Abstract
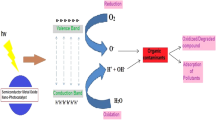
The continuous introduction of pollutants into the environment presents new challenges for their total removal and promotes the development of novel strategies with high efficiencies. Photocatalysis can be defined as a photoinduced reaction which is accelerated by the presence of a catalyst. Semiconductor nanomaterial-based photocatalysis is recognized as a promising alternative to the conventional methods for pollutant removal owing to its low cost, non-toxicity, reusability, and high stability. Nano-materials used for photocatalysis show many advantages compared to bulk materials due to their unique properties, such as increased surface area and particular quantum effects. Nanophotocatalysts can be classified as metal oxide-based (TiO2, ZnO, Fe2O3) or metal free-based (graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4), CdS, ZnS). Their wide or narrow band gap energies determine if the nanophotocatalysts require high or low energy UV light for their photocatalytic reactions. In this chapter, the most common pollutants and the importance of their removal from the environment have been discussed. Moreover, the principles of photocatalysis along with different variables like the structure of the catalyst, the pH, the amount of the catalyst, and the intensity of the light that affect the photocatalysis of these pollutants have also been mentioned comprehensively. The most commonly applied nanomaterials for this purpose with their advantages and disadvantages are presented. Different strategies adopted for extending the photocatalytic active region to the visible light have also been offered including metal/non-metal doping, photosensitive materials, combination with other nanoparticles, and composite formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abazari R, Mahjoub AR, Salehi G (2019) Preparation of amine functionalized g-C3N4@ H/SMOF NCs with visible light photocatalytic characteristic for 4-nitrophenol degradation from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 365:921–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.11.087
Abazari R, Morsali A, Dubal DP (2020) An advanced composite with ultrafast photocatalytic performance for the degradation of antibiotics by natural sunlight without oxidizing the source over TMU-5@ Ni–Ti LDH: mechanistic insight and toxicity assessment. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers 7(12):2287–2304. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0QI00050G
Ahmed SN, Haider W (2021) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of ZnO-graphene oxide nanocomposite by electron scavenging. Catalysts 11(2):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11020187
Ajmal A, Majeed I, Malik RN, Idriss H, Nadeem MA (2014) Principles and mechanisms of photocatalytic dye degradation on TiO2 based photocatalysts: a comparative overview. RSC Adv 4(70):37003–37026. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA06658H
Badreldin A, Imam MD, Wubulikasimu Y, Elsaid K, Abusrafa AE, Balbuena PB, Abdel-Wahab A (2021) Surface microenvironment engineering of black V2O5 nanostructures for visible light photodegradation of methylene blue. J Alloys Compd 871:159615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.159615
Bartolomeu M, Neves MGPMS, Faustino MAF, Almeida A (2018) Wastewater chemical contaminants: remediation by advanced oxidation processes. Photochem Photobiol Sci 17(11):1573–1598. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8PP00249E
Basavarajappa PS, Patil SB, Ganganagappa N, Reddy KR, Raghu AV, Reddy CV (2020) Recent progress in metal-doped TiO2, non-metal doped/codoped TiO2 and TiO2 nanostructured hybrids for enhanced photocatalysis. Int J Hydrog Energy 45(13):7764–7778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.07.241
Cantarella M, Di Mauro A, Gulino A, Spitaleri L, Nicotra G, Privitera V, Impellizzeri G (2018) Selective photodegradation of paracetamol by molecularly imprinted ZnO nanonuts. Appl Catal B Environ 238:509–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.07.055
Chen Q, Ji F, Guo Q, Fan J, Xu X (2014) Combination of heterogeneous Fenton-like reaction and photocatalysis using co–TiO2 nanocatalyst for activation of KHSO5 with visible light irradiation at ambient conditions. J Environ Sci 26(12):2440–2450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2014.03.003
Chen X, Xu X, Cui J, Chen C, Zhu X, Sun D, Qian J (2020) Visible-light driven degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride and 2, 4-dichlorophenol by film-like N-carbon@ N-ZnO catalyst with three-dimensional interconnected nanofibrous structure. J Hazard Mater 392:122331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122331
da Silva LJ, Rodrigues WV, Oliveira VV, Braga ADNS, da Silva RT, França AAC, da Paz EC, Oajima JA, da Silva Filho EC (2019) Modification of kaolinite from Pará/Brazil region applied in the anionic dye photocatalytic discoloration. Appl Clay Sci 168:295–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2018.11.028
Dhangar K, Kumar M (2020) Tricks and tracks in removal of emerging contaminants from the wastewater through hybrid treatment systems: a review. Sci Total Environ 738:140320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140320
Dhiman P, Naushad M, Batoo KM, Kumar A, Sharma G, Ghfar AA, Kumar G, Singh M (2017) Nano FexZn1− xO as a tuneable and efficient photocatalyst for solar powered degradation of bisphenol a from aqueous environment. J Clean Prod 165:1542–1556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.07.245
Ding Z, Liu Y, Fu Y, Chen F, Chen Z, Hu J (2020) Magnetically recyclable ag/TiO2 co-decorated magnetic silica composite for photodegradation of dibutyl phthalate with fluorescent lamps. Water Sci Technol 81(4):790–800. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2020.162
El-Sheikh M, Hadibarata T, Yuniarto A, Sathishkumar P, Abdel-Salam E, Alatar A (2021) Role of nanocatalyst in the treatment of organochlorine compounds - a review. Chemosphere 268:128873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128873
Eskandarian MR, Rasoulifard MH, Fazli M, Ghalamchi L, Choi H (2019) Synergistic decomposition of imidacloprid by TiO2-Fe3O4 nanocomposite conjugated with persulfate in a photovoltaic-powered UV-LED photoreactor. Korean J Chem Eng 36(6):965–974. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-018-0230-1
Esparza P, Hernández T, Borges ME, Álvarez-Galván MC, Ruiz-Morales JC, Fierro JLG (2013) TiO2 modifications by hydrothermal treatment and doping to improve its photocatalytic behaviour under visible light. Catal Today 210:135–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2012.12.011
Heidari Z, Alizadeh R, Ebadi A, Pelalak R, Oturan N, Oturan MA (2020) Degradation of furosemide using photocatalytic ozonation in the presence of ZnO/ICLT nanocomposite particles: experimental, modeling, optimization and mechanism evaluation. J Mol Liq 319:114193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114193
Heidarpour H, Padervand M, Soltanieh M, Vossoughi M (2020) Enhanced decolorization of rhodamine B solution through simultaneous photocatalysis and persulfate activation over Fe/C3N4 photocatalyst. Chem Eng Res Des 153:709–720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2019.09.007
Hu Q, Chen Y, Li M, Zhang Y, Wang B, Zhao Y, Xia J, Yin S, Li H (2019a) Construction of NH2-UiO-66/BiOBr composites with boosted photocatalytic activity for the removal of contaminants. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 579:123625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.123625
Hu J, Zhang P, An W, Liu L, Liang Y, Cui W (2019b) In-situ Fe-doped g-C3N4 heterogeneous catalyst via photocatalysis-Fenton reaction with enriched photocatalytic performance for removal of complex wastewater. Appl Catal B Environ 245:130–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.12.029
Kong W, Wang S, Wu D, Chen C, Luo Y, Pei Y, Tian B, Zhang J (2019) Fabrication of 3D sponge@ AgBr-AgCl/ag and tubular photoreactor for continuous wastewater purification under sunlight irradiation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7(16):14051–14063. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b02575
Lv SW, Liu JM, Li CY, Zhao N, Wang ZH, Wang S (2020a) Two novel MOFs@COFs hybrid-based photocatalytic platforms coupling with sulfate radical-involved advanced oxidation processes for enhanced degradation of bisphenol a. Chemosphere 243:125378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125378
Lv SW, Liu JM, Zhao N, Li CY, Yang FE, Wang ZH, Wang S (2020b) MOF-derived CoFe2O4/Fe2O3 embedded in g-C3N4 as high-efficient Z-scheme photocatalysts for enhanced degradation of emerging organic pollutants in the presence of persulfate. Sep Purif Technol 253:117413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117413
Ma D, Yi H, Lai C, Liu X, Huo X, An Z, Li L, Fu Y, Lia B, Zhang M, Qin L, Liu S, Yang L (2021) Critical review of advanced oxidation processes in organic wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 275:130104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130104
Miribangul A, Ma X, Zeng C, Zou H, Wu Y, Fan T, Su Z (2016) Synthesis of TiO2/CNT composites and its photocatalytic activity toward 13sudan (I) degradation. Photochem Photobiol 92(4):523–527. https://doi.org/10.1111/php.12604
Padmanaban VC, Nandagopal MG, Priyadharshini GM, Maheswari N, Sree GJ, Selvaraju N (2016) Advanced approach for degradation of recalcitrant by nanophotocatalysis using nanocomposites and their future perspectives. Int J Environ Sci Technol 13(6):1591–1606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-1000-9
Pawar M, Topcu Sendoğdular S, Gouma P (2018) A brief overview of TiO2 photocatalyst for organic dye remediation: case study of reaction mechanisms involved in Ce-TiO2 photocatalysts system. J Nanomater. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5953609
Posa VR, Annavaram V, Somala AR (2016) Fabrication of graphene–TiO2 nanocomposite with improved photocatalytic degradation for acid orange 7 dye under solar light irradiation. Bull Mater Sci 39(3):759–767. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-016-1215-x
Rani M, Shanker U (2018) Degradation of traditional and new emerging pesticides in water by nanomaterials: recent trends and future recommendations. Int J Environ Sci Technol 15(6):1347–1380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1512-y
Rani M, Shanker U (2021) Insight into sunlight-driven rapid photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes by hexacyanoferrate-based nanoparticles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(5):5637–5650. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10925-7
Rani M, Yadav J, Shanker U (2021) Green synthesis of sunlight responsive zinc oxide coupled cadmium sulfide nanostructures for efficient photodegradation of pesticides. J Colloid Interface Sci 601:689–703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.05.152
Rashid J, Barakat MA, Ruzmanova Y, Chianese A (2015) Fe3O4/SiO2/TiO2 nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation of 2-chlorophenol in simulated wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(4):3149–3157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3598-9
Saranya M, Ramachandran R, Kollu P, Jeong SK, Grace AN (2015) A template-free facile approach for the synthesis of CuS–rGO nanocomposites towards enhanced photocatalytic reduction of organic contaminants and textile effluents. RSC Adv 5(21):15831–15840. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA09029B
Sass DT, Massima Mouele ES, Ross N (2019) Nano silver-iron-reduced graphene oxide modified titanium dioxide photocatalytic remediation system for organic dye. Environments 6(9):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments6090106
Serrà A, Philippe L (2020) Simple and scalable fabrication of hairy ZnO@ ZnS core@ shell cu cables for continuous sunlight-driven photocatalytic water remediation. Chem Eng J 401:126164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126164
Shafi A, Bano S, Khan N, Sultana S, Rehman Z, Rahman MM, Sabir S, Coulon F, Khan MZ (2021) Nanoremediation technologies for sustainable remediation of contaminated environments: recent advances and challenges. Chemosphere 275:130065. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130065
Shahid M, Kashif A, Fuwad A, Choi Y (2021) Current advances in treatment technologies for removal of emerging contaminants from water–a critical review. Coord Chem Rev 442:213993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2021.213993
Shanker U, Rani M, Jassal V (2017) Degradation of hazardous organic dyes in water by nanomaterials. Environ Chem Lett 15(4):623–642. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-017-0650-2
Sharma S, Basu S (2021) Fabrication of centimeter-sized Sb2S3/SiO2 monolithic mimosa pudica nanoflowers for remediation of hazardous pollutants from industrial wastewater. J Clean Prod 280:124525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124525
Sousa JC, Ribeiro AR, Barbosa MO, Pereira MFR, Silva AM (2018) A review on environmental monitoring of water organic pollutants identified by EU guidelines. J Hazard Mater 344:146–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.09.058
Sun X, He W, Hao X, Ji H, Liu W, Cai Z (2021) Surface modification of BiOBr/TiO2 by reduced AgBr for solar-driven PAHs degradation: mechanism insight and application assessment. J Hazard Mater 412:125221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125221
Wang P, Dickon HLN, Zhou M, Li J (2019a) Freely standing MgAl-layered double hydroxides nanosheets and their derived metal oxides on g-C3N4 thin-layer designed for obtaining synergic effect of adsorption and photocatalysis. Appl Clay Sci 178:105131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2019.105131
Wang H, Zhang M, He X, Du T, Wang Y, Li Y, Hao T (2019b) Facile prepared ball-like TiO2 at GO composites for oxytetracycline removal under solar and visible lights. Water Res 160:197–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.05.073
Wang J, Wang H, Zuo S, Jin X, Zheng B, Deng R, Liu W, Wang J (2020) Synergistic effects of lanthanide surface adhesion and photon-upconversion for enhanced near-infrared responsive photodegradation of organic contaminants in wastewater. Environ Sci Nano 7(11):3333–3342. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EN00670J
Wang X, Xu P, Yang C, Shen T, Qu J, Wang P, Zhang G (2021) Enhanced 4-FP removal with MnFe2O4 catalysts under dielectric barrier discharge plasma: economical synthesis, catalytic performance and degradation mechanism. J Hazard Mater 414:125602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125602
World Health Organization (2019) World health statistics 2019: monitoring health for the SDGs. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/324835/9789241565707-eng.pdf. Accessed 5 Oct 2021.
Xi Q, Liu J, Wu Z, Bi H, Li Z, Zhu K, Zhuang J, Chen J, Lu S, Huang QG (2019) In-situ fabrication of MoO3 nanobelts decorated with MoO2 nanoparticles and their enhanced photocatalytic performance. Appl Surf Sci 480:427–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.03.009
Yan D, Hu H, Gao N, Ye J, Ou H (2019a) Fabrication of carbon nanotube functionalized MIL-101 (Fe) for enhanced visible-light photocatalysis of ciprofloxacin in aqueous solution. Appl Surf Sci 498:143836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.143836
Yan S, Shi Y, Tao Y, Zhang H (2019b) Enhanced persulfate-mediated photocatalytic oxidation of bisphenol a using bioelectricity and a g-C3N4/Fe2O3 heterojunction. Chem Eng J 359:933–943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.093
Zhang F, Wen Q, Hong M, Zhuang Z, Yu Y (2017a) Efficient and sustainable metal-free GR/C3N4/CDots ternary heterostructures for versatile visible-light-driven photoredox applications: toward synergistic interaction of carbon materials. Chem Eng J 307:593–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.120
Zhang G, Wu Z, Liu H, Ji Q, Qu J, Li J (2017b) Photoactuation healing of α-FeOOH@ g-C3N4 catalyst for efficient and stable activation of persulfate. Small 13(41):1702225. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201702225
Zhang M, Xia X, Cao C, Xue H, Yang Y, Li W, Chen Q, Xiao L, Qian Q (2020) A ZnO@ ABS/TPU/CaSiO 3 3D skeleton and its adsorption/photocatalysis properties for dye contaminant removal. RSC Adv 10(68):41272–41282. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA06661C
Zhang Q, Peng Y, Lin Y, Wu S, Yu X, Yang C (2021) Bisphenol S-doped g-C3N4 nanosheets modified by boron nitride quantum dots as efficient visible-light-driven photocatalysts for degradation of sulfamethazine. Chem Eng J 405:126661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126661
Zhao J, Nan J, Zhao Z, Li N (2017) Facile fabrication of novel Mn2O3 nanocubes with superior light-harvesting for ciprofloxacin degradation. Catal Commun 102:5–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2017.08.018
Zhou L, Wang L, Zhang J, Lei J, Liu Y (2016) Well-dispersed Fe2O3 nanoparticles on g-C3N4 for efficient and stable photo-Fenton Photocatalysis under visible-light irradiation. Eur J Inorg Chem 2016(34):5387–5392. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejic.201600959
Zhu W, Li Z, He C, Faqian S, Zhou Y (2018) Enhanced photodegradation of sulfamethoxazole by a novel WO3-CNT composite under visible light irradiation. J Alloys Compd 754:153–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.04.286
Zhu L, Kong X, Yang C, Ren B, Tang Q (2020) Fabrication and characterization of the magnetic separation photocatalyst C-TiO2@ Fe3O4/AC with enhanced photocatalytic performance under visible light irradiation. J Hazard Mater 381:120910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120910
Acknowledgments
Authors gratefully acknowledge the Universidad Nacional del Sur (PGI 24/ZQ17, PGI 24/Q086 and 24/Q099), the ANPCyT (PICT-2019-04458 and PICT 201-0659), and Comisión Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Napoli, F.S.R., Uriarte, D., Garrido, M., Domini, C., Acebal, C. (2022). Nanophotocatalysis for Degradation of Organic Contaminants. In: Shanker, U., Hussain, C.M., Rani, M. (eds) Handbook of Green and Sustainable Nanotechnology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-69023-6_43-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-69023-6_43-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-69023-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-69023-6
eBook Packages: Springer Reference Chemistry and Mat. ScienceReference Module Physical and Materials ScienceReference Module Chemistry, Materials and Physics