Abstract
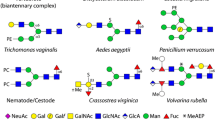
N-glycans from invertebrates and protists have often unusual structures which present analytical challenges. Both core and antennal modifications can be quite different from the more familiar vertebrate glycan motifs; thereby, contrary to the concept that “simple” organisms have “simple” N-glycans, rather complex oligosaccharides structures, including zwitterionic and anionic ones, have been found in a range of species. Thus, to facilitate the optimized elucidation of the maximal possible range of structures, the analytical workflow for glycomics of these organisms should include sequential release and fractionation steps. Peptide:N-glycosidase F is sufficient to isolate N-glycans from fungi and some protists, but in most invertebrates core α1,3-fucose is present, so release of the glycans from glycopeptides with peptide:N-glycosidases A is required. Subsequent solid-phase extraction with graphitized carbon and reversed phase resins enables different classes of N-glycans to be separated prior to high-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS). Depending on the types and numbers of glycans present, either reversed- or normal-phase HPLC (or both in series) enable even single isomeric or isobaric structures to be separated prior to MALDI-TOF MS and MS/MS. The use of enzymatic or chemical treatments allows further insights to be gained, although some glycan modifications (especially methylation) are resistant. Using a battery of methods, sometimes up to 100 structures from a single organism can be assigned, a complexity which raises evolutionary questions regarding the function of these glycans.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schachter H (2009) Paucimannose N-glycans in Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila melanogaster. Carbohydr Res 344:1391–1396
Sabotič J, Ohm RA, Künzler M (2015) Entomotoxic and nematotoxic lectins and protease inhibitors from fungal fruiting bodies. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:91–111
Rodrigues JA, Acosta-Serrano A, Aebi M, Ferguson MA, Routier FH, Schiller I, Soares S, Spencer D, Titz A, Wilson IB, Izquierdo L (2015) Parasite glycobiology: a bittersweet symphony. PLoS Pathog 11, e1005169
Samuelson J, Banerjee S, Magnelli P, Cui J, Kelleher DJ, Gilmore R, Robbins PW (2005) The diversity of dolichol-linked precursors to Asn-linked glycans likely results from secondary loss of sets of glycosyltransferases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:1548–1553
Schiller B, Hykollari A, Yan S, Paschinger K, Wilson IBH (2012) Complicated N-linked glycans in simple organisms. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler 393:661–673
Paschinger K, Hykollari A, Razzazi-Fazeli E, Greenwell P, Leitsch D, Walochnik J, Wilson IBH (2012) The N-glycans of Trichomonas vaginalis contain variable core and antennal modifications. Glycobiology 22:300–313
Schiller B, Makrypidi G, Razzazi-Fazeli E, Paschinger K, Walochnik J, Wilson IBH (2012) Exploring the unique N-glycome of the opportunistic human pathogen Acanthamoeba. J Biol Chem 287:43191–43204
Hykollari A, Balog CI, Rendić D, Braulke T, Wilson IBH, Paschinger K (2013) Mass spectrometric analysis of neutral and anionic N-glycans from a Dictyostelium discoideum model for human congenital disorder of glycosylation CDG IL. J Proteome Res 12:1173–1187
Hykollari A, Dragosits M, Rendić D, Wilson IBH, Paschinger K (2014) N-glycomic profiling of a glucosidase II mutant of Dictyostelium discoideum by “off-line” liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. Electrophoresis 35:2116–2129
Hykollari A, Eckmair B, Voglmeir J, Jin C, Yan S, Vanbeselaere J, Razzazi-Fazeli E, Wilson IBH, Paschinger K (2016) More than just oligomannose: an N-glycomic comparison of Penicillium species. Mol Cell Proteomics 15:73–92
Kurz S, Jin C, Hykollari A, Gregorich D, Giomarelli B, Vasta GR, Wilson IBH, Paschinger K (2013) Haemocytes and plasma of the eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica) display a diverse repertoire of sulphated and blood group A-modified N-glycans. J Biol Chem 288:24410–24428
Eckmair B, Jin C, Abed-Navandi D, Paschinger K (2016) Multi-step fractionation and mass spectrometry reveals zwitterionic and anionic modifications of the N- and O-glycans of a marine snail. Mol Cell Proteomics 15(2):573–97. doi:10.1074/mcp.M1115.051573
Kurz S, Aoki K, Jin C, Karlsson NG, Tiemeyer M, Wilson IB, Paschinger K (2015) Targetted release and fractionation reveal glucuronylated and sulphated N- and O-glycans in larvae of dipteran insects. J Proteomics 126:172–188
Yan S, Brecker L, Jin C, Titz A, Dragosits M, Karlsson N, Jantsch V, Wilson IBH, Paschinger K (2015) Bisecting galactose as a feature of N-glycans of wild-type and mutant Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Cell Proteomics 14:2111–2125
Yan S, Jin C, Wilson IBH, Paschinger K (2015) Comparisons of Caenorhabditis fucosyltransferase mutants reveal a multiplicity of isomeric N-glycan structures. J Proteome Res 14:5291–5305
Paschinger K, Wilson IBH (2015) Two types of galactosylated fucose motifs are present on N-glycans of Haemonchus contortus. Glycobiology 25:585–590
Wilson IBH, Paschinger K (2016) Sweet secrets of a therapeutic worm: mass spectrometric N-glycomic analysis of Trichuris suis. Anal Bioanal Chem 408:461–471
Dragosits M, Pflugl S, Kurz S, Razzazi-Fazeli E, Wilson IBH, Rendić D (2014) Recombinant Aspergillus β-galactosidases as a robust glycomic and biotechnological tool. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:3553–3567
Dragosits M, Yan S, Razzazi-Fazeli E, Wilson IBH, Rendić D (2015) Enzymatic properties and subtle differences in the substrate specificity of phylogenetically distinct invertebrate N-glycan processing hexosaminidases. Glycobiology 25:448–464
Iskratsch T, Braun A, Paschinger K, Wilson IBH (2009) Specificity analysis of lectins and antibodies using remodeled glycoproteins. Anal Biochem 386:133–146
Neville DC, Dwek RA, Butters TD (2009) Development of a single column method for the separation of lipid- and protein-derived oligosaccharides. J Proteome Res 8:681–687
Pöltl G, Kerner D, Paschinger K, Wilson IBH (2007) N-Glycans of the porcine nematode parasite Ascaris suum are modified with phosphorylcholine and core fucose residues. FEBS J 274:714–726
Tretter V, Altmann F, März L (1991) Peptide-N 4-(N-acetyl-β-glucosaminyl)asparagine amidase F cannot release glycans with fucose attached α1 → 3 to the asparagine-linked N-acetylglucosamine residue. Eur J Biochem 199:647–652
Paschinger K, Gonzalez-Sapienza GG, Wilson IBH (2012) Mass spectrometric analysis of the immunodominant glycan epitope of Echinococcus granulosus antigen Ag5. Int J Parasitol 42:279–285
Hase S, Ibuki T, Ikenaka T (1984) Reexamination of the pyridylamination used for fluorescence labelling of oligosaccharides and its application to glycoproteins. J Biochem 95:197–203
Song X, Xia B, Stowell SR, Lasanajak Y, Smith DF, Cummings RD (2009) Novel fluorescent glycan microarray strategy reveals ligands for galectins. Chem Biol 16:36–47
Yan S, Wilson IBH, Paschinger K (2015) Comparison of RP-HPLC modes to analyse the N-glycome of the free-living nematode Pristionchus pacificus. Electrophoresis 36:1314–1329
Selman MH, Hoffmann M, Zauner G, McDonnell LA, Balog CI, Rapp E, Deelder AM, Wuhrer M (2012) MALDI-TOF-MS analysis of sialylated glycans and glycopeptides using 4-chloro-alpha-cyanocinnamic acid matrix. Proteomics 12:1337–1348
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the Austrian Fonds zur Förderung der wissenschaftlichen Forschung (FWF; grants P26662, P25058, and P23922 to A.H., K.P., and I.B.H.W.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Hykollari, A., Paschinger, K., Eckmair, B., Wilson, I.B.H. (2017). Analysis of Invertebrate and Protist N-Glycans. In: Lauc, G., Wuhrer, M. (eds) High-Throughput Glycomics and Glycoproteomics. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1503. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6493-2_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6493-2_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-6491-8
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-6493-2
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols