Abstract
With the increase in the world population, urbanization and industrialization, the demand for energy has continuously increased during the last decades. Fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas and their derivatives) are directly related to land and water degradation and global warming mainly as a consequence of greenhouse gases (GHG) emissions generated by anthropogenic activity. As an alternative to reduce GHG emissions, several countries are looking to use renewable energy. Among the various renewable energies, solar energy is one of the renewable sources in the world. This article conducts a bibliometric study on the topics; life cycle assessment (LCA) and photovoltaic solar energy, looking for publications that cover the topic and make a network map of the main authors cited through the evaluation of 354 articles. The research was carried out through bibliometric analysis in the Scopus database, from 1998 to 2020. The result of this work may contribute to new research in the area of life cycle assessment and photovoltaic solar energy, since bibliometric analysis allows to draw a list of the main publications based on the construction of a theoretical framework.
Access provided by Autonomous University of Puebla. Download conference paper PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
1 Introduction
Throughout the world in recent decades, the concern with the environment has been increasingly highlighted, according to Haupt and Hellweg [1] due to the problems caused by human interference. The ability that human beings have to intervene in the environment to withdraw their livelihood and survival, allowed the exploration and consumption of resources without thinking about the conservation of the planet and its ecosystems, only due to environmental catastrophes, high levels of pollution and the verification of that the planet's capacity to recover was being exceeded is that a movement started in favor of the rational use of the planet's natural resources [2].
The need to reconcile economic efficiency with the conservation of natural resources and the preservation of existing ecosystems exposes the concept of sustainable development (SD) [3]. Being presented by the World Commission on Environment and Development in 1987 as “the ability of present generations to meet their needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs” [4] known as the “Our Common Future” report, a concept used until today when it comes to defining sustainable development.
This concept having gained strength in recent years, as well as the number of tools developed for managing and monitoring sustainable development [5]. Among these tools, the life cycle assessment (LCA) stands out, which aims to analyse systems, be it a product, service or process, from extraction of the raw material through its conception to its final disposal “from the cradle to the grave”, quantifying the possible associated environmental impacts [6].
With this, the present work aims to identify the global characteristics of the literature associated with the theme ACV and photovoltaic solar energy, in order to present associations and trends that provide a foundation for future work.
2 Theoretical Framework
2.1 Photovoltaic Energy
Solar energy is an important alternative source of energy to fossil fuels and, theoretically, the most available source of energy on earth [7]. Through the photovoltaic effect, solar cells directly convert energy from the sun into electrical energy in a static, silent, non-polluting and renewable way [8].
Photovoltaic conversion is the direct transformation of sunlight into electricity in photovoltaic devices, since these devices are robust and simple in design, requiring very little maintenance, their biggest advantage is the construction as independent systems to provide outputs from microwatts to megawatts [8, 9].
The basic building block of PV (photovoltaic) devices is a semiconductor element known as a photovoltaic cell. When the cells are interconnected, the PV module is integrated with a number of additional components, for example, inverters, batteries, basic components and assembly systems [10].
Photovoltaic systems produce electricity without polluting the air during their operation and have a very low “carbon footprint” over their lifetime, providing superior environmental performance compared to traditional electricity generation based on fossil fuel technologies [11].
3 Methodology
3.1 Sample
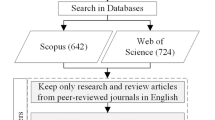
The first phase of the research (Fig. 1) was responsible for defining the sampling of the analysis, according to Ramos and Oliveira [12]. The “Scopus” database was selected for data collection. The search terms used were: (“life cycle assessment LCA”) AND (“photovoltaic solar energy”), where they were applied to the title, abstract and keywords fields. A total of 439 publications were extracted, and after refinement, 354 articles. To refine the research, the following exclusion criteria were applied.

Adapted from Ramos and Oliveira [12]
Phase 1 (sample definition).
Publication type: Only original articles and review articles were selected.
3.2 Data Analysis
For the second phase, with the sampling defined, all available metadata were imported, such as: abstract, authors, keywords, journal, references, number of citations, among other data. They were exported and later analysed using Microsoft Office Excel 2010 and Vos Viewer software. It was possible to extract the results sought in the work, such as: publications per year, journals with the largest number of publications, authors with the largest number of publications, most cited authors, institutions with the largest number of publications, countries with the largest number of publications, map of co -quotation and map of words co-occurrence.
4 Results and Discussion
Regarding the results of the survey with a sample of 354 articles, the first information extracted was the number of publications per year (Fig. 2). It is observed that the number of publications remains without much fluctuation until 2009, and from then on growing, until reaching a number of 78 publications in 2019, showing that there is a trend line, resulting from a possible maturation of this field of research.
314 different journals were found. The top 10 journals in terms of quantity of publications are shown in Table 1, with more than 50% of the total sample. The journals Journal of Cleaner Production and Applied Energy have the highest representation, with 37 and 28 publications respectively. Regarding the Impact Factor (IF) index, the periodical Renewable And Sustainable Energy Reviews stands out, which presented the highest index in 2018.
The 354 articles were analysed according to their origin, geographic and institutional, resulting in 56 countries and 160 different institutions. With regard to countries, shown in Table 2, the top ten in terms of quantity of publications represent almost 70% of publications. The United States leads the list in relation to the number of publications (64), followed by Italy (51) and the United Kingdom (44) in third position.
Due to the variety of institutions found in the sample, the majority with a low index of publications, it is inconclusive to cover the most representative portion of them. Given the above, only the nine main institutions were analysed in terms of quantity of publications, as shown in Table 3.
With regard to the main authors, shown in Table 4, the top ten in terms of quantity of publications represent almost 20% of the publications. The author Chemisana, D. has the largest number of publications (9), followed by Azapagic, A. and Lamnatou, C. both with 8 publications.
Through a cocitation analysis, in which the authors cited by the 354 articles in the sample, 1206 different authors were found. The analysis considers that when two authors are cited by the same article, they have a link and the set of these links form the chains of authors. Figure 3 shows the networks formed by the authors who were cited at least once within the sample, resulting in a total of 139 authors divided into 13 different streams, distinguished by colors. Regarding the relevance of the authors, the greater the circumference, the greater the number of citations.
The map resource was used to analyse the content of the articles, considering the words that occur in the title, in binary count, in which the occurrence in the article is verified, regardless of frequency. 1030 different words were found. Figure 4 shows the word map. This confirms that the publications address, in addition to LCA, the issues of environmental impact and photovoltaic solar energy, such as module, environmental impact, energy flow, solar PV, among others.
Table 5 shows the 10 most cited publications, including the average citation per year (CY) and journal name. With respect to publication sources, Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews tops the list, occurring twice. The most cited work was published by the journal Renewable Energy.
5 Conclusion
Bibliometric analyses were carried out based on a sample of 354 articles covering the topic of LCA applied to photovoltaic solar energy, which allowed observing the growth in bibliometric terms. It is observed that the use of LCA as a tool to support environmental management is growing, both in terms of the number of publications and its relevance. The works were classified into 19 different subject categories, the majority of which are in the Energy area. The main journals found were: Journal of Cleaner Production and Applied Energy.
There are 10 authors who have the greatest influence in the literature, with Chemisana, D. being the main one. The country with the largest number of publications is the United States, while the most relevant institution is the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in China.
The result of this work may help further research in the field of photovoltaic solar energy and life cycle analysis, since bibliometric analysis allows drawing a network map based on the construction of the theoretical framework.
References
Haupt, M.: Hellweg, S.: Measuring the environmental sustainability of a circular economy. Environmental and Sustainability Indicators 1–2, 100005 (2019).
Li, Y., Li, Y., Kappas, M.: PAVAO-ZUCKERMAN, M.: Identifying the key catastrophic variables of urban social-environmental resilience and early warning signal. Environment International 113, 184–190 (2018).
Eustachio, J. H. P. P.: Caldana, A. C. F.: Liboni, L. B.: Martinelli, D. P.: Systemic indicator of sustainable development: Proposal and application of a framework. Journal of Cleaner Production 241, 118383 (2019).
WCED – World Comission on Environment and Development. Our Common Future. Oxford University Press, Oxford, (1987).
Caiado, R. G. G.: Dias, R. D.: Mattos, L. V.: Quelhas, O. L. G.: Filho, W. L.: Towards sustainable development through the perspective of ecoefficiency - A systematic literature review. Journal of Cleaner Production 165, 890–904 (2017).
Ludin, N. A.: Mustafa, N. I.: Hanafiah, M. M.: Ibrahim, M. A.: Teridi, M. A. M.: Sepeai, S.: Zaharim, A.: Sopian, K..: Prospects of life cycle assessment of renewable energy from solar photovoltaic technologies: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 96, 11–28 (2018).
Desideri, U.: Zepparelli, F.: Morettini, V.: Garroni, E.: Comparative analysis of concentrating solar power and photovoltaic technologies: Technical and environmental evaluations. Applied Energy 102, 765–784 (2013).
Sampaio, P. G. V.: Gonzáles, M. O. A.: Photovoltaic solar energy: Conceptual framework. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 74, 590–601 (2017).
Parida, B.: Iniyan, S.: Goic, R.: A review of solar photovoltaic technologies. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 15, 1625–1636 (2011).
Aman, M. M.: Solang, K. H.: Hossain, M. S.: Badarudin, A.: Jasmon, G. B.: Mokhlis, H.: Bakar, A. H. A.: Kazi, S. N.: A review of Safety, Health and Environmental (SHE) issues of solar energy system. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 41, 1190–1204 (2015).
Yue, D.: You, F.: Darling, S. B.: Domestic and overseas manufacturing scenarios of silicon-based photovoltaics: Life cycle energy and environmental comparative analysis. Solar Energy 105, 669–678 (2014).
Ramos, M. O.: Oliveira, E. D.: Revisão Bibliométrica sobre a Manutenção Produtiva Total e o Pilar Saúde, Segurança e Meio Ambiente. In. Simpósio de engenharia, gestão e inovação. Águas de Lindoia, São Paulo (2019).
Acknowledgements
To the support provided by the PROSUP/CAPES program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
de Paula Teixeira, W. (2020). Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) Photovoltaic Solar Energy: A Bibliometric Literature Review. In: Thomé, A.M.T., Barbastefano, R.G., Scavarda, L.F., dos Reis, J.C.G., Amorim, M.P.C. (eds) Industrial Engineering and Operations Management. IJCIEOM 2020. Springer Proceedings in Mathematics & Statistics, vol 337. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-56920-4_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-56920-4_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-56919-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-56920-4
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)