Abstract
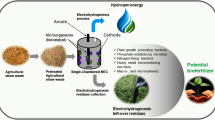
The production of bioelectricity is linked to sintróficos processes, hydrolization and fermentation of complex organic compounds to be used like by-products for the generation of volts of direct current “Vdc”. There is a great variety of substrates, ranging from pure compounds (organic and inorganic) to the complex mixture of organic matter present in wastewater, or inorganic matter of industrial waste.
Since 2016, the GIDAC Group has been studying the behavior of a bacterial strain from Páramo soils not intervened at altitudes of 4000 and 4200 masl as inoculum and producer of bioelectricity in different capacities of Microbial Fuel Cells “MFC” of simple configuration with the cathode partially exposed to air. The microbial consortium used in the organic mixture of organic residues of vegetables and fruits demonstrates a complete degradation in fruit waste, which suggests that the preference for waste is easily biodegradable. Of the MFCs positive correlations between the microbial abundance and the generation of electricity were not always observed, obtaining an average voltage of 330Vdc. However, when using inorganic compounds, lower voltage levels were obtained on average of 0.10 Vdc, but the voltage production had a significantly proportional relation to the concentration supplied, the same occurs at the highest concentration of heavy metals, voltage output shows a maximum of 228 Vdc, also achieving elimination efficiencies of 1.71% and 21.35% in 48 h, respectively, which indicates that certain microbial communities produce more bioelectricity if the appropriate substrate is supplied depending on the use and application of an MFC.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Revelo, D.M., Hurtado, N.H., Ruiz, J.O.: Celdas de Combustible Microbianas (CCMs): Un Reto Para La Remoción de Materia Orgánica y La Generación de Energía Eléctrica. Inf. tecnológica 24(6), 7–8 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-07642013000600004
Kiely, P.D., Regan, J.M., Logan, B.E.: The electric picnic: synergistic requirements for exoelectrogenic microbial communities. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 22(3), 378–385 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2011.03.003
Lefebvre, O., Ha Nguyen, T.T., Al-Mamun, A., Chang, I.S., Ng, H.Y.: T-RFLP reveals high β-proteobacteria diversity in microbial fuel cells enriched with domestic wastewater. J. Appl. Microbiol. 109(3), 839–850 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2010.04735.x
Wrighton, K.C., Virdis, B., Clauwaert, P., Read, S.T., Daly, R.A., Boon, N., Piceno, Y., Andersen, G.L., Coates, J.D., Rabaey, K.: Bacterial community structure corresponds to performance during cathodic nitrate reduction. ISME J. 4(11), 1443–1455 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2010.66
Liu, H., Cheng, S., Logan, B.E.: Production of electricity from acetate or butyrate using a single-chamber microbial fuel cell. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39(2), 658–662 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1021/es048927c
Chaudhuri, S.K., Lovley, D.R.: Electricity generation by direct oxidation of glucose in mediatorless microbial fuel cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 21(10), 1229–1232 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt867
Huang, L., Zeng, R.J., Angelidaki, I.: Electricity production from xylose using a mediator-less microbial fuel cell. Bioresour. Technol. 99(10), 4178–4184 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.08.067
Feng, Y., Wang, X., Logan, B.E., Lee, H.: Brewery wastewater treatment using air-cathode microbial fuel cells. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 78(5), 873–880 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1360-2
Huang, L., Logan, B.E.: Electricity generation and treatment of paper recycling wastewater using a microbial fuel cell. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 80(2), 349–355 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1546-7
Ghoreyshi, A.A., Jafary, T., Najafpour, G.D., Haghparast, F.: Effect of type and concentration of substrate on power generation in a dual chambered microbial fuel cell. In: Proceedings of the World Renewable Energy Congress – Sweden, 8–13 May 2011, vol. 57, pp. 1174–1181. Linköping University Electronic Press, Linköping (2011). https://doi.org/10.3384/ecp110571174.
Parot, S., Délia, M.L., Bergel, A.: Acetate to enhance electrochemical activity of biofilms from garden compost. Electrochim. Acta 53(6), 2737–2742 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2007.10.059
Guambo, A., Paña, S., Calderón, C., Echeverría, M., Recalde, C.: Environmental biosensor potential of microbial fuel cells for nitrate reduction. Sens. Transducers 217, 23–27 (2017)
Logroño, W.N., Echeverría, M.M., Recalde, C.G., Graziani, P.: Bioconversión de Residuos Sólidos Orgánicos Con Suelos de La Región Amazónica y Alto Andina Del Ecuador En Celdas de Combustible Microbiano de Cámara Simple. Inf. Tecnológica 26(2), 61–68 (2015). https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-07642015000200008
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Guambo, A., Calderón, C., Paña, S., Echeverría, M. (2021). Bioelectricity Production with Organic Substrates, Nitrates and Lead Using High Andean Soils. In: Botto-Tobar, M., Zambrano Vizuete, M., Díaz Cadena, A. (eds) Innovation and Research. CI3 2020. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1277. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60467-7_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60467-7_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-60466-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-60467-7
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)