Abstract
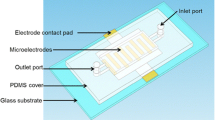
An on-chip whole-cell bioassay has been carried out using Escherichia coli tester strains for genotoxicity. In this assay format, the mutagen-responsive bioluminescence (BL) strains are immobilized in a chip assembly in which a silicon chip is placed between two poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) chips. In the chip assembly, microchannels fabricated on the two separate PDMS layers are connected via perforated microwells on the Si chip, and thus a three-dimensional microfluidic network is constructed. The strains mixed with agarose are loaded from the channels on one of the two PDMS layers into the wells on Si chip, followed by gelation. Induction of the expression of firefly luciferase in the tester strains and BL reaction are successively carried out by filling the channels on another PDMS layer with samples containing inducer (genotoxic substance) and then adenosine triphosphate/luciferin mixture, respectively. BL emission from each of the wells can be monitored by using a charge-coupled device camera to obtain an overall picture of the chip. The on-chip format based on a three-dimensional microfluidic network provides a combinatorial bioassay for multiple samples with multiple tester strains in a simple chip assembly. Thus, the presented method could be applied not only to various microbial sensing applications but also to other (bio)chemical analyses.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ames, B. N., McCann, J., and Yamasaki, E. (1975) Methods for detecting carcinogens and mutagens with the Salmonella/mammalian-microsome mutagenicity test. Mutat. Res. 31, 347–364.
Wegrzyn, G. and Czyz, A. (2003) Detection of mutagenic pollution of natural environment using microbiological assays. J. Appl. Microbiol. 95, 1175–1178.
Aryal, P., Terashita, T., Guengerich, F. P., Shimada, T., and Oda, Y. (2000) Use of genetically engineered Salmonella typhimurium OY1002/1A2 strain coexpressing human cytochrome P450 1A2 and NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase and bacterial O-acetyltransferase in SOS/umu assay. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 36, 121–126.
Baldi, P. and Hatfield, G. W. (2002) DNA Microarrays and Gene Expression: From Experiments to Data Analysis and Modeling, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
Baba, Y., Shoji, S., and van der Berg, A. (eds.) (2003) Micro Total Analysis Systems 2002, Volume 1 and; Proceedings of the µ TAS 2002 Symposium, Kluwer, Norwell, MA.
Tani, H., Maehana, K., and Kamidate, T. (2004) Chip-based bioassay using bacterial sensor strains immobilized in three-dimensional microfluidic network. Anal. Chem. 76, 6693–6697.
Bernard, A., Michel, B., and Delamarche, E. (2001) Micromosaic immunoassays. Anal. Chem. 73, 8–12.
Maehana, K., Tani, H., Shiba, T., and Kamidate, T. (2004) Effects of using a low-copy plasmid and controlling membrane permeability in SOS-based genotoxic bioassay. Anal. Chim. Acta 522, 189–195.
Maehana, K., Tani, H., and Kamidate, T. (2006) On-chip genotoxic bioassay based on bioluminescence reporter system using three-dimensional microfluidic network. Anal. Chim. Acta 560, 24–29.
Friedberg, E. C., Walker, G. C., and Siede, W. (1995) SOS response and DNA damage tolerance in prokaryotes, in DNA Repair and Mutagenesis, ASM Press, Washington, DC.
Fralick, J. A. (1996) Evidence that TolC is required for functioning of the Mar/AcrAB efflux pump of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 178, 5803–5805.
McDonald, J. C. and Whitesides, G. M. (2002) Poly(dimethylsiloxane) as a material for fabricating microfluidic devices. Acc. Chem. Res. 35, 491–499.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Humana Press Inc., Totowa, NJ
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Tani, H., Maehana, K., Kamidate, T. (2007). On-Chip Bioassay Using Immobilized Sensing Bacteria in Three-Dimensional Microfluidic Network. In: Floriano, P.N. (eds) Microchip-Based Assay Systems. Methods in Molecular Biology™, vol 385. Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-426-1_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-426-1_4
Publisher Name: Humana Press
Print ISBN: 978-1-58829-588-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-59745-426-1
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols