Abstract
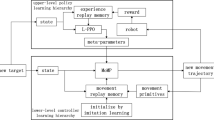
This paper presents a user-friendly method for programming humanoid robots without the need for expert knowledge. We propose a combination of imitation learning and reinforcement learning to teach and optimize demonstrated trajectories. An initial trajectory for reinforcement learning is generated using a stable whole-body motion imitation system. The acquired motion is then refined using a stochastic optimal control-based reinforcement learning algorithm called Policy Improvement with Path Integrals with Covariance Matrix Adaptation (\(\text {PI}^{2}\)-CMA). We tested the approach for programming humanoid robot reaching motion. Our experimental results show that the proposed approach is successful at learning reaching motions while preserving the postural balance of the robot. We also show how a stable humanoid robot trajectory learned in simulation can be effectively adapted to different dynamic environments, e.g. a different simulator or a real robot. The resulting learning methodology allows for quick and efficient optimization of the demonstrated trajectories while also taking into account the constraints of the desired task. The learning methodology was tested in a simulated environment and on the real humanoid robot TALOS.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Argall, B.D., Chernova, S., Veloso, M., Browning, B.: A survey of robot learning from demonstration. Robot. Auton. Syst. 57(5), 469–483 (2009)
Dillmann, R.: Teaching and learning of robot tasks via observation of human performance. Robot. Auton. Syst. 47(2–3), 109–116 (2004)
Ijspeert, A.J., Nakanishi, J., Hoffmann, H., Pastor, P., Schaal, S.: Dynamical movement primitives: learning attractor models for motor behaviors. Neural Comput. 25(2), 328–373 (2013)
Kajita, S., Kanehiro, F., Kaneko, K., Yokoi, K., Hirukawa, H.: The 3D linear inverted pendulum mode: a simple modeling for a biped walking pattern generation. In: IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Takamatsu, Japan, pp. 239–246 (2001)
Kober, J., Peters, J.: Policy search for motor primitives in robotics. Mach. Learn. 84, 171–203 (2010)
Koenemann, J., Burget, F., Bennewitz, M.: Real-time imitation of human whole-body motions by humanoids. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 2806–2812 (2014)
Savevska, K., Simonič, M., Ude, A.: Modular real-time system for upper-body motion imitation on humanoid robot talos. In: Zeghloul, S., Laribi, M.A., Sandoval, J. (eds.) RAAD 2021. MMS, vol. 102, pp. 229–239. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-75259-0_25
Schaal, S.: Learning from demonstration. In: 9th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1040–1046 (1996)
Stulp, F., Buchli, J., Theodorou, E., Schaal, S.: Reinforcement learning of full-body humanoid motor skills. In: 2010 10th IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots, pp. 405–410 (2010)
Stulp, F., Sigaud, O.: Path integral policy improvement with covariance matrix adaptation. In: Proceedings of the 10th European Workshop on Reinforcement Learning (EWRL 2012), vol. 1 (2012)
Sugihara, T., Nakamura, Y., Inoue, H.: Real-time humanoid motion generation through ZMP manipulation based on inverted pendulum control. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 1404–1409 (2002)
Theodorou, E., Buchli, J., Schaal, S.: Learning policy improvements with path integrals. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 9, 828–835 (2010)
Theodorou, E., Buchli, J., Schaal, S.: Reinforcement learning of motor skills in high dimensions: a path integral approach. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 2397–2403 (2010)
Ude, A., Atkeson, C., Riley, M.: Programming full-body movements for humanoid robots by observation. Robot. Auton. Syst. 47(2–3), 93–108 (2004)
Ude, A., Gams, A., Asfour, T., Morimoto, J.: Task-specific generalization of discrete and periodic dynamic movement primitives. IEEE Trans. Rob. 26(5), 800–815 (2010)
Vakanski, A., Janabi-Sharifi, F.: Robot Learning by Visual Observation. Wiley, Hoboken (2017)
Vukobratović, M., Stepanenko, J.: On the stability of anthropomorphic systems. Math. Biosci. 15(1), 1–37 (1972)
Yang, C., Yuan, K., Heng, S., Komura, T., Li, Z.: Learning natural locomotion behaviors for humanoid robots using human bias. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 5(2), 2610–2617 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Savevska, K., Ude, A. (2023). Teaching Humanoid Robot Reaching Motion by Imitation and Reinforcement Learning. In: Petrič, T., Ude, A., Žlajpah, L. (eds) Advances in Service and Industrial Robotics. RAAD 2023. Mechanisms and Machine Science, vol 135. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-32606-6_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-32606-6_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-32605-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-32606-6
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)