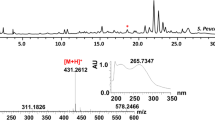
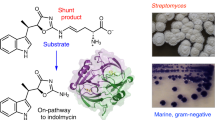
Abstract
The marine actinomycete Streptomyces maritimus produces a structurally diverse set of unusual polyketide natural products including the major metabolite enterocin. Investigations of enterocin biosynthesis revealed that the unique carbon skeleton is derived from an aromatic polyketide pathway which is genetically coded by the 21.3 kb enc gene cluster in S. maritimus. Characterization of the enc biosynthesis gene cluster and subsequent manipulation of it via heterologous expression and/or mutagenesis enabled the discovery of other enc-based metabolites that were produced in only very minor amounts in the wild type. Also described are techniques used to harness the enterocin biosynthetic machinery in order to generate unnatural enc-derived polyketide analogues. This review focuses upon the molecular methods used in combination with classical natural products detection and isolation techniques to access minor metabolites of the S. maritimus secondary metabolome.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Demain AL, Sanchez S (2009) Microbial drug discovery: 80 years of progress. J Antibiot 62:5–16
Omura S, Ikeda H, Ishikawa J, Hanamoto A, Takahashi C, Shinose M, Takahashi Y, Horikawa H, Nakazawa H, Osonoe T, Kikuchi H, Shiba T, Sakaki Y, Hattori M (2001) Genome sequence of an industrial microorganism Streptomyces avermitilis: deducing the ability of producing secondary metabolites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:12215–12220
Bentley SD, Chater KF, Cerdeno-Tarraga AM, Challis GL, Thomson NR, James KD, Harris DE, Quail MA, Kieser H, Harper D, Bateman A, Brown S, Chandra G, Chen CW, Collins M, Cronin A, Fraser A, Goble A, Hidalgo J, Hornsby T, Howarth S, Huang CH, Kieser T, Larke L, Murphy L, Oliver K, O’Neil S, Rabbinowitsch E, Rajandream MA, Rutherford K, Rutter S, Seeger K, Saunders D, Sharp S, Squares R, Squares S, Taylor K, Warren T, Wietzorrek A, Woodward J, Barrell BG, Parkhill J, Hopwood DA (2002) Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 417:141–147
Ikeda H, Ishikawa J, Hanamoto A, Shinose M, Kikuchi H, Shiba T, Sakaki Y, Hattori M, Omura S (2003) Complete genome sequence and comparative analysis of the industrial microorganism Streptomyces avermitilis. Nat Biotechnol 21:526–531
Udwary DW, Zeigler L, Asolkar RN, Singan V, Lapidus A, Fenical W, Jensen PR, Moore BS (2007) Genome sequencing reveals complex secondary metabolome in the marine actinomycete Salinispora tropica. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:10376–10381
Krug D, Zurek G, Revermann O, Vos M, Velicer GJ, Muller R (2008) Discovering the hidden secondary metabolome of Myxococcus xanthus: a study of intraspecific diversity. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:3058–3068
Winter JM, Behnken S, Hertweck C (2011) Genomics-inspired discovery of natural products. Curr Opin Chem Biol 15:22–31
Donadio S, Monciardini P, Sosio M (2007) Polyketide synthases and nonribosomal peptide synthetases: the emerging view from bacterial genomics. Nat Prod Rep 24:1073–1109
Fischbach MA, Walsh CT (2006) Assembly-line enzymology for polyketide and nonribosomal peptide antibiotics: logic, machinery, and mechanisms. Chem Rev 106:3468–3496
Nett M, Ikeda H, Moore BS (2009) Genomic basis for natural product biosynthetic diversity in the actinomycetes. Nat Prod Rep 26:1362–1384
Van Lanen SG, Shen B (2006) Microbial genomics for the improvement of natural product discovery. Curr Opin Microbiol 9:252–260
Lautru S, Deeth RJ, Bailey LM, Challis GL (2005) Discovery of a new peptide natural product by Streptomyces coelicolor genome mining. Nat Chem Biol 1:265–269
Kalaitzis JA, Lauro FM, Neilan BA (2009) Mining cyanobacterial genomes for genes encoding complex biosynthetic pathways. Nat Prod Rep 26:1447–1465
Walsh CT, Fischbach MA (2010) Natural products version 2.0: connecting genes to molecules. J Am Chem Soc 132:2469–2493
Piel J, Hoang K, Moore BS (2000) Natural metabolic diversity encoded by the enterocin biosynthesis gene cluster. J Am Chem Soc 122:5415–5416
Piel J, Hertweck C, Shipley PR, Hunt DM, Newman MS, Moore BS (2000) Cloning, sequencing and analysis of the enterocin biosynthesis gene cluster from the marine isolate ‘Streptomyces maritimus’: evidence for the derailment of an aromatic polyketide synthase. Chem Biol 7:943–955
Staunton J, Weissman KJ (2001) Polyketide biosynthesis: a millennium review. Nat Prod Rep 18:380–416
Hertweck C (2009) The biosynthetic logic of polyketide diversity. Angew Chem Int Ed 48:4688–4716
Austin MB, Noel JP (2003) The chalcone synthase superfamily of type III polyketide synthases. Nat Prod Rep 20:79–110
Khosla C, Kapur S, Cane DE (2009) Revisiting the modularity of modular polyketide synthases. Curr Opin Chem Biol 13:135–143
Shen B (2003) Polyketide biosynthesis beyond the type I, II and III polyketide synthase paradigms. Curr Opin Chem Biol 7:285–295
Van Lanen SG, Shen B (2008) Advances in polyketide synthase structure and function. Curr Opin Drug Disc 11:186–195
Hopwood DA (1997) Genetic contributions to understanding polyketide synthases. Chem Rev 97:2465–2497
Miyairi N, Sakai HI, Konomi T, Imanaka H (1976) Enterocin, a new antibiotic - taxonomy, isolation and characterization. J Antibiot 29:227–235
Tokuma Y, Miyairi N, Morimoto Y (1976) Structure of enterocin - x-ray analysis of m-bromobenzoyl enterocin dihydrate. J Antibiot 29:1114–1116
Seto H, Sato T, Urano S, Uzawa J, Yonehara H (1976) Utilization of C-13-C-13 coupling in structural and biosynthetic studies XII. Structure and biosynthesis of vulgamycin. Tetrahedron Lett 17:4367–4370
Kang H, Jensen PR, Fenical W (1996) Isolation of microbial antibiotics from a marine ascidian of the genus Didemnum. J Org Chem 61:1543–1546
Sitachitta N, Gadepalli M, Davidson BS (1996) New alpha-pyrone-containing metabolites from a marine-derived actinomycete. Tetrahedron 52:8073–8080
Yu TW, Shen YM, McDaniel R, Floss HG, Khosla C, Hopwood DA, Moore BS (1998) Engineered biosynthesis of novel polyketides from Streptomyces spore pigment polyketide synthases. J Am Chem Soc 120:7749–7759
Shen YM, Yoon P, Yu TW, Floss HG, Hopwood D, Moore BS (1999) Ectopic expression of the minimal whiE polyketide synthase generates a library of aromatic polyketides of diverse sizes and shapes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:3622–3627
Ziermann R, Betlach MC (1999) Recombinant polyketide synthesis in Streptomyces: engineering of improved host strains. Biotechniques 26:106–109
Ziermann R, Betlach MC (2000) A two-vector system for the production of recombinant polyketides in Streptomyces. J Ind Microbiol Biot 24:46–50
Alvarez MA, Fu H, Khosla C, Hopwood DA, Bailey JE (1996) Engineered biosynthesis of novel polyketides: properties of the whiE aromatase/cyclase. Nat Biotechnol 14:335–338
Xiang L, Kalaitzis JA, Nilsen G, Chen L, Moore BS (2002) Mutational analysis of the enterocin Favorskii biosynthetic rearrangement. Org Lett 4:957–960
Zhang HL, He XG, Adefarati A, Gallucci J, Cole SP, Beale JM, Keller PJ, Chang CJ, Floss HG (1990) Mutactin, a novel polyketide from Streptomyces coelicolor - structure and biosynthetic relationship to actinorhodin. J Org Chem 55:1682–1684
McDaniel R, Ebert Khosla S, Fu H, Hopwood DA, Khosla C (1994) Engineered biosynthesis of novel polyketides - influence of a downstream enzyme on the catalytic specificity of a minimal aromatic polyketide synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:11542–11546
Graziani EI, Ritacco FV, Bernan VS, Telliez JB (2005) Phaeochromycins A-E, anti-inflammatory polyketides isolated from the soil actinomycete Streptomyces phaeochromogenes LL-P018. J Nat Prod 68:1262–1265
Hertweck C, Moore BS (2000) A plant-like biosynthesis of benzoyl-CoA in the marine bacterium ‘Streptomyces maritimus’. Tetrahedron 56:9115–9120
Xiang L, Moore BS (2002) Inactivation, complementation, and heterologous expression of encP, a novel bacterial phenylalanine ammonia lyase gene. J Biol Chem 277:32505–32509
Xiang L, Moore BS (2003) Characterization of benzoyl coenzyme A biosynthesis genes in the enterocin-producing bacterium Streptomyces maritimus. J Bacteriol 185:399–404
Xiang L, Moore BS (2005) Biochemical characterization of a prokaryotic phenylalanine ammonia lyase. J Bacteriol 187:4286–4289
Izumikawa M, Cheng Q, Moore BS (2006) Priming type II polyketide synthases via a type II nonribosomal peptide synthetase mechanism. J Am Chem Soc 128:1428–1429
Kalaitzis JA, Izumikawa M, Xiang L, Hertweck C, Moore BS (2003) Mutasynthesis of enterocin and wailupemycin analogues. J Am Chem Soc 125:9290–9291
Hertweck C, Xiang L, Kalaitzis JA, Cheng Q, Palzer M, Moore BS (2004) Context-dependent behavior of the enterocin iterative polyketide synthase: a new model for ketoreduction. Chem Biol 11:461–468
Kalaitzis JA, Cheng Q, Meluzzi D, Xiang L, Izumikawa M, Dorrestein PC, Moore BS (2011) Policing starter unit selection of the enterocin type II polyketide synthase by the type II thioesterase EncL. Bioorgan Med Chem 19:6633–6638
Xiang L, Kalaitzis JA, Moore BS (2004) EncM, a versatile enterocin biosynthetic enzyme involved in Favorskii oxidative rearrangement, aldol condensation, and heterocycle-forming reactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:15609–15614
Werneburg M, Busch B, He J, Richter MEA, Xiang L, Moore BS, Roth M, Dahse HM, Hertweck C (2010) Exploiting enzymatic promiscuity to engineer a focused library of highly selective antifungal and antiproliferative aureothin analogues. J Am Chem Soc 132:10407–10413
Cheng Q, Xiang L, Izumikawa M, Meluzzi D, Moore BS (2007) Enzymatic total synthesis of enterocin polyketides. Nat Chem Biol 3:557–558
Kalaitzis JA, Cheng Q, Thomas PM, Kelleher NL, Moore BS (2009) In vitro biosynthesis of unnatural enterocin and wailupemycin polyketides. J Nat Prod 72:469–472
Acknowledgments
I wish to thank Professor Bradley S. Moore (Scripps Institution of Oceanography, UCSD) for providing me with the opportunity to work on the enterocin project, and also for his advice, support, and mentorship. I also thank many colleagues and collaborators who are referenced throughout this paper for their vast contributions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Kalaitzis, J.A. (2013). Discovery, Biosynthesis, and Rational Engineering of Novel Enterocin and Wailupemycin Polyketide Analogues. In: Roessner, U., Dias, D. (eds) Metabolomics Tools for Natural Product Discovery. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1055. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-577-4_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-577-4_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
Print ISBN: 978-1-62703-576-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-62703-577-4
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols