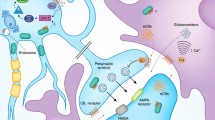
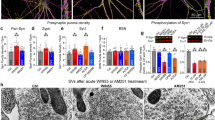
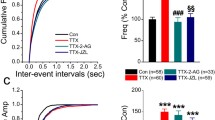
Abstract
Electrophysiological technique is an efficient tool for investigating the synaptic regulatory effects mediated by the endocannabinoid system. Stimulation of presynaptic type 1 cannabinoid receptor (CB1) is the principal mode by which endocannabinoids suppress transmitter release in the central nervous system, but a non-retrograde manner of functioning and other receptors have also been described. Endocannabinoids are key modulators of both short- and long-term plasticity. Here, we discuss ex vivo electrophysiological approaches to examine synaptic signaling induced by cannabinoid and endocannabinoid molecules in the mammalian brain.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Herkenham M, Lynn AB, Little MD et al (1990) Cannabinoid receptor localization in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 87:1932–1936. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.87.5.1932
Katona I, Freund TF (2012) Multiple functions of endocannabinoid signaling in the brain. Annu Rev Neurosci 35:529–558. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-neuro-062111-150420
Kano M, Ohno-Shosaku T, Hashimotodani Y et al (2009) Endocannabinoid-mediated control of synaptic transmission. Physiol Rev 89:309–380. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00019.2008
Chevaleyre V, Heifets BD, Kaeser PS et al (2007) Endocannabinoid-mediated long-term plasticity requires cAMP/PKA signaling and RIM1alpha. Neuron 54:801–812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2007.05.020
Heifets BD, Castillo PE (2009) Endocannabinoid signaling and long-term synaptic plasticity. Annu Rev Physiol 71:283–306. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.physiol.010908.163149
Lu H-C, Mackie K (2016) An introduction to the endogenous cannabinoid system. Biol Psychiatry 79:516–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.07.028
Monday HR, Younts TJ, Castillo PE (2018) Long-term plasticity of neurotransmitter release: emerging mechanisms and contributions to brain function and disease. Annu Rev Neurosci 41:299–322. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-neuro-080317-062155
Gerdeman G, Lovinger DM (2001) CB1 cannabinoid receptor inhibits synaptic release of glutamate in rat dorsolateral striatum. J Neurophysiol 85:468–471. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.2001.85.1.468
Morales P, Hurst DP, Reggio PH (2017) Molecular targets of the Phytocannabinoids: a complex picture. Prog Chem Org Nat Prod 103:103–131. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-45541-9_4
Morales P, Jagerovic N (2016) Advances towards the discovery of GPR55 ligands. Curr Med Chem 23:2087–2100. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867323666160425113836
Pertwee RG, Howlett AC, Abood ME et al (2010) International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXIX. Cannabinoid receptors and their ligands: beyond CB1 and CB2. Pharmacol Rev 62:588–631. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.110.003004
Muller C, Morales P, Reggio PH (2019) Cannabinoid ligands targeting TRP channels. Front Mol Neurosci 11:1–15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2018.00487
Gerdeman GL, Lovinger DM (2003) Emerging roles for endocannabinoids in long-term synaptic plasticity. Br J Pharmacol 140:781–789. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0705466
Castillo PE, Younts TJ, Chávez AE, Hashimotodani Y (2012) Endocannabinoid signaling and synaptic function. Neuron 76:70–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2012.09.020
Gerdeman GL, Ronesi J, Lovinger DM (2002) Postsynaptic endocannabinoid release is critical to long-term depression in the striatum. Nat Neurosci 5:446–451. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn832
Safo PK, Regehr WG (2005) Endocannabinoids control the induction of cerebellar LTD. Neuron 48:647–659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2005.09.020
Sjöström PJ, Turrigiano GG, Nelson SB (2003) Neocortical LTD via coincident activation of presynaptic NMDA and cannabinoid receptors. Neuron 39:641–654. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00476-8
Chevaleyre V, Castillo PE (2003) Heterosynaptic LTD of hippocampal GABAergic synapses: a novel role of endocannabinoids in regulating excitability. Neuron 38:461–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00235-6
Marsicano G, Wotjak CT, Azad SC et al (2002) The endogenous cannabinoid system controls extinction of aversive memories. Nature 418:530–534. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature00839
An D, Peigneur S, Hendrickx LA, Tytgat J (2020) Targeting cannabinoid receptors: current status and prospects of natural products. Int J Mol Sci 21:5064. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21145064
Shen M, Piser TM, Seybold VS, Thayer SA (1996) Cannabinoid receptor agonists inhibit glutamatergic synaptic transmission in rat hippocampal cultures. J Neurosci 16:4322. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-14-04322.1996
Schlicker E, Kathmann M (2001) Modulation of transmitter release via presynaptic cannabinoid receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22:565–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-6147(00)01805-8
Wilson RI, Nicoll RA (2001) Endogenous cannabinoids mediate retrograde signalling at hippocampal synapses. Nature 410:588–592. https://doi.org/10.1038/35069076
Daniel H, Rancillac A, Crepel F (2004) Mechanisms underlying cannabinoid inhibition of presynaptic Ca2+ influx at parallel fibre synapses of the rat cerebellum. J Physiol 557:159–174. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2004.063263
Robbe D, Kopf M, Remaury A et al (2002) Endogenous cannabinoids mediate long-term synaptic depression in the nucleus accumbens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:8384–8388. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.122149199
Auclair N, Otani S, Soubrie P, Crepel F (2000) Cannabinoids modulate synaptic strength and plasticity at glutamatergic synapses of rat prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol 83:3287–3293. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.2000.83.6.3287
Basavarajappa BS, Subbanna S (2014) CB1 receptor-mediated signaling underlies the hippocampal synaptic, learning, and memory deficits following treatment with JWH-081, a new component of spice/K2 preparations. Hippocampus 24:178–188. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.22213
Hoffman AF, Lycas MD, Kaczmarzyk JR et al (2017) Disruption of hippocampal synaptic transmission and long-term potentiation by psychoactive synthetic cannabinoid ‘Spice’ compounds: comparison with Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Addict Biol 22:390–399. https://doi.org/10.1111/adb.12334
Monday HR, Bourdenx M, Jordan BA, Castillo PE (2020) CB(1)-receptor-mediated inhibitory LTD triggers presynaptic remodeling via protein synthesis and ubiquitination. eLife 9:10.7554/eLife.54812
Báldi R, Ghosh D, Grueter BA, Patel S (2016) Electrophysiological measurement of cannabinoid-mediated synaptic modulation in acute mouse brain slices. Curr Protoc Neurosci 75:6.29.1–6.29.19. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpns.8
Ohno-Shosaku T, Tanimura A, Hashimotodani Y, Kano M (2012) Endocannabinoids and retrograde modulation of synaptic transmission. Neuroscientist 18:119–132. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858410397377
Maejima T, Hashimoto K, Yoshida T et al (2001) Presynaptic inhibition caused by retrograde signal from metabotropic glutamate to cannabinoid receptors. Neuron 31:463–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0896-6273(01)00375-0
Rouach N, Nicoll RA (2003) Endocannabinoids contribute to short-term but not long-term mGluR-induced depression in the hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci 18:1017–1020. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1460-9568.2003.02823.x
Kushmerick C, Price GD, Taschenberger H et al (2004) Retroinhibition of presynaptic Ca2+ currents by endocannabinoids released via postsynaptic mglur activation at a calyx synapse. J Neurosci 24:5955. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0768-04.2004
Varma N, Carlson GC, Ledent C, Alger BE (2001) Metabotropic glutamate receptors drive the endocannabinoid system in hippocampus. J Neurosci 21:RC188. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-24-j0003.2001
Hashimotodani Y, Ohno-shosaku T, Watanabe M, Kano M (2007) Roles of phospholipase Cβ and NMDA receptor in activity-dependent endocannabinoid release. J Physiol 584:373–380. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2007.137497
Fukudome Y, Ohno-Shosaku T, Matsui M et al (2004) Two distinct classes of muscarinic action on hippocampal inhibitory synapses: M2-mediated direct suppression and M1/M3-mediated indirect suppression through endocannabinoid signalling. Eur J Neurosci 19:2682–2692. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0953-816x.2004.03384.x
Musella A, de Chiara V, Rossi S et al (2010) Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 channels control acetylcholine/2-arachidonoylglicerol coupling in the striatum. Neuroscience 167:864–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.02.058
Földy C, Malenka RC, Südhof TC (2013) Autism-associated neuroligin-3 mutations commonly disrupt tonic endocannabinoid signaling. Neuron 78:498–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2013.02.036
Kim J, Alger BE (2010) Reduction in endocannabinoid tone is a homeostatic mechanism for specific inhibitory synapses. Nat Neurosci 13:592–600. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2517
Lee S-H, Ledri M, Tóth B et al (2015) Multiple forms of endocannabinoid and Endovanilloid signaling regulate the tonic control of GABA release. J Neurosci 35:10039–10057. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4112-14.2015
Ramikie TS, Nyilas R, Bluett RJ et al (2014) Multiple mechanistically distinct modes of endocannabinoid mobilization at central amygdala glutamatergic synapses. Neuron 81:1111–1125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2014.01.012
Hashimotodani Y, Ohno-Shosaku T, Kano M (2007) Presynaptic monoacylglycerol lipase activity determines basal endocannabinoid tone and terminates retrograde endocannabinoid signaling in the hippocampus. J Neurosci 27:1211–1219. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4159-06.2007
Pan B, Wang W, Zhong P et al (2011) Alterations of endocannabinoid signaling, synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory in monoacylglycerol lipase knock-out mice. J Neurosci 31:13420–13430. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2075-11.2011
Schlosburg JE, Blankman JL, Long JZ et al (2010) Chronic monoacylglycerol lipase blockade causes functional antagonism of the endocannabinoid system. Nat Neurosci 13:1113–1119. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2616
Szabo B, Urbanski MJ, Bisogno T et al (2006) Depolarization-induced retrograde synaptic inhibition in the mouse cerebellar cortex is mediated by 2-arachidonoylglycerol. J Physiol 577:263–280. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2006.119362
Gulyas AI, Cravatt BF, Bracey MH et al (2004) Segregation of two endocannabinoid-hydrolyzing enzymes into pre- and postsynaptic compartments in the rat hippocampus, cerebellum and amygdala. Eur J Neurosci 20:441–458. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03428.x
Kim J, Alger BE (2004) Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 potentiates retrograde endocannabinoid effects in hippocampus. Nat Neurosci 7:697–698. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1262
Gubellini P, Picconi B, Bari M et al (2002) Experimental parkinsonism alters endocannabinoid degradation: implications for striatal glutamatergic transmission. J Neurosci 22:6900–6907. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-16-06900.2002
Maccarrone M, Rossi S, Bari M et al (2008) Anandamide inhibits metabolism and physiological actions of 2-arachidonoylglycerol in the striatum. Nat Neurosci 11:152–159. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn2042
Cavanaugh DJ, Chesler AT, Bráz JM et al (2011) Restriction of transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 to the peptidergic subset of primary afferent neurons follows its developmental downregulation in nonpeptidergic neurons. J Neurosci 31:10119–10127. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1299-11.2011
Cristino L, de Petrocellis L, Pryce G et al (2006) Immunohistochemical localization of cannabinoid type 1 and vanilloid transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 receptors in the mouse brain. Neuroscience 139:1405–1415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.02.074
Roberts JC, Davis JB, Benham CD (2004) [3H]Resiniferatoxin autoradiography in the CNS of wild-type and TRPV1 null mice defines TRPV1 (VR-1) protein distribution. Brain Res 995:176–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2003.10.001
Tóth A, Boczán J, Kedei N et al (2005) Expression and distribution of vanilloid receptor 1 (TRPV1) in the adult rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 135:162–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molbrainres.2004.12.003
Mezey E, Tóth ZE, Cortright DN et al (2000) Distribution of mRNA for vanilloid receptor subtype 1 (VR1), and VR1-like immunoreactivity, in the central nervous system of the rat and human. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:3655–3660. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.060496197
Puente N, Cui Y, Lassalle O et al (2011) Polymodal activation of the endocannabinoid system in the extended amygdala. Nat Neurosci 14:1542–1547. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2974
Smart D, Gunthorpe MJ, Jerman JC et al (2000) The endogenous lipid anandamide is a full agonist at the human vanilloid receptor (hVR1). Br J Pharmacol 129:227–230. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0703050
Zygmunt PM, Petersson J, Andersson DA et al (1999) Vanilloid receptors on sensory nerves mediate the vasodilator action of anandamide. Nature 400:452–457. https://doi.org/10.1038/22761
Di Marzo V, De Petrocellis L, Fezza F et al (2002) Anandamide receptors. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 66:377–391. https://doi.org/10.1054/plef.2001.0349
Caterina MJ, Julius D (2001) The vanilloid receptor: a molecular gateway to the pain pathway. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:487–517. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.24.1.487
Musella A, de Chiara V, Rossi S et al (2009) TRPV1 channels facilitate glutamate transmission in the striatum. Mol Cell Neurosci 40:89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2008.09.001
Grueter BA, Brasnjo G, Malenka RC (2010) Postsynaptic TRPV1 triggers cell type-specific long-term depression in the nucleus accumbens. Nat Neurosci 13:1519–1525. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2685
Chávez AE, Chiu CQ, Castillo PE (2010) TRPV1 activation by endogenous anandamide triggers postsynaptic long-term depression in dentate gyrus. Nat Neurosci 13:1511–1518. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2684
Jhaveri MD, Richardson D, Kendall DA et al (2006) Analgesic effects of fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibition in a rat model of neuropathic pain. J Neurosci 26:13318–13327. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3326-06.2006
Maione S, Bisogno T, de Novellis V et al (2006) Elevation of endocannabinoid levels in the ventrolateral periaqueductal grey through inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase affects descending nociceptive pathways via both cannabinoid receptor type 1 and transient receptor potential vanilloid type-1 r. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 316:969–982. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.105.093286
Makara JK, Mor M, Fegley D et al (2005) Selective inhibition of 2-AG hydrolysis enhances endocannabinoid signaling in hippocampus. Nat Neurosci 8:1139–1141. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1521
Melis M, Pillolla G, Bisogno T et al (2006) Protective activation of the endocannabinoid system during ischemia in dopamine neurons. Neurobiol Dis 24:15–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2006.04.010
Lerner TN, Kreitzer AC (2012) RGS4 is required for dopaminergic control of striatal LTD and susceptibility to parkinsonian motor deficits. Neuron 73:347–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2011.11.015
Verme J, Fu J, Astarita G et al (2005) The nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor- mediates the anti-inflammatory actions of Palmitoylethanolamide. Mol Pharmacol 67:15–19. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.104.006353
Petrosino S, Iuvone T, di Marzo V (2010) N-palmitoyl-ethanolamine: biochemistry and new therapeutic opportunities. Biochimie 92:724–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2010.01.006
Marichal-Cancino BA, Fajardo-Valdez A, Ruiz-Contreras AE et al (2017) Advances in the physiology of GPR55 in the central nervous system. Curr Neuropharmacol 15:771–778. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X14666160729155441
di Marzo V, Bisogno T, de petrocellis L (2001) Anandamide: Some like it hot. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22:346–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-6147(00)01712-0
Ho W-SV, Barrett DA, Randall MD (2008) “Entourage” effects of N-palmitoylethanolamide and N-oleoylethanolamide on vasorelaxation to anandamide occur through TRPV1 receptors. Br J Pharmacol 155:837–846. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjp.2008.324
Musella A, Fresegna D, Rizzo FR et al (2017) A novel crosstalk within the endocannabinoid system controls GABA transmission in the striatum. Sci Rep 7:7363. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-07519-8
Navarrete M, Araque A (2008) Endocannabinoids mediate neuron-astrocyte communication. Neuron 57:883–893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2008.01.029
Min R, Nevian T (2012) Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses. Nat Neurosci 15:746–753. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3075
Smith NA, Bekar LK, Nedergaard M (2020) Astrocytic endocannabinoids mediate hippocampal transient heterosynaptic depression. Neurochem Res 45:100–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02834-0
Andersson MS, Hanse E (2011) Astrocyte-mediated short-term synaptic depression in the rat hippocampal CA1 area: two modes of decreasing release probability. BMC Neurosci 12:87. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2202-12-87
Marsicano G, Lafenêtre P (2009) Roles of the endocannabinoid system in learning and memory. Curr Top Behav Neurosci 1:201–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-88955-7_8
Gallego-Landin I, García-Baos A, Castro-Zavala A, Valverde O (2021) Reviewing the role of the endocannabinoid system in the pathophysiology of depression. Front Pharmacol 12:1–21. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.762738
Koch M (2017) Cannabinoid receptor signaling in central regulation of feeding behavior: a mini-review. Front Neurosci 11:293. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2017.00293
Buisseret B, Alhouayek M, Guillemot-Legris O, Muccioli GG (2019) Endocannabinoid and prostanoid crosstalk in pain. Trends Mol Med 25:882–896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2019.04.009
Cristino L, Bisogno T, Di Marzo V (2020) Cannabinoids and the expanded endocannabinoid system in neurological disorders. Nat Rev Neurol 16:9–29. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-019-0284-z
Navarrete F, García-Gutiérrez MS, Jurado-Barba R et al (2020) Endocannabinoid system components as potential biomarkers in psychiatry. Front Psych 11:1–30. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00315
Hill MN, Eiland L, Lee TTY et al (2019) Early life stress alters the developmental trajectory of corticolimbic endocannabinoid signaling in male rats. Neuropharmacology 146:154–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.11.036
Chiurchiù V, van der Stelt M, Centonze D, Maccarrone M (2018) The endocannabinoid system and its therapeutic exploitation in multiple sclerosis: clues for other neuroinflammatory diseases. Prog Neurobiol 160:82–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2017.10.007
Busquets-Garcia A, Gomis-González M, Guegan T et al (2013) Targeting the endocannabinoid system in the treatment of fragile X syndrome. Nat Med 19:603–607. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3127
Patricio F, Morales-Andrade AA, Patricio-Martínez A, Limón ID (2020) Cannabidiol as a therapeutic target: evidence of its neuroprotective and neuromodulatory function in Parkinson’s disease. Front Pharmacol 11:595635. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.595635
Acknowledgments
The authors were supported by Italian Ministry of Health (GR-2016-02361163 to AM; RF-2018-12366144 to DC), Ricerca corrente of IRCCS San Raffaele Roma, Ricerca corrente of IRCCS Neuromed, Italian Ministry of University and Research (PRIN 2017- cod. 2017K55HLC to DC), and FISM-Fondazione Italiana Sclerosi Multipla (cod. 2019/S/1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Musella, A., Centonze, D. (2023). Electrophysiology of Endocannabinoid Signaling. In: Maccarrone, M. (eds) Endocannabinoid Signaling. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2576. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2728-0_38
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2728-0_38
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-2727-3
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-2728-0
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols