N, Jouhara H (2017) Potential of pyrolysis processes in the waste management sector. Thermal Sci Eng Prog 3:171–197
Deckers J (2014) Treatment of radioactive waste. IAEA, Scientific forum, Radioactive waste meeting the challenge, Sept 23–24 Vienna, Austria
EPA (1992) Retech plasma centrifugal furnace application analysis report. EPA Risk Reduction Engineering Laboratory, Cincinnati OH, USA, June 1992, p. 9
Eschenbach RC (1989) Use of plasma torches for melting special metals and for destroying and stabilizing hazardous wastes. In: Boulos MI (ed) Proc workshop on industrial plasma applications, Pungnuochinso, Italy, pp 127–136
Eschenbach RC (1990) Plasma centrifugal furnace for destroying hazardous wastes. In: Proceedings of 1st international EPRI plasma symposium May
Eschenbach RC (1995) Plasma Arc Centrifugal Treatment (PACT) of Hazardous Waste. In: Paper presented at the 8th symposium on plasma science for materials, Tokyo, Japan, 15–16 June
Eschenbach RC, Boomer KD (1987) Plasma Arc Stabilization of Hazardous Mixed Wastes. In: Paper presented at the ANS Winter Meeting, Los Angeles, CA, 15–19 November
Eschenbach RC, Whitworth CG (1995) Glassy slag from rotary hearth vitrification. Paper presented at the American Ceramic Society Meeting, Cincinnati, Ohio, 30 April–4 May 1995.
Eschenbach RC, Feng X, Einziger RE (1996) A direct, single step plasma arc-vitreous ceramic process for stabilizing spent nuclear fuels, sludges, and associated wastes. Paper presented at the scientific basis for nuclear waste management XX, Boston, MA, 2–6 December
European Commission-Environment (2014) Landfill of waste. European Commission, Brussels
Europlasma Company (2011). Available: http://www.europlasma.com. Accessed 17 May 2011
Fabry F, Rehmet C, Rohani V-J, Fulcheri L (2013) Waste gasification by thermal plasma: a review. Waste Biomass Valoriz 4(3):421–439
Freeman HM et al (1987) Thermal destruction of hazardous waste, state of the art review. J Hazard Mater 14(1):103–135
Funfschilling MR, Bernhard W, Eschenbach RC (1992) Test results with the plasma centrifugal furnace. In: Bonizzoni G et al (eds) Proceedings of plasma technologies for hazardous waste destruction (Como, Italy). Editrice Compositori, Bologna
Gagliardi C, Gorodetsky A, Grichin B, James J, Newman A, Petrocelli F, Santoianni J (2014) The value of pilot plant studies in advancing the understanding of plasma gasification of municipal solid waste. In: IChemE – New horizons in gasification 12th European gasification conference March 10th–12th
Gilis R, Lewandowski P, Ooms B, Reusen N, Van Laer W, Walthéry R (2007) Concrete crushing and sampling, a method and technology for the unconditional release of concrete material from decommissioning. In: Proceedings of 11th international conference on environmental remediation and radioactive waste management ICEM07-7237, Sept 2–6 Bruges, Belgium
Gomez E, Amutha Rani D, Cheeseman CR, Deegan D, Wise M, Boccaccini AR (2009) Thermal plasma technology for the treatment of wastes: a critical review. J Hazard Mater 161:614–626
Goncalves MFS, Filho GP, Couto AA, da Silva Sobrinho AS, Miranda FS, Massi M (2022) Evaluation of thermal plasma process for treatment disposal of solid radioactive waste. J Environ Manag 311(114):895
Grouzillat G (1992) Aerospatiale plasma systems – applications in the field of metallurgy and waste treatment. In: International workshop on plasma technologies for hazardous waste destruction, Como, Italy
Guddeti RR, Knight R, Grossmann ED (2000) Depolymerization of polypropylene in an induction-coupled plasma (ICP) reactor. Ind Eng Chem Res 39:1171–1176
Harabovsky M (2002) Generation of thermal plasmas in liquid and hybrid DC arc torches. Pure & Applied Chemistry 74(3):429–433
Haun R, Eschenbach RC, Battleson D, Alsberg C, Jackson T (1992) Site tests results with the PCF-6. In: Proceedings of Incineration Conf
Heberlein JVR (1989a) New developments in non-transferred plasma torch. In: Proceedings of 2nd Japanese symposium on plasma chemistry, p 131
Heberlein JVR (1989b) Adaptation of plasma torches to new applications of plasma technology. In: Boulos MI (ed) Workshop of industrial plasma applications, Pugnochiuso, Italy, p 1
Heberlein J, Murphy AB (2008) Thermal plasma waste treatment. J Phys D Appl Phys 41:053001. 20 pp
Heberlein JVR, Melilli WJ, Dighe SV, Reed WH (1989) Adaptation of non-transferred plasma torches to new applications of plasma systems. In: Boulos MI (ed) Workshop on industrial plasma applications, Pugnochiuso, Italy, p 1
Heep W (2005) Die Verbrennungs-und Schmellzanlage de ZWILAG, KONTEC-2005. In: Proc. Comf. Berline, Germany
Hlina M, Hrabovsky M, Kavka T, Konrad M (2014) Production of high-quality syngas from argon/water plasma gasification of biomass and waste. Waste Manag 34:63–66
Hrabovsky M, Kopecky V, Sember V, Kavka T, Chumak O (2006) Properties of hybrid water/gas DC arc plasma torch. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 34:1566–1575
Hrabovsky M, Hlina M, Kopecky V, Maslani A, Zivny O, Krenek P, Serov A, Hurba O (2017) Steam plasma treatment of organic substances for hydrogen and syngas production. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 37:739–762
Huaiwei Z, Xin H (2011) An overview for the utilization of wastes from stainless steel industries. Resour Conserv Recycl 55:745–754
Huang H, Tang L (2007) Treatment of organic waste using thermal plasma pyrolysis technology. Energy Convers Manag 48:1331–1337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2006.08.013
IAEA (1995) The principles of radioactive waste management, international. Atomic Energy Agency, safety series no. 111-F Vienna, Austria
IAEA (2006) Application of thermal technologies for processing of radioactive waste. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, IAEA-TECDOC-1527, December 2006
Jain KP, Pruyn J (2018) Investigating the prospects of using a plasma gasification plant to improve the offer price of ships recycled on large-sized ‘green’ yards. J Clean Prod 171:1520–1531
Joseph MF, Barton TG (1987) Pyrolysis of hazardous waste with a mobile plasma arc system. In: Management of hazardous and toxic wastes. Elsevier Applied Science, Amsterdam
Joseph MF et al (1986) Incineration of PCBs by plasma arc. In: Proceedings of 33rd Ont. Ind. Waste Conf., pp 201–205
Kandasamy J, Gokalp I (2015) Pryolysis, combustion and steam gasification of various types of crap tires for energy recovery. Energy Fuels 29:346–354
Karatas H, Olgun H, Akgun F (2012) Experimental results of gasification of waste tire with air & CO2, air & steam and steam in a bubbling fluidized bed gasifier. Fuel Process Technol 102:166–174
Karatas H, Olgun H, Akgun F (2013) Experimental results of gasification of waste tire with air in a bubbling fluidized bed gasifier. Fuel 105:566–571
Kolak NP et al (1986) Trial burns-plasma arc technology. In: US EPA 12th Symp. Proc., pp 396–401
Lahijani P, Zainal ZA, Mohamed AR, Mohammadi M (2013) Co-gasification of tire and biomass for enhancement of tire-char reactivity in CO2 gasification process. Bioresour Technol 138:124–130
Lavoie S, Dubé C, Dubé G (1990) The ALCAN plasma dross treatment process. In: Rooy EL (ed) Light metals 1991. The Minerals and Metals Society, pp 981–985
Lemont F, Hugues S, Meillot E (2008) Plasma technology: one way to improve the nuclear waste processing. High Temp Mater Process Special Issue 27(5):375–382
Leung DYC, Wang CL (2003) Fluidized bed gasification of waste tire powders. Fuel Process Technol 84:175–196
Li J, Liu K, Yan S, Li Y, Han D (2016) Application of thermal plasma technology for the treatment of solid wastes in China: an overview. Waste Manag 58:260–269
Machin EA, Pedroso DT, Carvahlo J (2017) Energetic valorization of waste tires. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 68:306–315
Mac Rae DR (1989) Plasma arc process systems, reactors, and applications. Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing 9(1):85S–118S
Mazzoni L, Janajreh I (2017) Plasma gasification of municipal solid waste with variable content of plastic solid waste for enhanced energy recovery. Int J Hydrog Energy 42:19446–19457
Mazzoni L, Ahmed R, Janajreh I (2017) Plasma gasification of two waste streams: municipal solid waste and hazardous waste from the oil and gas industry. Energy Procedia 105:4159–4166
Meyer B, Wittle JK (1987) Arc pyrolysis project, progress report. In: Proceedings of EPRI-PCB Seminar, Kansas City, October, 4.15–4.18
Min B-Y, Kang Y, Song P-S, Choi W-K, Jung C-H, Oh W-Z (2007) Study on the vitrification of mixed radioactive waste by plasma arc melting. J Ind Eng Chem 13(1):57–64
Mitrasinovic A, Pershin L, Wen JZ, Mostaghimi J (2011) Recovery of Cu and valuable metals from E-waste using thermal plasma treatment. JOM Aug 24–28
Mossé AL, Savchin VV (2006) Analysis and simulation of the process of medico-biological waste treatment in a plasma chamber incinerator. J Eng Phys Thermo-physics 79(4):639–643
Mountouris A, Voutsas E, Tassios D (2006) Solid waste plasma gasification: equilibrium model development and exergy analysis. Energy Convers Manag 47:1723–1737
Murphy AB, McAllister T (1998) Destruction of ozone-depleting substances in a thermal plasma reactor. Appl Phys Lett 73(4):459–461
Nema SK, Ganeshprasad KS (2002) Plasma pyrolysis of medical waste. Curr Sci 83(3):271–278
Neuschütz D (1996) Plasma processing of dusts and residues. Pure & Appl Chem 68(5):1159–1165
Oboirien BO, North BC (2017) A review of waste tire gasification. J Environ Chem Eng 5:5169–5178
Ojha A, Reuben AC, Sharmac D (2012) Solid waste management in developing countries through plasma arc gasification- an alternative approach. APCBEE Procedia 1:193–198
Ooms B, Lievens B, Van Laer W, Etienne VC, Walthéry R (2009) Decommissioning of buildings 105X and 122X at Belgoprocess. In: Proceedings of the 12th international conference on environmental remediation and radioactive waste management ICEM2009-16052 October 11–15, 2009, Liverpool, UK
Orfeuil M (ed) (1988) Arc plasma processes, a manufacturing technology in industry, UIE Arc plasma review. Int Union for Electro Heat, Paris-La-Défence, France, “Plasma Processes” Working Group
Paik S, Hawkes G, Nguyen HD (1995) Effect of working gases on thermal plasma waste treatment. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 15(4):677–692
Papurello D, Lanzini A, Leone P, Pierluigi L, Santarelli M (2016) The effect of heavy tars (toluene and naphthalene) on the electrochemical performance of an anode-supported SOFC running on bio-syngas. Renew Energy 99:747–753
Pastor JM, Garcia LD, Quintana S, Peria J (2014) Glass reinforced concrete panels containing recycled tires: evaluation of the acoustic properties for their use as sound barriers. Construct Build Mater 54:541–549
Phoenix solutions Company (2011). Available: http://www.phoenixsolutionsco.com/psctorches.html. Accessed 16 May 2011
Plasma Pyrolysis Technology (2016) Central Pollution Control Board, Parivesh Bhawan, East Arjun Nagar, Delhi-110032
Poiroux R, Rollin M (1996) High temperature treatment of waste: from laboratories to the industrial stage. Pure Appl Chem 68(5):1035–1040
Prado ESP, Dellamano JC, Carneiro ALG, Santos RC, Petraconi G, Potiens Jr AJ (2017) Technical feasibility study on volumetric reduction of radioactive waste using plasma technology. In: Inter. Nuclear Atlantic Conf. – INAC 2017 Belo Horizonte, MG, Brazil, October 22–27
Raman KP, Walawender WP, Fan LT (1981) Gasification of waste tires in a fluid bed reactor. Conserv Recycl 4(2):79–88
Renkel MF, Lümmen N (2018) Supplying hydrogen vehicles and ferries in Western Norway with locally produced hydrogen from municipal solid waste. Int J Hydrog Energy 43:2585–2600
Riboldi L, Bolland O (2017) Overview on pressure swing adsorption (PSA) as CO2 capture technology: State of the art; limits and potentials. Energy Procedia 114:2390–2400
Sakai S-I, Hiraoka M (2000) Municipal solid waste incinerator residue recycling by thermal processes. Waste Manag 20:249–258
Schlienger MP (1988) Apparatus and method for high temperature disposal of hazardous waste materials. US Patent 4,770,109, 13 Sept 1988
Schlienger MP (1991) US Patent 5,005,494, 9 Apr 1991
Schlienger MP (1992) US Patent 5,136,137, 4 Aug 1992
Shuey MW, Ottmer PP (2006) LLW processing and operational experience using a plasma arc centrifugal treatment (PACT™) system. In: Proceedings of waste management conference, Tucson, AZ, USA
Siddique R, Naik TR (2004) Properties of concrete containing scrap-tires rubber an overview. Waste Manag 24:563–569
Spasiano D, Pirozzi F (2017) Treatments of asbestos containing wastes. J Environ Manag 204:82–91
Straka P, Bucko Z (2009) Co-gasification of a lignite/waste-tire mixture in a moving bed. Fuel Process Technol 90(10):1202–1206
Syngellakis S (ed) (2015) Waste to energy. WIT press, Southampton
Tetronics Company (2011). Available: http://www.tetronics.com. Accessed 19 May 2011
Torretta V, Rada EC, Ragazzi M, Trulli E, Istrate IA, Cioca LI (2015) Treatment and disposal of tires. Two EU approaches: a review. Waste Manag 24:563–569
Tsakalou C, Papamarkou S, Tsakiridis PE, Bartzas G, Tsakalakis K (2018) Characterization and leachability evaluation of medical wastes incineration fly and bottom ashes and their vitrification outgrowths. J Environ Chem Eng 6:367–376
Tzeng C-C, Kuo Y-Y, Huang T-F, Lin D-L, Yu Y-J (1998) Treatment of radioactive waste by plasma incineration and vitrification for final disposal. J Hazard Mater 58:207–220
US-EPA (2012) Wastes-Resource-Conservation-Common Waste and Materials-Scrap Tires, US EPA Environmental Protection Agency, Washington D.C
van Velzen LPM, Bruggeman M, Botte J (2007) Proficiency test for non-destructive assay of 220 liter radioactive waste drum by gama assay system. In: Proceedings of 11th international conference on environmental remediation and radioactive waste management ICEM07-7236, Sept 2–6 Bruges, Belgium
Womack RK (1999) Using the centrifugal method for the plasma-arc vitrification of waste. JOM 51(10):14–16
Womack R, Shuey M (2002) Development and use of the dual-mode plasma torch. In: WM’02 Conf. Feb 24–28, Tucson AZ, USA
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Boulos, M.I., Jurewicz, J.W., Fauchais, P.L., Pfender, E. (2023). Plasma in the Waste Treatment Industry. In: Handbook of Thermal Plasmas. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12183-3_40-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12183-3_40-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-12183-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-12183-3
eBook Packages: Springer Reference EngineeringReference Module Computer Science and Engineering