Abstract
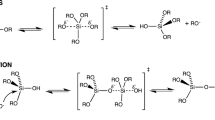
In recent years, fluorescent silica nanoparticles (FSNPs) received immense interest in cancer imaging. FSNPs are a new class of engineered optical probes consisting of silica NPs loaded with fluorescent dye molecules. These probes exhibit some attractive features, such as photostability and brightness, which allow sensitive imaging of cancer cells. In general, FSNPs are chemically synthesized in solution using appropriate silane-based precursors. Fluorescent dye molecules are entrapped during the synthesis process. The synthetic process involves hydrolysis and condensation reactions of silane precursors. Stöber’s sol–gel and water-in-oil (W/O) microemulsion methods are two popular chemical methods that have been used for synthesizing FSNPs. Silica matrix is capable of carrying hundreds of fluorescent dye molecules in each FSNP, resulting in bright fluorescence. In FSNPs, fluorescent molecules are somewhat protected by the surrounding silica layer, resulting in good photostability. For cancer cell imaging, surface modification of FSNPs is often necessary to obtain appropriate surface functional groups to improve NP aqueous dispersibility as well as bioconjugation capability. Using conventional bioconjugate chemistry, cancer cell-specific biomolecules are then attached to the surface-modified FSNPs. For targeting cancer cells, the FSNPs are often conjugated to specific biomolecules such as antibodies, aptamers, and folic acid. In this chapter, different approaches for the FSNP design will be discussed and some representative protocols for FSNP synthesis will be provided. We will also discuss FSNP surface modification and bioconjugation techniques that are useful for cancer cell imaging.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Herr, J. K., Smith, J. E., Medley, C. D., Shangguan, D. H., and Tan, W. H. (2006) Aptamer-conjugated nanoparticles for selective collection and detection of cancer cells. Anal Chem 78, 2918–2924.
Smith, J. E., Medley, C. D., Tang, Z. W., Shangguan, D., Lofton, C., and Tan, W. H. (2007) Aptamer-conjugated nanoparticles for the collection and detection of multiple cancer cells. Anal Chem 79, 3075–3082.
Trehin, R., Figueiredo, J. L., Pittet, M. J., Weissleder, R., Josephson, L., and Mahmood, U. (2006) Fluorescent nanoparticle uptake for brain tumor visualization. Neoplasia 8, 302–311.
Bagwe, R. P., Zhao, X. J., and Tan, W. H. (2003) Bioconjugated luminescent nanoparticles for biological applications. J Dispers Sci Technol 24, 453–464.
Santra, S., Xu, J. S., Wang, K. M. and Tan, W. H. (2004) Luminescent nanoparticle probes for bioimaging. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 4, 590–599.
Tan, W. H., Wang, K. M., He, X. X., Zhao, X. J., Drake, T., Wang, L., and Bagwe, R. P. (2004) Bionanotechnology based on silica nanoparticles. Med Res Rev 24, 621–638.
Yao, G., Wang, L., Wu, Y. R., Smith, J., Xu, J. S., Zhao, W. J., Lee, E. J., and Tan, W. H. (2006) FloDots: luminescent nanoparticles. Anal Bioanal Chem 385, 518–524.
He, X. X., Duan, J. H., Wang, K. M., Tan, W. H., Lin, X., and He, C. M. (2004) A novel fluorescent label based on organic dye-doped silica nanoparticles for HepG liver cancer cell recognition. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 4, 585–589.
Santra, S., Liesenfeld, B., Dutta, D., Chatel, D., Batich, C. D., Tan, W. H., Moudgil, B. M., and Mericle, R. A. (2005) Folate conjugated fluorescent silica nanoparticles for labeling neoplastic cells. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 5, 899–904.
Santra, S., Zhang, P., Wang, K. M., Tapec, R., and Tan, W. H. (2001) Conjugation of biomolecules with luminophore-doped silica nanoparticles for photostable biomarkers. Anal Chem 73, 4988–4993.
Brigger, I., Dubernet, C., and Couvreur, P. (2002) Nanoparticles in cancer therapy and diagnosis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 54, 631–51.
Reddy, G. R., Bhojani, M. S., McConville, P., Moody, J., Moffat, B. A., Hall, D. E., Kim, G., Koo, Y. E. L., Woolliscroft, M. J., Sugai, J. V., Johnson, T. D., Philbert, M. A., Kopelman, R., Rehemtulla, A., and Ross, B. D. (2006) Vascular targeted nanoparticles for imaging and treatment of brain tumors. Clin Cancer Res 12, 6677–6686.
van Vlerken, L. E. and Amiji, M. M. (2006) Multi-functional polymeric nanoparticles for tumour-targeted drug delivery. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 3, 205–216.
Bruchez, M., Moronne, M., Gin, P., Weiss, S., and Alivisatos, A. P. (1998) Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science 281, 2013–2016.
Chan, W. C. W., Maxwell, D. J., Gao, X. H., Bailey, R. E., Han, M. Y., and Nie, S. M. (2002) Luminescent quantum dots for multiplexed biological detection and imaging. Curr Opin Biotechnol 13, 40–46.
Gao, X. H., Yang, L. L., Petros, J. A., Marshal, F. F., Simons, J. W., and Nie, S. M. (2005) In vivo molecular and cellular imaging with quantum dots. Curr Opin Biotechnol 16, 63–72.
Smith, A. M., Ruan, G., Rhyner, M. N., and Nie, S. M. (2006) Engineering luminescent quantum dots for in vivo molecular and cellular imaging. Ann Biomed Eng 34, 3–14.
Wu, X. Y., Liu, H. J., Liu, J. Q., Haley, K. N., Treadway, J. A., Larson, J. P., Ge, N. F., Peale, F., and Bruchez, M. P. (2003) Immunofluorescent labeling of cancer marker Her2 and other cellular targets with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol 21, 41–46.
Alivisatos, A. P., Gu, W. W., and Larabell, C. (2005) Quantum dots as cellular probes. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 7, 55–76.
Medintz, I. L., Uyeda, H. T., Goldman, E. R., and Mattoussi, H. (2005) Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging, labelling and sensing. Nat Mater 4, 435–446.
Michalet, X., Pinaud, F. F., Bentolila, L. A., Tsay, J. M., Doose, S., Li, J. J., Sundaresan, G., Wu, A. M., Gambhir, S. S., and Weiss, S. (2005) Quantum dots for live cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostics. Science 307, 538–544.
Stroh, M., Zimmer, J. P., Duda, D. G., Levchenko, T. S., Cohen, K. S., Brown, E. B., Scadden, D. T., Torchilin, V. P., Bawendi, M. G., Fukumura, D., and Jain, R. K. (2005) Quantum dots spectrally distinguish multiple species within the tumor milieu in vivo. Nat Med 11, 678–682.
Wang, L., Yang, C. Y., and Tan, W. H. (2005) Dual-luminophore-doped silica nanoparticles for multiplexed signaling. Nano Lett 5, 37–43.
Wang, L., Zhao, W., and Tan, W. (2008) Bioconjugated silica nanoparticles: development and applications. Nano Res 1, 99–115.
Santra, S., Wang, K. M., Tapec, R., and Tan, W. H. (2001) Development of novel dye-doped silica nanoparticles for biomarker application. J Biomed Opt 6, 160–166.
Jin, Y. H., Kannan, S., Wu, M., and Zhao, J. X. J. (2007) Toxicity of luminescent silica nanoparticles to living cells. Chem Res Toxicol 20, 1126–1133.
Xue, Z. G., Liang, D. S., Li, Y. M., Long, Z. G., Pan, D. A., Liu, X. H., Wu, L. Q., Zhu, S. H., Cai, F., Dai, H. P., Tang, B. S., Xia, K., and Xia, J. H. (2005) Silica nanoparticle is a possible safe carrier for gene therapy. Chin Sci Bull 50, 2323–2327.
Charreyre, M. T., Yekta, A., Winnik, M. A., Delair, T., and Pichot, C. (1995) Fluorescence energy-transfer from fluorescein to tetramethylrhodamine covalently bound to the surface of polystyrene latex-particles. Langmuir 11, 2423–2428.
Charreyre, M. T., Zhang, P., Winnik, M. A., Pichot, C., and Graillat, C. (1995) Adsorption of rhodamine-60 onto polystyrene latex-particles with sulfate groups at the surface. J Colloid Interface Sci 170, 374–382.
Gao, H. F., Zhao, Y. Q., Fu, S. K., Li, B., and Li, M. Q. (2002) Preparation of a novel polymeric fluorescent nanoparticle. Colloid Polym Sci 280, 653–660.
Harma, H., Soukka, T., and Lovgren, T. (2001) Europium nanoparticles and time-resolved fluorescence for ultrasensitive detection of prostate-specific antigen. Clin Chem 47, 561–568.
Makarova, O. V., Ostafin, A. E., Miyoshi, H., Norris, J. R., and Meisel, D. (1999) Adsorption and encapsulation of fluorescent probes in nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B 103, 9080–9084.
Schlupen, J., Haegel, F. H., Kuhlmann, J., Geisler, H., and Schwuger, M. J. (1999) Sorption hysteresis of pyrene on zeolite. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 156, 335–347.
Bagwe, R. P., Yang, C. Y., Hilliard, L. R., and Tan, W. H. (2004) Optimization of dye-doped silica nanoparticles prepared using a reverse microemulsion method. Langmuir 20, 8336–8342.
Zhao, X. J., Bagwe, R. P., and Tan, W. H. (2004) Development of organic-dye-doped silica nanoparticles in a reverse microemulsion. Adv Mater 16, 173–176.
Tapec, R., Zhao, X. J. J., and Tan, W. H. (2002) Development of organic dye-doped silica nanoparticles for bioanalysis and biosensors. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 2, 405–409.
Wang, S. and Low, P. S. (1998) Folate-mediated targeting of antineoplastic drags, imaging agents, and nucleic acids to cancer cells. J Control Release 53, 39–48.
Zhao, X. J., Hilliard, L. R., Mechery, S. J., Wang, Y. P., Bagwe, R. P., Jin, S. G., and Tan, W. H. (2004) A rapid bioassay for single bacterial cell quantitation using bioconjugated nanoparticles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101, 15027–15032.
Ross, J. F., Chaudhuri, P. K., and Ratnam, M. (1994) Differential regulation of folate receptor isoforms in normal and malignant-tissues in-vivo and in established cell-lines – physiological and clinical implications. Cancer 73, 2432–2443.
Franklin, W. A., Waintrub, M., Edwards, D., Christensen, K., Prendegrast, P., Woods, J., Bunn, P. A., and Kolhouse, J. F. (1994) New anti-lung-cancer antibody cluster-12 reacts with human folate receptors present on adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer 89–95.
Lee, J. W., Lu, J. Y., Low, P. S., and Fuchs, P. L. (2002) Synthesis and evaluation of taxol-folic acid conjugates as targeted antineoplastics Bioorg Med Chem 10, 2397–2414.
Evans, C. O., Reddy, P., Brat, D. J., O'Neill, E. B., Craige, B., Stevens, V. L., and Oyesiku, N. M. (2003) Differential expression of folate receptor in pituitary adenomas. Cancer Res 63, 4218–4224.
Ke, C. Y., Mathias, C. J., and Green, M. A. (2003) The folate receptor as a molecular target for tumor-selective radionuclide delivery. Nucl Med Biol 30, 811–817.
Santra, S., Dutta, D., and Moudgil, B. M. (2005) Functional dye-doped silica nanoparticles for bioimaging, diagnostics and therapeutics. Food Bioprod Process 83, 136–140.
Santra, S., Yang, H., Dutta, D., Stanley, J. T., Holloway, P. H., Tan, W. H., Moudgil, B. M., and Mericle, R. A. (2004) TAT conjugated, FITC doped silica nanoparticles for bioimaging applications. Chem Commun 2810–2811.
Ellington, A. D. and Szostak, J. W. (1990) Invitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 346, 818–822.
Acknowledgments
This work has been partly supported by the grants, NSF CBET-63016011, NSF-NIRT EEC-0506560, and NIH 2P01HL059412-11A1. The author acknowledges Professor Weihong Tan and his research group (Department of Chemistry, University of Florida) for their contribution in the area of fluorescent dye-loaded silica nanoparticle technology. The author also acknowledges the kind help of Christine Malgoza for proofreading this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Santra, S. (2010). Fluorescent Silica Nanoparticles for Cancer Imaging. In: Grobmyer, S., Moudgil, B. (eds) Cancer Nanotechnology. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 624. Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-609-2_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-609-2_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press
Print ISBN: 978-1-60761-608-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-60761-609-2
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols