Abstract
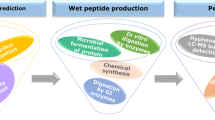
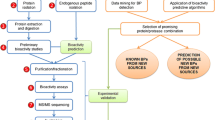
A workflow for the characterization of food-derived bioactive peptides is described in this chapter. The workflow integrates two consecutive steps: a discovery phase and a protein-based bioinformatic phase. In the first step (discovery phase), a shotgun bottom-up proteomics approach is used to create a reference data set for a selected food proteome. Afterward, in a second step (bioinformatic phase), the reference proteome is subjected to several in silico protein-based bioinformatic analyses to predict and characterize potential bioactive peptides after an in silico human gastrointestinal digestion. Using this workflow, bioactive collagen peptides, antihypertensive, antimicrobial, and antitumor peptides were predicted as potential valuable bioactive peptides from seafood and marine by-products. It is concluded that the combination of the global shotgun proteomic analysis and the analysis by protein-based bioinformatics can provide a rapid strategy for the characterization of new potential food-derived bioactive peptides.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vermeirssen V, Van Camp J, Verstraete W (2004) Bioavailability of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides. Br J Nutr 92:357–366
Sánchez A, Vazquez A (2017) Bioactive peptides: a review. Food Qual Saf 1:29–46
Yamamoto N (1997) Antihypertensive peptides derived from food proteins. Biopolymers 43:129–134
Guang C, Phillips RD (2009) Plant food-derived angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides. J Agric Food Chem 57:5113–5120
Suarez-Jimenez GM, Burgos-Hernandez A, Ezquerra-Brauer JM (2012) Bioactive peptides and depsipeptides with anticancer potential: sources from marine animals. Mar Drugs 10:963–986
Ryan JT, Ross RP, Bolton D, Fitzgerald GF, Stanton C (2011) Bioactive peptides from muscle sources: meat and fish. Nutrients 3:765–791
Cunsolo V, Saletti R, Muccilli V, Gallina S, Di Francesco A, Foti S (2017) Proteins and bioactive peptides from donkey milk: the molecular basis for its reduced allergenic properties. Food Res Int 99:41–57
Moller NP, Scholz-Ahrens KE, Roos N, Schrezenmeir J (2008) Bioactive peptides and proteins from foods: indication for health effects. Eur J Nutr 47:171–182
Amado IR, Vázquez JA, González P, Esteban-Fernández D, Carrera M, Piñeiro C (2014) Identification of the major ACE-inhibitory peptides produced by enzymatic hydrolysis of a protein concentrate from cuttlefish wastewater. Mar Drugs 12:1390–1405
Mora L, Gallego M, Toldrá F (2018) ACEI-inhibitory peptides naturally generated in meat and meat products and their health relevance. Nutrients 10:1259
Carrera M, Cañas B, Gallardo JM (2013) The sarcoplasmic fish proteome: pathways, metabolic networks and potential bioactive peptides for nutritional inferences. J Proteome 78:211–220
Agyei D, Tsopmo A, Udenigwe CC (2018) Bioinformatics and peptidomics approaches to the discovery and analysis of food-derived bioactive peptides. Anal Bioanal Chem 410:3463–3472
Anekthanakul K, Apiradee Hongsthong A, Jittisak Senachak J, Ruengjitchatchawalya M (2018) SpirPep: an in silico digestion-based platform to assist bioactive peptides discovery from a genome-wide database. BMC Bioinformatics 19:149
Arena S, Renzone G, Scaloni A (2020) A multi-approach peptidomic analysis of hen egg white reveals novel putative bioactive molecules. J Proteome 215:103646
Carrera M, Ezquerra-Brauer JM, Aubourg SP (2020) Characterization of the jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas) skin by-product by shotgun proteomics and protein-based bioinformatics. Mar Drugs 18:31
Gallardo JM, Carrera M, Ortea I (2013) Proteomics in food science. In: Cifuentes A (ed) Foodomics: advanced mass spectrometry in modern food science and nutrition. John Wiley & Sons Inc., Hoboken, NJ, USA, pp 125–165
Carrera M, González-Fernández A, Magadán S, Mateos J, Pedrós L, Medina I, Gallardo JM (2019) Molecular characterization of B-cell epitopes for the major fish allergen, parvalbumin, by shotgun proteomics, protein-based bioinformatics and IgE-reactive approaches. J Proteome 200:123–133
Perkins DN, Pappin DJC, Creasy DM, Cottrell JS (1999) Probability-based protein identification by searching sequence databases using mass spectrometry data. Electrophoresis 20:3551–3567
Eng JK, McCormack AL, Yates JR III (1994) An approach to correlate tandem mass spectral data of peptides with amino acid sequences in a protein database. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 5:976–989
Kall L, Canterbury JD, Weston J, Noble WS, MacCoss MJ (2007) Semi-supervised learning for peptide identification from shotgun proteomics datasets. Nat Methods 4:923–925
Keller A, Nesvizhskii AI, Kolker E, Aebersold R (2002) Empirical statistical model to estimate the accuracy of peptide identifications made by MS/MS and database search. Anal Chem 74:5383–5392
Capriotti AL, Cavaliere C, Foglia P, Piovesana S, Samperi R, Zenezini Chiozzi R, Laganà A (2015) Development of an analytical strategy for the identification of potential bioactive peptides generated by in vitro tryptic digestion of fish muscle proteins. Anal Bioanal Chem 407:845–854
Amorim FG, Coitinho LB, Dias AT, Friques AGF, Monteiro BL, Rezende LCD, Pereira TMC, Campagnaro BP, De Pauw E, Vasquez EC, Quinton L (2019) Identification of new bioactive peptides from kefir milk through proteopeptidomics: bioprospection of antihypertensive molecules. Food Chem 282:109–119
Wang G, Li X, Wang Z (2016) APD3: the antimicrobial peptide database as a tool for research and education. Nucleic Acids Res 4:D1087–D1093
Jimsheena VK, Gowda LR (2010) Arachin derived peptides as selective angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors: structure-activity relationship. Peptides 31:1165–1176
Minkiewicz P, Iwaniak A, Darewicz M (2019) BIOPEP-UWM database of bioactive peptides: current opportunities. Int J Mol Sci 20:5978
Shi L, Zhang Q, Rui W, Lu M, Jing X, Shang T, Tang J (2004) BioPD: a web-based information center for bioactive peptides. Regul Pept 120:1–3
Li Q, Zhang C, Chen H, Xue J, Guo X, Liang M, Chen M (2018) BioPepDB: an integrated data platform for food-derived bioactive peptides. Int J Food Sci Nutr 69:963–968
Thomas S, Karnik S, Barai RS, Jayaraman VK, Idicula-Thomas S (2010) CAMP: a useful resource for research on antimicrobial peptides. Nucleic Acids Res 38:D774–D780
Panyayai T, Ngamphiw C, Tongsima S, Mhuantong W, Limsripraphan W, Choowongkomon K, Sawatdichaikul O (2019) FeptideDB: a web application for new bioactive peptides from protein. Heliyon 5:e02076
Rong M, Zhou B, Zhou R, Liao Q, Zeng Y, Xu S, Liu Z (2019) PPIP: automated software for identification of bioactive endogenous peptides. J Proteome Res 18:721–727
Wang J, Yin T, Xiao X, He D, Xue Z, Jiang X, Wang Y (2018) StraPep: a structure database of bioactive peptides. Database (Oxford) 2018:bay038
Aguilera-Mendoza L, Marrero-Ponce Y, Beltran JA, Tellez Ibarra R, Guillen-Ramirez HA, Brizuela CA (2019) Graph-based data integration from bioactive peptide databases of pharmaceutical interest: towards an organized collection enabling visual network analysis. Bioinformatics 35:4739–4747
Mooney C, Haslam NJ, Pollastri DC (2012) Towards the improved discovery and design of functional peptides: common features of diverse classes permit generalized prediction of bioactivity. PLoS One 7:e45012
Gasteiger E, Hoogland C, Gattiker A, Duvaud S, Wilkins MR, Appel RD, Bairoch A (2005) Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. In: Walker JM (ed) The proteomics protocols handbook. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ, pp 571–607
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express their gratitude to Lorena Barros for her excellent technical assistance in this study. This work was supported by the GAIN-Xunta de Galicia Project (IN607D 2017/01) and the Spanish AEI/EU-FEDER (PID2019-103845RB-C21) project. Dr. Mónica Carrera is supported by the Ramón y Cajal contract (Ministry of Science and Innovation of Spain).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Carrera, M., Pazos, M., Aubourg, S.P., Gallardo, J.M. (2021). Shotgun Proteomics and Protein-Based Bioinformatics for the Characterization of Food-Derived Bioactive Peptides. In: Carrera, M., Mateos, J. (eds) Shotgun Proteomics. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2259. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1178-4_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1178-4_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1177-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1178-4
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols