Abstract
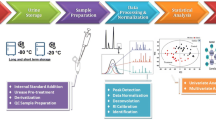
To maximize the utility of gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) in metabonomics research, all stages of the experimental design should be standardized, including sample collection, storage, preparation, and sample separation. Moreover, the prerequisite for any GC-MS analysis is that a compound must be volatile and thermally stable if it is to be analyzed using this technique. Since many metabolites are nonvolatile and polar in nature, they are not readily amenable to analysis by GC-MS and require initial chemical derivatization of the polar functional groups in order to reduce the polarity and to increase the thermal stability and volatility of the analytes. In this chapter, an overview is presented of the optimum approach to sample collection, storage, and preparation for gas chromatography–mass spectrometry-based metabonomics with particular focus on urine samples as example of biofluids.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang Y, Cruickshank C, Armstrong M et al (2013) New sample preparation approach for mass spectrometry-based profiling of plasma results in improved coverage of metabolome. J Chromatogr A 1300:217–226
Phua LC, Koh PK, Cheah PY et al (2013) Global gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GC/TOFMS)-based metabonomic profiling of lyophilized human feces. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 937:103–113
Ibanez C, Simo C, Barupal DK et al (2013) A new metabolomic workflow for early detection of Alzheimer's disease. J Chromatogr A 1302:65–71
Hu X, Li H, Tang P et al (2013) GC-MS-based metabolomics study of the responses to arachidonic acid in Blakeslea trispora. Fungal Genet Biol 57:33–41
Ruiz-Aracama A, Lommen A, Huber M et al (2012) Application of an untargeted metabolomics approach for the identification of compounds that may be responsible for observed differential effects in chickens fed an organic and a conventional diet. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess 29:323–332
Kang Y-R, Park YS, Park YC et al (2012) UPLC/Q-TOF MS based metabolomics approach to post-mortem-interval discrimination: mass spectrometry based metabolomics approach. J Pharm Invest 42:41–46
Ciborowski M, Teul J, Luis Martin-Ventura J et al (2012) Metabolomics with LC-QTOF-MS permits the prediction of disease stage in aortic abdominal aneurysm based on plasma metabolic fingerprint. PLoS One 7:1–9
Becker S, Kortz L, Helmschrodt C et al (2012) LC-MS-based metabolomics in the clinical laboratory. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 883:68–75
Wilson ID, Plumb R, Granger J et al (2005) HPLC-MS-based methods for the study of metabonomics. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 817:67–76
Morgenthal K, Wienkoop S, Scholz M et al (2005) Correlative GC-TOF-MS-based metabolite profiling and LC-MS-based protein profiling reveal time-related systemic regulation of metabolite-protein networks and improve pattern recognition for multiple biomarker selection. Metabolomics 1:109–121
Pohjanen E, Thysell E, Lindberg J et al (2006) Statistical multivariate metabolite profiling for aiding biomarker pattern detection and mechanistic interpretations in GC/MS based metabolomics. Metabolomics 2:257–268
Hummel J, Selbig J, Walther D et al (2007) The Golm Metabolome Database: a database for GC-MS based metabolite profiling. In: Nielsen J, Jewett MC (eds) Top Curr Genet. Topics in Current Genetics, Springer 18:75–95
Gaspari M, Verhoeckx KCM, Verheij ER et al (2006) Integration of two-dimensional LC-MS with multivariate statistics for comparative analysis of proteomic samples. Anal Chem 78:2286–2296
Chen C, Gonzalez FJ, Idle JR (2007) LC-MS-based metabolomics in drug metabolism. Drug Metab Rev 39:581–597
Allwood JW, Clarke A, Goodacre R et al (2010) Dual metabolomics: a novel approach to understanding plant-pathogen interactions. Phytochemistry 71:590–597
Hollywood KA, Maatje M, Shadi IT et al (2010) Phenotypic profiling of keloid scars using FT-IR microspectroscopy reveals a unique spectral signature. Arch Dermatol Res 302:705–715
Rodriguez-Fernandez JI, De Carvalho CJB, Pasquini C et al (2011) Barcoding without DNA? Species identification using near infrared spectroscopy. Zootaxa 2933:46–54
Wang H, Hollywood K, Jarvis RM et al (2010) Phenotypic characterization of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 under aerobic and anaerobic growth conditions by using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and high-performance liquid chromatography analyses. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:6266–6276
Al-Talla ZA, Akrawi SH, Emwas AHM (2011) Solid state NMR and bioequivalence comparison of the pharmacokinetic parameters of two formulations of clindamycin. Int J Clin Pharm Ther 49:469–476
Al-Talla ZA, Akrawi SH, Tolley LT et al (2011) Bioequivalence assessment of two formulations of ibuprofen. Drug Des Devel Ther 5:427–433
Argyri AA, Doulgeraki AI, Blana VA et al (2011) Potential of a simple HPLC-based approach for the identification of the spoilage status of minced beef stored at various temperatures and packaging systems. Int J Food Microbiol 150:25–33
van der Hooft JJJ, de Vos RCH, Mihaleva V et al (2012) Structural elucidation and quantification of phenolic conjugates present in human urine after tea intake. Anal Chem 84:7263–7271
Wang Z, Hu H, Chen F et al (2012) Metabolic profiling assisted quality assessment of Rhodiola rosea extracts by high-performance liquid chromatography. Planta Med 78:740–746
Yang J, Xu GW, Zheng YF et al (2004) Diagnosis of liver cancer using HPLC-based metabonomics avoiding false-positive result from hepatitis and hepatocirrhosis diseases. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 813:59–65
Zhang A-h, Sun H, Qiu S et al (2013) NMR-based metabolomics coupled with pattern recognition methods in biomarker discovery and disease diagnosis. Magn Reson Chem 51:549–556
Zhang X, Xu L, Shen J et al (2013) Metabolic signatures of esophageal cancer: NMR-based metabolomics and UHPLC-based focused metabolomics of blood serum. Biochim Biophys Acta 1832:1207–1216
Grimes JH, O'Connell TM (2011) The application of micro-coil NMR probe technology to metabolomics of urine and serum. J Biomol NMR 49:297–305
Verwaest KA, Vu TN, Laukens K et al (2011) H-1 NMR based metabolomics of CSF and blood serum: a metabolic profile for a transgenic rat model of Huntington disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1812:1371–1379
Tiziani S, Emwas AH, Lodi A et al (2008) Optimized metabolite extraction from blood serum for 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Anal Biochem 377:16–23
Oommen JM, Hussain MM, Emwas A-HM et al (2010) Nuclear magnetic resonance study of nanoscale ionic materials. Electrochem Solid-State Lett 13:K87–K88
Mroue KH, Emwas A-HM, Power WP (2010) Solid-state Al-27 nuclear magnetic resonance investigation of three aluminum-centered dyes. Can J Chem 88:111–123
Linenberger KJ, Emwas A-H, Peat I et al (2009) Using NMR to determine the structure of a peptide: an inquiry approach for an upper level undergraduate laboratory. Abstr Pap Am Chem Soc 237
Emwas A-HM, Al-Talla ZA, Guo X et al (2013) Utilizing NMR and EPR spectroscopy to probe the role of copper in prion diseases. Magn Reson Chem 51:255–268
Chu S, Maltsev S, Emwas AH et al (2010) Solid-state NMR paramagnetic relaxation enhancement immersion depth studies in phospholipid bilayers. J Magn Reson 207:89–94
Abuhijleh AL, Abu Ali H, Emwas A-H (2009) Synthesis, spectral and structural characterization of dinuclear rhodium (II) complexes of the anticonvulsant drug valproate with theophylline and caffeine. J Organomet Chem 694:3590–3596
Ravenscroft N, Dabrowski J, Romanowska E (1995) Structural elucidation of the biological repeating unit of O-specific polysaccharide from Citrobacter serotype O41. Eur J Biochem 229:299–307
Pliev TN (1987) Complex method of identification of molecular structures of substituted phenols from their IR, UV, and NMR spectra. J Appl Spectrosc 47:1259–1263
Oda Y, Uesugi S, Ikehara M et al (1991) NMR studies for identification of dI:dG mismatch base-pairing structure in DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 19:5263–5267
Sahloul N, Emwas A, Power W et al (2005) Ethyl acrylate-hydroxyethyl acrylate and hydroxyethyl acrylate-methacrylic acid: reactivity ratio estimation from cross-linked polymer using high resolution magic angle spinning spectroscopy. J Macromol Sci Pure Appl Chem A42:1369–1385
Atiqullah M, Anantawaraskul S, Emwas A-HM et al (2013) Effects of supported ((BuCp)-Bu-n)(2)ZrCl2 catalyst active-center distribution on ethylene-1-hexene copolymer backbone heterogeneity and thermal behaviors. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:9359–9373
Bouhrara M, Ranga C, Fihri A et al (2013) Nitridated fibrous silica (KCC-1) as a sustainable solid base nanocatalyst. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 1:1192–1199
Jackson MD, Moon J, Gotti E et al (2013) Material and elastic properties of Al-tobermorite in ancient roman seawater concrete. J Am Ceram Soc 96:2598–2606
Kamal MS, Bahuleyan BK, Sohail OB et al (2013) Crystallization analysis fractionation of poly(ethylene-co-styrene) produced by metallocene catalysts. Polym Bull 70:2645–2656
Nageeb A, Al-Tawashi A, Mohammad Emwas A-H et al (2013) Comparison of Artemisia annua bioactivities between traditional medicine and chemical extracts. Curr Bioact Compd 9:324–332
Khan MT, Busch M, Molina VG et al (2014) How different is the composition of the fouling layer of wastewater reuse and seawater desalination RO membranes? Water Res 59:271–282
Patil U, Fihri A, Emwas A-H et al (2012) Silicon oxynitrides of KCC-1, SBA-15 and MCM-41 for CO2 capture with excellent stability and regenerability. Chem Sci 3:2224–2229
Kirchheim A, Dal Molin D, Fischer P et al (2011) Real-time high-resolution X-ray imaging and nuclear magnetic resonance study of the hydration of pure and Na-doped C3A in the presence of sulfates. Inorg Chem 50:1203–1212
Jackson MD, Chae SR, Mulcahy SR et al (2013) Unlocking the secrets of Al-tobermorite in Roman seawater concrete. Am Mineral 98:1669–1687
Decken A, Mattar SM, Emwas A (2005) 1,4,11,12-Tetrahydro-9,10-anthraquinone. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online 61:O641–O642
Gloggler S, Colell J, Appelt S (2013) Para-hydrogen perspectives in hyperpolarized NMR. J Magn Reson 235:130–142
Ellena S, Viale A, Gobetto R et al (2012) Para-hydrogen induced polarization of Si-29 NMR resonances as a potentially useful tool for analytical applications. Magn Reson Chem 50:529–533
Hamans BC, Andreychenko A, Heerschap A et al (2011) NMR at earth's magnetic field using para-hydrogen induced polarization. J Magn Reson 212:224–228
Sze KH, Wu Q, Tse HS et al (2012) Dynamic nuclear polarization: new methodology and applications. In: Zhu G (ed) NMR of proteins and small biomolecules. Topics in Current Chemistry, Springer 326:215–242
Tuerke M-T, Tkach I, Reese M et al (2010) Optimization of dynamic nuclear polarization experiments in aqueous solution at 15 MHz/9.7 GHz: a comparative study with DNP at 140 MHz/94 GHz. Phys Chem Chem Phys 12:5893–5901
Ludwig C, Marin-Montesinos I, Saunders MG et al (2010) Application of ex situ dynamic nuclear polarization in studying small molecules. Phys Chem Chem Phys 12:5868–5871
Emwas AH, Saunders M, Ludwig C et al (2008) Determinants for optimal enhancement in ex situ DNP experiments. Appl Magn Reson 34:483–494
Mattar SM, Stephens AD, Emwas AH (2002) Generation and spectroscopic characterization of the 2,3,5,6-tetramethoxy-1,4-benzosemiquinone reactive intermediate. Chem Phys Lett 352:39–47
Raji M, Amad M, Emwas A-H (2013) Dehydrodimerization of pterostilbene during electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 27:1260–1266
Sannino A, Bolzoni L (2013) GC/CI-MS/MS method for the identification and quantification of volatile N-nitrosamines in meat products. Food Chem 141:3925–3930
Mitrevski BS, Kouremenos KA, Marriott PJ (2009) Accelerating analysis for metabolomics, drugs and their metabolites in biological samples using multidimensional gas chromatography. Bioanalysis 1:367–391
Lei Z, Huhman DV, Sumner LW (2011) Mass spectrometry strategies in metabolomics. J Biol Chem 286:25435–25442
Kim S, Fang A, Wang B et al (2011) An optimal peak alignment for comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography mass spectrometry using mixture similarity measure. Bioinformatics 27:1660–1666
Harder U, Koletzko B, Peissner W (2011) Quantification of 22 plasma amino acids combining derivatization and ion-pair LC-MS/MS. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 879:495–504
Wolfender J-L, Rudaz S, Choi YH et al (2013) Plant metabolomics: from holistic data to relevant biomarkers. Curr Med Chem 20:1056–1090
Van der Hooft JJJ, Vervoort J, Bino RJ et al (2012) Spectral trees as a robust annotation tool in LC-MS based metabolomics. Metabolomics 8:691–703
Marti G, Erb M, Boccard J et al (2013) Metabolomics reveals herbivore-induced metabolites of resistance and susceptibility in maize leaves and roots. Plant Cell Environ 36:621–639
Cho K, Kim Y, Wi SJ et al (2012) Nontargeted metabolite profiling in compatible pathogen-inoculated tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L. cv. Wisconsin 38) using UPLC-Q-TOF/MS. J Agric Food Chem 60:11015–11028
Wolfender J-L, Glauser G, Boccard J et al (2009) MS-based plant metabolomic approaches for biomarker discovery. Nat Prod Commun 4:1417–1430
Koenig S (2011) Urine molecular profiling distinguishes health and disease: new methods in diagnostics? Focus on UPLC-MS. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 11:383–391
Goulitquer S, Potin P, Tonon T (2012) Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics to elucidate functions in marine organisms and ecosystems. Mar Drugs 10:849–880
De Vos RCH, Schipper B, Hall RD (2012) High-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of plant metabolites in brassicaceae. Methods Mol Biol 860:111–128
Kopka J (2006) Current challenges and developments in GC-MS based metabolite profiling technology. J Biotechnol 124:312–322
Kim J, Choi JN, Kim P et al (2009) LC-MS/MS profiling-based secondary metabolite screening of Myxococcus xanthus. J Microbiol Biotechnol 19:51–54
Hagel JM, Facchini PJ (2008) Plant metabolomics: analytical platforms and integration with functional genomics. Phytochem Rev 7:479–497
Lee SJ, Choi JY, Park S et al (2010) Determination of phospholipids in soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr) cultivars by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Food Compos Anal 23:314–318
Kumar MS, Pandita NS, Pal AK (2012) LC-MS/MS as a tool for identification of bioactive compounds in marine sponge Spongosorites halichondriodes. Toxicon 60:1135–1147
Jin Y, Xiao Y-s, Zhang F-f et al (2008) Systematic screening and characterization of flavonoid glycosides in Carthamus tinctorius L. by liquid chromatography/UV diode-array detection/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal 46:418–430
Cao X-w, Shen W-j, Zhu J et al (2013) A comparative study of the ionization modes in GC-MS multi-residue method for the determination of organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in crayfish. Food Anal Methods 6:445–456
Osemwengie LI (2006) Determination of synthetic musk compounds in sewage biosolids by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. J Environ Monit 8:897–903
Kalachova K, Pulkrabova J, Cajka T et al (2013) Gas chromatography-triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry: a powerful tool for the (ultra)trace analysis of multiclass environmental contaminants in fish and fish feed. Anal Bioanal Chem 405:7803–7815
Kalachova K, Cajka T, Sandy C et al (2013) High throughput sample preparation in combination with gas chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry (GC-MS/MS): a smart procedure for (ultra)trace analysis of brominated flame retardants in fish. Talanta 105:109–116
Hook GL, Kimm GL, Hall T et al (2002) Solid-phase microextraction (SPME) for rapid field sampling and analysis by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Trends Anal Chem 21:534–543
Datta S, Do LV, Young TM (2004) A simplified method for sampling and analysis of high volume surface water for organic contaminants using XAD-2. J Environ Sci Health B 39:225–234
Cohen S, Manat A, Dumont B et al (2010) Toxicologic blood emergency screening. Comparison of two techniques: Remedi versus GC-MS. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 68:163–172
Bourdeaux D, Sautou-Miranda V, Montagner A et al (2010) Simple assay of plasma sevoflurane and its metabolite hexafluoroisopropanol by headspace GC-MS. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 878:45–50
Wang H, Zhang J, Gao F et al (2011) Simultaneous analysis of synthetic musks and triclosan in human breast milk by gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 879:1861–1869
Wang G, Tang H, Chen D et al (2012) Determination of five synthetic musks in perfume by headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Se Pu 30:135–140
Ramirez N, Maria Marce R, Borrull F (2011) Development of a stir bar sorptive extraction and thermal desorption-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry method for determining synthetic musks in water samples. J Chromatogr A 1218:156–161
Jellum E, Stokke O, Eldjarn L (1973) Application of gas chromatography, mass spectrometry, and computer methods in clinical biochemistry. Anal Chem 46:1099–1106
Shoemaker JD, Elliott WH (1991) Automated screening of urine samples for carbohydrates, organic and amino acids after treatment with urease. J Chromatogr B 562:125–138
Kuhara T (2005) Gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric urinary metabolome analysis to study mutations of inborn errors of metabolism. Mass Spectrom Rev 24:814–827
Nieman DC, Shanely RA, Gillitt ND et al (2013) Serum metabolic signatures induced by a three-day intensified exercise period persist after 14 h of recovery in runners. J Proteome Res 12:4577–4584
Pasikanti KK, Ho PC, Chan ECY (2008) Development and validation of a gas chromatography/mass spectrometry metabonomic platform for the global profiling of urinary metabolites. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 22:2984–2992
Fancy S-A, Beckonert O, Darbon G et al (2006) Gas chromatography/flame ionisation detection mass spectrometry for the detection of endogenous urine metabolites for metabonomic studies and its, use as a complementary tool to nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 20:2271–2280
Chen J, Zhao X, Fritsche J et al (2008) Practical approach for the identification and isomer elucidation of biomarkers detected in a metabonomic study for the discovery of individuals at risk for diabetes by integrating the chromatographic and mass spectrometric information. Anal Chem 80:1280–1289
Dettmer K, Aronov PA, Hammock BD (2007) Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. Mass Spectrom Rev 26:51–78
Nakamizo S, Sasayama T, Shinohara M et al (2013) GC/MS-based metabolomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from glioma patients. J Neurooncol 113:65–74
Emond P, Mavel S, Aidoud N et al (2013) GC-MS-based urine metabolic profiling of autism spectrum disorders. Anal Bioanal Chem 405:5291–5300
Tsugawa H, Bamba T, Shinohara M et al (2011) Practical non-targeted gas chromatography/mass spectrometry-based metabolomics platform for metabolic phenotype analysis. J Biosci Bioeng 112:292–298
Ooi M, Nishiumi S, Yoshie T et al (2011) GC/MS-based profiling of amino acids and TCA cycle-related molecules in ulcerative colitis. Inflamm Res 60:831–840
Gao X, Zhao A, Zhou M et al (2011) GC/MS-based urinary metabolomics reveals systematic differences in metabolism and ethanol response between Sprague-Dawley and Wistar rats. Metabolomics 7:363–374
Cevallos-Cevallos JM, Garcia-Torres R, Etxeberria E et al (2011) GC-MS analysis of headspace and liquid extracts for metabolomic differentiation of citrus Huanglongbing and zinc deficiency in leaves of ‘Valencia’ sweet orange from commercial groves. Phytochem Anal 22:236–246
Zhang Q, Wang G-j, A J-y et al (2009) Application of GC/MS-based metabonomic profiling in studying the lipid-regulating effects of Ginkgo biloba extract on diet-induced hyperlipidemia in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 30:1674–1687
Kuhara T, Ohse M, Inoue Y et al (2009) Urinary metabolic profile of phenylketonuria in patients receiving total parenteral nutrition and medication. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 23:3167–3172
Chan ECY, Pasikanti KK, Nicholson JK (2011) Global urinary metabolic profiling procedures using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Nat Protoc 6:1483–1499
Bernini P, Bertini I, Luchinat C et al (2011) Standard operating procedures for pre-analytical handling of blood and urine for metabolomic studies and biobanks. J Biomol NMR 49:231–243
Diaz SO, Barros AS, Goodfellow BJ et al (2013) Following healthy pregnancy by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) metabolic profiling of human urine. J Proteome Res 12:969–979
Emwas A-HM, Salek RM, Griffin JL et al (2013) NMR-based metabolomics in human disease diagnosis: applications, limitations, and recommendations. Metabolomics 9:1048–1072
Rist MJ, Muhle-Goll C, Görling B et al (2013) Influence of freezing and storage procedure on human urine samples in NMR-based metabolomics. Metabolites 3:243–258
Gika HG, Theodoridis GA, Wilson ID (2008) Liquid chromatography and ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry fingerprinting of human urine—sample stability under different handling and storage conditions for metabonomics studies. J Chromatogr A 1189:314–322
Lauridsen M, Hansen SH, Jaroszewski JW et al (2007) Human urine as test material in H-1 NMR-based metabonomics: recommendations for sample preparation and storage. Anal Chem 79:1181–1186
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank King Abdullah University of Science and Technology for the financial support and Dr. Virginia Unkefer from KAUST and Dr. Christina Morris for their assistance and helpful editorial remarks.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Emwas, AH.M., Al-Talla, Z.A., Kharbatia, N.M. (2015). Sample Collection and Preparation of Biofluids and Extracts for Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. In: Bjerrum, J. (eds) Metabonomics. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1277. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2377-9_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2377-9_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-2376-2
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-2377-9
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols