Abstract
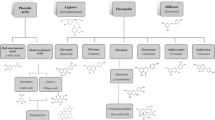
Phenolic compounds (PC) are a diverse class of phytochemicals that are thought to be among the major responsible for the association between high intake of fruits and vegetables and low risk of chronic diseases. Despite promising protective effects in vitro and in animal models, human studies associating PC intake to beneficial health effects have showed more variable results. The accurate assessment of dietary intake of the different classes of PC is a critical step in epidemiological or intervention studies and biomarkers of PC intake are an alternative to the traditional dietary assessment tools. This chapter focuses on the relation between PC intake and the concentration of PC and their metabolites in body fluids (plasma and urine). The biotransformation of PC during digestive process and their kinetics following exposure, as well as the methods used for estimating dietary intake of PC are also discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BBB:
-
Blood-brain barrier
- CBG:
-
Cytosolic β-glucosidase
- FFQ:
-
Food frequency questionaries
- GC:
-
Gas chromatography
- HepG2:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma cell line
- HRMAS:
-
High-resolution magic angle spinning
- LC:
-
Liquid chromatography
- LPH:
-
Lactase-phlorizin hydrolase
- MCT:
-
Monocarboxylic acid transporter
- MS:
-
Mass spectrometry analyzer
- NMR:
-
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
- ODMA:
-
O-desmethylangolensin
- PC:
-
Phenolic compounds
- SGLT1:
-
Sodium-glucose-linked transporter 1
- UDP:
-
Uridine diphosphate
References
Albuquerque BR, Heleno SA, MBPP O, et al. Phenolic compounds: current industrial applications, limitations and future challenges. Food Funct. 2021;12:14–29. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0fo02324h.
Andrei V, Copolovici D, Munteanu FD, et al. Detection of biomedically relevant stilbenes from wines by mass spectrometry. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1140:665–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-15950-4_40.
Appeldoorn MM, Vincken JP, Aura AM, et al. Procyanidin dimers are metabolized by human microbiota with 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)acetic acid and 5-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-γ-valerolactone as the major metabolites. J Agric Food Chem. 2009;57:1084–92. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf803059z.
Augusti PR, Conterato GMM, Denardin CC, et al. Bioactivity, bioavailability, and gut microbiota transformations of dietary phenolic compounds: implications for covid-19. J Nutr Biochem. 2021;97:108787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2021.108787.
Beckonert O, Coen M, Keun HC, et al. High-resolution magic-angle-spinning NMR spectroscopy for metabolic profiling of intact tissues. Nat Protoc. 2010;5:1019–32. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2010.45.
Bohn T. Dietary factors affecting polyphenol bioavailability. Nutr Rev. 2014;72:429–52. https://doi.org/10.1111/nure.12114.
Bolvig AK, Adlercreutz H, Theil PK, et al. Absorption of plant lignans from cereals in an experimental pig model. Br J Nutr. 2016;115:1711–20. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114516000829.
Burkholder-Cooley NM, Rajaram SS, Haddad EH, et al. Validating polyphenol intake estimates from a food-frequency questionnaire by using repeated 24-h dietary recalls and a unique method-of-triads approach with 2 biomarkers. Am J Clin Nutr. 2017;105:685–94. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.116.137174.
Cajka T, Smilowitz JT, Fiehn O. Validating quantitative untargeted lipidomics across nine liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry platforms. Anal Chem. 2017;89:12360–8. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b03404.
Cao H, Liu X, Ulrih NP, et al. Plasma protein binding of dietary polyphenols to human serum albumin: a high performance affinity chromatography approach. Food Chem. 2019;270:257–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.07.111.
Carecho R, Carregosa D, Dos Santos CN. Low molecular weight (poly)phenol metabolites across the blood-brain barrier: the underexplored journey. Brain Plast. 2020;6:193–214. https://doi.org/10.3233/bpl-200099.
Cassidy A, Minihane AM. The role of metabolism (and the microbiome) in defining the clinical efficacy of dietary flavonoids. Am J Clin Nutr. 2017;105:10–22. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.116.136051.
Catalkaya G, Venema K, Lucini L, et al. Interaction of dietary polyphenols and gut microbiota: microbial metabolism of polyphenols, influence on the gut microbiota, and implications on host health. Food Front. 2020;1:109–33. https://doi.org/10.1002/FFT2.25.
Clarke ED, Rollo ME, Collins CE, et al. The relationship between dietary polyphenol intakes and urinary polyphenol concentrations in adults prescribed a high vegetable and fruit diet. Nutrients. 2020;12:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113431.
Clarke ED, Collins CE, Rollo ME, et al. The relationship between urinary polyphenol metabolites and dietary polyphenol intakes in young adults. Br J Nutr. 2021;1–10 https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114521001343.
Clifford MN, Copeland EL, Bloxsidge JP, Mitchell LA. Hippuric acid as a major excretion product associated with black tea consumption. Xenobiotica. 2000;30:317–26. https://doi.org/10.1080/004982500237703.
Cortés-Martín A, Selma MV, Tomás-Barberán FA, et al. Where to look into the puzzle of polyphenols and health? The Postbiotics and gut microbiota associated with human Metabotypes. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2020;64:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201900952.
Crespy V, Morand C, Besson C, et al. Comparison of the intestinal absorption of quercetin, phloretin and their glucosides in rats. J Nutr. 2001;131:2109–14. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/131.8.2109.
Crozier A, Jaganath IB, Clifford MN. Dietary phenolics: chemistry, bioavailability and effects on health. Nat Prod Rep. 2009;26:1001–43. https://doi.org/10.1039/b802662a.
Crozier A, Del Rio D, Clifford MN. Bioavailability of dietary flavonoids and phenolic compounds. Mol Asp Med. 2010;6:446–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2010.09.007.
Cui Q, Du R, Liu M, Rong L. Lignans and their derivatives from plants as antivirals. Molecules. 2020;25:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010183.
da Silva DT, Smaniotto FA, Costa IF, et al. Natural deep eutectic solvent (NADES): a strategy to improve the bioavailability of blueberry phenolic compounds in a ready-to-use extract. Food Chem. 2021;364:130370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130370.
Day AJ, Mellon F, Barron D, et al. Human metabolism of dietary flavonoids: identification of plasma metabolites of quercetin. Free Radic Res. 2001;35:941–52. https://doi.org/10.1080/10715760100301441.
Daykin CA, Van Duynhoven JPM, Groenewegen A, et al. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic based studies of the metabolism of black tea polyphenols in humans. J Agric Food Chem. 2005;53:1428–34. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf048439o.
Donovan JL, Manach C, Faulks RM, et al. Absorption and metabolism of dietary secondary metabolites. In: Crozier A, Clifford MN, Ashihara H, editors. Plant secondary metabolites. Occurrence, structure and role in the human diet. Oxford, New York: Blackwell Publishing; 2006. p. 303–51.
Fan TWM, Lane AN. Applications of NMR spectroscopy to systems biochemistry. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2016;92–93:18–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnmrs.2016.01.005.
Fornasaro S, Ziberna L, Gasperotti M, et al. Determination of cyanidin 3-glucoside in rat brain, liver and kidneys by UPLC/MS-MS and its application to a short-term pharmacokinetic study. Sci Rep. 2016;6:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep228152.
Gibbons H, O’Gorman A, Brennan L. Metabolomics as a tool in nutritional research. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2015;26:30–4. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOL.0000000000000140.
Grabska-Kobylecka I, Kaczmarek-Bak J, Figlus M, et al. The presence of caffeic acid in cerebrospinal fluid: evidence that dietary polyphenols can cross the blood-brain barrier in humans. Nutrients. 2020;12:1–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051531.
Grgić J, Šelo G, Planinić M, et al. Role of the encapsulation in bioavailability of phenolic compounds. Antioxidant. 2020;9:1–35. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9100923.
Hatamipour M, Ramezani M, Tabassi SAS, et al. Demethoxycurcumin: a naturally occurring curcumin analogue for treating non-cancerous diseases. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:19320–30. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28626.
Hussain MB, Hassan S, Waheed M, et al. Bioavailability and metabolic pathway of phenolic compounds. In: Plant physiological aspects of phenolic compounds. IntechOpen; 2019. p. 1–18. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.84745.
Ichiyanagi T, Shida Y, Rahman MM, et al. Bioavailability and tissue distribution of anthocyanins in bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L.) extract in rats. J Agric Food Chem. 2006;54:6578–87. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0602370.
Kalt W. Anthocyanins and their c6-c3-c6 metabolites in humans and animals. Molecules. 2019;24:1–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24224024.
Kamonpatana K, Failla ML, Kumar SP, et al. Anthocyanin structure determines susceptibility to microbial degradation and bioavailability to the buccal mucosa. J Agric Food Chem. 2014;62:6903–10. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf405180k.
Kawabata K, Yoshioka Y, Terao J. Role of intestinal microbiota in the bioavailability and physiological functions of dietary polyphenols. Molecules. 2019;24:370. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020370.
Kotha RR, Luthria DL. Curcumin: biological, pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and analytical aspects. Molecules. 2019;24:2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162930.
Krupp D, Doberstein N, Shi L, Remer T. Hippuric acid in 24-hour urine collections is a potential biomarker for fruit and vegetable consumption in healthy children and adolescents. J Nutr. 2012;142:1314–20. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.112.159319.
Lee MJ, Maliakal P, Chen L, et al. Pharmacokinetics of tea catechins after ingestion of green tea and (_)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate by humans: formation of different metabolites and individual variability. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2002;11:1025–32.
Lin SP, Hou YC, Tsai SY, et al. Tissue distribution of naringenin conjugated metabolites following repeated dosing of naringin to rats. Biomedicine. 2014;4:1–6. https://doi.org/10.7603/s40681-014-0016-z.
Manach C, Scalbert A, Morand C, et al. Polyphenols: food sources and bioavailability. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;79:727–47. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/79.5.727.
Manach C, Williamson G, Morand C, et al. Bioavailability and bioefficacy of polyphenols in humans. I. Review of 97 bioavailability studies. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005;81:230–42. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/81.1.230s.
Margalef M, Pons Z, Bravo FI, et al. Tissue distribution of rat flavanol metabolites at different doses. J Nutr Biochem. 2015;26:987–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.04.006.
Markley JL, Brüschweiler R, Edison AS, Eghbalnia HR, Powers R, Raftery D, Wishart DS. The future of NMR-based metabolomics. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2017;43:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2016.08.001.
Mateos R, Goya L, Bravo L. Uptake and metabolism of hydroxycinnamic acids (chlorogenic, caffeic, and ferulic acids) by HepG2 cells as a model of the human liver. J Agric Food Chem. 2006;54:8724–32. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf061664g.
Matuschek MC, Hendriks WH, McGhie TK, et al. The jejunum is the main site of absorption for anthocyanins in mice. J Nutr Biochem. 2006;17:31–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2005.04.005.
Mayo B, Vázquez L, Flórez AB. Equol: a bacterial metabolite from the daidzein isoflavone and its presumed beneficial health effects. Nutrients. 2019;11:2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11092231.
McKay DL, Chen CYO, Zampariello CA, Blumberg JB. Flavonoids and phenolic acids from cranberry juice are bioavailable and bioactive in healthy older adults. Food Chem. 2015;168:233–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.07.062.
Mena P, Bresciani L, Brindani N, et al. Phenyl-γ-valerolactones and phenylvaleric acids, the main colonic metabolites of flavan-3-ols: synthesis, analysis, bioavailability, and bioactivity. Nat Prod Rep. 2019;36:714–52. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8np00062j.
Meng X, Lee MJ, Li C, et al. Formation and identification of 4’-Omethyl-( ) epigallocatechin in humans. Drug Metab Dispos. 2001;29:789–93.
Mennen LI, Sapinho D, Ito H, et al. Urinary flavonoids and phenolic acids as biomarkers of intake for polyphenol-rich foods. Br J Nutr. 2006;96:191–8. https://doi.org/10.1079/bjn20061808.
Mennen LI, Sapinho D, Ito H, et al. Urinary excretion of 13 dietary flavonoids and phenolic acids in free-living healthy subjects – variability and possible use as biomarkers of polyphenol intake. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2008;62:519–25. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602744.
Nagana Gowda GA, Raftery D. Can NMR solve some significant challenges in metabolomics? J Magn Reson. 2015;260:144–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmr.2015.07.014.
O’Leary KA, Day AJ, Needs PW, et al. Metabolism of quercetin-7- and quercetin-3-glucuronides by an in vitro hepatic model: the role of human beta-glucuronidase, sulfotransferase, catechol-O-methyltransferaseandmulti-resistant protein2 (MRP2) in flavonoid metabolism. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003;65:479–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-2952(02)01510-1.
Ottaviani J, Fong R, Ottaviani JI, et al. Evaluation at scale of microbiome-derived metabolites as biomarker of flavan-3-ol intake in epidemiological studies. Sci Rep. 2018;8 https://doi.org/10.1038/S41598-018-28333-W.
Ottaviani JI, Fong R, Kimball J, et al. Evaluation of(−)-epicatechin metabolites as recovery biomarker of dietary flavan-3-ol intake. Sci Rep. 2019;9 https://doi.org/10.1038/S41598-019-49702-Z.
Pan Z, Raftery D. Comparing and combining NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry in metabolomics. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2007;387:525–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-006-0687-8.
Pérez-Jiménez J, Hubert J, Hooper L, et al. Urinary metabolites as biomarkers of polyphenol intake in humans: a systematic review. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;92:801–9. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2010.29924.
Picó C, Serra F, Rodríguez AM, et al. Biomarkers of nutrition and health: new tools for new approaches. Nutrients. 2019;11:1–30. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11051092.
Pinto P, Santos CN. Worldwide (poly)phenol intake: assessment methods and identified gaps. Eur J Nutr. 2017;56:1393–408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-016-1354-2.
Piskula MK, Terao J. Accumulation of (_)-epicatechin metabolites in rat plasma after oral administration and distribution of conjugation enzymes in rat tissues. J Nutr. 1998;128:1172–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/128.7.1172.
Putri SP, Yamamoto S, Tsugawa H, et al. Current metabolomics: technological advances. J Biosci Bioeng. 2013;116:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2013.01.004.
Quatrin A, Rampelotto C, Pauletto R, et al. Bioaccessibility and catabolism of phenolic compounds from Jaboticaba (Myrciaria trunciflora) fruit peel during in vitro gastrointestinal digestion and colonic fermentation. J Funct Foods. 2020;65 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2019.103714.
Rios LY, Gonthier M-P, Rémésy C, et al. Chocolate intake increases urinary excretion of polyphenol-derived phenolic acids in healthy human subjects. Am J Clin Nutr. 2003;77:912–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/77.4.912.
Roberts K, Grainger E, Thomas-Ahner J, et al. Dose-dependent increases in ELLAGITANNIN metabolites as biomarkers of intake in humans consuming standardized black raspberry food products designed for clinical trials. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2020;64:1900800. https://doi.org/10.1002/MNFR.201900800.
Rolin D. Metabolomics coming of age with its technological diversity, vol. 67. Oxford, UK: Academic Press; 2012.
Sandoval-Ramírez BA, Catalán Ú, Fernández-Castillejo S, et al. Anthocyanin tissue bioavailability in animals: possible implications for human health. A systematic review. J Agric Food Chem. 2018;66:11531–43. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b04014.
Scalbert A, Williamson G. Dietary intake and bioavailability of polyphenols. J Nutr. 2000;130:2073S–85S. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/130.8.2073S.
Scalbert A, Brennan L, Manach C, et al. The food metabolome: a window over dietary exposure. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014;99:1286–308. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.113.076133.
Sensoy I. A review on the food digestion in the digestive tract and the used in vitro models. Curr Res Food Sci. 2021;4:308–19.
Serrano J, Puupponen-Pimiä R, Dauer A, et al. Tannins: current knowledge of food sources, intake, bioavailability and biological effects. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2009;53:S310–29. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.200900039.
Shahidi F, Yeo J. Insoluble-bound phenolics in food. Molecules. 2016;21:1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21091216.
Shinn LM, Li Y, Mansharamani A, et al. Fecal bacteria as biomarkers for predicting food intake in healthy adults. J Nutr. 2021;151:423–33. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/nxaa285.
Sparkman OD, Penton Z, Kitson F. Gas chromatography and mass spectrometry: a practical guide. 2nd ed. Oxford, UK: Academic Press Elsevier; 2011.
Spencer JPE, Abd El Mohsen MM, Minihane A-M, Mathers JC. Biomarkers of the intake of dietary polyphenols: strengths, limitations and application in nutrition research. Br J Nutr. 2008;99:12–22. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114507798938.
Stalmach A, Mullen W, Steiling H, et al. Absorption, metabolism, and excretion of green tea flavan-3-ols in humans with an ileostomy. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2010;54:323–34. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.200900194.
Stringlis IA, De Jonge R, Pieterse CMJ. The age of Coumarins in plant-microbe interactions. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019;60:1405–19. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcz076.
Tsao R. Chemistry and biochemistry of dietary polyphenols. Nutrients. 2010;2:1231–46. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu2121231.
Ulaszewska MM, Weinert CH, Trimigno A, et al. Nutrimetabolomics: an integrative action for metabolomic analyses in human nutritional studies. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2019;63:1–86. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201800384.
Velderrain-Rodríguez GR, Palafox-Carlos H, Wall-Medrano A, et al. Phenolic compounds: their journey after intake. Food Funct. 2014;5:189–97. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3fo60361j.
Vitaglione P, Donnarumma G, Napolitano A, et al. Protocatechuic acid is the major human metabolite of cyanidin-glucosides. J Nutr. 2007;137:2043–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/137.9.2043.
Wang D, Xia M, Yan X, et al. Gut microbiota metabolism of anthocyanin promotes reverse cholesterol transport in mice via repressing miRNA-10b. Circ Res. 2012;111:967–81. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.266502.
Williamson G, Clifford MN. Role of the small intestine, colon and microbiota in determining the metabolic fate of polyphenols. Biochem Pharmacol. 2017;139:24–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2017.03.012.
Wishart DS. Metabolomics: applications to food science and nutrition research. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2008;19:482–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2008.03.003.
Wittig J, Herderich M, Graefe EU, et al. Identification of quercetin glucuronides in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography– tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 2001;753:237–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-4347(00)00549-1.
Wu B, Basu S, Meng S, et al. Regioselective sulfation and glucuronidation of phenolics: insights into the structural basis. Curr Drug Metab. 2011;12:900–16. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920011797470100.
Yang L, Xiao N, Li XW, et al. Pharmacokinetic comparison between quercetin and quercetin 3-O-β-glucuronide in rats by UHPLC-MS/MS. Sci Rep. 2016;6:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep35460.
Yang R, Xiu H, Zhou Q, et al. Application of urinary polyphenol biomarkers measured by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry to assess polyphenol intake and their association with overweight and obesity in free-living healthy subjects. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019 https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4809836.
Zamora-Ros R, Rabassa M, Llorach R, et al. Application of dietary phenolic biomarkers in epidemiology: past, present, and future. J Agric Food Chem. 2012;60:6648–57. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf204742e.
Zamora-Ros R, Knase V, Luján-Barroso L, et al. Differences in dietary intakes, food sources and determinants of total flavonoids between Mediterranean and non-Mediterranean countries participating in the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (EPIC) study. Br J Nutr. 2013;109:1498–507. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114512003273.
Zamora-Ros R, Knase V, Rothwell JA, et al. Dietary polyphenol intake in Europe: the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (EPIC) study. Eur J Nutr. 2016;55:1359–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00394-015-0950-X.
Zhong S, Sandhu A, Edirisinghe I, Burton-Freeman B. Characterization of wild blueberry polyphenols bioavailability and kinetic profile in plasma over 24-h period in human subjects. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2017;61:1700405. https://doi.org/10.1002/MNFR.201700405.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Augusti, P.R. et al. (2022). Biological Markers of Plant Phenolic Compounds Intake. In: Patel, V.B., Preedy, V.R. (eds) Biomarkers in Nutrition . Biomarkers in Disease: Methods, Discoveries and Applications. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-81304-8_60-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-81304-8_60-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-81304-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-81304-8
eBook Packages: Springer Reference Biomedicine and Life SciencesReference Module Biomedical and Life Sciences