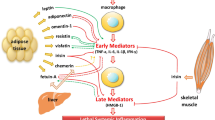
Abstract
In addition to energy storage and insulation, the white adipose tissue is a complex endocrine organ responsible for the secretion of a high number of adipocyte-originated signaling molecules. These so-called adipokines are involved in the control of metabolism, linking the nutrient status to the tissues involved in energy intake and expenditure and affecting insulin sensitivity. Additionally, resident and recruited macrophages constitute an important part of the adipose tissue, responsible for the secretion of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines. Up until now, more than 40 different adipokines have been described. From these, leptin and adiponectin are the most studied during critical illness.
Although knowledge is still limited, current available literature suggests that the endocrine functions of adipose tissue might play an adaptive role during critical illness. In the acute phase of illness, the anti-inflammatory and insulin-sensitizing adiponectin is reduced, while pro-inflammatory cytokine expression in adipose tissue is upregulated. In the prolonged phase of critical illness, both adiponectin and anti-inflammatory cytokine production are increasing. Reports on the pro-inflammatory leptin during critical illness are controversial in both humans and animal investigations, possibly due to confounders such as gender, body mass index, and nutritional strategy.
Observational studies report lower mortality in obese than in lean critically ill patients, an association referred to as the “obesity paradox.” Potentially, the altered adipokine secretion profile observed in obesity plays a protective role during critical illness.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AdipoR:
-
Adiponectin receptor
- ARDS:
-
Acute respiratory distress syndrome
- CXCL10:
-
C-X-C motif chemokine 10
- EMR1:
-
EGF-like module-containing mucin-like hormone receptor
- HMW:
-
High molecular weight
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- kDa:
-
Kilodalton
- LMW:
-
Low molecular weight
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- MCP-1:
-
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
- MMW:
-
Medium molecular weight
- PAI-1:
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1
- PPARγ:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ
- RBP4:
-
Retinol-binding protein 4
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
References
Abhyankar S, Leishear K, Callaghan FM, Demner-Fushman D, McDonald CJ. Lower short- and long-term mortality associated with overweight and obesity in a large cohort study of adult intensive care unit patients. Crit Care. 2012;16:R235.
Ahfeldt T, Schinzel RT, Lee YK, Hendrickson D, Kaplan A, Lum DH, Camahort R, Xia F, Shay J, Rhee EP, Clish CB, Deo RC, Shen T, Lau FH, Cowley A, Mowrer G, Al-Siddiqi H, Nahrendorf M, Musunuru K, Gerszten RE, Rinn JL, Cowan CA. Programming human pluripotent stem cells into white and brown adipocytes. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14:209–19.
Ahima RS, Lazar MA. Adipokines and the peripheral and neural control of energy balance. Mol Endocrinol. 2008;22:1023–31.
Akinnusi ME, Pineda LA, El Solh AA. Effect of obesity on intensive care morbidity and mortality: a meta-analysis. Crit Care Med. 2008;36:151–8.
Arnalich F, Lopez J, Codoceo R, Jim NM, Madero R, Montiel C. Relationship of plasma leptin to plasma cytokines and human survival in sepsis and septic shock. J Infect Dis. 1999;180:908–11.
Behnes M, Brueckmann M, Lang S, Putensen C, Saur J, Borggrefe M, Hoffmann U. Alterations of leptin in the course of inflammation and severe sepsis. BMC Infect Dis. 2012;12:217.
Boden G, Chen X, Mozzoli M, Ryan I. Effect of fasting on serum leptin in normal human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996;81:3419–23.
Bornstein SR, Licinio J, Tauchnitz R, Engelmann L, Negrao AB, Gold P, Chrousos GP. Plasma leptin levels are increased in survivors of acute sepsis: associated loss of diurnal rhythm, in cortisol and leptin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998;83:280–3.
Cowley MA, Smart JL, Rubinstein M, Cerdan MG, Diano S, Horvath TL, Cone RD, Low MJ. Leptin activates anorexigenic POMC neurons through a neural network in the arcuate nucleus. Nature. 2001;411:480–4.
de Oliveira C, de Mattos AB, Biz C, Oyama LM, Ribeiro EB, do Nascimento CM. High-fat diet and glucocorticoid treatment cause hyperglycemia associated with adiponectin receptor alterations. Lipids Health Dis. 2011;10:11.
Faggioni R, Fantuzzi G, Fuller J, Dinarello CA, Feingold KR, Grunfeld C. IL-1 beta mediates leptin induction during inflammation. Am J Physiol. 1998;274:R204–8.
Fantuzzi G. Adiponectin and inflammation: consensus and controversy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;121:326–30.
Gavrila A, Chan JL, Yiannakouris N, Kontogianni M, Miller LC, Orlova C, Mantzoros CS. Serum adiponectin levels are inversely associated with overall and central fat distribution but are not directly regulated by acute fasting or leptin administration in humans: cross-sectional and interventional studies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:4823–31.
Gordon S, Martinez FO. Alternative activation of macrophages: mechanism and functions. Immunity. 2010;32:593–604.
Gordon S, Taylor PR. Monocyte and macrophage heterogeneity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:953–64.
Graham TE, Yang Q, Bluher M, Hammarstedt A, Ciaraldi TP, Henry RR, Wason CJ, Oberbach A, Jansson PA, Smith U, Kahn BB. Retinol-binding protein 4 and insulin resistance in lean, obese, and diabetic subjects. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2552–63.
Grunfeld C, Feingold KR. Tumor necrosis factor, cytokines, and the hyperlipidemia of infection. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 1991;2:213–9.
Grunfeld C, Zhao C, Fuller J, Pollack A, Moser A, Friedman J, Feingold KR. Endotoxin and cytokines induce expression of leptin, the ob gene product, in hamsters. J Clin Invest. 1996;97:2152–7.
Heuer JG, Bailey DL, Sharma GR, Zhang T, Ding C, Ford A, Stephens EJ, Holmes KC, Grubbs RL, Fynboe KA, Chen YF, Jakubowski JA. Cecal ligation and puncture with total parenteral nutrition: a clinically relevant model of the metabolic, hormonal, and inflammatory dysfunction associated with critical illness. J Surg Res. 2004;121:178–86.
Hillenbrand A, Weiss M, Knippschild U, Stromeyer HG, Henne-Bruns D, Huber-Lang M, Wolf AM. Association of adiponectin levels and insulin demand in critically ill patients. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2011;4:45–51.
Hogue Jr CW, Stearns JD, Colantuoni E, Robinson KA, Stierer T, Mitter N, Pronovost PJ, Needham DM. The impact of obesity on outcomes after critical illness: a meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2009;35:1152–70.
Jain M, Budinger GR, Lo A, Urich D, Rivera SE, Ghosh AK, Gonzalez A, Chiarella SE, Marks K, Donnelly HK, Soberanes S, Varga J, Radigan KA, Chandel NS, Mutlu GM. Leptin promotes fibroproliferative acute respiratory distress syndrome by inhibiting peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;183:1490–8.
Janke J, Engeli S, Boschmann M, Adams F, Bohnke J, Luft FC, Sharma AM, Jordan J. Retinol-binding protein 4 in human obesity. Diabetes. 2006;55:2805–10.
Jeevanandam M, Begay CK, Petersen SR. Plasma leptin levels in trauma patients: effect of adjuvant recombinant human growth hormone in intravenously fed multiple trauma patients. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1998;22:340–6.
Jernas M, Olsson B, Sjoholm K, Sjogren A, Rudemo M, Nellgard B, Carlsson LM, Sjostrom CD. Changes in adipose tissue gene expression and plasma levels of adipokines and acute-phase proteins in patients with critical illness. Metabolism. 2009;58:102–8.
Koch A, Weiskirchen R, Sanson E, Zimmermann HW, Voigt S, Duckers H, Trautwein C, Tacke F. Circulating retinol binding protein 4 in critically ill patients before specific treatment: prognostic impact and correlation with organ function, metabolism and inflammation. Crit Care. 2010;14:R179.
Kolaczynski JW, Nyce MR, Considine RV, Boden G, Nolan JJ, Henry R, Mudaliar SR, Olefsky J, Caro JF. Acute and chronic effects of insulin on leptin production in humans: Studies in vivo and in vitro. Diabetes. 1996;45:699–701.
Konner AC, Bruning JC. Selective insulin and leptin resistance in metabolic disorders. Cell Metab. 2012;16:144–52.
Kotnik P, Fischer-Posovszky P, Wabitsch M. RBP4: a controversial adipokine. Eur J Endocrinol. 2011;165:703–11.
Kremen J, Dolinkova M, Krajickova J, Blaha J, Anderlova K, Lacinova Z, Haluzikova D, Bosanska L, Vokurka M, Svacina S, Haluzik M. Increased subcutaneous and epicardial adipose tissue production of proinflammatory cytokines in cardiac surgery patients: possible role in postoperative insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:4620–7.
La Cava A, Matarese G. The weight of leptin in immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:371–9.
Langouche L, Vander Perre S, Wouters PJ, D’Hoore A, Hansen TK, Van den Berghe G. Effect of intensive insulin therapy on insulin sensitivity in the critically ill. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:3890–7.
Langouche L, Vander Perre S, Frystyk J, Flyvbjerg A, Hansen TK, Van den Berghe G. Adiponectin, retinol binding protein 4 and leptin in protracted critical illness of pulmonary origin. Crit Care. 2009;13:R112.
Langouche L, Vander Perre S, Thiessen S, Gunst J, Hermans G, D’Hoore A, Kola B, Korbonits M, Van den Berghe G. Alterations in adipose tissue during critical illness: an adaptive and protective response? Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;182:507–16.
Langouche L, Marques MB, Ingels C, Gunst J, Derde S, Vander Perre S, D’Hoore A, Van den Berghe G. Critical illness induces alternative activation of M2 macrophages in adipose tissue. Crit Care. 2011;15:R245.
Langouche L, Vander PS, Marques M, Boelen A, Wouters PJ, Casaer MP, Van den BG. Impact of early nutrient restriction during critical illness on the nonthyroidal illness syndrome and its relation with outcome: a randomized, controlled clinical study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98:1006–13.
LeGall-Salmon E, Stevens WD, Levy JR. Total parenteral nutrition increases serum leptin concentration in hospitalized, undernourished patients. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1999;23:38–42.
Leuwer M, Welters I, Marx G, Rushton A, Bao H, Hunter L, Trayhurn P. Endotoxaemia leads to major increases in inflammatory adipokine gene expression in white adipose tissue of mice. Pflugers Arch. 2009;457:731–41.
Mancuso P, Gottschalk A, Phare SM, Peters-Golden M, Lukacs NW, Huffnagle GB. Leptin-deficient mice exhibit impaired host defense in Gram-negative pneumonia. J Immunol. 2002;168:4018–24.
Mantovani A, Sozzani S, Locati M, Allavena P, Sica A. Macrophage polarization: tumor-associated macrophages as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends Immunol. 2002;23:549–55.
Marik PE, Varon J. Sepsis: state of the art. Dis Mon. 2001;47:465–532.
Marques MB, Langouche L. Endocrine, metabolic, and morphologic alterations of adipose tissue during critical illness. Crit Care Med. 2013;41:317–25.
Martino JL, Stapleton RD, Wang M, Day AG, Cahill NE, Dixon AE, Suratt BT, Heyland DK. Extreme obesity and outcomes in critically ill patients. Chest. 2011;140:1198–206.
Maruna P, Lindner J, Kubzova KM. Leptin and soluble leptin receptor changes after pulmonary endarterectomy: relations to cortisol and cytokine network. Physiol Res. 2009;58:569–76.
McCowen KC, Ling PR, Friel C, Sternberg J, Forse RA, Burke PA, Bistrian BR. Patterns of plasma leptin and insulin concentrations in hospitalized patients after the initiation of total parenteral nutrition. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002;75:931–5.
Mehta NN, McGillicuddy FC, Anderson PD, Hinkle CC, Shah R, Pruscino L, Tabita-Martinez J, Sellers KF, Rickels MR, Reilly MP. Experimental endotoxemia induces adipose inflammation and insulin resistance in humans. Diabetes. 2010;59:172–81.
Meyer C, Robson D, Rackovsky N, Nadkarni V, Gerich J. Role of the kidney in human leptin metabolism. Am J Physiol. 1997;273:E903–7.
Minokoshi Y, Alquier T, Furukawa N, Kim YB, Lee A, Xue B, Mu J, Foufelle F, Ferre P, Birnbaum MJ, Stuck BJ, Kahn BB. AMP-kinase regulates food intake by responding to hormonal and nutrient signals in the hypothalamus. Nature. 2004;428:569–74.
Moody BJ. Changes in the serum concentrations of thyroxine-binding prealbumin and retinol-binding protein following burn injury. Clin Chim Acta. 1982;118:87–92.
Moshyedi AK, Josephs MD, Abdalla EK, Mackay SL, Edwards III CK, Copeland III EM, Moldawer LL. Increased leptin expression in mice with bacterial peritonitis is partially regulated by tumor necrosis factor alpha. Infect Immun. 1998;66:1800–2.
Odegaard JI, Chawla A. Mechanisms of macrophage activation in obesity-induced insulin resistance. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2008;4:619–26.
Okamoto Y, Kihara S, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Libby P. Adiponectin: a key adipocytokine in metabolic syndrome. Clin Sci (Lond). 2006;110:267–78.
Oliveros H, Villamor E. Obesity and mortality in critically ill adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008;16:515–21.
Orbak Z, Ertekin V, Akcay F, Ozkan B, Ors R. Serum leptin levels in neonatal bacterial septicemia. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2003;16:727–31.
Ouedraogo R, Gong Y, Berzins B, Wu X, Mahadev K, Hough K, Chan L, Goldstein BJ, Scalia R. Adiponectin deficiency increases leukocyte-endothelium interactions via upregulation of endothelial cell adhesion molecules in vivo. J Clin Invest. 2007;117:1718–26.
Papaspyrou-Rao S, Schneider SH, Petersen RN, Fried SK. Dexamethasone increases leptin expression in humans in vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997;82:1635–7.
Papathanassoglou ED, Moynihan JA, Ackerman MH, Mantzoros CS. Serum leptin levels are higher but are not independently associated with severity or mortality in the multiple organ dysfunction/systemic inflammatory response syndrome: a matched case control and a longitudinal study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2001;54:225–33.
Quasim T, McMillan DC, Wallace AM, Kinsella J. The relationship between leptin concentrations, the systemic inflammatory response and illness severity in surgical patients admitted to ITU. Clin Nutr. 2004;23:233–8.
Roberts R, Hodson L, Dennis AL, Neville MJ, Humphreys SM, Harnden KE, Micklem KJ, Frayn KN. Markers of de novo lipogenesis in adipose tissue: associations with small adipocytes and insulin sensitivity in humans. Diabetologia. 2009;52:882–90.
Robinson K, Kruger P, Prins J, Venkatesh B. The metabolic syndrome in critically ill patients. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;25:835–45.
Shapiro NI, Khankin EV, Van MM, Shih SC, Lu S, Yano M, Castro PR, Maratos-Flier E, Parikh SM, Karumanchi SA, Yano K. Leptin exacerbates sepsis-mediated morbidity and mortality. J Immunol. 2010;185:517–24.
Sica A, Mantovani A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization: in vivo veritas. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:787–95.
Starr ME, Evers BM, Saito H. Age-associated increase in cytokine production during systemic inflammation: adipose tissue as a major source of IL-6. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2009;64:723–30.
Sweeney G. Cardiovascular effects of leptin. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2010;7:22–9.
Teoh H, Quan A, Bang KW, Wang G, Lovren F, Vu V, Haitsma JJ, Szmitko PE, Al-Omran M, Wang CH, Gupta M, Peterson MD, Zhang H, Chan L, Freedman J, Sweeney G, Verma S. Adiponectin deficiency promotes endothelial activation and profoundly exacerbates sepsis-related mortality. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008;295:E658–64.
Tschop J, Nogueiras R, Haas-Lockie S, Kasten KR, Castaneda TR, Huber N, Guanciale K, Perez-Tilve D, Habegger K, Ottaway N, Woods SC, Oldfield B, Clarke I, Chua Jr S, Farooqi IS, O’Rahilly S, Caldwell CC, Tschop MH. CNS leptin action modulates immune response and survival in sepsis. J Neurosci. 2010;30:6036–47.
Tzanela M, Orfanos SE, Tsirantonaki M, Kotanidou A, Sotiropoulou C, Christophoraki M, Vassiliadi D, Thalassinos NC, Roussos C. Leptin alterations in the course of sepsis in humans. In Vivo. 2006;20:565–70.
Van den Berghe G, Wouters P, Carlsson L, Baxter RC, Bouillon R, Bowers CY. Leptin levels in protracted critical illness: effects of growth hormone-secretagogues and thyrotropin-releasing hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998;83:3062–70.
Vassiliadi DA, Tzanela M, Kotanidou A, Orfanos SE, Nikitas N, Armaganidis A, Koutsilieris M, Roussos C, Tsagarakis S, Dimopoulou I. Serial changes in adiponectin and resistin in critically ill patients with sepsis: associations with sepsis phase, severity, and circulating cytokine levels. J Crit Care. 2012;27:400–9.
Venkatesh B, Hickman I, Nisbet J, Cohen J, Prins J. Changes in serum adiponectin concentrations in critical illness: a preliminary investigation. Crit Care. 2009;13:R105.
Walkey AJ, Rice TW, Konter J, Ouchi N, Shibata R, Walsh K, deBoisblanc BP, Summer R. Plasma adiponectin and mortality in critically ill subjects with acute respiratory failure. Crit Care Med. 2010;38:2329–34.
Wang Y, Lam KS, Yau MH, Xu A. Post-translational modifications of adiponectin: mechanisms and functional implications. Biochem J. 2008;409:623–33.
Weisberg SP, Hunter D, Huber R, Lemieux J, Slaymaker S, Vaddi K, Charo I, Leibel RL, Ferrante Jr AW. CCR2 modulates inflammatory and metabolic effects of high-fat feeding. J Clin Invest. 2006;116:115–24.
Wu J, Bostrom P, Sparks LM, Ye L, Choi JH, Giang AH, Khandekar M, Virtanen KA, Nuutila P, Schaart G, Huang K, Tu H, van Marken Lichtenbelt WD, Hoeks J, Enerback S, Schrauwen P, Spiegelman BM. Beige adipocytes are a distinct type of thermogenic fat cell in mouse and human. Cell. 2012;150:366–76.
Yang Q, Graham TE, Mody N, Preitner F, Peroni OD, Zabolotny JM, Kotani K, Quadro L, Kahn BB. Serum retinol binding protein 4 contributes to insulin resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2005;436:356–62.
Yousef AA, Amr YM, Suliman GA. The diagnostic value of serum leptin monitoring and its correlation with tumor necrosis factor-alpha in critically ill patients: a prospective observational study. Crit Care. 2010;14:R33.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this entry
Cite this entry
Marques, M., Langouche, L. (2014). Adipose Tissue and Endocrine Function in Critical Care. In: Rajendram, R., Preedy, V., Patel, V. (eds) Diet and Nutrition in Critical Care. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-8503-2_28-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-8503-2_28-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Online ISBN: 978-1-4614-8503-2
eBook Packages: Springer Reference MedicineReference Module Medicine