Abstract
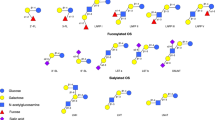
Human milk oligosaccharides (HMOS) are the third most abundant solid fraction in breast milk, and that exerts various health benefits to infants. Biosynthesis of lactose and different HMOS is carried out in the Golgi apparatus of lactocytes. Once lactose is synthesized, glycosyltransferases gradually catalyze the linkage of different monosaccharides to its structure. More than 1000 different compounds are thought to be produced via that pathway. They have been classified into fucosyl (FUCOS), nonfucosyl neutral, and sialyl milk oligosaccharides (SIAMOS). Moreover, the ratio between these structures depends on genetic factors such as the secretory gene (Se). In fact, this gene encodes the biosynthesis of FUCOS such as 2’-fucosyllactose (2’FL), which is the most abundant and studied HMO. Due to the important role HMOS play in infant feeding, many in vitro production strategies have been developed and include chemical, enzymatic, and chemoenzymatic synthesis, as well as fermentation. In addition, biological activity of various HMOS has been studied at different levels, both in cell lines and in infants. Among the most important functions associated with HMOS are inhibition of pathogens, prebiotic activity, stimulation of the immune system, and neuronal development. For these reasons, HMOS offer several important potential applications such as additives in the design of infant formulas, functional foods, and food supplements. However, these types of products must comply with strict rules of regulatory agencies. In that regard, it is necessary to increasingly study these compounds to provide a high number of HMOS that can be incorporated and approved for their use and commercialization in functional foods for human health in the future.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agoston K, Hederos MJ, Bajza I, Dekany G. Kilogram scale chemical synthesis of 2’-fucosyllactose. Carbohydr Res. 2019;476:71–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2019.03.006.
Alderete TL, Autran C, Brekke BE, Knight R, Bode L, Goran MI, et al. Associations between human milk oligosaccharides and infant body composition in the first 6 mo of life. Am J Clin Nutr. 2015;102(6):1381–8. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.115.115451.
Bae B, Kim H, Park H, Koh YJ, Bae SJ, Ha KT. Anti-angiogenic property of free human oligosaccharides. Biomol Ther. 2021;11(775):1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11060775.
Bai Y, Tao J, Zhou J, Fan Q, Liu M, Hu Y, et al. Fucosylated human milk oligosaccharides and N-glycans in the milk of Chinese mothers regulate the gut microbiome of their breast-fed infants during different lactation stages. mSystems. 2018;3(6):e00206–18. https://doi.org/10.1128/mSystems.00206-18.
Bandara MD, Stine KJ, Demchenko AV. The chemical synthesis of human milk oligosaccharides: lacto-N-tetraose (Galβ1→3GlcNAcβ1→3Galβ1→4Glc). Carbohydr Res. 2019;486:107824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2019.107824.
Baumgärtner F, Seitz L, Sprenger GA, Albermann C. Construction of Escherichia coli strains with chromosomally integrated expression cassettes for the synthesis of 2’-fucosyllactose. Microb Cell Factories. 2013;12(1):40. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-12-40.
Baumgärtner F, Conrad J, Sprenger GA, Albermann C. Synthesis of the human milk oligosaccharide lacto-N-tetraose in metabolically engineered, plasmid-free E. coli. Chembiochem. 2014;15(13):1896–900. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201402070.
Baumgärtner F, Jurzitza L, Conrad J, Beifuss U, Sprenger GA, Albermann C. Synthesis of fucosylated lacto-N-tetraose using whole-cell biotransformation. Bioorg Med Chem. 2015;23(21):6799–806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2015.10.005.
Berger PK, Plows JF, Jones RB, Alderete TL, Yonemitsu C, Poulsen M, et al. Human milk oligosaccharide 2’-fucosyllactose links feedings at 1 month to cognitive development at 24 months in infants of normal and overweight mothers. PLoS One. 2020;15(2):e0228323. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0228323.
Binia A, Lavalle L, Chen C, Austin S, Agosti M, Al-Jashi I, et al. Human milk oligosaccharides, infant growth, and adiposity over the first 4 months of lactation. Pediatr Res. 2021; https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-020-01328-y.
Bode L. The functional biology of human milk oligosaccharides. Early Hum Dev. 2015;91:619–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2015.09.001.
Bode L, Campbell S, Furneaux R, Beauprez J, Muscroft-Taylor A. Making human milk oligosaccharides available for research and application – approaches, challenges, and future opportunities. In: McGuire MK, McGuire MA, Bode L, editors. Prebiotics and probiotics and human Milk. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2017. [cited 2021 Oct 10]. Chapter 9. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128027257000099.
Boudry G, Charton E, Huerou-Luron I, Ferret-Bernard S, Gall S, Even S, et al. The relationship between breast milk components and the infant gut microbiota. Front Nutr. 2021;8:629740. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2021.629740.
Bunesova V, Lacroix C, Schwab C. Fucosyllactose and L-fucose utilization of infant Bifidobacterium longum and Bifidobacterium kashiwanohense. BMC Microbiol. 2016;16(1):248. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-016-0867-4.
Castillo-Courtade L, Han S, Lee S, Mian FM, Buck R, Forsythe P. Attenuation of food allergy symptoms following treatment with human milk oligosaccharides in a mouse model. Allergy. 2015;70(9):1091–102. https://doi.org/10.1111/all.12650.
Charbonneau MR, O’Donnell D, Blanton LV, Totten SM, Davis JCC, Barratt MJ, et al. Sialylated milk oligosaccharides promote microbiota-dependent growth in models of infant undernutrition. Cell. 2016;164:859–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.01.024.
Chaturvedi P, Warren CD, Altaye M, Morrow AL, Ruiz-Palacios G, Pickering LK, et al. Fucosylated human milk oligosaccharides vary between individuals and over the course of lactation. Glycobiology. 2001;11(5):365–72. https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/11.5.365.
Cheng L, Kong C, Wang W, Groeneveld A, Nauta A, Groves MR, et al. The human milk oligosaccharides 3-FL, lacto-N-neotetraose, and LDFT attenuate tumor necrosis factor-alpha induced inflammation in fetal intestinal epithelial cells in vitro through shedding or interacting with tumor necrosis factor receptor 1. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2021;65(7):e2000425. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.202000425.
Cho S, Zhu Z, Li T, Baluyot K, Howell BR, Hazlett HC, et al. Human milk 3’-sialyllactose is positively associated with language development during infancy. Am J Clin Nutr. 2021;114(2):588–97. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/nqab103.
Choi YH, Kim JH, Park BS, Kim BG. Solubilization and iterative saturation mutagenesis of α1,3-fucosyltransferase from helicobacter pylori to enhance its catalytic efficiency. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2016;113(8):1666–75. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.25944.
Coppa GV, Zampini L, Galeazzi T, Facinelli B, Ferrante L, Capretti R, et al. Human milk oligosaccharides inhibit the adhesion to Caco-2 cells of diarrheal pathogens: Escherichia coli, vibrio cholerae, and salmonella fyris. Pediatr Res. 2006;59(3):377–82. https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000200805.45593.17.
Craft KM, Townsend SD. Synthesis of lacto-N-tetraose. Carbohydr Res. 2017;440(441):43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2017.02.001.
Deng J, Gu L, Chen T, Huang H, Yin X, Lv X, et al. Engineering the substrate transport and cofactor regeneration systems for enhancing 2’-fucosyllactose synthesis in Bacillus subtilis. ACS Synth Biol. 2019;8(10):2418–27. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.9b00314.
Derya SM, Spiegel H, Hanisch FG, Morozov V, Schroten H, Jennewein S, et al. Biotechnologically produced fucosylated oligosaccharides inhibit the binding of human noroviruses to their natural receptors. J Biotechnol. 2020;318:31–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2020.05.001.
Donovan SM, Comstock SS. Human milk oligosaccharides influence neonatal mucosal and systemic immunity. Ann Nutr Metab. 2016;69(Suppl 2):42–51. https://doi.org/10.1159/000452818.
Drouillard S, Mine T, Kajiwara H, Yamamoto T, Samain E. Efficient synthesis of 6’-sialyllactose, 6,6’-disialyllactose, and 6’-KDO-lactose by metabolically engineered E. coli expressing a multifunctional sialyltransferase from the Photobacterium sp JT-ISH-224. Carbohydr Res. 2010;345(10):1394–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2010.02.018.
Duska-McEwen G, Senft AP, Ruetschilling TL, Barrett EG, Buck RH. Human milk oligosaccharides enhance innate immunity to respiratory syncytial virus and influenza in vitro. Food Nutr Sci. 2014;5(14):1387–98. https://doi.org/10.4236/fns.2014.514151.
Engels L, Elling L. WbgL: a novel bacterial α1,2-fucosyltransferase for the synthesis of 2’-fucosyllactose. Glycobiology. 2014;24(2):170–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cwt096.
Faijes M, Castejón-Vilatersana M, Val-Cid C, Planas. Enzymatic and cell factory approaches to the production of human milk oligosaccharides. Biotechnol Adv. 2019;37(5):667–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.03.014.
Fair RJ, Hahm HS, Seeberger PH. Combination of automated solid-phase and enzymatic oligosaccharide synthesis provides access to α(2,3)-sialylated glycans. Chem Commun. 2015;51(28):6183–5.
Fierfort N, Samain E. Genetic engineering of Escherichia coli for the economical production of sialylated oligosaccharides. J Biotechnol. 2008;134(3–4):261–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2008.02.010.
Fonvig CE, Amundsen ID, Vigsnæs LK, Sørensen N, Frithioff-Bøjsøe C, Christiansen M, et al. Human milk oligosaccharides modulate fecal microbiota and are safe for use in children with overweight: a randomized controlled trial. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2021;73(3):408–14.
Gabrielli O, Zampini L, Galeazzi T, Padella L, Santoro L, Peila C, et al. Preterm milk oligosaccharides during the first month of lactation. Pediatrics. 2011;128:e1520. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2011-1206.
Gangwar L, Sahu S, Deepak D. Synthesis of reverse building blocks of milk oligosaccharides. Chem Biol Int. 2018;8(3):162–76.
Goehring KC, Marriage BJ, Oliver JS, Wilder JA, Barrett EG, Buck RH. Similar to those who are breastfed, infants fed a formula containing 2’-fucosyllactose have lower inflammatory cytokines in a randomized controlled trial. J Nutr. 2016;146(12):2559–66. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.116.236919.
Guo Y, Jers C, Meyer AS, Arnous A, Li H, Kirpekar F, et al. A Pasteurella multocida sialyltransferase displaying dual trans-sialidase activities for production of 3’-sialyl and 6’-sialyl glycans. J Biotechnol. 2014;170:60–7.
Guo L, Chen X, Xu L, Xiao M, Lu L. Enzymatic synthesis of 6’-sialyllactose, a dominant sialylated human milk oligosaccharide, by a novel exo-a-sialidase from Bacteroides fragilis NCTC9343. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018;84(13):e00071. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00071-18.
Guzmán-Rodríguez F, Alatorre-Santamaría S, Gómez-Ruiz L, Rodríguez-Serrano G, García-Garibay M, Cruz-Guerrero A. Synthesis of a fucosylated trisaccharide via transglycosylation by α-L-fucosidase from Thermotoga maritima. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2018;186(3):681–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-018-2771-x.
Hauser J, Pisa E, Vásquez AA, Tomasi F, Traversa A, Chiodi V, et al. Sialylated human milk oligosaccharides program cognitive development through a non-genomic transmission mode. Mol Psychiatry. 2021;26:2854–71. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-021-01054-9.
Hegar B, Wibowo Y, Basrowi RW, Ranuh RG, Sudarmo SM, Munasir Z, et al. The role of two human milk oligosaccharides, 2’-fucosyllactose and lacto-N-neotetraose, in infant nutrition. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2019;22(4):330–40. https://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2019.22.4.330.
Hollands K, Baron CM, Gibson KJ, Kelly KJ, Krasley EA, Laffend LA, et al. Engineering two species of yeast as cell factories for 2’-fucosyllactose. Metab Eng. 2019;52:232–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.12.005.
Huang D, Yang K, Liu J, Xu Y, Wang Y, Wang R, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of 2’-fucosyllactose and 3-fucosyllactose through modular pathway enhancement. Metab Eng. 2017;41:23–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2017.03.001.
Jorgensen JM, Young R, Ashorn P, Ashorn U, Chaima D, Davis JC, et al. Associations of human milk oligosaccharides and bioactive proteins with infant morbidity and inflammation in Malawian mother-infant dyads. Curr Dev Nutr. 2021;5(5):nzab072. https://doi.org/10.1093/cdn/nzab072.
Korpela K, Salonen A, Hickman B, Kunz C, Sprenger N, Kukkonen K, et al. Fucosylated oligosaccharides in mother’s milk alleviate the effects of caesarean birth on infant gut microbiota. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):13757. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-32037-6.
Larsson MW, Lind MV, Laursen RP, Yonemitsu C, Larnkjaer A, Molgaard C, et al. Human milk oligosaccharide composition is associated with excessive weight gain during exclusive breastfeeding-an explorative study. Front Pediatr. 2019;7:297. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2019.00297.
McArthur JB, Yu H, Chen X. A bacterial β1–3-galactosyltransferase enables multigram-scale synthesis of human milk lacto-N-tetraose (LNT) and its fucosides. ACS Catal. 2019;9(12):10721–6. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.9b03990.
Morrow AL, Ruiz-Palacios GM, Altaye M, Jiang X, Guerrero ML, Meinzen-Derr JK, et al. Human milk oligosaccharides are associated with protection against diarrhea in breast-fed infants. J Pediatr. 2004;145(3):297–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2004.04.054.
Nowak-Wegrzyn A, Czerkies L, Reyes K, Collins B, Heine RG. Confirmed hypoallergenicity of a novel whey-based extensively hydrolyzed infant formula containing two human milk oligosaccharides. Nutrients. 2019;11(7):1447. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11071447.
Oliveira DL, Wilbey RA, Grandison AS, Roseiro LB. Milk oligosaccharides: a review. Int J Dairy Technol. 2015;68(3):305–21. https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-0307.12209.
Oliveros E, Ramirez M, Vazquez E, Barranco A, Gruart A, Delgado-Garcia JM, et al. Oral supplementation of 2’-fucosyllactose during lactation improves memory and learning in rats. J Nutr Biochem. 2016;31:20–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.12.014.
Orczyk-Pawiłowicz M, Lis-Kuberka J. The impact of dietary fucosylated oligosaccharides and glycoproteins of human milk on infant Well-being. Nutrients. 2020;12(4):1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041105.
Perna VN, Dehlholm C, Meyer AS. Enzymatic production of 3’-sialyllactose in milk. Enzyme Microbiol Technol. 2021;148:109829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2021.109829.
Prudden AR, Liu L, Capicciotti CJ, Wolfert MA, Wang S, Gao Z, et al. Synthesis of asymmetrical multiantennary human milk oligosaccharides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(27):6954–9. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1701785114.
Ruzic L, Bolivar JM, Nidetzky B. Glycosynthase reaction meets the flow: continuous synthesis of lacto-N-triose II by engineered β-hexosaminidase immobilized on solid support. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2020;117(5):1597–602. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.27293.
Schmidt D, Thiem J. Chemical synthesis using enzymatically generated building units for construction of the human milk pentasaccharides sialyllacto-N-tetraose and sialyllacto-N-neotetraose epimer. Beilstein J Org Chem. 2010;6(18):1–7. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjoc.6.18.
Schmölzer K, Czabany T, Luley-Goedl C, Pavkov-Keller T, Ribitsch D, Schwab H, et al. Complete switch from α-2,3- to α-2,6-regioselectivity in Pasteurella dagmatis β-D-galactoside sialyltransferase by active-site redesign. Chem Commun. 2015;51(15):3083–6. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CC09772F.
Schmölzer K, Weingarten M, Baldenius K, Nidetzky B. Lacto-N-tetraose synthesis by wild-type and glycosynthase variants of the β-N-hexosaminidase from Bifidobacterium bifidum. Org Biomol Chem. 2019;17(23):5661–5.
Shi R, Ma J, Yan Q, Yang S, Fan Z, Jiang Z. Biochemical characterization of a novel α-L-fucosidase from Pedobacter sp. and its application in synthesis of 3’-fucosyllactose and 2’-fucosyllactose. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020;104(13):5813–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10630-y.
Sotgiu S, Arru G, Fois ML, Sanna A, Musumeci M, Rosati G, et al. Immunomodulation of fucosyl-lactose and lacto-N-fucopentaose on mononuclear cells from multiple sclerosis and healthy subjects. Int J Biomed Sci. 2006;2(2):114–20.
Thongaram T, Hoeflinger JL, Chow J, Miller MJ. Human milk oligosaccharide consumption by probiotic and human-associated bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. J Dairy Sci. 2017;100(10):7825–33. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2017-12753.
Thurl S, Munzert M, Boehm G, Matthews C, Stahl B. Systematic review of the concentrations of oligosaccharides in human milk. Nutr Rev. 2017;75(11):920–33. https://doi.org/10.1093/nutrit/nux044.
Tuplin EWN, Chleilat F, Alukic E, Reimer RA. The effects of human milk oligosaccharide supplementation during critical periods of development on the mesolimbic dopamine system. Neuroscience. 2021;459:166–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2021.02.006.
Urashima T, Hirabayashi J, Sato S, Kobata A. Human milk oligosaccharides as essential tools for basic and application studies on galectins. Trends Glycosci Glycotechnol. 2018;30(172):SE51–65. https://doi.org/10.4052/tigg.1734.1SE.
van Leeuwen S. Challenges and pitfalls in human milk oligosaccharide analysis. Nutrients. 2019;11:2684. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112684.
Walsh C, Lane JA, van Sinderen D, Hickey RM. From lab bench to formulated ingredient: characterization, production, and commercialization of human milk oligosaccharides. J Funct Foods. 2020;72:104052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2020.104052.
Weichert S, Jennewein S, Hufner E, Weiss C, Borkowski J, Putze J, et al. Bioengineered 2’-fucosyllactose and 3-fucosyllactose inhibit the adhesion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and enteric pathogens to human intestinal and respiratory cell lines. Nutr Res. 2013;33(10):831–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nutres.2013.07.009.
Wen L, Edmunds G, Gibbons C, Zhang J, Gadi MR, Zhu H, et al. Toward automated enzymatic synthesis of oligosaccharides. Chem Rev. 2018;118(17):8151–87. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00066.
Wicinski M, Sawicka E, Gebalski J, Kubiak K, Malinowski B. Human milk oligosaccharides: health benefits, potential applications in infant formulas, and pharmacology. Nutrients. 2020;12:266. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010266.
Williams JE, McGuire MK, Meehan CL, McGuire MA, Brooker SL, Kamau-Mbuthia EW, et al. Key genetic variants associated with variation of milk oligosaccharides from diverse human populations. Genomics. 2021;113:1867–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2021.04.004.
Yu ZT, Chen C, Newburg DS. Utilization of major fucosylated and sialylated human milk oligosaccharides by isolated human gut microbes. Glycobiology. 2013;23(11):1281–92. https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cwt065.
Yu H, Lau K, Thon V, Autran CA, Jantscher-Krenn E, Xue M, et al. Synthetic disialyl hexasaccharides protect neonatal rats from necrotizing enterocolitis. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2014;53(26):6687–91. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201403588.
Yu ZT, Nanthakumar NN, Newburg DS. The human milk oligosaccharide 2’-fucosyllactose quenches Campylobacter jejuni-induced inflammation in human epithelial cells HEp-2 and HT-29 and in mouse intestinal mucosa. J Nutr. 2016;146(10):1980–90. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.116.230706.
Yu H, Li Y, Wu Z, Li L, Zeng J, Zhao C, et al. H. Pylori α1-3/4-fucosyltransferase (Hp3/4FT)-catalyzed one-pot multienzyme (OPME) synthesis of Lewis antigens and human milk fucosides. Chem Commun. 2017;53(80):11012–5. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CC05403C.
Zeuner B, Vuillemin M, Holck J, Muschiol J, Meyer AS. Loop engineering of an α-1, 3/4-L-fucosidase for improved synthesis of human milk oligosaccharides. Enzym Microb Technol. 2018;115:37–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2018.04.008.
Zeuner B, Teze D, Muschiol J, Meyer AS. Synthesis of human milk oligosaccharides: protein engineering strategies for improved enzymatic transglycosylation. Molecules. 2019;24:2019–33. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112033.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Section Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Guzmán-Rodríguez, F., Alatorre-Santamaría, S., Cruz-Guerrero, A. (2022). Human Milk Oligosaccharides (HMOS). In: Jafari, S.M., Rashidinejad, A., Simal-Gandara, J. (eds) Handbook of Food Bioactive Ingredients. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-81404-5_35-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-81404-5_35-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-81404-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-81404-5
eBook Packages: Springer Reference Biomedicine and Life SciencesReference Module Biomedical and Life Sciences