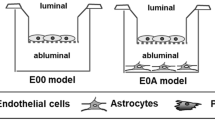
Abstract
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is essential to maintain the proper microenvironment for brain function. Although formed by different cell types, the endothelial cells (ECs) of the brain microvessels provide the BBB with its selective permeability. To study the BBB in vitro, EC lines as well as primary isolated ECs have been used. In this chapter, we will provide a detailed protocol on how to isolate and culture primary brain microvascular endothelial cells from different species for use as in vitro models of the BBB. When performed properly, this protocol will allow one to obtain a pure culture of brain microvascular endothelial cells with which to analyze the effects of therapeutic and toxic agents on BBB functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernacki J, Dobrowolska A, Nierwinska K, Malecki A (2008) Physiology and pharmacological role of the blood-brain barrier. Pharmacol Rep 60(5):600–622
Hawkins BT, Davis TP (2005) The blood-brain barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev 57(2):173–185. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.57.2.4
Cardoso FL, Brites D, Brito MA (2010) Looking at the blood-brain barrier: molecular anatomy and possible investigation approaches. Brain Res Rev 64(2):328–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresrev.2010.05.003
Weksler BB, Subileau EA, Perriere N, Charneau P, Holloway K, Leveque M, Tricoire-Leignel H, Nicotra A, Bourdoulous S, Turowski P, Male DK, Roux F, Greenwood J, Romero IA, Couraud PO (2005) Blood-brain barrier-specific properties of a human adult brain endothelial cell line. FASEB J 19(13):1872–1874. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.04-3458fje
Ebnet K (2008) Organization of multiprotein complexes at cell-cell junctions. Histochem Cell Biol 130(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-008-0418-7
Forster C (2008) Tight junctions and the modulation of barrier function in disease. Histochem Cell Biol 130(1):55–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-008-0424-9
Helms HC, Abbott NJ, Burek M, Cecchelli R, Couraud PO, Deli MA, Forster C, Galla HJ, Romero IA, Shusta EV, Stebbins MJ, Vandenhaute E, Weksler B, Brodin B (2016) In vitro models of the blood-brain barrier: an overview of commonly used brain endothelial cell culture models and guidelines for their use. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 36(5):862–890. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678x16630991
Steiner O, Coisne C, Engelhardt B, Lyck R (2011) Comparison of immortalized bEnd5 and primary mouse brain microvascular endothelial cells as in vitro blood-brain barrier models for the study of T cell extravasation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31(1):315–327. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2010.96
Urich E, Lazic SE, Molnos J, Wells I, Freskgard PO (2012) Transcriptional profiling of human brain endothelial cells reveals key properties crucial for predictive in vitro blood-brain barrier models. PLoS One 7(5):e38149. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0038149
Audus KL, Borchardt RT (1987) Bovine brain microvessel endothelial-cell monolayers as a model system for the blood-brain-barrier. Ann N Y Acad Sci 507:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb45787.x
Trickler WJ, Lantz SM, Murdock RC, Schrand AM, Robinson BL, Newport GD, Schlager JJ, Oldenburg SJ, Paule MG, Slikker W Jr, Hussain SM, Ali SF (2011) Brain microvessel endothelial cells responses to gold nanoparticles: in vitro pro-inflammatory mediators and permeability. Nanotoxicology 5(4):479–492. https://doi.org/10.3109/17435390.2010.540356
Trickler WJ, Lantz SM, Schrand AM, Robinson BL, Newport GD, Schlager JJ, Paule MG, Slikker W, Biris AS, Hussain SM, Ali SF (2012) Effects of copper nanoparticles on rat cerebral microvessel endothelial cells. Nanomedicine (Lond) 7(6):835–846. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm.11.154
Trickler WJ, Lantz-McPeak SM, Robinson BL, Paule MG, Slikker W Jr, Biris AS, Schlager JJ, Hussain SM, Kanungo J, Gonzalez C, Ali SF (2014) Porcine brain microvessel endothelial cells show pro-inflammatory response to the size and composition of metallic nanoparticles. Drug Metab Rev 46(2):224–231. https://doi.org/10.3109/03602532.2013.873450
Imam SZ, Lantz-McPeak SM, Cuevas E, Rosas-Hernandez H, Liachenko S, Zhang YB, Sarkar S, Ramu J, Robinson BL, Jones Y, Gough B, Paule MG, Ali SF, Binienda ZK (2015) Iron oxide nanoparticles induce dopaminergic damage: in vitro pathways and in vivo imaging reveals mechanism of neuronal damage. Mol Neurobiol 52(2):913–926. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9259-2
Rosas-Hernandez H, Cuevas E, Lantz SM, Rice KC, Gannon BM, Fantegrossi WE, Gonzalez C, Paule MG, Ali SF (2016) Methamphetamine, 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) and 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) induce differential cytotoxic effects in bovine brain microvessel endothelial cells. Neurosci Lett 629:125–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2016.06.029
Rosas-Hernandez H, Cuevas E, Lantz-McPeak SM, Ali SF, Gonzalez C (2013) Prolactin protects against the methamphetamine-induced cerebral vascular toxicity. Curr Neurovasc Res 10(4):346–355
Rosas-Hernandez H, Cuevas E, Lantz SM, Hamilton WR, Ramirez-Lee MA, Ali SF, Gonzalez C (2013) Prolactin and blood-brain barrier permeability. Curr Neurovasc Res 10(4):278–286
Imam SZ, Trickler W, Kimura S, Binienda ZK, Paule MG, Slikker W Jr, Li S, Clark RA, Ali SF (2013) Neuroprotective efficacy of a new brain-penetrating C-Abl inhibitor in a murine Parkinson’s disease model. PLoS One 8(5):e65129. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0065129
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by an appointment (H.R.-H.) to the Research Participation Program at the National Center for Toxicological Research administered by the Oak Ridge Institute for Science and Education through an interagency agreement between the US Department of Energy and the US Food and Drug Administration.
Disclaimer The views expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the US Food and Drug Administration. Mention of trade names or commercial products does not constitute endorsement or recommendation for use.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Rosas-Hernandez, H., Cuevas, E., Lantz, S.M., Paule, M.G., Ali, S.F. (2018). Isolation and Culture of Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells for In Vitro Blood-Brain Barrier Studies. In: Skaper, S. (eds) Neurotrophic Factors. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1727. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7571-6_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7571-6_23
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-7570-9
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-7571-6
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols