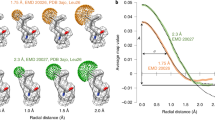
Abstract
Electron microscopy (EM) has made possible to solve the structure of many proteins. However, the resolution of some of the EM maps is too low for interpretation at the atomic level, which is particularly important to describe function. We describe methods that combine low-resolution EM data with atomic structures for different conformations of the same protein in order to produce atomic models compatible with the EM map.
We illustrate these methods with EM data from decavanadate-induced tubular crystals of a pseudo-phosphorylated intermediate of Ca-ATPase and the various atomic structures of other intermediates available in the Protein Data Bank (PDB). Determination of atomic structure permits not only to analyse protein–protein interactions in the crystals, but also to localize residues in the proximity of the crystallizing agent both within Ca-ATPase and between Ca-ATPase molecules.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Electron Microscopy Data Bank. http://www.emdatabank.org/
Volkmann N, Hanein D (1999) Quantitative fitting of atomic models into observed densities derived by electron microscopy. J Struct Biol 125:176–184
Roseman AM (2000) Docking structures of domains into maps from cryo-electron microscopy using local correlation. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 56:1332–1340
Rossmann MG (2000) Fitting atomic models into electron-microscopy maps. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 56:1341–1349
Wriggers W, Chacon P (2001) Modeling tricks and fitting techniques for multiresolution structures. Structure 9:779–788
Chacon P, Wriggers W (2002) Multi-resolution contour-based fitting of macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol 317:375–384
Navaza JJ, Lepault F, Rey A, Alvarez-Rua C, Borge J (2002) On the fitting of model electron densities into EM reconstructions: a reciprocal-space formulation. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 58:1820–1825
Wu X, Milne JLS, Borgnia MJ, Rostapshov AV, Subramaniam S, Brooks BR (2002) A core-weighted fitting method for docking atomic structures into low-resolution maps: application to cryo-electron microscopy. J Struct Biol 141:63–76
Tama F, Miyashita O, Brooks CL (2004) Flexible multi-scale fitting of atomic structures into low-resolution electron density maps with elastic network normal mode analysis. J Mol Biol 337:985–999
Hinsen K, Reuter N, Navaza J, Stokes DL, Lacapère J-J (2005) Normal mode-based fitting of atomic structure into electron density maps: application to sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase. Biophys J 88:818–827
Schröder GF, Brunger AT, Levitt M (2007) Combining efficient conformational sampling with a deformable elastic network model facilitates structure refinement at low resolution. Structure 15:1630–1641
Topf M, Lasker K, Webb B, Wolfson H, Chiu W, Sali A (2008) Protein structure fitting and refinement guided by cryo-EM density. Structure 16:295–307
Jolley CC, Wells SA, Fromme P, Thorpe MF (2008) Fitting low-resolution cryo-EM maps of proteins using constrained geometric simulations. Biophys J 94:1613–1621
Møller JV, Jull B, Le Maire M (1996) Structural organization, ion transport, and energy transduction of P-type ATPases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1286:1–51
Forge V, Mintz E, Guillain F (1993) Ca binding to sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase revisited. I. Mechanism of affinity and cooperativity modulation by H and Mg. J Biol Chem 268:10953–10960
Yu X, Carroll S, Rigaud J, Inesi G (1993) H countertransport and electrogenicity of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca pump in reconstituted proteoliposomes. Biophys J 64:1232–1242
Buoninsegni TF, Bartolommei G, Moncelli MR, Inesi G, Guidelli R (2004) Time-resolved charge translocation by sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase measured on a solid supported membrane. Biophys J 86:3671–3686
Stokes DL, Green NM (2003) Structure and function of the calcium pump. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 32:445–468
Toyoshima C, Inesi G (2004) Structural basis of ion pumping by Ca2+-ATPase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Biochem 73:269–92
Inesi G, Lewis DMH, Prasad A, Toyoshima C (2006) Concerted conformational effects of Ca and ATP are required for activation of sequential reactions in the Ca-ATPase (SERCA) catalytic cycle. Biochemistry 45:13769–13778
Toyoshima C, Nakasako M, Nomura H, Ogawa H (2000) Crystal structure of the calcium pump of sarcoplasmic reticulum at 2.6 Å resolution. Nature 405:647–655
Sorensen T, Moller JV, Nissen P (2004) Phosphoryl transfer and calcium ion occlusion in the calcium pump. Science 304:1672–1675
Toyoshima C, Mitzutani T (2004) Crystal structure of the calcium pump with a bond ATP analogue. Nature 430:529–535
Toyoshima C, Nomura H, Tsuda T (2004) Lumenal gating mechanism revealed in calcium pump crystal structures with phosphate analogues. Nature 432:361–368
Toyoshima C, Nomura H (2002) Structural changes in the calcium pump accompanying the dissociation of calcium. Nature 418:605–611
Obara K, Miyashita N, Xu C, Toyoshima I, Sugita Y, Inesi G, Toyoshima C (2005) Structural role of countertransport revealed in Ca-ATPase pump crystal structure in the absence of Ca. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:14489–14496
Jensen A-M, Sorensen T-L, Olesen C, Moller JV, Nissen P (2006) Modulatory and catalytic modes of ATP binding by the calcium pump. EMBO J 25:2305–2314
Olesen C, Sorensen T, Nielsen RK, Moller JV, Nissen P (2004) Dephosphorylation of the calcium pump coupled to counterion occlusion. Science 306:2251–2255
Toyoshima C, Sasabe H, Stokes DL (1993) Three-dimensional cryo-electron microscopy of the calcium ion pump in the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. Nature 362:467–471
Zhang P, Toyoshima C, Yonekura K, Green NM, Stokes DL (1998) Structure of the calcium pump from sarcoplasmic reticulum at 8 Å resolution. Nature 392:835–839
Xu C, Rice WJ, He W, Stokes DL (2002) A structural model for the catalytic cycle of Ca-ATPase. J Mol Biol 316:201–211
Stokes DL, Delavoie F, Rice WJ, Champeil P, McIntosh D, Lacapère J-J (2005) Structural studies of a stabilized phosphoenzyme intermediate of Ca-ATPase. J Biol Chem 280:18063–18072
McIntosh D, Montigny C, Champeil P (2008) Unexpected phosphoryl transfer from Asp351 to fluorescein attached to Lys515 in sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase. Biochemistry 47:6386–6393
Hinsen K (2000) The molecular modeling toolkit: a new approach to molecular simulations. J Comp Chem 21:79–85
Hinsen K, Petrescu AJ, Dellerue S, Bellissent-Funel M-C, Kneller GR (2000) Harmonicity in slow protein dynamics. Chem Phys 261:25–37
Hinsen K ScientificPython. http://dirac.cnrs-orleans.fr/ScientificPython/
Hinsen K, Thomas A, Field MJ (1999) Analysis of domain motions in large proteins. Proteins 34:369–382
Hinsen K DomainFinder. http://dirac.cnrs-orleans.fr/DomainFinder/
Reuter N, Hinsen K, Lacapere J-J (2003) Transconformations of the SERCA1 Ca-ATPase: a normal mode study. Biophys J 85:2186–2197
Ma H, Lewis D, Xu C, Inesi G, Toyoshima C (2005) Functional and structural roles of critical amino acids within the “N”, “P”, and “A” domains of the Ca-ATPase (SERCA) headpiece. Biochemistry 44:8090–8100
Clausen JD, McIntosh DB, Anthonisen AN, Woolley DG, Vilsen B, Andersen JP (2007) ATP-binding modes and functionally important interdomain bonds of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase revealed by mutation of glycine 438, glutamate 439, and arginine 678. J Biol Chem 282:20686–97
Ferreira da Silva JL, Minas da Piedade MF, Duarte MT (2003) Decavanadates: a building block for supramolecular assemblies. Inorganica Chim Acta 356:222–242
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank Professor D.L. Stokes for generously providing the EM map. This work was supported by CNRS (Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique) and CEA (Commissariat à l’Energie Atomique).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Hinsen, K., Beaumont, E., Fournier, B., Lacapère, JJ. (2010). From Electron Microscopy Maps to Atomic Structures Using Normal Mode-Based Fitting. In: Lacapère, JJ. (eds) Membrane Protein Structure Determination. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 654. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-762-4_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-762-4_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
Print ISBN: 978-1-60761-761-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-60761-762-4
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols