Abstract
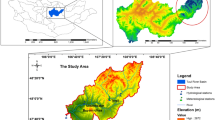
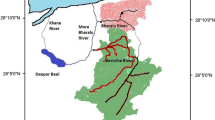
In ecologically fragile areas with arid climate, such as the Heihe River Basin in Northwestern China, sustainable social and economic development depends largely on the availability and sustainable uses of water resource. However, under the influence of the rapidly changing climate and human activities, the Heihe River Basin undergoes serious water shortage and water productivity decline. In this chapter we adopted a semi-distributed conceptual hydrological model (SWAT – Soil Water Assessment Tool) coupled with a glacier melting algorithm to investigate the sensitivity of streamflow to climatic and glacial changes in the upstream of the Heihe River Basin. The glacier mass balance was calculated at daily time-step using a distributed temperature-index melting and accumulation algorithm embedded in the SWAT model. Specifically, the model was calibrated and validated using daily streamflow data measured at Yingluoxia Hydrological Station and decadal ice volume changes derived from survey maps and remote sensing images between 1960 and 2010. This study highlights the effects of glacier melting on streamflow and their future changes in the mountainous watersheds. Further, we used improved CGE model to analyze the difference and change between different industries in middle stream of the Heihe River Basin. Simulation results indicate that industrial transformation and development of water-saving industries will also improve water productivity. Lastly, we put forward some strategies on how to mitigate climate change impacts for optimizing water productivity from three perspectives: (1) scientific research needed by scientists, (2) management and institution formulation needed by governments, and (3) water resource optimal allocation by the manager at all administrative levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Alcamo, M. Flörke, M. Märker, Future long-term changes in global water resources driven by socio-economic and climatic changes. Hydrol. Sci. J. 52, 247–275 (2007)
K. Bakker, Water security: Research challenges and opportunities. Science 337, 914–915 (2012)
C. Bao, C.l. Fang, Water resources constraint force on urbanization in water deficient regions: A case study of the Hexi Corridor, arid area of NW China. Ecol. Econ. 62, 508–517 (2007)
B. Bates, Z. Kundzewicz, S. Wu, J. Palutikof, Climate Change and Water, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2008)
M. Berrittella, K. Rehdanz, R.S. Tol, The Economic Impact of the South-North Water Transfer Project in China: A Computable General Equilibrium Analysis (Fondazione Eni Enrico Mattei (FEEM), Milano, 2006)
L. Bracken, E. Oughton, Interdisciplinarity within and beyond geography: Introduction to special section. Area 41, 371–373 (2009)
P. Cardei, V. Herea, V. Muraru, R. Sfaru, Vector representation for the soil erosion model USLE, a point of view. Bulletin of University of Agricultural Sciences and Veterinary Medicine Cluj-Napoca. Agriculture 66, 46–53 (2009)
C.R. Castillo, I. Güneralp, B. Güneralp, Influence of changes in developed land and precipitation on hydrology of a coastal Texas watershed. Appl. Geogr. 47, 154–167 (2014)
I.P.O.C. Change, Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Agenda 6, 333 (2007)
G. Cheng, H. Xiao, C. Li, J. Ren, S. Wang, Water saving eco-agriculture and integrated water resources management in the Heihe River Basin, northwest China. Adv. Earth Sci. 23, 661–665 (2008)
G. Cheng, X. Li, W. Zhao, Z. Xu, Q. Feng, S. Xiao, H. Xiao, Integrated study of the water–ecosystem–economy in the Heihe River Basin. Natl. Sci. Rev. 1, 413–428 (2014)
X. Deng, Y. Wang, F. Wu, T. Zhang, Z. Li, The integrated CGE model construction, in Integrated River Basin Management (Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, 2014a), pp. 57–78
X. Deng, F. Zhang, Z. Wang, X. Li, T. Zhang, An extended input output table. Compiled for analyzing water demand and consumption at county level in China. Sustainability 6, 3301–3320 (2014b)
R. Ding, F.-c. Wang, J. Wang, J.-n. Liang, Analysis on spatial-temporal characteristics of precipitation in Heihe River Basin and forecast evaluation in recent 47 years. J. Desert Res. 29, 335–341 (2009)
C.-l. Fang, C. Bao, J.c. Huang, Management implications to water resources constraint force on socio-economic system in rapid urbanization: A case study of the Hexi Corridor, NW China. Water Resour. Manag. 21, 1613–1633 (2007)
S. Feng, L.X. Li, Z.G. Duan, J.L. Zhang, Assessing the impacts of south-to-north water transfer project with decision support systems. Decis. Support. Syst. 42, 1989–2003 (2007)
T. Fontaine, T. Cruickshank, J. Arnold, R. Hotchkiss, Development of a snowfall–snowmelt routine for mountainous terrain for the soil water assessment tool (SWAT). J. Hydrol. 262, 209–223 (2002)
S. Giri, A.P. Nejadhashemi, S.A. Woznicki, Evaluation of targeting methods for implementation of best management practices in the Saginaw River Watershed. J. Environ. Manag. 103, 24–40 (2012)
J.W. Glen, The creep of polycrystalline ice. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Sci. 228, 519–538 (1955)
Q. Guo, Q. Feng, J. Li, Environmental changes after ecological water conveyance in the lower reaches of Heihe River, northwest China. Environ. Geol. 58, 1387–1396 (2009)
GWP, Integrated Water Resources Management (Technical Advisory Committee (TAC), 2004)
W. Hagg, L. Braun, M. Kuhn, T. Nesgaard, Modelling of hydrological response to climate change in glacierized central Asian catchments. J. Hydrol. 332, 40–53 (2007)
R. Hock, Temperature index melt modelling in mountain areas. J. Hydrol. 282, 104–115 (2003)
M. Howells, S. Hermann, M. Welsch, M. Bazilian, R. Segerström, T. Alfstad, D. Gielen, H. Rogner, G. Fischer, H. van Velthuizen, Integrated analysis of climate change, land-use, energy and water strategies. Nat. Clim. Chang. 3, 621–626 (2013)
M. Huss, A. Bauder, M. Funk, R. Hock, Determination of the seasonal mass balance of four Alpine glaciers since 1865. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. (2003–2012) 113 (2008a)
M. Huss, D. Farinotti, A. Bauder, M. Funk, Modelling runoff from highly glacierized alpine drainage basins in a changing climate. Hydrol. Process. 22, 3888–3902 (2008b)
W. Immerzeel, P. Kraaijenbrink, J. Shea, A. Shrestha, F. Pellicciotti, M. Bierkens, S. De Jong, High-resolution monitoring of Himalayan glacier dynamics using unmanned aerial vehicles. Remote Sens. Environ. 150, 93–103 (2014)
J. Kim, J. Choi, C. Choi, S. Park, Impacts of changes in climate and land use/land cover under IPCC RCP scenarios on streamflow in the Hoeya River Basin, Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 452, 181–195 (2013)
M. Kummu, P.J. Ward, H. de Moel, O. Varis, Is physical water scarcity a new phenomenon? Global assessment of water shortage over the last two millennia. Environ. Res. Lett. 5, 034006 (2010)
X. Li, X. Yang, Q. Gao, Y. Li, S. Dong, Integrative assessment of hydrological, ecological, and economic systems for water resources management at river basin scale. Front. Earth Sci. China 3, 198–207 (2009)
X. Li, G. Cheng, L. Wu, Digital Heihe River Basin. 1: an information infrastructure for the watershed science. Adv. Earth Sci. 25, 297–305 (2010)
Y. Luo, J. Arnold, S. Liu, X. Wang, X. Chen, Inclusion of glacier processes for distributed hydrological modeling at basin scale with application to a watershed in Tianshan Mountains, northwest China. J. Hydrol. 477, 72–85 (2013)
F. Martin-Carrasco, L. Garrote, A. Iglesias, L. Mediero, Diagnosing causes of water scarcity in complex water resources systems and identifying risk management actions. Water Resour. Manag. 27, 1693–1705 (2013)
B. Mitchell, Integrated water resource management, institutional arrangements, and land-use planning. Environ Plan A 37, 1335 (2005)
J. Nye, The flow of a glacier in a channel of rectangular, elliptic or parabolic cross-section. J. Glaciol. 5, 661–690 (1965)
S. Neitsch, J. Arnold, J. Kiniry, J. Williams, K. King, Soil and Water Assessment Tool: Theoretical Documentation, Version 2005 (Texas, 2005)
J.J. Pigram, Economic instruments in the management of Australia’s water resources: a critical view. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 15, 493–509 (1999)
S.M. Pradhanang, A. Anandhi, R. Mukundan, M.S. Zion, D.C. Pierson, E.M. Schneiderman, A. Matonse, A. Frei, Application of SWAT model to assess snowpack development and streamflow in the Cannonsville watershed, New York, USA. Hydrol. Process. 25, 3268–3277 (2011)
S.-Z. Qi, F. Luo, Water environmental degradation of the Heihe River Basin in arid northwestern China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 108, 205–215 (2005)
F.R. Rijsberman, Water scarcity: fact or fiction? Agric. Water Manag. 80, 5–22 (2006)
T. Thorsteinsson, T. Jóhannesson, Á. Snorrason, Glaciers and ice caps: vulnerable water resources in a warming climate. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 5, 590–598 (2013)
C. Tortajada, Institutions for integrated water resources management in Latin America: lessons for Asia, in Integrated Water Resources Management in South and South-East Asia (Oxfor University Press, New Delhi, 2005). pp. 297–319
D. Viviroli, R. Weingartner, The hydrological significance of mountains: from regional to global scale. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 8, 1017–1030 (2004)
C.J. Vörösmarty, P. Green, J. Salisbury, R.B. Lammers, Global water resources: vulnerability from climate change and population growth. Science 289, 284–288 (2000)
Y. Wang, H. Xiao, J. Ren, M. Lu, Study on water resources utilization in Zhangye city based on CGE model. Arid Zone Res. 1, 28–34 (2008) (in Chinese)
Y. Wang, H.-l. Xiao, R.-f. Wang, Water scarcity and water use in economic systems in Zhangye City, northwestern China. Water Resour. Manag. 23, 2655–2668 (2009)
J. Warner, P. Wester, A. Bolding, Going with the flow: river basins as the natural units for water management. Water Policy 10, 121–138 (2008)
G.F. White, A perspective of river basin development. Law Contemp. Probl., 157–187 (1957)
F. Wu, J. Zhan, C. Shi, C. Zhao, An extended input–output table. For environmental and resources accounting. Chinese J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 12, 33–41 (2014)
F. Wu, J. Zhan, Z. Wang, Q. Zhang, Streamflow variation due to glacier melting and climate change in upstream Heihe River Basin, Northwest China. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A B C 79, 11–19 (2015)
H. Xi, Q. Feng, W. Liu, J. Si, Z. Chang, Y. Su, The research of groundwater flow model in Ejina Basin, northwestern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 60, 953–963 (2010)
Z. Yin, H. Xiao, S. Zou, R. Zhu, Z. Lu, Y. Lan, Y. Shen, Simulation of hydrological processes of mountainous watersheds in inland river basins: taking the Heihe Mainstream River as an example. J. Arid. Land 6, 16–26 (2014)
L. Yu, H. Jikun, W. Jinxia, S. Rozelle, Determinants of agricultural water saving technology adoption: an empirical study of 10 provinces of China. Ecol. Econ. 4, 462–472 (2008)
J. Zhan, Z. Sun, Z. Wang, J. Chen, Z. Li, Simulated water productivity in Gansu Province, China. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A B C 79–82, 67–75 (2015)
Y. Zhao, X. Deng, Q. Lu, W. Huang, Regional rural development, nitrogen input and output in farming-grazing system and its environmental impacts—a case study of the Wuliangsuhai catchment. Procedia Environ Sci 2, 542–556 (2010)
Z. Zheng, J. Liu, P. Koeneman, E. Zarate, A. Hoekstra, Assessing water footprint at river basin level: a case study for the Heihe River Basin in northwest China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 16, 2771–2781 (2012)
H. Zhou, X. Zhang, H. Xu, H. Ling, P. Yu, Influences of climate change and human activities on Tarim River runoffs in China over the past half century. Environ. Earth Sci. 67, 231–241 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this entry
Cite this entry
Sun, Z., Wu, F., Arowolo, A., Zhao, C., Deng, X. (2018). Mitigating Climate Change Impacts for Optimizing Water Productivity. In: Deng, X., Gibson, J. (eds) River Basin Management. Ecohydrology. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-0841-2_5-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-0841-2_5-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-0841-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-0841-2
eBook Packages: Springer Reference Earth and Environm. ScienceReference Module Physical and Materials ScienceReference Module Earth and Environmental Sciences