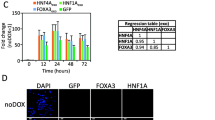
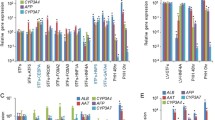
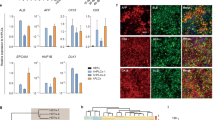
Abstract
Primary hepatocytes are widely used in regenerative medicine, drug metabolism analysis, and in vitro drug screens. To overcome the shortage of liver donors, several strategies, such as differentiation of pluripotent stem cells and transdifferentiation from somatic cells, were developed to generate hepatocytes from alternative sources. Here, we describe in detail lenti-virus-based procedure for direct conversion of human fibroblasts to hepatocytes (hiHep cells) in vitro. A detailed protocol for preparation of human fibroblasts from scar tissues is also provided. Based on this protocol, FOXA3, HNF1A, and HNF4A are introduced into SV40-large-T-antigen-expressing human scar fibroblasts by lenti-virus. It usually takes about 5–7 days to get epithelial hiHep colonies. SV40-large-T-antigen-expressing hiHep (hiHepLT) cells are proliferative and can be expanded to a large number for potential uses.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scarpelli DG, Rao MS (1981) Differentiation of regenerating pancreatic cells into hepatocyte-like cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 78(4):2577–2581
Shen CN, Horb ME, Slack JM, Tosh D (2003) Transdifferentiation of pancreas to liver. Mech Dev 120(1):107–116
Reddy JK, Rao MS, Qureshi SA, Reddy MK, Scarpelli DG, Lalwani ND (1984) Induction and origin of hepatocytes in rat pancreas. J Cell Biol 98(6):2082–2090
Shen CN, Slack JM, Tosh D (2000) Molecular basis of transdifferentiation of pancreas to liver. Nat Cell Biol 2(12):879–887. https://doi.org/10.1038/35046522
Huang P, He Z, Ji S, Sun H, Xiang D, Liu C, Hu Y, Wang X, Hui L (2011) Induction of functional hepatocyte-like cells from mouse fibroblasts by defined factors. Nature 475(7356):386–389. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10116
Huang P, Zhang L, Gao Y, He Z, Yao D, Wu Z, Cen J, Chen X, Liu C, Hu Y, Lai D, Hu Z, Chen L, Zhang Y, Cheng X, Ma X, Pan G, Wang X, Hui L (2014) Direct reprogramming of human fibroblasts to functional and expandable hepatocytes. Cell Stem Cell 14(3):370–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2014.01.003
Shi XL, Gao YM, Yan YP, Ma HC, Sun LL, Huang PY, Ni X, Zhang LD, Zhao X, Ren HZ, Hu D, Zhou Y, Tian F, Ji Y, Cheng X, Pan GY, Ding YT, Hui LJ (2016) Improved survival of porcine acute liver failure by a bioartificial liver device implanted with induced human functional hepatocytes. Cell Res 26(2):206–216. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2016.6
Zhou T, Benda C, Dunzinger S, Huang YH, Ho JC, Yang JY, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Zhuang Q, Li YH, Bao XC, Tse HF, Grillari J, Grillari-Voglauer R, Pei DQ, Esteban MA (2012) Generation of human induced pluripotent stem cells from urine samples. Nat Protoc 7(12):2080–2089. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2012.115
Gao Y, Zhang X, Zhang L, Cen J, Ni X, Liao X, Yang C, Li Y, Chen X, Zhang Z, Shu Y, Cheng X, Hay DC, Lai D, Pan G, Wei G, Hui L (2017) Distinct gene expression and epigenetic signatures in hepatocyte-like cells produced by different strategies from the same donor. Stem Cell Reports 9(6):1813–1824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.10.019
Du Y, Wang J, Jia J, Song N, Xiang C, Xu J, Hou Z, Su X, Liu B, Jiang T, Zhao D, Sun Y, Shu J, Guo Q, Yin M, Sun D, Lu S, Shi Y, Deng H (2014) Human hepatocytes with drug metabolic function induced from fibroblasts by lineage reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell 14(3):394–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2014.01.008
Ji S, Zhu L, Gao Y, Zhang X, Yan Y, Cen J, Li R, Zeng R, Liao L, Hou C, Gao Y, Gao S, Wei G, Hui L (2017) Baf60b-mediated ATM-p53 activation blocks cell identity conversion by sensing chromatin opening. Cell Res 27(5):642–656. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2017.36
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Huang, P., Sun, L., Zhang, L., Hui, L. (2019). Conversion of Fibroblasts to Hepatocytes In Vitro. In: Tanimizu, N. (eds) Hepatic Stem Cells . Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1905. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8961-4_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8961-4_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-8960-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-8961-4
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols