Abstract
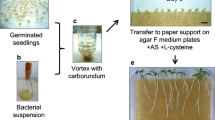
Agrobacterium rhizogenes has the ability to transform plant cells by transferring the T-DNA from the Ri plasmid to the plant cell genome. These infected plant cells divide and organize the formation of adventitious roots, called hairy roots. When the A. rhizogenes is additionally transformed with a binary vector, the cells infected can indeed be transformed with this second T-DNA producing transgenic hairy roots. In this chapter, we present the protocol to produce transgenic hairy roots from in vitro potato (Solanum tuberosum) plants injected with transformed A. rhizogenes, generating plants with a wild-type shoot and a transgenic root system. Specifically, we detail the procedure to obtain in vitro-cultured hairy roots with a downregulated gene of interest, by using a Gateway-based binary vector able to produce a RNA hairpin triggering the RNA interference mechanism (hpRNAi). We also present the protocol to analyze the downregulation of the target gene in hairy roots by means of reverse-transcription reaction followed by real-time PCR (qPCR).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang W, Zhang Z, Fan G et al (2017) Development and application of a universal and simplified multiplex RT-PCR assay to detect five potato viruses. J Gen Plant Pathol 83:33–45
Almasia NI, Molinari MP, Maroniche GA et al (2017) Successful production of the potato antimicrobial peptide Snakin-1 in baculovirus-infected insect cells and development of specific antibodies. BMC Biotechnol 17:1–11
White FF, Taylor BH, Huffman GA et al (1985) Molecular and genetic analysis of the transferred DNA regions of the root-inducing plasmid of Agrobacterium rhizogenes. J Bacteriol 164:33–44
Tarkowski P, Vereecke D (2014) Threats and opportunities of plant pathogenic bacteria. Biotechnol Adv 32:215–229
Ding Y, Kalo P, Yendrek C et al (2008) Abscisic acid coordinates nod factor and cytokinin signaling during the regulation of nodulation in Medicago truncatula. Plant Cell 20:2681–2695
Horn P, Santala J, Nielsen SL et al (2014) Composite potato plants with transgenic roots on non-transgenic shoots: a model system for studying gene silencing in roots. Plant Cell Rep 33:1977–1992
Plasencia A, Soler M, Dupas A et al (2015) Eucalyptus hairy roots, a fast, efficient and versatile tool to explore function and expression of genes involved in wood formation. Plant Biotechnol J 14(6):1381–1393
Ron M, Kajala K, Pauluzzi G et al (2014) Hairy root transformation using Agrobacterium rhizogenes as a tool for exploring cell type-specific gene expression and function using tomato as a model. Plant Physiol 166:455–469
Fernández-Piñán S, López J, Armendariz I et al (2019) Agrobacterium tumefaciens and Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated transformation of potato and the promoter activity of a suberin gene by GUS staining. J Vis Exp (145). https://doi.org/10.3791/59119
Serra O, Soler M, Hohn C et al (2009) CYP86A33-targeted gene silencing in potato tuber alters suberin composition, distorts suberin lamellae, and impairs the periderm’s water barrier function. Plant Physiol 149:1050–1060
Koressaar T, Remm M (2007) Enhancements and modifications of primer design program Primer3. Bioinformatics 23:1289–1291
Nicot N, Hausman J-F, Hoffmann L, Evers D (2005) Housekeeping gene selection for real-time RT-PCR normalization in potato during biotic and abiotic stress. J Exp Bot 56:2907–2914
Nolan T, Hands RE, Bustin SA (2006) Quantification of mRNA using real-time RT-PCR. Nat Protoc 1:1559–1582
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad and Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación and European Regional Development Fund (AGL2015-67495-C2-1-R and PID2019-110330GB-C21), and the University of Girona (MPCUdG2016/078 and PhD contracts to SF and CS). The authors are grateful to Dr. Inge Broer (Institute for Land Use, University of Rostock, Germany) for providing the A. rhizogenes strain, and Dr. Marçal Soler and Dr. Anna Plasencia for the help and support received in initial stages of the A. rhizogenes transformation experiments (Toulouse III Paul Sabatier University—CNRS, Plant Research Laboratory (LRSV), France). The authors thank Ferran Fontdecaba and Jennifer López who assisted with some of the experiments while they were doing their final degree projects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Fernández-Piñán, S., Sànchez-Guirado, C., Figueras, M., Serra, O. (2021). Gene Downregulation in Potato Roots Using Agrobacterium rhizogenes-Mediated Transformation. In: Dobnik, D., Gruden, K., Ramšak, Ž., Coll, A. (eds) Solanum tuberosum. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2354. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1609-3_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1609-3_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1608-6
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1609-3
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols