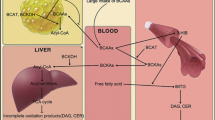
Abstract
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disease with serious health consequences for a modern civilization that often lead to premature death. With the rapid increase in the number of people diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, early identification of those individuals at higher risk of progression to diabetes is a key criterion enabling the timely intervention or treatment. In recent years, omics-based technologies have given us unprecedented insight into circulating biomarkers in common diseases. Branched-chain amino acids: valine, leucine, isoleucine, and aromatic amino acids, that is, tyrosine and phenylalanine, have been demonstrated as the most consistent metabolite biomarkers for diabetes, in particular type 2.
Therefore, amino acids quantification in biological material, primarily in plasma could be a valuable prognostic tool for determining metabolic abnormalities leading to this disease. Revealing these interactions and possible mechanisms may prove beneficial for the prediction and treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2-AAA:
-
2-aminoadipic acid
- 2-h PG:
-
2-h plasma glucose test
- 3-HIB:
-
3-hydroxyisobutyrate
- AAAs:
-
Aromatic amino acids
- AAs:
-
Amino acids
- AILS:
-
AminoIndex LifeStyle diseases test
- AKT:
-
Protein kinase B, PKB
- Ala:
-
Alanine
- Arg :
-
Arginine
- Asn:
-
Asparagine
- Asp:
-
Aspartic acid
- BAIBA:
-
β-aminoisobutyric acid
- BCAAs:
-
Branched-chain amino acids
- BCKA:
-
Branched-chain α-ketoacid
- BCKDC:
-
Branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex
- BCKDH:
-
Branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase
- BHBA:
-
3-hydroxybutyrate
- BMI:
-
Body Mass Index
- Cit:
-
Citrulline
- CoA:
-
Coenzyme A
- CVD:
-
Cardiovascular disease
- Cys:
-
Cysteine
- DAG:
-
Diacylglycerol
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- FAAs:
-
Free amino acids
- FFAs:
-
Free fatty acids
- FGF21:
-
Fibroblast growth factor 21
- FHS:
-
Framingham Heart Study
- FOXO :
-
Forkhead Box O transcription factor
- FPG:
-
Fasting plasma glucose
- GC :
-
Gas chromatography
- GDM :
-
Gestational Diabetes mellitus
- GDR:
-
Glucose disposal rate
- Gln:
-
Glutamine
- Glu:
-
Glutamic acid
- Gly :
-
Glycine
- GSK-3:
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3
- HbA1c:
-
Glycated hemoglobin
- HECP:
-
Hperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp procedure
- His:
-
Histidine
- HOMA-IR:
-
Homeostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance
- IDF :
-
International Diabetes Federation
- IGF:
-
Insulin-like growth factor
- IGT :
-
Impaired glucose tolerance
- Ile:
-
Isoleucine
- Ins120 min:
-
2-h post-challenge insulin
- IR:
-
Insulin Resistance
- IRAS :
-
Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study
- IRS-1:
-
Insulin receptor substrate 1
- JNK :
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinase
- LC:
-
Liquid chromatography
- Leu:
-
Leucine
- L-GPC:
-
linoleoyl- glycerophosphocholine
- LPC:
-
Lysophosphatidylcholine
- MDC:
-
Malmö Diet and Cancer Study
- MetS:
-
Metabolic syndrome
- METSIM:
-
Metabolic Syndrome in Men Study
- mmBCFA:
-
Monomethyl branched-chain fatty acids
- MS :
-
Mass spectrometry
- mTORC1:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1
- NEFAs:
-
Non-esterified fatty acids
- NGT:
-
Normal glucose tolerance
- NMR:
-
Nuclear magnetic resonance
- OGTT:
-
Oral glucose tolerance test
- Orn:
-
Ornithine
- PCs:
-
Phosphatidylcholines
- PFAAs:
-
Plasma-free amino acids
- Phe:
-
Phenylalanine
- PPARα:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α
- Pro:
-
Proline
- QMDiab :
-
Qatar Metabolomics Study on Diabetes
- RISC:
-
Relationship of Insulin Sensitivity to Cardiovascular Risk study
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- RQ:
-
Resting respiratory quotient
- SABRE:
-
Southall And Brent REvisited Study
- Ser:
-
Serine
- T1DM :
-
Type 1 Diabetes mellitus
- T2DM:
-
Type 2 Diabetes mellitus
- TCA :
-
Tricarboxylic acid cycle
- TKR:
-
Tyrosine kinase receptor
- Trp :
-
Tryptophan
- TüF :
-
Tübingen Family study for T2DM
- Tyr:
-
Tyrosine
- UCD-T2D:
-
University of California-Davis T2DM rat model
- Val:
-
Valine
- VFA:
-
Visceral fat area
- α-HB:
-
α-hydroxybutyrate
- α-KB :
-
α-ketobutyrate
References
Adams SH, et al. Plasma acylcarnitine profiles suggest incomplete long-chain fatty acid β-Oxidation and altered tricarboxylic acid cycle activity in type 2 diabetic African-American Women. J Nutr. 2009;139(6):1073–81. https://doi.org/10.3945/JN.108.103754.
Ahola-Olli AV, et al. Circulating metabolites and the risk of type 2 diabetes: a prospective study of 11,896 young adults from four Finnish cohorts. Diabetologia. 2019;62(12):2298–309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-019-05001-w.
Al-Abbasi FA. Trend analysis of the correlation of amino acid plasma profile with glycemic status in Saudi diabetic patients. J Adv Res. 2012;3(4):305–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2011.10.001.
Allam-Ndoul, B. et al. Associations between branched chain amino acid levels, obesity and cardiometabolic complications. Integr Obes Diab. 2015;1(6). https://doi.org/10.15761/IOD.1000134.
Association AD. Standards of medical care in diabetes – 2016 abridged for primary care providers. Clin Diabetes. 2016;34(1):3–21. https://doi.org/10.2337/diaclin.34.1.3.
Association AD. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes – 2018. Diabetes Care. 2018;41(Supplement 1):S13–27. https://doi.org/10.2337/DC18-S002.
Bi X, Henry CJ. Plasma-free amino acid profiles are predictors of cancer and diabetes development. Nutr Diabetes. 2017;7(3):e249:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/nutd.2016.55.
Biswas D, Duffley L, Pulinilkunnil T. Role of branched-chain amino acid–catabolizing enzymes in intertissue signaling, metabolic remodeling, and energy homeostasis. FASEB J Wiley and Sons Inc. 2019:8711–31. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201802842RR.
Chen ZZ, Gerszten RE. Metabolomics and proteomics in type 2 diabetes. Circ Res. 2020;126(11):1613–27. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.315898.
Chen T, et al. Branched-chain and aromatic amino acid profiles and diabetes risk in Chinese populations. Sci Rep. 2016;6(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep20594.
Chen S, et al. Serum amino acid profiles and risk of type 2 diabetes among Japanese adults in the Hitachi Health Study. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-43431-z.
Cheng S, et al. Metabolite profiling identifies pathways associated with metabolic risk in humans. Circulation. 2012;125(18):2222. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.067827.
“Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus”. Diabetes Care. American Diabetes Association Inc.; 2004. p. s5–s10. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.27.2007.s5.
Felig P, Marliss E, Cahill GF Jr. Plasma amino acid levels and insulin secretion in obesity. N Engl J Med. 1969;281(15):811–6. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM196910092811503.
Ferrannini E, et al. Early metabolic markers of the development of dysglycemia and type 2 diabetes and their physiological significance. Diabetes. 2013;62(5):1730. https://doi.org/10.2337/DB12-0707.
Fiehn O, et al. Plasma metabolomic profiles reflective of glucose homeostasis in non-diabetic and type 2 diabetic obese African-American Women. PLoS One. 2010;5(12):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0015234.
Floegel A, et al. Identification of serum metabolites associated with risk of type 2 diabetes using a targeted metabolomic approach. Diabetes. 2013;62(2):639. https://doi.org/10.2337/DB12-0495.
Flores-Guerrero JL, et al. Plasma branched-chain amino acids and risk of incident type 2 diabetes: results from the PREVEND Prospective Cohort Study. J Clin Med. 2018;7(12):513. https://doi.org/10.3390/JCM7120513.
Freitas PAC, Ehlert LR, Camargo JL. Glycated albumin: a potential biomarker in diabetes. Arch Endocrinol Metabol. Sociedade Brasileira de Endocrinologia e Metabologia; 2017;61:296–304. https://doi.org/10.1590/2359-3997000000272.
Gall WE, et al. α-Hydroxybutyrate is an early biomarker of insulin resistance and glucose intolerance in a nondiabetic population. PLoS One. 2010;5(5) https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0010883.
Gan WZ, et al. Omics-based biomarkers in the diagnosis of diabetes. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol De Gruyter. 2020; https://doi.org/10.1515/jbcpp-2019-0120.
George J. Branched chain amino acids: causal or predictive of type 2 diabetes. undefined [Preprint]. 2017.
Giesbertz P, Daniel H. Branched-chain amino acids as biomarkers in diabetes. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. 2016:48–54. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCO.0000000000000235.
Gross DN, Wan M, Birnbaum MJ. The role of FOXO in the regulation of metabolism. Curr Diabetes Rep. 2009;9(3):208–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11892-009-0034-5.
Guasch-Ferré M, et al. Metabolomics in prediabetes and diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care. 2016;39(5):833–46. https://doi.org/10.2337/DC15-2251.
Hameed A, et al. Altered metabolome of lipids and amino acids species: a source of early signature biomarkers of T2DM. J Clin Med. 2020;9(7):2257. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072257.
Harris L-ALS, et al. Alterations in 3-Hydroxyisobutyrate and FGF21 metabolism are associated with protein ingestion–induced insulin resistance. Diabetes. 2017;66(7):1871. https://doi.org/10.2337/DB16-1475.
Haufe S, et al. Branched-chain amino acid catabolism rather than amino acids plasma concentrations is associated with diet-induced changes in insulin resistance in overweight to obese individuals. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2017;27(10):858–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.NUMECD.2017.07.001.
Ianni, F. et al. Branched-chain amino acids as potential diagnostic and prognostic disease biomarkers. Int J Clin Res Trials. 2017;2(1). https://doi.org/10.15344/2456-8007/2017/112.
International Diabetes Federation (IDF). Diabetes Atlas. 7th Edition, International Diabetes Federation, Brussels, Belgium. – References – Scientific Research Publishing (no date). 2015. https://www.scirp.org/(S(vtj3fa45qm1ean45vvffcz55))/reference/ReferencesPapers.aspx?ReferenceID=2085700. Accessed 15 June 2021.
Kubota T, Kubota N, Kadowaki T. Imbalanced insulin actions in obesity and type 2 diabetes: key mouse models of insulin signaling pathway. Cell Metab. 2017;25(4):797–810. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CMET.2017.03.004.
Lackey DE, et al. Regulation of adipose branched-chain amino acid catabolism enzyme expression and cross-adipose amino acid flux in human obesity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013;304(11):E1175. https://doi.org/10.1152/AJPENDO.00630.2012.
Lee CC, et al. Branched-Chain amino acids and insulin metabolism: the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study (IRAS). Diabetes Care. 2016;39(4):582. https://doi.org/10.2337/DC15-2284.
Lian K, et al. Impaired adiponectin signaling contributes to disturbed catabolism of branched-chain amino acids in diabetic mice. Diabetes. 2015;64(1):49–59. https://doi.org/10.2337/DB14-0312.
Lopez MJ, Mohiuddin SS. Biochemistry, essential amino acids. StatPearls [Preprint]. 2021.
Lynch CJ, Adams SH. Branched-chain amino acids in metabolic signalling and insulin resistance. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2014;10(12):723–36. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2014.171.
Magnusson M, et al. A diabetes-predictive amino acid score and future cardiovascular disease. Eur Heart J. 2013;34(26):1982–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/EURHEARTJ/EHS424.
Mai M, et al. Serum levels of acylcarnitines are altered in prediabetic conditions. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e82459. https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0082459.
McCormack SE, et al. Circulating branched-chain amino acid concentrations are associated with obesity and future insulin resistance in children and adolescents. Pediatr obes. 2013;8(1):52. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.2047-6310.2012.00087.X.
Nagao K, Kimura T. Use of plasma-free amino acids as biomarkers for detecting and predicting disease risk. Nutr Rev. 2020;78(Supplement_3):79–85. https://doi.org/10.1093/NUTRIT/NUAA086.
Nagata C, et al. Branched-chain amino acid intake and the risk of diabetes in a Japanese Community The Takayama Study. Am J Epidemiol. 2013;178(8):1226–32. https://doi.org/10.1093/AJE/KWT112.
Nakamura H, et al. Plasma amino acid profiles are associated with insulin, C-peptide and adiponectin levels in type 2 diabetic patients. Nutr Diabetes. 2014;4:133. https://doi.org/10.1038/nutd.2014.32.
Newgard CB, et al. A branched-chain amino acid-related metabolic signature that differentiates obese and lean humans and contributes to insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2009;9(4):311. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CMET.2009.02.002.
Nie C, et al. Branched chain amino acids: beyond nutrition metabolism. Int J Mol Sci MDPI AG. 2018; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19040954.
Palmer ND, et al. Metabolomic profile associated with insulin resistance and conversion to diabetes in the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(3):E463. https://doi.org/10.1210/JC.2014-2357.
Rawshani A, et al. Mortality and cardiovascular disease in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(15):1407–18. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMOA1608664.
Roberts LD, et al. β-Aminoisobutyric acid induces browning of white fat and hepatic β-oxidation and is inversely correlated with cardiometabolic risk factors. Cell Metab. 2014;19(1):96. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CMET.2013.12.003.
Saeedi P, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;157:107843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843.
Seibert R, et al. Relationship between insulin resistance and amino acids in women and men. Phys Rep. 2015;3(5):e12392. https://doi.org/10.14814/PHY2.12392.
Shah SH, et al. Branched-chain amino acid levels are associated with improvement in insulin resistance with weight loss. Diabetologia. 2012;55(2):321. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00125-011-2356-5.
She P, et al. Obesity-related elevations in plasma leucine are associated with alterations in enzymes involved in branched-chain amino acid metabolism. 2007;293(6):1552–63. https://doi.org/10.1152/AJPENDO.00134.2007.
Shi L, et al. Plasma metabolites associated with type 2 diabetes in a Swedish population: a case–control study nested in a prospective cohort. Diabetologia. 2018;61(4):849. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00125-017-4521-Y.
Shin AC, et al. Brain insulin lowers circulating BCAA levels by inducing hepatic BCAA catabolism. Cell Metab. 2014;20(5):898. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CMET.2014.09.003.
Stančáková A, et al. Hyperglycemia and a common variant of GCKR are associated with the levels of eight amino acids in 9,369 Finnish Men. Diabetes. 2012;61(7):1895. https://doi.org/10.2337/DB11-1378.
Su X, et al. Adipose tissue monomethyl branched chain fatty acids and insulin sensitivity: effects of obesity and weight loss. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md). 2015;23(2):329. https://doi.org/10.1002/OBY.20923.
Tai ES, et al. Insulin resistance is associated with a metabolic profile of altered protein metabolism in Chinese and Asian-Indian men. Diabetologia. 2010;53(4):757. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00125-009-1637-8.
Tillin T, et al. Diabetes risk and amino acid profiles: cross-sectional and prospective analyses of ethnicity, amino acids and diabetes in a South Asian and European cohort from the SABRE (Southall And Brent REvisited) Study. Diabetologia. 2015;58(5):968. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00125-015-3517-8.
Tochikubo O, et al. Weight loss is associated with plasma free amino acid alterations in subjects with metabolic syndrome. Nutr Diabetes. 2016;6(2):e197. https://doi.org/10.1038/NUTD.2016.5.
Tricò D, et al. Elevated α-Hydroxybutyrate and branched-chain amino acid levels predict deterioration of glycemic control in adolescents. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2017;102(7):2473–81. https://doi.org/10.1210/JC.2017-00475.
Vamos EP, et al. Changes in the incidence of lower extremity amputations in individuals with and without diabetes in England between 2004 and 2008. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(12):2592. https://doi.org/10.2337/DC10-0989.
Wang TJ, et al. Metabolite profiles and the risk of developing diabetes. Nat Med. 2011;17(4):448–53. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2307.
Wang TJ, et al. 2-Aminoadipic acid is a biomarker for diabetes risk. J Clin Investig. 2013;123(10):4309–17. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI64801.
Wang-Sattler R, et al. Novel biomarkers for pre-diabetes identified by metabolomics. Mol Syst Biol. 2012;8(1):615. https://doi.org/10.1038/MSB.2012.43.
White PJ, Newgard CB. Branched-chain amino acids in disease. Science. 2019;363(6427):582–3. https://doi.org/10.1126/SCIENCE.AAV0558.
Würtz P, et al. Branched-chain and aromatic amino acids are predictors of insulin resistance in young adults. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(3):648–55. https://doi.org/10.2337/DC12-0895.
Xie G, et al. The metabolite profiles of the obese population are gender-dependent. J Proteome Res. 2014;13(9):4062–73. https://doi.org/10.1021/PR500434S.
Yamakado M. Technology for lifestyle-related disease risk screening. Ningen Dock Int. 2018;5(1):3–14.
Yamakado M, et al. Plasma amino acid profile is associated with visceral fat accumulation in obese Japanese subjects. Clin Obesity. 2012;2(1–2):29–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1758-8111.2012.00039.X.
Yamakado M. et al. Plasma free amino acid profiles predict four-year risk of developing diabetes, metabolic syndrome, dyslipidemia, and hypertension in Japanese Population. Sci Rep. 2015;5. https://doi.org/10.1038/SREP11918.
Yoon M.-S. The emerging role of branched-chain amino acids in insulin resistance and metabolism. Nutrients. 2016;8(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/NU8070405.
Yousri NA, et al. A systems view of type 2 diabetes-associated metabolic perturbations in saliva, blood and urine at different timescales of glycaemic control. Diabetologia. 2015;58(8):1855. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00125-015-3636-2.
Zabielski P, et al. The effect of high-fat diet and inhibition of ceramide production on insulin action in liver. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(2):1851–61. https://doi.org/10.1002/JCP.27058.
Zeng M, et al. GC–MS based plasma metabolic profiling of type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Chromatographia. 2009;69(9):941–8. https://doi.org/10.1365/S10337-009-1040-0.
Zhao J, et al. Novel metabolic markers for the risk of diabetes development in American Indians. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(2):220. https://doi.org/10.2337/DC14-2033.
Zhao Q, et al. Exploring potential biomarkers and determining the metabolic mechanism of type 2 diabetes mellitus using liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry. RSC Adv. 2017;7(70):44186–98. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra05722a.
Zhao H, et al. Branched-chain amino acids exacerbate obesity-related hepatic glucose and lipid metabolic disorders via attenuating Akt2 signaling. Diabetes. 2020;69(6):1164–77. https://doi.org/10.2337/DB19-0920.
Zheng Y, et al. Cumulative consumption of branched-chain amino acids and incidence of type 2 diabetes. Int J Epidemiol. 2016;45(5):1482–92. https://doi.org/10.1093/IJE/DYW143.
Zhou M, et al. Targeting BCAA catabolism to treat obesity-associated insulin resistance. Diabetes. 2019;68(9):1730–46. https://doi.org/10.2337/db18-0927.
Ziemke F, Mantzoros CS. Adiponectin in insulin resistance: lessons from translational research. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;91(1):258S–61S. https://doi.org/10.3945/AJCN.2009.28449C.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Czajkowska, A., Hameed, A., Galli, M., Ijaz, M.U., Kretowski, A., Ciborowski, M. (2022). Altered Metabolome of Amino Acids Species: A Source of Signature Early Biomarkers of T2DM. In: Patel, V.B., Preedy, V.R. (eds) Biomarkers in Diabetes. Biomarkers in Disease: Methods, Discoveries and Applications. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-81303-1_5-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-81303-1_5-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-81303-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-81303-1
eBook Packages: Springer Reference Biomedicine and Life SciencesReference Module Biomedical and Life Sciences