Abstract
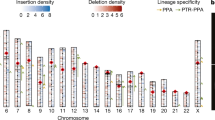
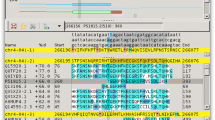
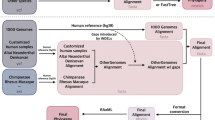
The UC Santa Cruz Genome Browser provides a number of resources that can be used for phylogenomic studies, including (1) whole-genome sequence data from a number of vertebrate species, (2) pairwise alignments of the human genome sequence to a number of other vertebrate genome, (3) a simultaneous alignment of 17 vertebrate genomes (most of them incompletely sequenced) that covers all of the human sequence, (4) several independent sets of multiple alignments covering 1% of the human genome (ENCODE regions), (5) extensive sequence annotation for interpreting those sequences and alignments, and (6) sequence, alignments, and annotations from certain other species, including an alignment of nine insect genomes. We illustrate the use of these resources in the context of assigning rare genomic changes to the branch of the phylogenetic tree where they appear to have occurred, or of looking for evidence supporting a particular possible tree topology. Sample source code for performing such studies is available.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rokas, A. and Holland, P. W. H. (2000) Rare genomic changes as a tool for phylogenetics. Trends Ecol. Evol. 15, 454–459.
Kent, W. J., Sugnet, C. W., Furey, T. S., et al. (2002) The human genome browser at UCSC. Genome Res. 12, 996–1006.
Hinrichs, A. S., Karolchik, D., Baertsch, R., et al. (2006) The UCSC genome browser database: update 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 34 (Database issue), D590–D598.
Karolchik, D., Baertsch, R., Diekhans, M., et al. (2003) The UCSC genome browser database. Nucleic Acids Res. 31, 51–54.
Murphy, W. J., Eizirik, E., Johnson, W. E., Zhang, Y. P., Ryder, O. A., and O’Brien, S. J. (2001) Molecular phylogenetics and the origins of placental mammals. Nature 409, 614–618.
Birney, E., Andrews, D., Caccamo, M., et al. (2006) Ensembl 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 34 (Database issue), D556–D561.
Wheeler, D. L., Church, D. M., Edgar, R., et al. (2004) Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information: update. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, D35–D40.
Giardine, B., Riemer, C., Hardison, R. C., et al. (2005) Galaxy: a platform for interactive large-scale genome analysis. Genome Res. 15, 1451–1455.
Karolchik, D., Hinrichs, A. S., Furey, T. S., et al. (2004) The UCSC Table Browser data retrieval tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 32(Suppl 1), D493–D496.
Blanchette, M., Green, E., Miller, W., and Haussler, D. (2004) Reconstructing large regions of an ancestral mammalian genome in silico. Genome Res. 14, 2412–2423.
The ENCODE Project Consortium (2004) The ENCODE (ENCyclopedia of DNA Elements) project. Science 306, 636–640.
Thomas, J. W., Touchman, J. W., Blakesley, R. W., et al. (2003) Comparative analyses of multi-species sequences from targeted genomic regions. Nature 424, 788–793.
Schwartz, S., Elnitski, E., Li, M., et al. (2003) MultiPipMaker and supporting tools: alignments and analysis of multiple genomic DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 31, 3518–3524.
Waterston, R. H., et al. (2002) Initial sequencing and comparative analysis of the mouse genome. Nature 420, 520–562.
Schwartz, S., Kent, W. J., Smit, A., et al. (2003) Human-mouse alignments with blastz. Genome Res. 13, 103–107.
De Jong, W. W., van Dijk, M. A. M., Poux, C., Kappe, G., van Rheede, T., and Madsen, O. (2003) Indels in protein-coding sequences of Euarchontoglires constrain the rooting of the eutherian tree. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 28, 328–340.
Poux, C., van Rheede, T., Madsen, O., and de Jong, W. W. (2002) Sequence gaps join mice and men: phylogenetic evidence from deletions in two proteins. Mol. Biol. Evol. 19, 2035–2037.
Dobzhansky, T. and Sturtevant, A. H. (1938) Inversions in the chromosomes of Drosophila pseudoobscura. Genetics 23, 28–64.
Dobzhansky, T. (1944) Chromosomal races in Drosophila pseudoobscura and Drosophila persimilis. Carnegie Inst. Washington Publ. 554, 47–144.
Anderson, W. W., Arnold, J., Baldwin, D. G., et al. (1991) Four decades of inversion polymorphism in Drosophila pseudoobscura. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 88, 10,367–10,371.
Sperlich, D. and Pfriem, P. (1986) Chromosomal polymorphism in natural and experimental populations. In: The Genetics and Biology of Drosophila, 3rd edition (Ashburner, M., Carson, H. L., and Thomson, J. N., eds), pp. 257–309, Academic, New York.
Richards, S., Liu, Y., Bettencourt, B. R., et al. (2005) Comparative genome sequencing of Drosophila pseudoobscura: chromosomal, gene and cis-element evolution. Genome Res. 15, 1–18.
Stolc, V., Gauhar, Z., Mason, C., et al. (2004) A gene expression map for the euchromatic genome of Drosophila melanogaster. Science 306, 655–660.
Kriegs, J. O., Churakow, G., Kiefmann, M., Jordan, U., Brosius, J., and Schmitz, J. (2006) Retroposed elements as archives for the evolutionary history of placental mammals. PLoS Biol. 4, e91.
Nishihara, H., Hasegawa, M., and Okada, N. (2006) Pegasoferae, an unexpected mammalian clade revealed by tracking ancient retroposon insertions. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. U S A 103, 9929–9934.
Murphy, W. J., Pringle, T. H., Crider, T., Springer, M. S., and Miller, W. (2006) Using genomic data to unravel the root of the placental mammal phylogeny. Submitted.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2008 Humana Press Inc., Totowa, NJ
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Rosenbloom, K., Taylor, J., Schaeffer, S., Kent, J., Haussler, D., Miller, W. (2008). Phylogenomic Resources at the UCSC Genome Browser. In: Murphy, W.J. (eds) Phylogenomics. Methods in Molecular Biology™, vol 422. Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-581-7_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-581-7_9
Publisher Name: Humana Press
Print ISBN: 978-1-58829-764-8
Online ISBN: 978-1-59745-581-7
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols