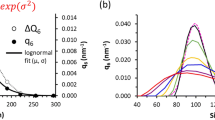
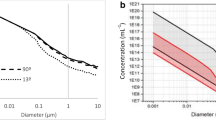
Abstract
Particle size characterization is of particular importance to nanomedicine. The size similarity of nanoparticles to biological moieties is believed to impart many of their unique medical properties. Here we present a method for sample preparation and the determination of mean nanoparticle size (hydrodynamic diameter) using batch-mode dynamic light scattering (DLS) in dilute aqueous suspensions. We then demonstrate this method for 30 nm colloidal gold.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dong, Q., Hurst, D., Weinmann, H., Chenevert, T., Londy, F. and Prince, M. (1998) Magnetic resonance angiography with gadomer-17. An animal study original investigation. Invest Radiol 33, 699–708.
Sato, N., Kobayashi, H. and Hiraga A. et al. (2001) Pharmacokinetics and enhancement patterns of macromolecular MR contrast agents with various sizes of polyamidoamine dendrimer cores. Magn Reson Med 46, 1169–1173.
Kobayashi, H. and Brechbiel, M. (2005) Nano-sized MRI contrast agents with dendrimer cores. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 57, 2271–2286.
ISO 13321:1996(E). Particle Size Analysis – Photon Correlation Spectroscopy. International Organization for Standardization (provides information and guidance on instrumentation, sample preparation, measurement, and data analysis – available for electronic purchase and download at http://www.iso.org/).
Lomakin, A., Teplow, D.B. and Benedek, G.B. (2005) Quasielastic light scattering for protein assembly study in Amyloid Proteins: Methods and Protocols, Methods in Molecular Biology, vol. 299 (edited by Sigurdsson, E.M.), Humana, Totowa, NJ, pp. 153–174.
Berne, J. and Pecora, R. (2000) Dynamic Light Scattering – with Applications to Chemistry, Biology, and Physics. Dover Publications, Mineola, NY.
ISO 22412:2008. Particle Size Analysis – Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS). Updates and extends ISO 13321:1996(E).
Santos, N.C. and Castanho, M.A.R.B. (1996) Teaching light scattering spectroscopy: the dimension and shape of tobacco mosaic virus. Biophys J 71, 1641–1646.
Finsy, R. (1994) Particle sizing by quasi-elastic light scattering. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 52, 79–143.
Brown, W. (ed.) (1993) Dynamic Light Scattering – The Method and Some Applications. Clarendon Press, Oxford, UK.
Johnsen, R.M. and Brown, W. (1992) An overview of current methods of analyzing QLS data in Laser Light Scattering in Biochemistry (edited by Harding, S.E., Sattelle, D.B. and Bloomfield, V.A.), The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, UK, pp. 78–91.
Weiner, B.B. and Tscharnuter, W.W. (1987) Uses and abuses of photon correlation spectroscopy in particle sizing in Particle Size Distribution: Assessment and Characterization (edited by Provder, T.), American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp. 49–61.
Morrison, I.D., Grabowski, E.F. and Herb, C.A. (1985) Improved techniques for particle size determination by quasi-elastic light scattering. Langmuir 1, 496–501.
Lide, D.R. (ed.). (2006) Concentrative properties of aqueous solutions: density, refractive index, freezing point depression, and viscosity in CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Internet Version 2006 (http://www.hbcpnetbase.com/), Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL.
Lemmon, E.W., McLinden, M.O. and Friend, D.G. (2005) Thermophysical properties of fluid systems in NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69 (edited by Linstrom, P.J. and Mallard, W.G.). National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg MD (http://www.webbook.nist.gov/).
IAPWS. (1997) Release on Refractive Index of Ordinary Water Substance as a Function of Wave length, Temperature and Pressure, International Association for the Properties of Water and Steam (IAPWS), Erlangen, Germany.
Acknowledgments
This project has been funded in whole or in part with federal funds from the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, under contract N01-CO-12400. The content of this publication does not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the Department of Health and Human Services, nor does mention of trade names, commercial products, or organizations imply endorsement by the U.S. Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Hackley, V.A., Clogston, J.D. (2011). Measuring the Hydrodynamic Size of Nanoparticles in Aqueous Media Using Batch-Mode Dynamic Light Scattering. In: McNeil, S. (eds) Characterization of Nanoparticles Intended for Drug Delivery. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 697. Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60327-198-1_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60327-198-1_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press
Print ISBN: 978-1-60327-197-4
Online ISBN: 978-1-60327-198-1
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols