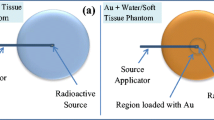
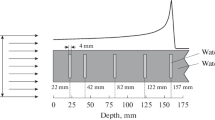
Abstract
In radiotherapy, ionizing radiation causes deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) damage in cancer cells, so that the cancer can be controlled by terminating the reproduction of these affected cells. DNA is a biological molecule in nanometer scale in a living cell necessary for cell reproduction. Adding heavy-atom nanomaterial as radiosensitizer to the cancer cells can enhance the DNA damage in the cells, as the irradiated cancer cells can be more easily detected by medical imaging. This is because the addition of heavy-atom nanomaterial in the cancer cell increases the compositional atomic number of the cell, resulting in a photoelectric interaction enhancement with increased secondary electron yield for energy deposition. The gold nanomaterial addition to the cancer tumour benefits radiotherapy that produces a highly conformal dose distribution covering the cancer target, while sparing the surrounding critical organs. We use Monte Carlo simulation to study the nanodosimetry of DNA, guiding us to evaluate the effectiveness of nanomaterials such as gold nanoparticles transported to the cancer cells. Monte Carlo simulation is a mathematical method to model the interaction between the DNA and radiation beam. In this chapter, we review the basic concept and recent progress of Monte Carlo simulation used in predicting the dose and imaging contrast enhancement in gold nanoparticle-enhanced radiotherapy. We also review the dose and imaging contrast enhancement ratios among different nanoparticle materials using different photon beam energies in the kilovoltage range. In gold nanoparticle-enhanced radiotherapy using the flattening-filter-free and flattening-filter photon beams, we examine the recent results of dose and imaging contrast enhancement between these photon beams using Monte Carlo simulation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Her S, Jaffray DA, Allen C (2017) Gold nanoparticles for applications in cancer radiotherapy: mechanisms and recent advancements. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 109:84–101
Chow JCL (2018) Monte Carlo nanodosimetry in gold nanoparticle-enhanced radiotherapy. In: Chan MF (ed) Recent advancements and applications in dosimetry, Chapter 2. Nova Science Publishers, New York
Chow JCL (2017) Dose enhancement effect in radiotherapy: adding gold nanoparticle to tumour in cancer treatment. Nanostruct Cancer Ther 2017:383–400
Chow JCL (2017) Application of nanoparticle materials in radiation therapy. In: Martinez LMT, Kharissova OV, Kharisov BI (eds) Handbook of ecomaterials. Springer Nature, Cham
Chow JCL (2016) Photon and electron interactions with gold nanoparticles: a Monte Carlo study on gold nanoparticle-enhanced radiotherapy. Nanobiomater Med Imaging 8:45–70
Chow JCL (2015) Characteristics of secondary electrons from irradiated gold nanoparticle in radiotherapy, Chapter 10. In: Aliofkhazraei M (ed) Handbook of nanoparticles. Springer, Cham, pp 41–65
Albayedh F, Chow JCL (2018) Monte Carlo simulation on the imaging contrast enhancement in nanoparticle-enhanced radiotherapy. J Med Phys 43:195–199
He C, Chow JCL (2016) Gold nanoparticle DNA damage in radiotherapy: a Monte Carlo study. AIMS Bioeng 3:352–361
Zhang XD, Guo ML, Wu HY, Sun YM, Ding YQ, Feng X, Zhang LA (2009) Irradiation stability and cytotoxicity of gold nanoparticles for radiotherapy. Int J Nanomedicine 4:165
Berbeco RI, Korideck H, Ngwa W, Kumar R, Patel J, Sridhar S, Johnson S, Price BD, Kimmelman A, Makrigiorgos GM (2012) DNA damage enhancement from gold nanoparticles for clinical MV photon beams. Radiat Res 178(6):604–608
Hainfeld JF, Slatkin DN, Smilowitz HM (2004) The use of gold nanoparticles to enhance radiotherapy in mice. Phys Med Biol 49(18):N309
Leung MK, Chow JC, Chithrani BD, Lee MJ, Oms B, Jaffray DA (2011) Irradiation of gold nanoparticles by x-rays: Monte Carlo simulation of dose enhancements and the spatial properties of the secondary electrons production. Med Phys 38(2):624–631
Chow JCL (2018) Recent progress in Monte Carlo simulation on gold nanoparticle radiosensitization. AIMS Biophys 5(4):231–244
Andreo P (1991) Monte Carlo techniques in medical radiation physics. Phys Med Biol 36(7):861
Rogers DW (2006) Fifty years of Monte Carlo simulations for medical physics. Phys Med Biol 51(13):R287
Chow JC, Owrangi AM (2014) Dosimetric dependences of bone heterogeneity and beam angle on the unflattened and flattened photon beams: a Monte Carlo comparison. Radiat Phys Chem 101:46–52
Chow JC, Owrangi AM (2016) A surface energy spectral study on the bone heterogeneity and beam obliquity using the flattened and unflattened photon beams. Report Pract Oncol Radiother 21(1):63–70
Zubizarreta E, Van DJ, Lievens Y (2016) Analysis of global radiotherapy needs and costs by geographic region and income level. Clin Oncol 29:84–92
Medintz IL, Uyeda HT, Goldman ER, Mattoussi H (2005) Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging, labelling and sensing. Nat Mater 4(6):435
Kimling J, Maier M, Okenve B, Kotaidis V, Ballot H, Plech A (2006) Turkevich method for gold nanoparticle synthesis revisited. J Phys Chem B 110(32):15700–15707
Eastoe J, Hollamby MJ, Hudson L (2006) Recent advances in nanoparticle synthesis with reversed micelles. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 128:5–15
Zhao P, Li N, Astruc D (2013) State of the art in gold nanoparticle synthesis. Coord Chem Rev 257(3–4):638–665
Chithrani BD, Chan WC (2007) Elucidating the mechanism of cellular uptake and removal of protein-coated gold nanoparticles of different sizes and shapes. Nano Lett 7(6):1542–1550
Chow JC, Leung MK, Fahey S, Chithrani DB, Jaffray DA (2012) Monte Carlo simulation on low-energy electrons from gold nanoparticle in radiotherapy. J Phys Conf Ser 341(1):012012. IOP Publishing
Zheng XJ, Chow JCL (2017) Radiation dose enhancement in skin therapy with nanoparticle addition: a Monte Carlo study on kilovoltage photon and megavoltage electron beams. World J Radiol 9:63–71
Hainfeld JF, Slatkin DN, Focella TM, Smilowitz HM (2006) Gold nanoparticles: a new X-ray contrast agent. Br J Radiol 79(939):248–253
Cho SH (2005) Estimation of tumour dose enhancement due to gold nanoparticles during typical radiation treatments: a preliminary Monte Carlo study. Phys Med Biol 50(15):N163
Rahman WN, Bishara N, Ackerly T, He CF, Jackson P, Wong C, Davidson R, Geso M (2009) Enhancement of radiation effects by gold nanoparticles for superficial radiation therapy. Nanomedicine 5(2):136–142
Berbeco RI, Ngwa W, Makrigiorgos GM (2011) Localized dose enhancement to tumor blood vessel endothelial cells via megavoltage X-rays and targeted gold nanoparticles: new potential for external beam radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81(1):270–276
Herold M, Das IJ, Stobbe CC, Iyer RV, Chapman JD (2000) Gold microspheres: a selective technique for producing biologically effective dose enhancement. Int J Radiat Biol 76(10):1357–1364
Boudaı̈ffa B, Cloutier P, Hunting D, Huels MA, Sanche L (2000) Resonant formation of DNA strand breaks by low-energy (3 to 20 eV) electrons. Science 287(5458):1658–1660
Zheng Y, Wagner JR, Sanche L (2006) DNA damage induced by low-energy electrons: electron transfer and diffraction. Phys Rev Lett 96(20):208101
Barrios R, Skurski P, Simons J (2002) Mechanism for damage to DNA by low-energy electrons. J Phys Chem B 106(33):7991–7994
Bird GA (1981) Monte-Carlo simulation in an engineering context. Prog Astronaut Aeronaut 74:239–255
Oran ES, Oh CK, Cybyk BZ (1998) Direct simulation Monte Carlo: recent advances and applications. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 30(1):403–441
Chow JC, Leung MK, Van Dyk J (2009) Variations of lung density and geometry on inhomogeneity correction algorithms: a Monte Carlo dosimetric evaluation. Med Phys 36(8):3619–3630
Verhaegen F, Seuntjens J (2003) Monte Carlo modelling of external radiotherapy photon beams. Phys Med Biol 48(21):R107
Agostinelli S, Allison J, Amako KA, Apostolakis J, Araujo H, Arce P, Asai M, Axen D, Banerjee S, G B, Behner F (2003) GEANT4 – a simulation toolkit. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect A 506(3):250–303
Battistoni G, Cerutti F, Fasso A, Ferrari A, Muraro S, Ranft J, Roesler S, Sala PR (2007) The FLUKA code: description and benchmarking. AIP Conf Proc 896(1):31–49. AIP
Salvat F, Fernández-Varea JM, Sempau J (2006) PENELOPE-2006: a code system for Monte Carlo simulation of electron and photon transport. In: Workshop proceedings, vol. 4, no. 7. Nuclear Energy Agency, Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development, Barcelona
El Naqa I, Pater P, Seuntjens J (2012) Monte Carlo role in radiobiological modelling of radiotherapy outcomes. Phys Med Biol 57(11):R75
Kawrakow I (2001) The EGSnrc code system, Monte Carlo simulation of electron and photon transport. NRCC report Pirs-701
Briesmeister JF (1986) MCNP: a general Monte Carlo code for neutron and photon transport. Version 3A. Revision 2. Los Alamos National Lab, Los Alamos
Chow JC, Leung MK, Lindsay PE, Jaffray DA (2010) Dosimetric variation due to the photon beam energy in the small-animal irradiation: a Monte Carlo study. Med Phys 37(10):5322–5329
Chow JC, Leung MK (2007) Treatment planning for a small animal using Monte Carlo simulation. Med Phys 34(12):4810–4817
Incerti S, Baldacchino G, Bernal M, Capra R, Champion C, Francis Z, Guèye P, Mantero A, Mascialino B, Moretto P, Nieminen P (2010) The Geant4-DNA project. Int J Model Simul Sci Comput 1(02):157–178
Li J, Li C, Qiu R, Yan C, Xie W, Wu Z, Zeng Z, Tung C (2015) DNA strand breaks induced by electrons simulated with Nanodosimetry Monte Carlo Simulation Code: NASIC. Radiat Prot Dosim 166(1–4):38–43
Montenegro M, Nahar SN, Pradhan AK, Huang K, Yu Y (2009) Monte Carlo simulations and atomic calculations for Auger processes in biomedical nanotheranostics. J Phys Chem A 113(45):12364–12369
He X, Cheng F, Chen ZX (2016) The Lattice Kinetic Monte Carlo simulation of atomic diffusion and structural transition for gold. Sci Rep 6:33128
Martinov MP, Thomson RM (2017) Heterogeneous multiscale Monte Carlo simulations for gold nanoparticle radiosensitization. Med Phys 44(2):644–653
Sakata D, Incerti S, Bordage MC, Lampe N, Okada S, Emfietzoglou D, Kyriakou I, Murakami K, Sasaki T, Tran H, Guatelli S (2016) An implementation of discrete electron transport models for gold in the Geant4 simulation toolkit. J Appl Phys 120(24):244901
Zabihzadeh M, Moshirian T, Ghorbani M, Knaup C, Behrooz MA (2018) A Monte Carlo study on dose enhancement by homogeneous and inhomogeneous distributions of gold nanoparticles in radiotherapy with low energy X-rays. J Biomed Phys Eng 8(1):13
Brivio D, Zygmanski P, Arnoldussen M, Hanlon J, Chell E, Sajo E, Makrigiorgos GM, Ngwa W (2015) Kilovoltage radiosurgery with gold nanoparticles for neovascular age-related macular degeneration (AMD): a Monte Carlo evaluation. Phys Med Biol 60(24):9203
Chow JCL, Owrangi AM (2018) Mucosal dosimetry on unflattened photon beams: a Monte Carlo phantom study. Biomed Phys Eng Express 5:015007. https://doi.org/10.1088/2057-1976/aaeaaa
Chow JC, Jiang R (2012) Bone and mucosal dosimetry in skin radiation therapy: a Monte Carlo study using kilovoltage photon and megavoltage electron beams. Phys Med Biol 57(12):3885
Chow JC, Leung MK, Jaffray DA (2012) Monte Carlo simulation on a gold nanoparticle irradiated by electron beams. Phys Med Biol 57(11):3323
Swinehart DF (1962) The Beer-Lambert law. J Chem Educ 39(7):333
Georg D, Knöös T, McClean B (2011) Current status and future perspective of flattening filter free photon beams. Med Phys 38(3):1280–1293
Martelli S, Chow JCL (2019) Dose enhancement in gold nanoparticle-enhanced Prostate VMAT: a Monte Carlo Phantom study. Med Phys 46:e490
Abdulle A, Chow JCL (2019) Contrast enhancement of MV portal imaging in nanoparticle-enhanced radiotherapy: a Monte Carlo Phantom study. Med Phys 46:e437
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Chow, J.C.L. (2021). Recent Progress of Gold Nanomaterials in Cancer Therapy. In: Kharissova, O.V., Torres-Martínez, L.M., Kharisov, B.I. (eds) Handbook of Nanomaterials and Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36268-3_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36268-3_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-36267-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-36268-3
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceReference Module Physical and Materials ScienceReference Module Chemistry, Materials and Physics