Abstract
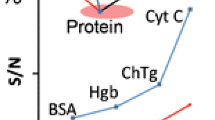
The interest in quantum dots (QD) and a number of reported life sciences applications increased dramatically over the last decade. The popularity of QDs stems from better photostability, higher extinction co-efficients, and unique optical properties such as superior light absorption. Here we report methods for improving matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization desorption of crude tryptic protein digests by using CdSe/ZnS QDs. The addition of QDs to the matrix improves the signal-to-noise ratio, peak quality and increases the number of detected peptides and the overall sequence coverage.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruchez M, Moronne M, Gin P et al (1998) Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science 281(5385):2013–2016
JaiswalJK GER, Mattoussi H et al (2004) Use of quantum dots for live cell imaging. Nat Methods 1(1):73–78
Gao XH, Yang LL, Petros JA et al (2005) In vivo molecular and cellular imaging with quantum dots. Curr Opin Biotechnol 16(1):63–72
Michalet X, Pinaud FF, Bentolila LA et al (2005) Quantum dots for live cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostics. Science 307(5709):538–544
Xing Y, Rao J (2008) Quantum dot bioconjugates for in vitro diagnostics & in vivo imaging. Cancer Biomark 4(6):307–319
Sukhanova A, Devy M, Venteo L et al (2004) Biocompatible fluorescent nanocrystals for immunolabeling of membrane proteins and cells. Anal Biochem 324(1):60–67
Xing Y, Chaudry Q, Shen C et al (2007) Bioconjugated quantum dots for multiplexed and quantitative immunohistochemistry. Nat Protoc 2(5):1152–1165
Medintz IL, Clapp AR, Mattoussi H et al (2003) Selfassembled nanoscale biosensors based on quantum dot FRET donors. Nat Mater 2(9):630–638
Zhang CY, Hu J (2010) Single quantum dot-based nanosensor for multiple DNA detection. Anal Chem 82(5):1921–1927
Ebenstein Y, Gassman N, Kim S et al (2009) Lighting up individual DNA binding proteins with quantum dots. Nano Lett 9(4):1598–1603
Giraud G, Schulze H, Bachmann TT et al (2009) Fluorescence lifetime imaging of quantum dot labeled DNA microarrays. Int J Mol Sci 10(4):1930–1941
Liang RQ, Li W, Li Y et al (2005) An oligonucleotide microarray for microRNA expression analysis based on labeling RNA with quantum dot and nanogold probe. Nucleic Acids Res 33(2):e17
Shingyoji M, Gerion D, Pinkel D et al (2005) Quantum dots-based reverse phase protein microarray. Talanta 67(3):472–478
Zajac A, Song D, Qian W et al (2007) Protein microarrays and quantum dot probes for early cancer detection. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 58(2):309–314
Gokarna A, Jin LH, Hwang JS et al (2008) Quantum dot-based protein micro- and nanoarrays for detection of prostate cancer biomarkers. Proteomics 8(9):1809–1818
Han MY, Gao XH, Su JZ et al (2001) Quantum-dot-tagged microbeads for multiplexed optical coding of biomolecules. Nat Biotechnol 19:631–635
Zhao Y, Zhao X, Tang B et al (2010) Quantum-dot-tagged bioresponsive hydrogel suspension array for multiplex label-free DNA detection. Adv Funct Mater 20(6):976–982
Bae WK, Kwak J, Lim J et al (2009) Deep blue light-emitting diodes based on Cd1-xZnxS@ZnS quantum dots. Nanotechnology 20(7):075202
Cho KS, Lee EK, Joo WJ et al (2009) High-performance crosslinked colloidal quantum-dot light-emitting diodes. Nat Photonics 3:341–345
Sun Q, Wang YA, Li LS et al (2007) Bright, multicoloured light-emitting diodes based on quantum dots. Nat Photonics 1:717–722
Beard MC, Ellingson RJ (2008) Multiple exciton generation in semiconductor nanocrystals: toward efficient solar energy conversion. Laser Photonics Rev 2(5):377–399
Sablon KA, Little JW, Mitin V et al (2011) Strong enhancement of solar cell efficiency due to quantum dots with built-in charge. Nano Lett 11(6):2311–2317
Ardalan P, Brennan TP, Lee HB et al (2011) Effects of self-assembled monolayers on solid-state CdS quantum dot sensitized solar cells. ACS Nano 5(2):1495–1504
Kamat PV (2008) Quantum dot solar cells. Semiconductor nanocrystals as light harvesters. J Phys Chem C 112(48):18737–18753
Nizamoglu S, Ozel T, Sari E et al (2007) White light generation using CdSe/ZnS core-shell nanocrystals hybridized with InGaN/GaN light emitting diodes. Nanotechnology 18:065709
Yeh DM, Huang CF, Lu YC et al (2008) White-light light-emitting device based on surface plasmon-enhanced CdSe/ZnS nanocrystal wavelength conversion on a blue/green twocolor light-emitting diode. Appl Phys Lett 92(9):09112
Noone KM, Ginger DS (2009) Doping for speed: colloidal nanoparticles for thin-film optoelectronics. ACS Nano 3(2):261–265
Lee HJ, Yum JH, Leventis HC et al (2008) CdSe quantum dot-sensitized solar cells exceeding efficiency 1 % at full-sun intensity. J Phys Chem B 112(30):11600–11608
Kongkanand A, Tvrdy K, Takechi K et al (2008) Quantum dot solar cells. Tuning photoresponse through size and shape control of CdSe − TiO2 architecture. J Am Chem Soc 130(12):4007–4015
Tanaka K, Waki H, Ido Y et al (1988) Protein and polymer analyses up to m/z 100,000 by laser ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 2(8):151–153
Tanaka K (2003) The origin of macromolecule ionization by laser irradiation. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 42(33):3860–3870
Wei J, Buriak JM, Siuzdak G (1999) Desorption-ionization mass spectrometry on porous silicon. Nature 399(6733):243–246
Thomas JJ, Shen ZX, Crowell JE et al (2001) Desorption/ionization on silicon (DIOS): a diverse mass spectrometry platform for protein characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98(9):4932–4937
Lin YS, Chen YC (2002) Laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry on sol-gel derived 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid film. Anal Chem 74(22):5793–5798
Chen WY, Chen YC (2003) Reducing the alkali cation adductions of oligonucleotides using sol-gel-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 75(16):4223–4228
Lin YS, Yang CH, Chen YC (2004) Glass-chip-based sample preparation and on-chip trypic digestion for matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometric analysis using a sol-gel/2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid hybrid matrix. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 18(3):313–318
Chen CT, Chen YC (2004) Desorption/ionization mass spectrometry on nanocrystalline titania sol-gel-deposited films. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 18(17):1956–1964
Chen CT, Chen YC (2004) Molecularly imprinted TiO2-matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry for selectively detecting alpha-cyclodextrin. Anal Chem 76(5):1453–1457
Tang N, Tornatore P, Weinberger SR (2004) Current developments in SELDI affinity technology. Mass Spectrom Rev 23(1):34–44
Seibert V, Wiesner A, Buschmann T et al (2004) Surface-enhanced laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (SELDI TOF-MS) and ProteinChip technology in proteomics research. Pathol Res Pract 200(2):83–94
Berkenkamp S, Menzel C, Karas M et al (1997) Performance of infrared matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry with lasers emitting in the 3 um wavelength range. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 11(13):1399–1406
Kinumi T, Saisu T, Takayama M et al (2000) Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry using an inorganic particle matrix for small molecule analysis. J Mass Spectrom 35(3):417–422
Okuno S, Nakano M, Matsubayashi G et al (2004) Reduction of organic dyes in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization and desorption/ionization on porous silicon. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 18(23):2811–2817
Shrivas K, Wu HF (2008) Modified silver nanoparticle as a hydrophobic affinity probe for analysis of peptides and proteins in biological samples by using liquid-liquid microextraction coupled to AP-MALDI-ion trap and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 80(7):2583–2589
Shrivas K, Wu HF (2008) Applications of silver nanoparticles capped with different functional groups as the matrix and affinity probes in surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight and atmospheric pressure matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization ion trap mass spectrometry for rapid analysis of sulfur drugs and biothiols in human urine. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 22(18):2863–2872
Sudhir PR, Shrivas K, Zhou ZC et al (2008) Single drop microextraction using silver nanoparticles as electrostatic probes for peptide analysis in atmospheric pressure matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry and comparison with gold electrostatic probes and silver hydrophobic probes. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 22(19):3076–3086
Honda A, Sonobe H, Ogata A et al (2005) Improved method of the MALDI-TOF analysis of DNA with nanodot sample target plate. Chem Commun 42:5340–5342
Seino T, Sato H, Yamamoto A et al (2007) Matrix-free laser desorption/ionization-mass spectrometry using self-assembled germanium nanodots. Anal Chem 79(13):4827–4832
Bailes J, Vidal L, Ivanov DA et al (2009) Quantum dots improve peptide detection in MALDI MS in a size dependent manner. Nanobiotechnology 7:10
Shrivas K, Kailasa SK, Wu HF (2009) Quantum dots laser desorption/ionization MS: multifunctional CdSe quantum dots as the matrix, concentrating probes and acceleration for microwave enzymatic digestion for peptide analysis and high resolution detection of proteins in a linear MALDI-TOF MS. Proteomics 9(10):2656–2667
Liu CW, Chien MW, Chen GF et al (2011) Quantum dot enhancement of peptide detection by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 83(17):6593–6600
Finehout EJ, Cantor JR, Le KH (2005) Kinetic characterization of sequencing grade modified trypsin. Proteomics 5(9):2319–2321
Rivers J, Simpson DM, Robertson DH et al (2007) Absolute multiplexed quantitative analysis of protein expression during muscle development using QconCAT. Mol Cell Proteomics 6(8):1416–1427
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Bailes, J., Soloviev, M. (2012). The Application of Semiconductor Quantum Dots for Enhancing Peptide Desorption, Improving Peak Resolution and Sensitivity of Detection in Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization (MALDI) Mass Spectrometry. In: Soloviev, M. (eds) Nanoparticles in Biology and Medicine. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 906. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-953-2_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-953-2_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
Print ISBN: 978-1-61779-952-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-61779-953-2
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols