Abstract
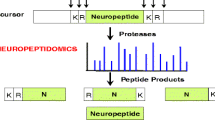
Peptidomic techniques are powerful tools to identify peptides in a biological sample. This protocol describes a targeted peptidomic approach that uses affinity chromatography to purify peptides that are substrates of carboxypeptidase E (CPE), an enzyme present in the secretory pathway of neuroendocrine cells. Many CPE products function as neuropeptides and/or peptide hormones, and therefore represent an important subset of the peptidome. Because CPE removes C-terminal Lys and Arg residues from peptide-processing intermediates, organisms lacking CPE show a large decrease in the levels of the mature forms of most neuropeptides and peptide hormones, and a very large increase in the levels of the processing intermediates that contain C-terminal Lys and/or Arg (i.e., the CPE substrates). These CPE substrates can be purified on an anhydrotrypsin-agarose affinity resin, which specifically binds peptides with C-terminal basic residues. Not all peptides with basic C-terminal residues within a cell are CPE substrates, and these other peptides will also be purified on the anhydrotrypsin affinity column. However, a comparison of peptides purified from wild-type mice and from mice lacking CPE allows for the rapid identification of CPE substrates based on their large increase in the absence of CPE.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fricker LD (2012) In: Fricker LD, Devi L (eds) Neuropeptides and other bioactive peptides. Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences, Charleston, SC
Fuller RS, Sterne RE, Thorner J (1988) Enzymes required for yeast prohormone processing. Ann Rev Physiol 50:345–362
Bayliss WM, Starling EH (1902) The mechanism of pancreatic secretion. J Physiol 28:325–353
Andren PE, Caprioli RM (1999) Determination of extracellular release of neurotensin in discrete rat brain regions utilizing in vivo microdialysis/electrospray mass spectrometry. Brain Res 845:123–129
Garden RW, Shippy SA, Li L et al (1998) Proteolytic processing of the Aplysia egg-laying hormone prohormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:3972–3977
Fricker LD (2010) Analysis of mouse brain peptides using mass spectrometry-based peptidomics: implications for novel functions ranging from non-classical neuropeptides to microproteins. Mol Biosyst 6:1355–1365
Fricker LD, Gelman JS, Castro LM et al (2012) Peptidomic analysis of HEK293T cells: effect of the proteasome inhibitor epoxomicin on intracellular peptides. J Proteome Res 11:1981–1990
Ferro ES, Hyslop S, Camargo AC (2004) Intracellular peptides as putative natural regulators of protein interactions. J Neurochem 91:769–777
Fricker LD, Snyder SH (1982) Enkephalin convertase: purification and characterization of a specific enkephalin-synthesizing carboxypeptidase localized to adrenal chromaffin granules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 79:3886–3890
Eipper BA, Mains RE (1988) Peptide alpha-amidation. Ann Rev Physiol 50:333–344
Varlamov O, Leiter EH, Fricker LD (1996) Induced and spontaneous mutations at Ser202 of carboxypeptidase E: effect on enzyme expression, activity, and intracellular routing. J Biol Chem 271:13981–13986
Naggert JK, Fricker LD, Varlamov O et al (1995) Hyperproinsulinemia in obese fat/fat mice associated with a point mutation in the carboxypeptidase E gene and reduced carboxypeptidase E activity in the pancreatic islets. Nat Genet 10:135–142
Rodriguiz RM, Wilkins JJ, Creson TK et al (2013) Emergence of anxiety-like behaviours in depressive-like Cpe(fat/fat) mice. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 16:1623–1634
Zhang X, Che FY, Berezniuk I et al (2008) Peptidomics of Cpe(fat/fat) mouse brain regions: implications for neuropeptide processing. J Neurochem 107:1596–1613
Che FY, Yan L, Li H et al (2001) Identification of peptides from brain and pituitary of Cpe fat/Cpe fat mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:9971–9976
Fricker LD, McKinzie AA, Sun J et al (2000) Identification and characterization of proSAAS, a granin-like neuroendocrine peptide precursor that inhibits prohormone processing. J Neurosci 20:639–648
Jacob TC, Kaplan JM (2003) The EGL-21 carboxypeptidase E facilitates acetylcholine release at Caenorhabditis elegans neuromuscular junctions. J Neurosci 23:2122–2130
Husson SJ, Janssen T, Baggerman G et al (2007) Impaired processing of FLP and NLP peptides in carboxypeptidase E (EGL-21)-deficient Caenorhabditis elegans as analyzed by mass spectrometry. J Neurochem 102:246–260
Zasloff M (1992) Antibiotic peptides as mediators of innate immunity. Curr Opin Immunol 4:3–7
Che FY, Lim J, Biswas R et al (2005) Quantitative neuropeptidomics of microwave-irradiated mouse brain and pituitary. Mol Cell Proteomics 4:1391–1405
Refojo D, Kovalovsky D, Young JI et al (2002) Increased splenocyte proliferative response and cytokine production in beta-endorphin-deficient mice. J Neuroimmunol 131:126–134
Svensson M, Skold K, Svenningsson P et al (2003) Peptidomics-based discovery of novel neuropeptides. J Proteome Res 2:213–219
Skold K, Svensson M, Norrman M et al (2007) The significance of biochemical and molecular sample integrity in brain proteomics and peptidomics: stathmin 2-20 and peptides as sample quality indicators. Proteomics 7:4445–4456
Scholz B, Skold K, Kultima K et al (2011) Impact of temperature dependent sampling procedures in proteomics and peptidomics—a characterization of the liver and pancreas post mortem degradome. Mol Cell Proteomics 10:M900229MCP900200
Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ (2001) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic, San Diego
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Fricker, L. (2018). Affinity Purification of Neuropeptide Precursors from Mice Lacking Carboxypeptidase E Activity. In: Schrader, M., Fricker, L. (eds) Peptidomics. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1719. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7537-2_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7537-2_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-7536-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-7537-2
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols