Abstract
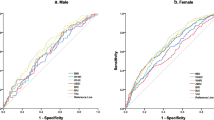
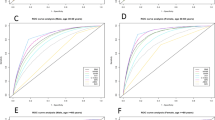
Metabolic dysfunctions such as obesity, insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and glucose tolerance are strongly related to each other. The presence of any of them in a person translates into a high risk of diseases such as diabetes, heart failure, and cardiovascular disease. Anthropometric measurements such as body circumferences, body folds, and anthropometric indices such as waist-height ratio (WHtR) and body mass index (BMI) have been widely used in the study of metabolic diseases. This study aims to look for relationships between WHtR and anthropometric measurements such as subcutaneous folds and body circumferences. For this purpose, a database of 1863 subjects was used, 16 anthropometric variables were measured for each participant in the database and the BMI was calculated. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to assess the ability of BMI and each anthropometric measurement was used to diagnose BMI impairment. The findings reported in this research strongly suggest that the diagnosis of WHtR deficiency can be made from circumferences, skinfolds, and BMI. In this study, the anthropometric measures that best detect subjects with WHtR deficiency were BMI, subscapular skinfold, supra iliac skinfold, and arm circumference with a high probability of detecting normal WHtR-deficient subjects. Abdominal circumference is one of the areas that have the most direct relationship with cardiac metabolic risk, however, the findings of this study open the possibility of studying accumulated fat tissue in the arms and back as areas that could also indicate a risk of metabolic dysfunction.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansaldo, A.M., Montecucco, F., Sahebkar, A., Dallegri, F., Carbone, F.: Epicardial adipose tissue and cardiovascular diseases. Int. J. Cardiol. 278, 254–260 (2019)
Ashwell, M., Gunn, P., Gibson, S.: Waist-to-height ratio is a better screening tool than waist circumference and BMI for adult cardiometabolic risk factors: systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 13(3), 275–286 (2012)
Barroso, T.A., Marins, L.B., Alves, R., Gonçalves, A.C.S., Barroso, S.G., Rocha, G.D.S.: Association of central obesity with the incidence of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Sci. 30(5), 416–424 (2017)
Browning, L.M., Hsieh, S.D., Ashwell, M.: A systematic review of waist-to-height ratio as a screening tool for the prediction of cardiovascular disease and diabetes: 0.5 could be a suitable global boundary value. Nutr. Res. Rev. 23(2), 247–269 (2010)
Cardinal, T.R., Vigo, A., Duncan, B.B., Matos, S.M.A., da Fonseca, M.D.J.M., Barreto, S.M., Schmidt, M.I.: Optimal cut-off points for waist circumference in the definition of metabolic syndrome in brazilian adults: baseline analyses of the longitudinal study of adult health (Elsa-Brasil). Diabetology Metab. Syndr. 10(1), 1–9 (2018)
Chen, X., Liu, Y., Sun, X., Yin, Z., Li, H., Deng, K., Cheng, C., Liu, L., Luo, X., Zhang, R., et al.: Comparison of body mass index, waist circumference, conicity index, and waist-to-height ratio for predicting incidence of hypertension: the rural Chinese cohort study. J. Hum. Hypertens. 32(3), 228–235 (2018)
Chung, I.H., Park, S., Park, M.J., Yoo, E.G.: Waist-to-height ratio as an index for cardiometabolic risk in adolescents: results from the 1998–2008 knhanes. Yonsei Med. J. 57(3), 658–663 (2016)
Correa, M.M., Thume, E., De Oliveira, E.R.A., Tomasi, E.: Performance of the waist-to-height ratio in identifying obesity and predicting non-communicable diseases in the elderly population: a systematic literature review. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 65, 174–182 (2016)
Dong, J., Wang, S.S., Chu, X., Zhao, J., Liang, Y.Z., Yang, Y.B., Yan, Y.X.: Optimal cut-off point of waist to height ratio in Beijing and its association with clusters of metabolic risk factors. Curr. Med. Sci. 39(2), 330–336 (2019)
Ehrampoush, E., Arasteh, P., Homayounfar, R., Cheraghpour, M., Alipour, M., Naghizadeh, M.M., Davoodi, S.H., Askari, A., Razaz, J.M., et al.: New anthropometric indices or old ones: which is the better predictor of body fat? Diabetes Metab. Syndr.: Clinic. Res. Rev. 11(4), 257–263 (2017)
Farina, P.V.R., Severeyn, E., Wong, S., Turiel, J.P.: Study of cardiac repolarization during oral glucose tolerance test in metabolic syndrome patients. In: 2012 Computing in Cardiology, pp. 429–432. IEEE (2012)
Gonzalez-Cantero, J., Martin-Rodriguez, J.L., Gonzalez-Cantero, A., Arrebola, J.P., Gonzalez-Calvin, J.L.: Insulin resistance in lean and overweight non-diabetic caucasian adults: study of its relationship with liver triglyceride content, waist circumference and BMI. PLoS One 13(2), e0192663 (2018)
Greenfield, J.R., Campbell, L.V.: Relationship between inflammation, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes:’cause or effect? Curr. Diab. Rev. 2(2), 195–211 (2006)
Guan, X., Sun, G., Zheng, L., Hu, W., Li, W., Sun, Y.: Associations between metabolic risk factors and body mass index, waist circumference, waist-to-height ratio and waist-to-hip ratio in a chinese rural population. J. Diab. Investig. 7(4), 601–606 (2016)
He, J., Ma, R., Liu, J., Zhang, M., Ding, Y., Guo, H., Mu, L., Zhang, J., Wei, B., Yan, Y., et al.: The optimal ethnic-specific waist-circumference cut-off points of metabolic syndrome among low-income rural Uyghur adults in far western China and implications in preventive public health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 14(2), 158 (2017)
Herrera, H., Rebato, E., Arechabaleta, G., Lagrange, H., Salces, I., Susanne, C.: Body mass index and energy intake in Venezuelan university students. Nutr. Res. 23(3), 389–400 (2003)
Hetherington-Rauth, M., Bea, J.W., Lee, V.R., Blew, R.M., Funk, J., Lohman, T.G., Going, S.B.: Comparison of direct measures of adiposity with indirect measures for assessing cardiometabolic risk factors in preadolescent girls. Nutr. J. 16(1), 15 (2017)
Ho, S.Y., Lam, T.H., Janus, E.D.: Waist to stature ratio is more strongly associated with cardiovascular risk factors than other simple anthropometric indices. Ann. Epidemiol. 13(10), 683–691 (2003)
Janssen, I., Ross, R.: Linking age-related changes in skeletal muscle mass and composition with metabolism and disease. J. Nutr. Health Aging 9(6), 408 (2005)
Ji, B., Qu, H., Wang, H., Wei, H., Deng, H.: Association between the visceral adiposity index and homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance in participants with normal waist circumference. Angiol. 68(8), 716–721 (2017)
Kaur, N., Barna, B., et al.: Inter-relationship of waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), body mass index (BMI) and subcutaneous fat with blood pressure among university-going Punjabi sikh and hindu females. Int. J. Med. Med. Sci. 2(1), 005–011 (2010)
Kopelman, P.G.: Obesity as a medical problem. Nature 404(6778), 635–643 (2000)
Kumari, M., Heeren, J., Scheja, L.: Regulation of immunometabolism in adipose tissue. Semin Immunopathol 40(2), 189–202 (2018)
Kurniawan, L.B., Bahrun, U., Hatta, M., Arif, M.: Body mass, total body fat percentage, and visceral fat level predict insulin resistance better than waist circumference and body mass index in healthy young male adults in Indonesia. J. Clin. Med. 7(5), 96 (2018)
Lanas, F., Serón, P., Munoz, S., Margozzini, P., Puig, T.: Latin American clinical epidemiology network series-paper 7: central obesity measurements better identified risk factors for coronary heart disease risk in the chilean national health survey (2009–2010). J. Clin. Epidemiol. 86, 111–116 (2017)
Lee, C.H., Lam, K.S.: Obesity-induced insulin resistance and macrophage infiltration of the adipose tissue: a vicious cycle. J. Diab. Investig. 10(1), 29 (2019)
Luna-Luna, M., Medina-Urrutia, A., Vargas-Alarcón, G., Coss-Rovirosa, F., Vargas-Barrón, J., Perez-Mendez, O.: Adipose tissue in metabolic syndrome: onset and progression of atherosclerosis. Arch. Med. Res. 46(5), 392–407 (2015)
Marusteri, M., Bacarea, V.: Comparing groups for statistical differences: how to choose the right statistical test? Biochemia Medica: Biochemia Medica 20(1), 15–32 (2010)
Miyazaki, Y., Mahankali, A., Matsuda, M., Mahankali, S., Hardies, J., Cusi, K., Mandarino, L.J., DeFronzo, R.A.: Effect of pioglitazone on abdominal fat distribution and insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 87(6), 2784–2791 (2002)
Mohamed-Ali, V., Pinkney, J., Coppack, S.: Adipose tissue as an endocrine and paracrine organ. Int. J. Obes. 22(12), 1145–1158 (1998)
Moretto, M.C., Fontaine, A.M., Garcia, C.D.A.M.S., Neri, A.L., Guariento, M.E.: Association between race, obesity and diabetes in elderly community dwellers: data from the fibra study. Cadernos de saude publica, 32, e00081315 (2016)
Mortensen, M.B., Fuster, V., Muntendam, P., Mehran, R., Baber, U., Sartori, S., Falk, E.: Negative risk markers for cardiovascular events in the elderly. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 74(1), 1–11 (2019)
World Health Organization., et al.: Global status report on non communicable diseases 2014. World Health Organization, vol. 2014 (2014)
Özer, S., Kazanc, N.Ö., Sönmezgöz, E., Karaaslan, E., Altunta, B., Kuyucu, Y.E., et al.: Higher HDL levels are a preventive factor for metabolic syndrome in obese Turkish children. Nutricion hospitalaria 31(1), 307–312 (2015)
Parikh, R., Mathai, A., Parikh, S., Sekhar, G.C., Thomas, R.: Understanding and using sensitivity, specificity and predictive values. Ind. J. Ophthalmol. 56(1), 45 (2008)
Park, S.H., Choi, S.J., Lee, K.S., Park, H.Y.: Waist circumference and waist-to-height ratio as predictors of cardiovascular disease risk in Korean adults. Circ. J. 73(9), 1643–1650 (2009)
Perpiñan, G., Severeyn, E., Altuve, M., Wong, S.: Classification of metabolic syndrome subjects and marathon runners with the k-means algorithm using heart rate variability features. In: 2016 XXI Symposium on Signal Processing, Images and Artificial Vision (STSIVA), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2016)
Perrone-Filardi, P., Paolillo, S., Costanzo, P., Savarese, G., Trimarco, B., Bonow, R.O.: The role of metabolic syndrome in heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 36(39), 2630–2634 (2015)
Polsky, S., Ellis, S.L.: Obesity, insulin resistance, and type 1 diabetes mellitus. Curr. Opinion Endocrinol. Diab. Obes. 22(4), 277–282 (2015)
Raz, I., Eldor, R., Cernea, S., Shafrir, E.: Diabetes: insulin resistance and derangements in lipid metabolism. Cure through intervention in fat transport and storage. Diab. Metab. Res. Rev. 21(1), 3–14 (2005)
Reitsma, J.B., Glas, A.S., Rutjes, A.W., Scholten, R.J., Bossuyt, P.M., Zwinderman, A.H.: Bivariate analysis of sensitivity and specificity produces informative summary measures in diagnostic reviews. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 58(10), 982–990 (2005)
Rönnecke, E., Vogel, M., Bussler, S., Grafe, N., Jurkutat, A., Schlingmann, M., Koerner, A., Kiess, W.: Age-and sex-related percentiles of skinfold thickness, waist and hip circumference, waist-to-hip ratio and waist-to-height ratio: results from a population-based pediatric cohort in Germany (life child). Obes. Facts 12(1), 25–39 (2019)
Rose, D., Komninou, D., Stephenson, G.: Obesity, adipocytokines, and insulin resistance in breast cancer. Obes. Rev. 5(3), 153–165 (2004)
Schneider, H.J., Friedrich, N., Klotsche, J., Pieper, L., Nauck, M., John, U., Dorr, M., Felix, S., Lehnert, H., Pittrow, D., et al.: The predictive value of different measures of obesity for incident cardiovascular events and mortality. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 95(4), 1777–1785 (2010)
Sjöström, C.D., Håkangård, A.C., Lissner, L., Sjöström, L.: Body compartment and subcutaneous adipose tissue distribution-risk factor patterns in obese subjects. Obes. Res. 3(1), 9–22 (1995)
Velásquez, J., Severeyn, E., Herrera, H., Encalada, L., Wong, S.: Anthropometric index for insulin sensitivity assessment in older adults from Ecuadorian highlands. In: 12th International Symposium on Medical Information Processing and Analysis, vol. 10160, p. 101600S. International Society for Optics and Photonics (2017)
Velásquez, J., Herrera, H., Encalada, L., Wong, S., Severeyn, E.: Análisis dimensional de variables antropométricas y bioquímicas para diagnosticar el síndrome metabólico. Maskana 8, 57–67 (2017)
Vintimilla, C., Wong, S., Astudillo-Salinas, F., Encalada, L., Severeyn, E.: An AIDE diagnosis system based on k-means for insulin resistance assessment in eldery people from the Ecuadorian highlands. In: 2017 IEEE Second Ecuador Technical Chapters Meeting (ETCM), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2017)
Wei, Y., Wang, J., Han, X., Yu, C., Wang, F., Yuan, J., Miao, X., Yao, P., Wei, S., Wang, Y., et al.: Metabolically healthy obesity increased diabetes incidence in a middle-aged and elderly Chinese population. Diab./Metab. Res. Rev. 36(1), e3202 (2020)
Zhou, C., Zhan, L., Yuan, J., Tong, X., Peng, Y., Zha, Y.: Comparison of visceral, general and central obesity indices in the prediction of metabolic syndrome in maintenance hemodialysis patients, pp. 1–8. Eating and Weight Disorders-Studies on Anorexia, Bulimia and Obesity (2019)
Acknowledgment
This work was funded by the Research and Development Deanery of the Simón Bolívar University (DID) and the Research Direction of the Ibagué University. Full acknowledgment is given to Rajul Parikh, author of “Understanding and using sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values” (BioInfo Publications™).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Severeyn, E., La Cruz, A., Wong, S., Perpiñan, G. (2021). Analysis of Anthropometric Measurements Using Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve for Impaired Waist to Height Ratio Detection. In: Botto-Tobar, M., S. Gómez, O., Rosero Miranda, R., Díaz Cadena, A. (eds) Advances in Emerging Trends and Technologies. ICAETT 2020. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1302. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-63665-4_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-63665-4_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-63664-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-63665-4
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)