Abstract
Maternal substance abuse is an ongoing concern and detecting drug use during pregnancy is an important component of neonatal care when drug abuse is suspected. Meconium is the preferred specimen for drug testing because it is easier to collect than neonatal urine and it provides a much broader time frame of drug exposure. We describe a method for quantifying 11-carboxy-delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC-COOH) in meconium. After adding a labeled internal standard (THC-COOH D9) and acetonitrile, samples are sonicated to release both free and conjugated THC-COOH. The acetonitrile/aqueous layer is removed and mixed with a strong base to hydrolyze the conjugated THC-COOH. The samples are then extracted with an organic solvent mixture as part of a sample “cleanup.” The organic solvent layer is discarded and the remaining aqueous sample is acidified. Following extraction with a second organic mixture, the organic layer is removed and concentrated to dryness. The resulting residue is converted to a trimethylsilyl (TMS) derivative and analyzed using gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) in selective ion monitoring (SIM) mode.
Access provided by CONRICYT – Journals CONACYT. Download protocol PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Key words
1 Introduction
Illicit drugs use during pregnancy remains a significant concern, and is associated with adverse fetal and maternal outcome. Amongst abused substances, cannabis remains the most commonly abused in the United States [1]. Various methods such as interviewing the mother in person or by questionnaire and drug testing in different specimen matrices are used to determine prenatal drug exposure [2–5]. Due to the legal repercussions of admitting illicit drug use, self-reported drug use is not reliable [2–4]. Urine from mother or infant is typically positive only for few days after the drug exposure. Meconium is a preferred sample to determine fetal drug exposure as it can provide maternal drug abuse history for several months because it begins forming between the 12th and 16th weeks of gestation, and it accumulates until shortly after birth. Meconium is a gelatinous, heterogeneous substance comprised of epithelial and squamous cells and amniotic fluid, swallowed by the fetus during the last half of pregnancy , and voided as first stools following birth. It is hypothesized that the fetus excretes drug into bile and amniotic fluid, and then the drug accumulates in meconium by direct disposition or by swallowing amniotic fluid [2, 3].
Because meconium is a thick and heterogeneous material, it is a difficult sample to work with, and requires special preparation before drug extraction. In general meconium is homogenized in an organic solvent for drug extraction. The extract is either used directly or dried and reconstituted in an aqueous buffer, and tested by immunoassay or mass spectrometric methods. Immunoassay positive results should be confirmed by a mass spectrometry method. Both gas and liquid chromatography mass spectrometric methods have been described in the literature [6–9]. We describe a GC/MS method for measuring total THC-COOH levels in meconium. The method is simple and reproducible, and has a linear range of 10–500 ng/g.
2 Materials
2.1 Sample
1 g meconium.
2.2 Solvents and Reagents
-
1.
Bis-(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide (BSTFA) with 1 % trimethylchlorosilane (TMCS) (United Chemical Technologies, Bristol, PA).
-
2.
11.8 N Potassium hydroxide: Add approximately 500 mL of deionized water to a 1 L volumetric flask. Slowly add 662 g of KOH pellets and bring the volume to 1 L with deionized water. Store in an amber bottle. Stable for 1 year at room temperature.
-
3.
Hexanes: Ethyl acetate (8:2): Combine 800 mL hexanes with 200 mL of ethyl acetate. Store in an amber bottle. Stable for 1 year at room temperature.
-
4.
0.1 M acetic acid: Add approximately 400 mL of deionized water to a 500 mL volumetric flask. Slowly add 2.87 mL glacial acetic acid and bring the volume to 500 mL with deionized water. Stable for 6 months at room temperature.
-
5.
0.2 N Sodium hydroxide: Add 10 mL 1.0 N NaOH to a 50 mL volumetric flask and bring the volume to 50 mL with deionized water. Stable for 6 months at room temperature.
2.3 Standards
-
1.
Primary standard: 100 μg/mL THC-COOH (Cerilliant).
-
2.
Primary internal standard: 100 μg/mL THC-COOH D9 (Cerilliant).
-
3.
Working secondary standard, 10 μg/mL THC-COOH: Add 1 mL primary standard to a 10 mL volumetric flask and bring the volume to 10 mL with methanol. Stable for 1 year at −20 °C.
-
4.
Working tertiary standard, 1 μg/mL THC-COOH: Add 1 mL of working secondary standard to a 10 mL volumetric flask and bring the volume to 10 mL with methanol. Stable for 1 year at −20 °C.
-
5.
Working internal standard, 2 μg/mL THC-COOH D9: Add 1 mL primary internal standard to 50 mL volumetric flask and bring the volume to 50 mL with methanol. Stable for 1 year at −20 °C.
2.4 Calibrators and Controls
-
1.
Prepare working calibrators and controls according to Table 1 by adding the indicated tertiary or secondary standard volume to extraction tubes which have been pre-coated with 1 g negative meconium (see Note 1 ).
Table 1 Preparation of calibrators and controls -
2.
In-house meconium controls: Bio-Rad (Bio-Rad Laboratories) THC-COOH urine controls (two levels) were used to prepare THC-COOH meconium controls. 1 mL urine control was added to 1 g negative meconium and vortexed to mix.
2.5 Analytical Supplies
-
1.
16 × 100 screw-cap glass tubes for extraction.
-
2.
13 × 100 screw-cap glass tubes for extract concentration.
-
3.
Transfer pipets (Samco Scientific, San Fernando CA).
-
4.
Auto sampler vials (12 × 32 mm with crimp caps) with 0.3 mL limited volume inserts (P.J. Cobert Associates, St. Louis, MO).
-
5.
GC column: Zebron ZB-1 with dimensions of 15 m × 0.25 mm × 0.25 μm (Phenomenex, Torrance, California).
-
6.
Plain wood applicators: These are used to evenly spread the meconium around the glass tube (Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.6 Equipment
-
1.
A gas chromatograph/mass spectrometer system (GC/MS; 6890/5975 or 5890/5972) with autosampler and operated in electron impact mode (Agilent Technologies, Wilmington, DE).
-
2.
TurboVap®IV Evaporator (Zymark Corporation, Hopkinton, MA, USA).
3 Method
3.1 Stepwise Procedure
-
1.
Weigh out 1 g of each patient meconium into a 16 × 100 mm test tube. Record weight to within two decimal places. Spread meconium as evenly as possible onto the sides of the tube for a uniform thin coating of sample. Freeze until analysis, at least overnight (see Note 2 ).
-
2.
For each of the four calibrators, the blank (negative control) and the three controls, weigh out 1 g of negative meconium into appropriately labeled 16 × 100 mm test tubes. Spread meconium evenly onto the sides of the tube. Add working THC-COOH for each calibrator and the 20 ng/g in-house control (see Table 1). Add 1 mL of each control, prepared from Bio-Rad controls, to appropriately labeled tubes. Cap and vortex to mix. Freeze all meconium specimens until analysis (at least overnight) and thaw for 15 min at room temperature before analysis.
-
3.
Prepare an unextracted standard by adding 100 μL working THC-COOH tertiary standard and 100 μL working THC-COOH D9 internal standard to a concentration tube. Set aside until step 18.
-
4.
Add 4 mL acetonitrile to each tube.
-
5.
Add 100 μL of working THC-COOH D9 IS to each tube. Cap and vortex to mix. Sonicate tubes (using a beaker or test tube rack) for 5 min. Centrifuge for 5 min at 1200 × g.
-
6.
Transfer organic layer to appropriately labeled clean concentration tubes.
-
7.
Spread meconium around the sides of the original extraction tube as much as possible for a uniform thin coating of sample.
-
8.
Add 2 mL of acetonitrile to the original sample tubes for a second extraction. Cap and vortex to mix. Sonicate for 5 min. Centrifuge for 5 min at 1200 × g.
-
9.
Add the 2 mL organic to the concentration tube containing the first 4 mL acetonitrile extract.
-
10.
Concentrate the combined organic extract to less than 1 mL under nitrogen at 40 °C (see Note 3 ).
-
11.
Add 2 mL 0.2 N NaOH to each tube.
-
12.
Add 100 μL 11.8 N KOH to each tube. Vortex. Let sit for a minimum of 15 min.
-
13.
Add 5 mL hexane:ethyl acetate (8:2) to each tube. Cap and rock for a minimum of 15 min. Centrifuge for 5 min at 1200 × g.
-
14.
Discard upper organic layer. To the bottom aqueous layer add 2 mL 0.1 M acetic acid.
-
15.
Add 200 μL glacial acetic acid.
-
16.
Add 3 mL hexane:ethyl acetate (8:2). Cap and rock for 15 min. Centrifuge for 5 min at 1200 × g.
-
17.
Transfer upper organic layer to a clean concentration tube.
-
18.
Concentrate to dryness under nitrogen at 40 °C.
-
19.
Reconstitute with 100 μL BSTFA + TMCS.
-
20.
Cap and incubate for 10 min at 65 °C in heating block.
-
21.
Cool and transfer to appropriately labeled autosampler vials.
-
22.
Inject 1 μL onto GC/MS for analysis (GC-MS operating condition are given in Table 2).
Table 2 GC-MS operating conditions
3.2 Data Analysis
-
1.
Data are analyzed using Target Software (Thru-Put Systems, Orlando, FL) or similar software.
-
2.
Standard curves are generated based on linear regression of the analyte/IS peak area ratio (y) versus analyte concentration (x) using the quantifying ion listed in Table 3.
Table 3 Quantification and qualifier ions for THC-COOH and THC-COOH D9 -
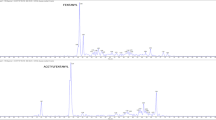
3.
Typical total and SIM chromatogram are shown in Fig. 1.
-
4.
Analytical run is considered acceptable if the control values are within 20 %.
-
5.
Typical coefficient of correlation is >0.99.
-
6.
Linearity of the method is from 10 to 500 ng/g.
-
7.
Typical intra- and inter-assay imprecision is <10 %.
4 Notes
-
1.
Calibrators and controls are prepared independently.
-
2.
Freezing the meconium specimen overnight at −20 °C increases extraction recovery.
-
3.
Concentration of organic extract takes ~30 min.
References
http://www.monitoringthefuture.org/, Accessed 6/11/15
Ostrea EM Jr, Brady MJ, Parks PM, Asensio DC, Naluz A (1989) Drug screening of meconium in infants of drug-dependent mothers: an alternative to urine testing. J Pediatr 115:474–477
Ostrea EM Jr, Knapp DK, Tannenbaum L, Ostrea AR, Romero A, Salari V, Ager J (2001) Estimates of illicit drug use during pregnancy by maternal interview, hair analysis, and meconium analysis. J Pediatr 138:344–348
Wingert WE, Feldman MS, Kim MH, Noble L, Hand I, Yoon JJ (1994) A comparison of meconium, maternal urine and neonatal urine for detection of maternal drug use during pregnancy. J Forensic Sci 39:150–158
Kwong TC, Ryan RM (1997) Detection of intrauterine illicit drug exposure by newborn drug testing. National Academy of Clinical Biochemistry. Clin Chem 43:235–242
Coles R, Clements TT, Nelson GJ, McMillin GA, Urry FM (2005) Simultaneous analysis of the Delta9-THC metabolites 11-nor-9-carboxy-Delta9-THC and 11-hydroxy-Delta9-THC in meconium by GC-MS. J Anal Toxicol 29:522–527
Tynon M, Porto M, Logan BK (2015) Simplified analysis of 11-hydroxy-delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol and 11-carboxy-delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol in human meconium: method development and validation. J Anal Toxicol 39:35–40
Gray TR, Shakleya DM, Huestis MA (2009) A liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous quantification of 20 drugs of abuse and metabolites in human meconium. Anal Bioanal Chem 393:1977–1990
Ristimaa J, Gergov M, Pelander A, Halmesmaki E, Ojanpera I (2010) Broad-spectrum drug screening of meconium by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry and time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 398:925–935
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Peat, J., Davis, B., Frazee, C., Garg, U. (2016). Quantification of 11-Carboxy-Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC-COOH) in Meconium Using Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (GC/MS). In: Garg, U. (eds) Clinical Applications of Mass Spectrometry in Drug Analysis. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1383. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-3252-8_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-3252-8_11
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-3251-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-3252-8
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols