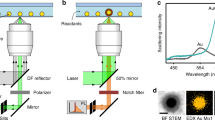
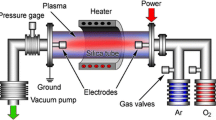
Abstract
This chapter presents a review of work on the laser synthesis and functionalization of semiconductor nanowires and nanoparticles in the context of fabricating high-performance electronic devices. Laser-aided sintering of nanoparticles (NPs) is examined. Laser irradiation can access time scales from the continuous to ultrafast and length scales down to submicron, therefore enabling precise control of the induced temperature field. Furthermore, the coupling of the laser energy with the target material is a strong function of the wavelength and is sensitive to the size of the irradiated structure, particularly as the dimensions shrink to the nanoscale range. In this case, one may expect resonant effects allowing efficient radiant energy coupling and processing. Vapor-liquid-solid (VLS) mechanism has been adopted as a bottom-up approach in the synthesis of semiconducting nanowires (NWs). In contrast to blanket heating methods, laser irradiation offers high spatial selectivity and precise control of the heating mechanism in the time domain. These attributes enable elucidation of the fundamental process of nanowire nucleation and early stage of nanostructure growth. Site- and shape-selective on-demand direct integration of oriented NWs is accomplished. Growth of discrete silicon nanowires is reported with nanoscale location selectivity by employing near-field laser illumination in conjunction with highly localized electric fields. Control of the location-selective metal oxide NW growth is accomplished by modulated laser irradiation via an adaptation of hydrothermal growth. Understanding of kinetics of laser hydrothermal growth enabled optimization of efficient growth of various metal oxide NWs, and even heterostructures could be demonstrated on arbitrary substrates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
An K, Hong S, Han S, Lee H, Yeo J, Ko SH (2014) Selective sintering of metal nanoparticle ink for maskless fabrication of an electrode micropattern using a spatially modulated laser beam by a digital micromirror device. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(4):2786–2790. https://doi.org/10.1021/am405323c
Andritsos K, Theodorakos I, Zacharatos F, Zergioti I (2020) The effect of electromigration on the lifetime and performance of flexible interconnections fabricated by laser printing and sintering. Appl Surf Sci 506:144968
Arcidiacono S, Bieri N, Poulikakos D, Grigoropoulos C (2004) On the coalescence of gold nanoparticles. Int J Multiphase Flow 30(7–8):979–994
Arico AS, Bruce P, Scrosati B, Tarascon J-M, Van Schalkwijk W (2011) Nanostructured materials for advanced energy conversion and storage devices. In: Materials for sustainable energy: a collection of peer-reviewed research and review articles from Nature Publishing Group. World Scientific, Hackensack, pp 148–159
Bäuerle DW (2011) Laser processing and chemistry. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg
Birkelund K, Thomsen EV, Rasmussen JP, Hansen O, Tang PT, Moller P, Grey F (1997) New approaches to atomic force microscope lithography on silicon. J Vac Sci Technol B Microelectron Nanometer Struct Process Meas Phenom 15(6):2912–2915
Buffat P, Borel JP (1976) Size effect on the melting temperature of gold particles. Phys Rev A 13(6):2287
Cao L, Barsic DN, Guichard AR, Brongersma ML (2007) Plasmon-assisted local temperature control to pattern individual semiconductor nanowires and carbon nanotubes. Nano Lett 7(11):3523–3527
Cao Y-Y, Takeyasu N, Tanaka T, Duan X-M, Kawata S (2009) 3D metallic nanostructure fabrication by surfactant-assisted multiphoton-induced reduction. Small 5(10):1144–1148. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.200801179
Chan CK, Peng H, Liu G, McIlwrath K, Zhang XF, Huggins RA, Cui Y (2008) High-performance lithium battery anodes using silicon nanowires. Nat Nanotechnol 3(1):31
Chung J, Ko S, Bieri NR, Grigoropoulos CP, Poulikakos D (2004) Conductor microstructures by laser curing of printed gold nanoparticle ink. Appl Phys Lett 84(5):801–803
Coombes C (1972) The melting of small particles of lead and indium. J Phys F 2(3):441
de Vries AJ, Kooij ES, Wormeester H, Mewe AA, Poelsema B (2007) Ellipsometric study of percolation in electroless deposited silver films. J Appl Phys 101(5):053703
Dean RN, Nordine PC, Christodoulou CG (1999) Novel method for fabricating 3D helical THz antennas directly on semiconductor substrates, vol 3617. Optoelectronics ‘99 – integrated optoelectronic devices. SPIE
Duty C, Jean D, Lackey WJ (2001) Laser chemical vapour deposition: materials, modelling, and process control. Int Mater Rev 46(6):271–287. https://doi.org/10.1179/095066001771048727
Fox M (2001) Optical properties of solids, Oxford master series in condensed matter physics. Oxford University Press, New York, p 305
Garnett EC, Cai W, Cha JJ, Mahmood F, Connor ST, Greyson Christoforo M, Cui Y, McGehee MD, Brongersma ML (2012) Self-limited plasmonic welding of silver nanowire junctions. Nat Mater 11:241. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3238. https://www.nature.com/articles/nmat3238#supplementary-information
Grigoropoulos CP (2009) Transport in laser microfabrication: fundamentals and applications. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Han S, Hong S, Ham J, Yeo J, Lee J, Kang B, Lee P, Kwon J, Lee SS, Yang M-Y, Ko SH (2014) Fast plasmonic laser nanowelding for a Cu-nanowire percolation network for flexible transparent conductors and stretchable electronics. Adv Mater 26(33):5808–5814. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201400474
Han S, Hong S, Yeo J, Kim D, Kang B, Yang M-Y, Ko SH (2015) Nanorecycling: monolithic integration of copper and copper oxide nanowire network electrode through selective reversible photothermochemical reduction. Adv Mater 27(41):6397–6403. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201503244
He G-C, Zheng M-L, Dong X-Z, Jin F, Liu J, Duan X-M, Zhao Z-S (2017) The conductive silver nanowires fabricated by two-beam laser direct writing on the flexible sheet. Sci Rep 7:41757
Heavens OS (1991) Optical properties of thin solid films. Courier Corporation, Dover Publications, New York
Hirt L, Reiser A, Spolenak R, Zambelli T (2017) Additive manufacturing of metal structures at the micrometer scale. Adv Mater 29(17):1604211. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201604211
Hong S, Yeo J, Manorotkul W, Kang HW, Lee J, Han S, Rho Y, Suh YD, Sung HJ, Ko SH (2013) Digital selective growth of a ZnO nanowire array by large scale laser decomposition of zinc acetate. Nanoscale 5(9):3698–3703. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR34346D
Hsu YF, Xi YY, Tam KH, Djurišić AB, Luo J, Ling CC, Cheung CK, Ng AMC, Chan WK, Deng X (2008) Undoped p-type ZnO nanorods synthesized by a hydrothermal method. Adv Funct Mater 18(7):1020–1030
Huang MH, Mao S, Feick H, Yan H, Wu Y, Kind H, Weber E, Russo R, Yang P (2001a) Room-temperature ultraviolet nanowire nanolasers. Science 292(5523):1897–1899
Huang MH, Wu Y, Feick H, Tran N, Weber E, Yang P (2001b) Catalytic growth of zinc oxide nanowires by vapor transport. Adv Mater 13(2):113–116
Hung WH, Hsu I-K, Bushmaker A, Kumar R, Theiss J, Cronin SB (2008) Laser directed growth of carbon-based nanostructures by plasmon resonant chemical vapor deposition. Nano Lett 8(10):3278–3282
Hwang DJ, Ryu S-G, Grigoropoulos CP (2011a) Multi-parametric growth of silicon nanowires in a single platform by laser-induced localized heat sources. Nanotechnology 22(38):385303
Hwang DJ, S-g R, Kim E, Grigoropoulos CP, Carraro C (2011b) On demand-direct synthesis of Si and Ge nanowires on a single platform by focused laser illumination. Appl Phys Lett 99(12):123109
In JB, Kwon HJ, Lee D, Ko SH, Grigoropoulos CP (2014) In situ monitoring of laser-assisted hydrothermal growth of ZnO nanowires: thermally deactivating growth kinetics. Small 10(4):741–749
Ishikawa A, Tanaka T, Kawata S (2006) Improvement in the reduction of silver ions in aqueous solution using two-photon sensitive dye. Appl Phys Lett 89(11):113102. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2345601
Jang WS, Lee TI, Oh JY, Hwang SH, Shon SW, Kim DH, Xia Y, Myoung JM, Baik HK (2012) Kinetically controlled way to create highly uniform mono-dispersed ZnO sub-microrods for electronics. J Mater Chem 22(38):20719–20727
Joo J, Chow BY, Prakash M, Boyden ES, Jacobson JM (2011) Face-selective electrostatic control of hydrothermal zinc oxide nanowire synthesis. Nat Mater 10:596. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3069. https://www.nature.com/articles/nmat3069#supplementary-information
Kang B, Han S, Kim J, Ko S, Yang M (2011) One-step fabrication of copper electrode by laser-induced direct local reduction and agglomeration of copper oxide nanoparticle. J Phys Chem C 115(48):23664–23670. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp205281a
Kempa TJ, Tian B, Kim DR, Hu J, Zheng X, Lieber CM (2008) Single and tandem axial pin nanowire photovoltaic devices. Nano Lett 8(10):3456–3460
Kikkawa J, Ohno Y, Takeda S (2005) Growth rate of silicon nanowires. Appl Phys Lett 86(12):123109
Ko SH, Pan H, Grigoropoulos CP, Luscombe CK, Fréchet JM, Poulikakos D (2007a) Air stable high resolution organic transistors by selective laser sintering of ink-jet printed metal nanoparticles. Appl Phys Lett 90(14):141103
Ko SH, Pan H, Grigoropoulos CP, Luscombe CK, Fréchet JM, Poulikakos D (2007b) All-inkjet-printed flexible electronics fabrication on a polymer substrate by low-temperature high-resolution selective laser sintering of metal nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 18(34):345202
Ko SH, Lee D, Kang HW, Nam KH, Yeo JY, Hong SJ, Grigoropoulos CP, Sung HJ (2011) Nanoforest of hydrothermally grown hierarchical ZnO nanowires for a high efficiency dye-sensitized solar cell. Nano Lett 11(2):666–671
Kofman R, Cheyssac P, Aouaj A, Lereah Y, Deutscher G, Ben-David T, Penisson J, Bourret A (1994) Surface melting enhanced by curvature effects. Surf Sci 303(1-2):231–246
Kooij ES, Poelsema B (2006) Shape and size effects in the optical properties of metallic nanorods. Phys Chem Chem Phys 8(28):3349–3357
Kotecki DE, Herman IP (1988) A real time Monte Carlo simulation of thin film nucleation in localized-laser chemical vapor deposition. J Appl Phys 64(10):4920–4942
Kruth J-P, Levy G, Klocke F, Childs T (2007) Consolidation phenomena in laser and powder-bed based layered manufacturing. CIRP Ann 56(2):730–759
Kwon J, Cho H, Eom H, Lee H, Suh YD, Moon H, Shin J, Hong S, Ko SH (2016) Low-temperature oxidation-free selective laser sintering of Cu nanoparticle paste on a polymer substrate for the flexible touch panel applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(18):11575–11582
Lao CS, Park M-C, Kuang Q, Deng Y, Sood AK, Polla DL, Wang ZL (2007) Giant enhancement in UV response of ZnO nanobelts by polymer surface-functionalization. J Am Chem Soc 129(40):12096–12097
Law M, Greene LE, Johnson JC, Saykally R, Yang P (2005) Nanowire dye-sensitized solar cells. Nat Mater 4(6):455
Lee M-T, Lee D, Sherry A, Grigoropoulos CP (2011) Rapid selective metal patterning on polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) fabricated by capillarity-assisted laser direct write. J Micromech Microeng 21(9):095018
Lee D, Pan H, Ko SH, Park HK, Kim E, Grigoropoulos CP (2012a) Non-vacuum, single-step conductive transparent ZnO patterning by ultra-short pulsed laser annealing of solution-deposited nanoparticles. Appl Phys A 107(1):161–171
Lee P, Lee J, Lee H, Yeo J, Hong S, Nam KH, Lee D, Lee SS, Ko SH (2012b) Highly stretchable and highly conductive metal electrode by very long metal nanowire percolation network. Adv Mater 24(25):3326–3332. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201200359
Lee J, Lee P, Lee HB, Hong S, Lee I, Yeo J, Lee SS, Kim T-S, Lee D, Ko SH (2013) Room-temperature nanosoldering of a very long metal nanowire network by conducting-polymer-assisted joining for a flexible touch-panel application. Adv Funct Mater 23(34):4171–4176. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201203802
Lee D, Paeng D, Park HK, Grigoropoulos CP (2014) Vacuum-free, maskless patterning of Ni electrodes by laser reductive sintering of NiO nanoparticle ink and its application to transparent conductors. ACS Nano 8(10):9807–9814
Lee H, Hong S, Kwon J, Suh YD, Lee J, Moon H, Yeo J, Ko SH (2015) All-solid-state flexible supercapacitors by fast laser annealing of printed metal nanoparticle layers. J Mater Chem A 3(16):8339–8345. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TA07120D
Leggett GJ (2011) Direct writing of metal nanostructures: lithographic tools for nanoplasmonics research. ACS Nano 5(3):1575–1579. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn2006442
Luk‘yanchuk BS, Arnold N, Huang SM, Wang ZB, Hong MH (2003) Three-dimensional effects in dry laser cleaning. Appl Phys A 77(2):209–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-003-2139-z
Mahajan B, Yu X, Shou W, Pan H, Huang X (2017) Mechanically milled irregular zinc nanoparticles for printable bioresorbable electronics. Small 13(17):1700065
Mincuzzi G, Schulz-Ruhtenberg M, Vesce L, Reale A, Di Carlo A, Gillner A, Brown TM (2014) Laser processing of TiO2 films for dye solar cells: a thermal, sintering, throughput and embodied energy investigation. Prog Photovolt Res Appl 22(3):308–317. https://doi.org/10.1002/pip.2261
Morales AM, Lieber CM (1998) A laser ablation method for the synthesis of crystalline semiconductor nanowires. Science 279(5348):208–211
Nam W, Mitchell JI, Xu X (2016) Laser direct writing of modulation-doped nanowire p/n junctions. Nanotechnology 27(48):485205
Nan C-W, Birringer R, Clarke DR, Gleiter H (1997) Effective thermal conductivity of particulate composites with interfacial thermal resistance. J Appl Phys 81(10):6692–6699
Noguez C (2007) Surface plasmons on metal nanoparticles: the influence of shape and physical environment. J Phys Chem C 111(10):3806–3819
Olson TY, Chernov AA, Drabek BA, Satcher JH, Han TY-J (2013) Experimental validation of the geometrical selection model for hydrothermally grown zinc oxide nanowire arrays. Chem Mater 25(8):1363–1371. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm300679x
Paeng D, Lee D, Yeo J, Yoo J-H, Allen FI, Kim E, So H, Park HK, Minor AM, Grigoropoulos CP (2015a) Laser-induced reductive sintering of nickel oxide nanoparticles under ambient conditions. J Phys Chem C 119(11):6363–6372
Paeng D, Yeo J, Lee D, Moon S-J, Grigoropoulos CP (2015b) Laser wavelength effect on laser-induced photo-thermal sintering of silver nanoparticles. Appl Phys A 120(4):1229–1240
Pan H, Ko S, Grigoropoulos C (2008a) The coalescence of supported gold nanoparticles induced by nanosecond laser irradiation. Appl Phys A 90(2):247–253
Pan H, Ko SH, Grigoropoulos CP (2008b) The solid-state neck growth mechanisms in low energy laser sintering of gold nanoparticles: a molecular dynamics simulation study. J Heat Transf 130(9):092404
Pan H, Ko SH, Misra N, Grigoropoulos CP (2009a) Laser annealed composite titanium dioxide electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells on glass and plastics. Appl Phys Lett 94(7):071117
Pan H, Misra N, Ko SH, Grigoropoulos CP, Miller N, Haller EE, Dubon O (2009b) Melt-mediated coalescence of solution-deposited ZnO nanoparticles by excimer laser annealing for thin-film transistor fabrication. Appl Phys A 94(1):111–115
Pan H, Hwang DJ, Ko SH, Clem TA, Fréchet JM, Bäuerle D, Grigoropoulos CP (2010) High-throughput near-field optical nanoprocessing of solution-deposited nanoparticles. Small 6(16):1812–1821
Pan H, Lee D, Ko SH, Grigoropoulos CP, Park HK, Hoult T (2011) Fiber laser annealing of indium-tin-oxide nanoparticles for large area transparent conductive layers and optical film characterization. Appl Phys A 104(1):29–38
Park T, Kim D (2015) Excimer laser sintering of indium tin oxide nanoparticles for fabricating thin films of variable thickness on flexible substrates. Thin Solid Films 578:76–82
Park T, Kim D (2016) Laser plasma sintering for fabricating indium tin oxide thin films. Thin Solid Films 615:177–182
Pauzauskie PJ, Yang P (2006) Nanowire photonics. Mater Today 9(10):36–45
Pauzauskie PJ, Radenovic A, Trepagnier E, Shroff H, Yang P, Liphardt J (2006) Optical trapping and integration of semiconductor nanowire assemblies in water. Nat Mater 5(2):97
Piqué A, Auyeung RCY, Kim H, Charipar NA, Mathews SA (2016) Laser 3D micro-manufacturing. J Phys D Appl Phys 49(22):223001. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/49/22/223001
Qing Q, Pal SK, Tian B, Duan X, Timko BP, Cohen-Karni T, Murthy VN, Lieber CM (2010) Nanowire transistor arrays for mapping neural circuits in acute brain slices. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107(5):1882
Rho Y, Kang K-T, Lee D (2016) Highly crystalline Ni/NiO hybrid electrodes processed by inkjet printing and laser-induced reductive sintering under ambient conditions. Nanoscale 8(16):8976–8985. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NR00708B
Ryu S-G, Kim E, Yoo J-H, Hwang DJ, Xiang B, Dubon OD, Minor AM, Grigoropoulos CP (2013) On demand shape-selective integration of individual vertical germanium nanowires on a Si (111) substrate via laser-localized heating. ACS Nano 7(3):2090–2098
Ryu S-G, Hwang DJ, Kim E, Grigoropoulos CP (2014) Tip-based nanoscale selective growth of discrete silicon nanowires by near-field laser illumination. Appl Phys A 116(1):51–58
Ryu S-G, Kim E, Hwang DJ, Grigoropoulos CP (2015) Selective and directed growth of silicon nanowires by tip-enhanced local electric field. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 121(1):255–260
Ryu S-G, Kim E, Allen FI, Hwang DJ, Minor AM, Grigoropoulos CP (2016) Incubation behavior of silicon nanowire growth investigated by laser-assisted rapid heating. Appl Phys Lett 109(7):073106
Schierning G, Stoetzel J, Chavez R, Kessler V, Hall J, Schmechel R, Schneider T, Petermann N, Wiggers H, Angst S (2016) Silicon-based nanocomposites for thermoelectric application. Phys Status Solidi A 213(3):497–514
Shin J, Jeong B, Kim J, Nam VB, Yoon Y, Jung J, Hong S, Lee H, Eon H, Yeo J, Choi J, Lee D, Ko SH (2020) Wearable temperature sensors: sensitive wearable temperature sensor with seamless monolithic integration. Adv Mater. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202070014
Shou W, Mahajan BK, Ludwig B, Yu XW, Staggs J, Huang X, Pann H (2017) Low-cost manufacturing of bioresorbable conductors by evaporation-condensation-mediated laser printing and sintering of Zn nanoparticles. Adv Mater 29:170072
Skylar-Scott MA, Gunasekaran S, Lewis JA (2016) Laser-assisted direct ink writing of planar and 3D metal architectures. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113(22):6137–6142. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1525131113
Son Y, Yeo J, Moon H, Lim TW, Hong S, Nam KH, Yoo S, Grigoropoulos CP, Yang DY, Ko SH (2011) Nanoscale electronics: digital fabrication by direct femtosecond laser processing of metal nanoparticles. Adv Mater 23(28):3176–3181
Swanwick ME, Pfaendler SML, Akinwande AI, Flewitt AJ (2012) Near-ultraviolet zinc oxide nanowire sensor using low temperature hydrothermal growth. Nanotechnology 23(34):344009. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/23/34/344009
Takai T, Nakao H, Iwata F (2014) Three-dimensional microfabrication using local electrophoresis deposition and a laser trapping technique. Opt Express 22(23):28109–28117. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.22.028109
Theodorakos I, Zacharatos F, Geremia R, Karnakis D, Zergioti I (2015) Selective laser sintering of Ag nanoparticles ink for applications in flexible electronics. Appl Surf Sci 336:157–162
Visser CW, Pohl R, Sun C, Römer G-W, Huis in ‘t Veld B, Lohse D (2015) Toward 3D printing of pure metals by laser-induced forward transfer. Adv Mater 27(27):4087–4092. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201501058
Wagner R, Ellis W (1964) Vapor-liquid-solid mechanism of single crystal growth. Appl Phys Lett 4(5):89–90
Wang ZL (2012) From nanogenerators to piezotronics – a decade-long study of ZnO nanostructures. MRS Bull 37(9):814–827
Wang J, Auyeung RCY, Kim H, Charipar NA, Piqué A (2010) Three-dimensional printing of interconnects by laser direct-write of silver nanopastes. Adv Mater 22(40):4462–4466. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201001729
Wanke MC, Lehmann O, Müller K, Wen Q, Stuke M (1997) Laser rapid prototyping of photonic band-gap microstructures. Science 275(5304):1284–1286. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.275.5304.1284
Wormeester H, Henry A-I, Kooij ES, Poelsema B, Pileni M-P (2006) Ellipsometric identification of collective optical properties of silver nanocrystal arrays. J Chem Phys 124(20):204713
Xu S, Wang ZL (2011) One-dimensional ZnO nanostructures: solution growth and functional properties. Nano Res 4(11):1013–1098
Yan R, Gargas D, Yang P (2009) Nanowire photonics. Nat Photonics 3(10):569
Yeo J, Hong S, Lee D, Hotz N, Lee M-T, Grigoropoulos CP, Ko SH (2012) Next generation non-vacuum, maskless, low temperature nanoparticle ink laser digital direct metal patterning for a large area flexible electronics. PLoS One 7(8):e42315
Yeo J, Hong S, Wanit M, Kang HW, Lee D, Grigoropoulos CP, Sung HJ, Ko SH (2013) Rapid, one-step, digital selective growth of ZnO nanowires on 3D structures using laser induced hydrothermal growth. Adv Funct Mater 23(26):3316–3323
Yeo J, Hong S, Manorotkul W, Suh YD, Lee J, Kwon J, Ko SH (2014a) Digital 3D local growth of iron oxide micro- and nanorods by laser-induced photothermal chemical liquid growth. J Phys Chem C 118(28):15448–15454. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp501642j
Yeo J, Kim G, Hong S, Kim MS, Kim D, Lee J, Lee HB, Kwon J, Suh YD, Kang HW, Sung HJ, Choi J-H, Hong W-H, Ko JM, Lee S-H, Choa S-H, Ko SH (2014b) Flexible supercapacitor fabrication by room temperature rapid laser processing of roll-to-roll printed metal nanoparticle ink for wearable electronics application. J Power Sources 246:562–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.08.012
Yeo J, Hong S, Kim G, Lee H, Suh YD, Park I, Grigoropoulos CP, Ko SH (2015) Laser-induced hydrothermal growth of heterogeneous metal-oxide nanowire on flexible substrate by laser absorption layer design. ACS Nano 9(6):6059–6068. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b01125
Zacharatos F, Karvounis P, Theodorakos I, Hatziapostolou A, Zergioti I (2018) Single step laser transfer and laser curing of Ag nanowires: a digital process for the fabrication of flexible and transparent microelectrodes. Materials 11:1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11061036
Zhao W, Rovere T, Weerawarne D, Osterhoudt G, Kang N, Joseph P, Luo J, Shim B, Poliks M, Zhong C-J (2015) Nanoalloy printed and pulse-laser sintered flexible sensor devices with enhanced stability and materials compatibility. ACS Nano 9(6):6168–6177
Zheng G, Patolsky F, Cui Y, Wang WU, Lieber CM (2005) Multiplexed electrical detection of cancer markers with nanowire sensor arrays. Nat Biotechnol 23(10):1294
Acknowledgments
The research done by C.G. and his co-workers at the Laser Thermal Laboratory of UC Berkeley was supported by the DARPA/MTO, the US Department of Energy, and the US National Science Foundation. The laser-induced nanowire growth and doping was conducted on the LACVD apparatus in the UC Berkeley Marvell Nanofabrication Laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Section Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Rho, Y., Grigoropoulos, C.P. (2020). Laser-Induced Processing of Nanoparticles and Growth of Nanowires. In: Sugioka, K. (eds) Handbook of Laser Micro- and Nano-Engineering. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-69537-2_28-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-69537-2_28-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-69537-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-69537-2
eBook Packages: Springer Reference Physics and AstronomyReference Module Physical and Materials ScienceReference Module Chemistry, Materials and Physics