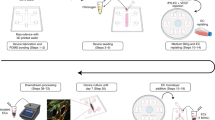
Abstract
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) plays an essential role in maintaining the homeostasis of the brain microenvironment by controlling the influx and efflux of biological substances that are necessary to sustain the neuronal metabolic activity and functions. This barrier is established at the blood-brain interface of the brain microcapillaries by different cells. These include microvascular endothelial cells, astrocytes, and pericytes besides other components such as microglia, basal membrane, and neuronal cells forming together what is commonly referred to as the neurovascular unit; different in vivo and in vitro platforms are available to study the BBB where each system provides specific benefits and drawbacks. Recently, organ-on-a-chip platforms combine the elegance of microengineering technology with the complexity of biological systems to create near-ideal experimental models for various diseases and organs. These microfluidic devices with micron-sized channels allow the cells to be grown in a more biologically relevant environment, enabling cell to cell communications with continuous bathing in biological fluids in a tissue-like fashion. They also closely represent tissue and organ functionality by recapitulating mechanical forces as well as vascular perfusion. Here, we describe the use of humanized BBB model created with microfluidic organ-on-a-chip technology where human brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs) are cocultured with primary human pericytes and astrocytes. We thoroughly described the method to assess BBB integrity using a microfluidic chip and various sizes of labeled dextran as permeability markers. In addition, we provide a detailed protocol on how to microscopically investigate the tight junction proteins expression between hBMECs.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liebner S, Czupalla CJ, Wolburg H (2011) Current concepts of blood-brain barrier development. Int J Dev Biol 55(4–5):467–476
Abbott NJ, Patabendige AA, Dolman DE, Yusof SR, Begley DJ (2010) Structure and function of the blood-brain barrier. Neurobiol Dis 37(1):13–25
Cucullo L, Hossain M, Puvenna V, Marchi N, Janigro D (2011) The role of shear stress in Blood-Brain Barrier endothelial physiology. BMC Neurosci 12:40
Ballabh P, Braun A, Nedergaard M (2004) The blood-brain barrier: an overview: structure, regulation, and clinical implications. Neurobiol Dis 16(1):1–13
Zlokovic BV (2011) Neurovascular pathways to neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and other disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 12(12):723–738
Cecchelli R, Berezowski V, Lundquist S, Culot M, Renftel M, Dehouck MP et al (2007) Modelling of the blood-brain barrier in drug discovery and development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6(8):650–661
Ramsauer M, Krause D, Dermietzel R (2002) Angiogenesis of the blood-brain barrier in vitro and the function of cerebral pericytes. FASEB J 16(10):1274–1276
Stewart PA, Wiley MJ (1981) Developing nervous tissue induces formation of blood-brain barrier characteristics in invading endothelial cells: a study using quail—chick transplantation chimeras. Dev Biol 84(1):183–192
Janzer RC, Raff MC (1987) Astrocytes induce blood-brain barrier properties in endothelial cells. Nature 325(6101):253–257
Rubin LL, Barbu K, Bard F, Cannon C, Hall DE, Horner H et al (1991) Differentiation of brain endothelial cells in cell culture. Ann N Y Acad Sci 633:420–425
Neuhaus J, Risau W, Wolburg H (1991) Induction of blood-brain barrier characteristics in bovine brain endothelial cells by rat astroglial cells in transfilter coculture. Ann N Y Acad Sci 633:578–580
Wolff A, Antfolk M, Brodin B, Tenje M (2015) In vitro blood-brain barrier models-an overview of established models and new microfluidic approaches. J Pharm Sci 104(9):2727–2746
van der Helm MW, van der Meer AD, Eijkel JC, van den Berg A, Segerink LI (2016) Microfluidic organ-on-chip technology for blood-brain barrier research. Tissue Barriers 4(1):e1142493
Faria A, Pestana D, Teixeira D, Azevedo J, De Freitas V, Mateus N et al (2010) Flavonoid transport across RBE4 cells: a blood-brain barrier model. Cell Mol Biol Lett 15(2):234–241
Hatherell K, Couraud PO, Romero IA, Weksler B, Pilkington GJ (2011) Development of a three-dimensional, all-human in vitro model of the blood-brain barrier using mono-, co-, and tri-cultivation Transwell models. J Neurosci Methods 199(2):223–229
Abbott NJ, Dolman DE, Drndarski S, Fredriksson SM (2012) An improved in vitro blood-brain barrier model: rat brain endothelial cells co-cultured with astrocytes. Methods Mol Biol 814:415–430
Paolinelli R, Corada M, Ferrarini L, Devraj K, Artus C, Czupalla CJ et al (2013) Wnt activation of immortalized brain endothelial cells as a tool for generating a standardized model of the blood brain barrier in vitro. PLoS One 8(8):e70233
Lippmann ES, Al-Ahmad A, Azarin SM, Palecek SP, Shusta EV (2014) A retinoic acid-enhanced, multicellular human blood-brain barrier model derived from stem cell sources. Sci Rep 4:4160
Helms HC, Abbott NJ, Burek M, Cecchelli R, Couraud PO, Deli MA et al (2016) In vitro models of the blood-brain barrier: an overview of commonly used brain endothelial cell culture models and guidelines for their use. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 36(5):862–890
Ott MJ, Olson JL, Ballermann BJ (1995) Chronic in vitro flow promotes ultrastructural differentiation of endothelial cells. Endothelium 3(1):21–30
Akimoto S, Mitsumata M, Sasaguri T, Yoshida Y (2000) Laminar shear stress inhibits vascular endothelial cell proliferation by inducing cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21(Sdi1/Cip1/Waf1). Circ Res 86(2):185–190
Ngai AC, Winn HR (1995) Modulation of cerebral arteriolar diameter by intraluminal flow and pressure. Circ Res 77(4):832–840
Bhatia SN, Ingber DE (2014) Microfluidic organs-on-chips. Nat Biotechnol 32(8):760–772
Booth R, Kim H (2014) Permeability analysis of neuroactive drugs through a dynamic microfluidic in vitro blood-brain barrier model. Ann Biomed Eng 42(12):2379–2391
Cho H, Seo JH, Wong KH, Terasaki Y, Park J, Bong K et al (2015) Three-dimensional blood-brain barrier model for in vitro studies of neurovascular pathology. Sci Rep 5:15222
Maoz BM, Herland A, FitzGerald EA, Grevesse T, Vidoudez C, Pacheco AR et al (2018) A linked organ-on-chip model of the human neurovascular unit reveals the metabolic coupling of endothelial and neuronal cells. Nat Biotechnol 36(9):865–874
Prabhakarpandian B, Shen MC, Nichols JB, Garson CJ, Mills IR, Matar MM et al (2015) Synthetic tumor networks for screening drug delivery systems. J Control Release 201:49–55
Park TE, Mustafaoglu N, Herland A, Hasselkus R, Mannix R, FitzGerald EA et al (2019) Hypoxia-enhanced blood-brain barrier chip recapitulates human barrier function and shuttling of drugs and antibodies. Nat Commun 10(1):2621
Saunders NR, Dziegielewska KM, Mollgard K, Habgood MD (2015) Markers for blood-brain barrier integrity: how appropriate is Evans blue in the twenty-first century and what are the alternatives? Front Neurosci 9:385
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Kadry, H., Cucullo, L. (2024). Evaluation of Barrier Integrity Using a Two-Layered Microfluidic Device Mimicking the Blood-Brain Barrier. In: Tharakan, B. (eds) Vascular Hyperpermeability. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2711. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3429-5_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3429-5_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-3428-8
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-3429-5
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols