Abstract
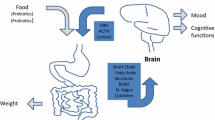
In the present chapter, we provide a comprehensive review of the potential role of gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of anorexia nervosa (AN) and discuss the potential of modifying the gut microbiota as an adjunct to standard nutritional treatment protocols for AN patients. Recently, the gut microbiota has been increasingly recognized as an important factor contributing to various diseases, including psychiatric disorders. Gut microbiota communicates with the central nervous system on the gut-brain axis and potentially affects mental health. In patients with AN, the microbial composition and related microbial products differ from healthy individuals. The microbiota in the gastrointestinal tract is a very important antigenic source for the host immune system. Evidence is now emerging for an association between specific psychiatric disorders and altered immune reactions, some of which have been described in patients with AN. Some immune components have the potential to regulate brain functions and may underlie the pathology of anorexia nervosa.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
Activity-based anorexia
- AN:
-
Anorexia nervosa
- ATB:
-
Antibiotic
- BCAA:
-
Branched-chain amino acid
- BED:
-
Binge eating disorder
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- BN:
-
Bulimia nervosa
- ClpB:
-
Caseinolytic protease B
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- DNA:
-
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- FMT:
-
Fecal microbiota transplantation
- fT4:
-
Free thyroxine
- GABA:
-
Gamma-aminobutyric acid
- GF:
-
Germ-free
- HPA axis:
-
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis
- IBD:
-
Inflammatory bowel disease
- IBS:
-
Irritable bowel syndrome
- IgG:
-
Immunoglobulin G
- IL-17:
-
Interleukin 17
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin 6
- MC:
-
Melanocortin
- NPY/AGRP:
-
Neuropeptide Y/agouti-related peptide
- OTU:
-
Operational taxonomic unit
- PANDAS:
-
Pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorder associated with streptococcal infections
- POMC/CART:
-
Pro-opiomelanocortin/cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript
- SAM:
-
S-Adenosyl-l-methionine
- SCFA:
-
Short-chain fatty acid
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor alpha
- TSH:
-
Thyroid-stimulating hormone
- α-MSH:
-
Alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone
References
Armougom F, Henry M, Vialettes B et al (2009) Monitoring bacterial community of human gut microbiota reveals an increase in Lactobacillus in obese patients and methanogens in anorexic patients. PLoS One 4(9):e7125
Aslam H, Green J, Jacka FN et al (2020) Fermented foods, the gut and mental health: a mechanistic overview with implications for depression and anxiety. Nutr Neurosci 23(9):659–671
Attia S, Versloot CJ, Voskuijl W et al (2016) Mortality in children with complicated severe acute malnutrition is related to intestinal and systemic inflammation: an observational cohort study. Am J Clin Nutr 104(5):1441–1449
Blanton LV, Charbonneau MR, Salih T et al (2016) Gut bacteria that prevent growth impairments transmitted by microbiota from malnourished children. Science 351(6275)
Borgo F, Riva A, Benetti A et al (2017) Microbiota in anorexia nervosa: the triangle between bacterial species, metabolites and psychological tests. PLoS One 12(6):e0179739
Breton J, Tirelle P, Hasanat S et al (2021) Gut microbiota alteration in a mouse model of anorexia nervosa. Clin Nutr 40(1):181–189
Burokas A, Arboleya S, Moloney RD et al (2017) Targeting the microbiota-gut-brain axis: prebiotics have anxiolytic and antidepressant-like effects and reverse the impact of chronic stress in mice. Biol Psychiatry 82(7):472–487
Chambers ES, Morrison DJ, Frost G (2015) Control of appetite and energy intake by SCFA: what are the potential underlying mechanisms? Proc Nutr Soc 74(3):328–336
Chevalier G, Siopi E, Guenin-Mace L et al (2020) Effect of gut microbiota on depressive-like behaviors in mice is mediated by the endocannabinoid system. Nat Commun 11(1):6363
Claesson MJ, Jeffery IB, Conde S et al (2012) Gut microbiota composition correlates with diet and health in the elderly. Nature 488(7410):178–184
Couto MR, Goncalves P, Magro F et al (2020) Microbiota-derived butyrate regulates intestinal inflammation: focus on inflammatory bowel disease. Pharmacol Res 159:104947
Crovesy L, Masterson D, Rosado EL (2020) Profile of the gut microbiota of adults with obesity: a systematic review. Eur J Clin Nutr 74(9):1251–1262
Cryan JF, Kaupmann K (2005) Don’t worry ‘B’ happy!: a role for GABA(B) receptors in anxiety and depression. Trends Pharmacol Sci 26(1):36–43
David LA, Maurice CF, Carmody RN et al (2014) Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 505(7484):559–563
De Berardis D, Orsolini L, Serroni N et al (2016) A comprehensive review on the efficacy of S-Adenosyl-l-methionine in major depressive disorder. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 15(1):35–44
de Clercq NC, Frissen MN, Davids M et al (2019) Weight gain after fecal microbiota transplantation in a patient with recurrent underweight following clinical recovery from anorexia nervosa. Psychother Psychosom 88(1):58–60
De Vadder F, Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Goncalves D et al (2014) Microbiota-generated metabolites promote metabolic benefits via gut-brain neural circuits. Cell 156(1–2):84–96
Ellekilde M, Selfjord E, Larsen CS et al (2014) Transfer of gut microbiota from lean and obese mice to antibiotic-treated mice. Sci Rep 4:5922
Estour B, Germain N, Diconne E et al (2010) Hormonal profile heterogeneity and short-term physical risk in restrictive anorexia nervosa. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95(5):2203–2210
Evans SJ, Bassis CM, Hein R et al (2017) The gut microbiome composition associates with bipolar disorder and illness severity. J Psychiatr Res 87:23–29
Fetissov SO, Hokfelt T (2019) On the origin of eating disorders: altered signaling between gut microbiota, adaptive immunity and the brain melanocortin system regulating feeding behavior. Curr Opin Pharmacol 48:82–91
Fetissov SO, Hallman J, Oreland L et al (2002) Autoantibodies against alpha -MSH, ACTH, and LHRH in anorexia and bulimia nervosa patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99(26):17155–17160
Fetissov SO, Hamze Sinno M, Coeffier M et al (2008) Autoantibodies against appetite-regulating peptide hormones and neuropeptides: putative modulation by gut microflora. Nutrition 24(4):348–359
Fitzpatrick Z, Frazer G, Ferro A et al (2020) Gut-educated IgA plasma cells defend the meningeal venous sinuses. Nature 587(7834):472–476
Frost G, Sleeth ML, Sahuri-Arisoylu M et al (2014) The short-chain fatty acid acetate reduces appetite via a central homeostatic mechanism. Nat Commun 5:3611
Galusca B, Prevost G, Germain N et al (2015) Neuropeptide Y and alpha-MSH circadian levels in two populations with low body weight: anorexia nervosa and constitutional thinness. PLoS One 10(3):e0122040
Gao J, Cahill CM, Huang X et al (2018) S-Adenosyl Methionine and transmethylation pathways in neuropsychiatric diseases throughout life. Neurotherapeutics 15(1):156–175
Genton L, Cani PD, Schrenzel J (2015) Alterations of gut barrier and gut microbiota in food restriction, food deprivation and protein-energy wasting. Clin Nutr 34(3):341–349
Ghoshal U, Shukla R, Srivastava D et al (2016) Irritable bowel syndrome, particularly the constipation-predominant form, involves an increase in Methanobrevibacter smithii, which is associated with higher methane production. Gut Liver 10(6):932–938
Gilbert JA, Blaser MJ, Caporaso JG et al (2018) Current understanding of the human microbiome. Nat Med 24(4):392–400
Goodrich JK, Waters JL, Poole AC et al (2014) Human genetics shape the gut microbiome. Cell 159(4):789–799
Guilherme MDS, Nguyen VTT, Reinhardt C et al (2021) Impact of gut microbiome manipulation in 5xFAD mice on Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology. Microorganisms 9(4):815
Haghighat N, Rajabi S, Mohammadshahi M (2021) Effect of synbiotic and probiotic supplementation on serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor level, depression and anxiety symptoms in hemodialysis patients: a randomized, double-blinded, clinical trial. Nutr Neurosci 24(6):490–499
Haleem DJ (2012) Serotonin neurotransmission in anorexia nervosa. Behav Pharmacol 23(5–6):478–495
Hanachi M, Manichanh C, Schoenenberger A et al (2019) Altered host-gut microbes symbiosis in severely malnourished anorexia nervosa (AN) patients undergoing enteral nutrition: an explicative factor of functional intestinal disorders? Clin Nutr 38(5):2304–2310
Hao Z, Wang W, Guo R et al (2019) Faecalibacterium prausnitzii (ATCC 27766) has preventive and therapeutic effects on chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression-like and anxiety-like behavior in rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 104:132–142
Ilzarbe L, Fabrega M, Quintero R et al (2017) Inflammatory bowel disease and eating disorders: a systematized review of comorbidity. J Psychosom Res 102:47–53
Jesus P, Ouelaa W, Francois M et al (2014) Alteration of intestinal barrier function during activity-based anorexia in mice. Clin Nutr 33(6):1046–1053
Jiang H, Ling Z, Zhang Y et al (2015) Altered fecal microbiota composition in patients with major depressive disorder. Brain Behav Immun 48:186–194
Kleiman SC, Watson HJ, Bulik-Sullivan EC et al (2015) The intestinal microbiota in acute anorexia nervosa and during renourishment: relationship to depression, anxiety, and eating disorder psychopathology. Psychosom Med 77(9):969–981
Kleiman SC, Bulik-Sullivan EC, Glenny EM et al (2017) The gut-brain axis in healthy females: lack of significant association between microbial composition and diversity with psychiatric measures. PLoS One 12(1):e0170208
Lee CJ, Sears CL, Maruthur N (2020) Gut microbiome and its role in obesity and insulin resistance. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1461(1):37–52
Levy M, Kolodziejczyk AA, Thaiss CA et al (2017) Dysbiosis and the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 17(4):219–232
Liang D, Leung RK, Guan W et al (2018) Involvement of gut microbiome in human health and disease: brief overview, knowledge gaps and research opportunities. Gut Pathog 10:3
Liu RT, Walsh RFL, Sheehan AE (2019) Prebiotics and probiotics for depression and anxiety: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 102:13–23
Louis P, Flint HJ (2017) Formation of propionate and butyrate by the human colonic microbiota. Environ Microbiol 19(1):29–41
Lucas N, Legrand R, Bole-Feysot C et al (2019) Immunoglobulin G modulation of the melanocortin 4 receptor signaling in obesity and eating disorders. Transl Psychiatry 9(1):87
Lurie I, Yang YX, Haynes K et al (2015) Antibiotic exposure and the risk for depression, anxiety, or psychosis: a nested case-control study. J Clin Psychiatry 76(11):1522–1528
Ma ZS (2020) Testing the Anna Karenina principle in human microbiome-associated diseases. iScience 23(4):101007
Mack I, Cuntz U, Gramer C et al (2016) Weight gain in anorexia nervosa does not ameliorate the faecal microbiota, branched chain fatty acid profiles, and gastrointestinal complaints. Sci Rep 6:26752
Maier SF, Watkins LR (1998) Cytokines for psychologists: implications of bidirectional immune-to-brain communication for understanding behavior, mood, and cognition. Psychol Rev 105(1):83–107
Marcos A, Nova E, Montero A (2003) Changes in the immune system are conditioned by nutrition. Eur J Clin Nutr 57(Suppl 1):S66–S69
Million M, Angelakis E, Maraninchi M et al (2013) Correlation between body mass index and gut concentrations of Lactobacillus reuteri, Bifidobacterium animalis, Methanobrevibacter smithii and Escherichia coli. Int J Obes 37(11):1460–1466
Mohammadi AA, Jazayeri S, Khosravi-Darani K et al (2016) The effects of probiotics on mental health and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in petrochemical workers. Nutr Neurosci 19(9):387–395
Monteleone P, Carratu R, Carteni M et al (2004) Intestinal permeability is decreased in anorexia nervosa. Mol Psychiatry 9(1):76–80
Monteleone AM, Troisi J, Serena G et al (2021) The gut microbiome and metabolomics profiles of restricting and binge-purging type anorexia nervosa. Nutrients 13(2):507
Morita C, Tsuji H, Hata T et al (2015) Gut Dysbiosis in patients with anorexia nervosa. PLoS One 10(12):e0145274
Morkl S, Lackner S, Muller W et al (2017) Gut microbiota and body composition in anorexia nervosa inpatients in comparison to athletes, overweight, obese, and normal weight controls. Int J Eat Disord 50(12):1421–1431
Muller N (2017) Immunological aspects of the treatment of depression and schizophrenia. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 19(1):55–63
Murray E, Sharma R, Smith KB et al (2019) Probiotic consumption during puberty mitigates LPS-induced immune responses and protects against stress-induced depression- and anxiety-like behaviors in adulthood in a sex-specific manner. Brain Behav Immun 81:198–212
Neuman H, Debelius JW, Knight R et al (2015) Microbial endocrinology: the interplay between the microbiota and the endocrine system. FEMS Microbiol Rev 39(4):509–521
Ni J, Wu GD, Albenberg L et al (2017) Gut microbiota and IBD: causation or correlation? Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 14(10):573–584
Pfleiderer A, Lagier JC, Armougom F et al (2013) Culturomics identified 11 new bacterial species from a single anorexia nervosa stool sample. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 32(11):1471–1481
Prochazkova P, Roubalova R, Dvorak J et al (2019) Microbiota, microbial metabolites, and barrier function in a patient with anorexia nervosa after fecal microbiota transplantation. Microorganisms 7(9):338
Prochazkova P, Roubalova R, Dvorak J et al (2021) The intestinal microbiota and metabolites in patients with anorexia nervosa. Gut Microbes 13(1):1–25
Queipo-Ortuno MI, Seoane LM, Murri M et al (2013) Gut microbiota composition in male rat models under different nutritional status and physical activity and its association with serum leptin and ghrelin levels. PLoS One 8(5):e65465
Ridaura VK, Faith JJ, Rey FE et al (2013) Gut microbiota from twins discordant for obesity modulate metabolism in mice. Science 341(6150):1241214
Rocks T, West M, Hockey M et al (2021) Possible use of fermented foods in rehabilitation of anorexia nervosa: the gut microbiota as a modulator. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 107:110201
Roubalova R, Prochazkova P, Papezova H et al (2020) Anorexia nervosa: gut microbiota-immune-brain interactions. Clin Nutr 39(3):676–684
Roubalova R, Prochazkova P, Dvorak J et al (2021) Altered serum immunological and biochemical parameters and microbiota composition in patients with AN during realimentation. Front Nutr 8:680870
Safadi JM, Quinton AMG, Lennox BR et al (2021) Gut dysbiosis in severe mental illness and chronic fatigue: a novel trans-diagnostic construct? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry 27(1):141–153
Savignac HM, Couch Y, Stratford M et al (2016) Prebiotic administration normalizes lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced anxiety and cortical 5-HT2A receptor and IL1-beta levels in male mice. Brain Behav Immun 52:120–131
Schulz N, Belheouane M, Dahmen B et al (2021) Gut microbiota alteration in adolescent anorexia nervosa does not normalize with short-term weight restoration. Int J Eat Disord 54(6):969–980
Sender R, Fuchs S, Milo R (2016) Revised estimates for the number of human and bacteria cells in the body. PLoS Biol 14(8):e1002533
Shanahan F, van Sinderen D, O’Toole PW et al (2017) Feeding the microbiota: transducer of nutrient signals for the host. Gut 66(9):1709–1717
Singh RK, Chang HW, Yan D et al (2017) Influence of diet on the gut microbiome and implications for human health. J Transl Med 15(1):73
Smitka K, Prochazkova P, Roubalova R et al (2021) Current aspects of the role of autoantibodies directed against appetite-regulating hormones and the gut microbiome in eating disorders. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 12:613983
Sodersten P, Bergh C, Leon M et al (2016) Dopamine and anorexia nervosa. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 60:26–30
Sokol MS (2000) Infection-triggered anorexia nervosa in children: clinical description of four cases. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 10(2):133–145
Speranza E, Cioffi I, Santarpia L et al (2018) Fecal short chain fatty acids and dietary intake in Italian women with restrictive anorexia nervosa: a pilot study. Front Nutr 5:119
Teixeira TF, Souza NC, Chiarello PG et al (2012) Intestinal permeability parameters in obese patients are correlated with metabolic syndrome risk factors. Clin Nutr 31(5):735–740
Tennoune N, Chan P, Breton J et al (2014) Bacterial ClpB heat-shock protein, an antigen-mimetic of the anorexigenic peptide alpha-MSH, at the origin of eating disorders. Transl Psychiatry 4:e458
Tidjani Alou M, Million M, Traore SI et al (2017) Gut bacteria missing in severe acute malnutrition, can we identify potential probiotics by culturomics? Front Microbiol 8:899
Tirelle P, Breton J, Kauffmann A et al (2021) Gut microbiota depletion affects nutritional and behavioral responses to activity-based anorexia model in a sex-dependent manner. Clin Nutr 40(5):2734–2744
Tomasova P, Prochazkova P, Roubalova R et al (2021) NMR- and MS-based untargeted metabolomic study of stool and serum samples from patients with anorexia nervosa. J Proteome Res 21:778–787
Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA et al (2006) An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 444(7122):1027–1031
Turnbaugh PJ, Hamady M, Yatsunenko T et al (2009) A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 457(7228):480–484
Valcarce DG, Martinez-Vazquez JM, Riesco MF et al (2020) Probiotics reduce anxiety-related behavior in zebrafish. Heliyon 6(5):e03973
van de Wouw M, Schellekens H, Dinan TG et al (2017) Microbiota-gut-brain axis: modulator of host metabolism and appetite. J Nutr 147(5):727–745
Yang J, Wang C, Huang K et al (2020) Compound Lactobacillus sp. administration ameliorates stress and body growth through gut microbiota optimization on weaning piglets. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104(15):6749–6765
Zaneveld JR, McMinds R, Vega Thurber R (2017) Stress and stability: applying the Anna Karenina principle to animal microbiomes. Nat Microbiol 2:17121
Zhu F, Guo R, Wang W et al (2020) Transplantation of microbiota from drug-free patients with schizophrenia causes schizophrenia-like abnormal behaviors and dysregulated kynurenine metabolism in mice. Mol Psychiatry 25(11):2905–2918
Acknowledgments
Supported by Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic, grant nr. NU22-04-00010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Roubalova, R., Prochazkova, P., Papezova, H. (2023). Linking Anorexia Nervosa with the Gut Microbiota. In: Patel, V.B., Preedy, V.R. (eds) Eating Disorders. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16691-4_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16691-4_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-16690-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-16691-4
eBook Packages: MedicineReference Module Medicine