Abstract
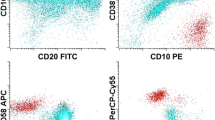
Flow-cytometric demonstration of the typical chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) immunophenotype is vital for diagnosis. CLL has a characteristic immunophenotype, expressing CD5, CD19, dim CD20, dim CD22, CD23, bright CD43, dim CD45, dim to negative CD79b, dim CD81, CD200, and dim monoclonal surface immunoglobulin. This characteristic immunophenotype allows a definitive diagnosis and the ruling out of another leukemia or lymphoma. Flow cytometry also provides important prognostic information and accurate assessment of response to therapy. Here we describe optimal specimen collection, red cell lysis, appropriate panel, cell staining, acquisition on a flow cytometer, and analysis for CLL specimens.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campo E, Ghia P, Montserrat E et al (2017) Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma. In: Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Pileri SA, Jaffe ES, Stein H, Thiele J et al (eds) WHO classification of tumours of hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues, 4th edn. IRAC, Lyon, pp 216–221
Rawstron AC, Villamor N, Ritgen M et al (2007) International standardized approach for flow cytometric residual disease monitoring in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Leukemia 21(5):956–964. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404584
Muller-Hermelink HKME, Catovsky D, Campo E, Harris NL, Stien H (2007) Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma. WHO classification of hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. IARC, Lyon
Alapat D, Coviello-Malle J, Owens R et al (2012) Diagnostic usefulness and prognostic impact of CD200 expression in lymphoid malignancies and plasma cell myeloma. Am J Clin Pathol 137(1):93–100. https://doi.org/10.1309/ajcp59uorcyzevqo
Marti G, Rawstron AC, Ghia P, Hillmen P, Houlston RS, Kay N, Aurran Schleinitz T, Caporaso N, on behalf of The International Familial CLL Consortium (2005) Diagnostic criteria for monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis (MBL). Br J Haematol 130:325–332
Ahmad E, Steinberg SM, Goldin L, Hess CJ, Caporaso N, Kreitman RJ, Wiestner A, Wilson W, White T, Marti G, Stetler-Stevenson M (2008) Immunophenotypic features distinguishing familial chronic lymphocytic leukemia from sporadic chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 74:221–226
Kingma DW, Imus P, Xie XY, Jasper G, Sorbara L, Stewart C, Stetler-Stevenson M (2002) CD2 is expressed by a sub-population of normal B cells and is frequently present in mature B cell neoplasms. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 50:243–248
Kampalath B, Barcos MP, Stewart C (2003) Phenotypic heterogeneity of B cells in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma. Am J Clin Pathol 119(6):824–832. https://doi.org/10.1309/4agut3lkeurd7t7k
Damle R, Wasil T, Fais F et al (1999) Ig V gene mutation status and CD38 expression as novel prognostic indicators in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 94:1840–1847
Durig J, Naschar M, Schmucker U, Renzing-Kohler K, Holter A, Huttmann T, Duhrsen U (2002) CD38 expression is an important prognostic marker in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Leukemia 16:30–35
Hamblin TJ, Orchard JA, Ibotson RE et al (2002) CD38 expression and immunoglobulin variable region mutations are independent prognostic variables in chronic lymphocytic leukemia but CD38 expression may vary during the course of the disease. Blood 99:1023–1029
Bulian P, Shanafelt TD, Fegan C et al (2014) CD49d is the strongest flow cytometry-based predictor of overall survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 32(9):897–904. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2013.50.8515
Chiorazzi N (2012) Implications of new prognostic markers in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2012:76–87. https://doi.org/10.1182/asheducation-2012.1.76
Gattei V, Bulian P, Del Principe MI et al (2008) Relevance of CD49d protein expression as overall survival and progressive disease prognosticator in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 111(2):865–873. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2007-05-092486
Gooden CE, Jones P, Bates R et al (2018) CD49d shows superior performance characteristics for flow cytometric prognostic testing in chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 94(1):129–135. https://doi.org/10.1002/cyto.b.21384
Rawstron AC, Kennedy B, Evans PA et al (2001) Quantitation of minimal disease levels in chronic lymphocytic leukemia using a sensitive flow cytometric assay improves the prediction of outcome and can be used to optimize therapy. Blood 98:29–35
Moreton P, Kennedy B, Lucas G et al (2005) Eradication of minimal residual disease in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia after alemtuzumab therapy is associated with prolonged survival. J Clin Oncol 23(13):2971–2979. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2005.04.021
Wayne P (2007) Clinical flow Cytometric analysis of neoplastic Hematolymphoid cells; approved guideline, 2nd ed. CLSI document H43-A2, 2nd edn. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne
Stelzer GT, Marti G, Hurley A et al (1997) U.S.-Canadian consensus recommendations on the immunophenotypic analysis of hematologic neoplasia by flow cytometry: standardization and validation of laboratory procedures. Cytometry 30(5):214–230
Cadena-Herrera D, Esparza-De Lara JE, Ramirez-Ibanez ND et al (2015) Validation of three viable-cell counting methods: manual, semi-automated, and automated. Biotechnol Rep (Amst) 7:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2015.04.004
Rawstron AC, Bottcher S, Letestu R et al (2013) Improving efficiency and sensitivity: European research initiative in CLL (ERIC) update on the international harmonised approach for flow cytometric residual disease monitoring in CLL. Leukemia 27(1):142–149. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.216
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Salem, D.A., Stetler-Stevenson, M. (2019). Clinical Flow-Cytometric Testing in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. In: McCoy, Jr, J. (eds) Immunophenotyping. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2032. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9650-6_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9650-6_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-9649-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-9650-6
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols