Abstract
Plummer-Vinson syndrome consists of the triad of dysphagia, esophagitis, and iron deficiency anemia. The disease is more common in women than in men and often occurs in the menopausal period after age 50. The gastrointestinal symptoms associated with this disease are:
Intermittent dysphagia to solids that progresses over years
Occasionally weight loss
The classic clinical signs and findings include:
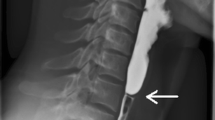
Triad of dysphagia, iron deficiency anemia, upper esophageal webs
Signs and symptoms of iron deficiency often predominate
Esophageal webs are smooth, thin, and gray with a central lumen. Usually extend from the anterior wall laterally and are found in the proximal part of the esophagus
Access provided by Autonomous University of Puebla. Download chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.
Plummer-Vinson syndrome consists of the triad of dysphagia, esophagitis, and iron deficiency anemia. The disease is more common in women than in men and often occurs in the menopausal period after age 50. The gastrointestinal symptoms [1] associated with this disease are:
-
Intermittent dysphagia to solids that progresses over years
-
Occasionally weight loss
The classic clinical signs and findings include [1]:
-
Triad of dysphagia, iron deficiency anemia, upper esophageal webs (see Fig. 3.1)
-
Signs and symptoms of iron deficiency often predominate
-
Esophageal webs are smooth, thin, and gray with a central lumen. Usually extend from the anterior wall laterally and are found in the proximal part of the esophagus
-
More common in Caucasians
-
Incidence decreases with improved nutrition
-
Typically presents in women in fourth to seventh decades of life
The pathogenesis of Plummer-Vinson syndrome is unclear [1]:
-
Iron deficiency is important, but it is neither necessary nor sufficient to cause the syndrome
The pathology of mucosal biopsies will show [1]:
-
One or more thin horizontal membranes consisting of squamous epithelium and submucosa
The diagnosis is made by finding [1]:
-
One or more esophageal webs in a patient with postcricoid dysphagia and iron deficiency anemia
-
Esophageal webs can be visualized by barium swallow or upper endoscopy
-
Endoscopy needs to begin under direct visualization in order not to push through and rupture the webs
The differential diagnosis of Plummer-Vinson syndrome should include [1, 2]:
-
Malignant tumors
-
Esophageal strictures
-
Diverticula
-
Motility disorders
-
Scleroderma
-
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
-
Diabetes mellitus
-
Neuromuscular disorders
-
Skeletal muscle disorders
The treatment involves [1]:
-
Iron replacement to treat iron deficiency
-
Determination of the cause of iron deficiency
References
Novacek G. Plummer-Vinson syndrome. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2006;1:36.
Baron R, Darber RPR, Hanske E, et al. Text atlas of nail disorders: techniques, investigation, and diagnosis. 3rd ed. London: Martin Dunitz/Taylor & Francis; 2003. p. 23–7. Chapter 2, section 2, Koilonychia. Available at www.rusmedserv.com/mycology/html/Atlas_of_Nail_Disorders.pdf. Accessed June 5, 2012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Zakko, L. (2013). Plummer-Vinson Syndrome: Gastrointestinal Features. In: Wu, G., Selsky, N., Grant-Kels, J. (eds) Atlas of Dermatological Manifestations of Gastrointestinal Disease. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-6191-3_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-6191-3_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4614-6190-6
Online ISBN: 978-1-4614-6191-3
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)